(b) Assuming that Thai Curry Ltd claims relief for its trading loss against total profits under s.393A ICTA 1988,calculate the company’s corporation tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2005. (10 marks)
题目
(b) Assuming that Thai Curry Ltd claims relief for its trading loss against total profits under s.393A ICTA 1988,calculate the company’s corporation tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2005. (10 marks)
相似考题
更多“(b) Assuming that Thai Curry Ltd claims relief for its trading loss against total profits under s.393A ICTA 1988,calculate the company’s corporation tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2005. (10 marks)”相关问题
-
第1题:
(ii) Illustrate the benefit of revising the corporate structure by calculating the corporation tax (CT) payable
for the year ended 31 March 2006, on the assumptions that:
(1) no action is taken; and
(2) an amended structure as recommended in (i) above is implemented from 1 June 2005. (3 marks)
正确答案:
-
第2题:
(ii) Assuming that Donald operates through a company, advise Donald on the corporation tax (CT) that
would be payable for the year ended 31 March 2007 if he pays himself a gross salary of £31,000, plus
a net dividend of £10,000, instead of a gross salary of £42,648. (4 marks)
正确答案:
-
第3题:
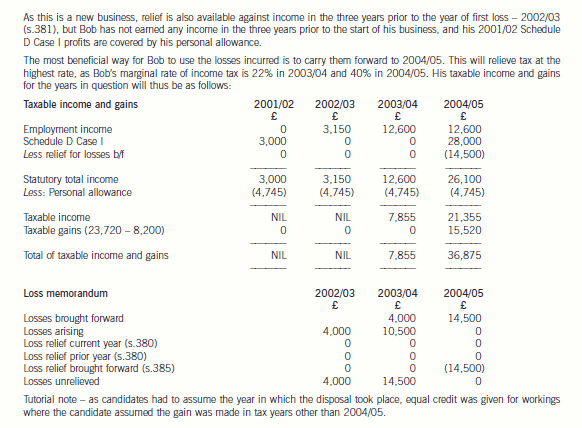
(b) Assuming that the income from the sale of the books is not treated as trading income, calculate Bob’s taxable
income and gains for all relevant tax years, using any loss reliefs in the most tax-efficient manner. Your
answer should include an explanation of the loss reliefs available and your reasons for using (or not using)
them. (12 marks)
Assume that the rates and allowances for 2004/05 apply throughout this part of the question.
正确答案:
-
第4题:
3 On 1 January 2007 Dovedale Ltd, a company with no subsidiaries, intends to purchase 65% of the ordinary share
capital of Hira Ltd from Belgrove Ltd. Belgrove Ltd currently owns 100% of the share capital of Hira Ltd and has no
other subsidiaries. All three companies have their head offices in the UK and are UK resident.
Hira Ltd had trading losses brought forward, as at 1 April 2006, of £18,600 and no income or gains against which
to offset losses in the year ended 31 March 2006. In the year ending 31 March 2007 the company expects to make
further tax adjusted trading losses of £55,000 before deduction of capital allowances, and to have no other income
or gains. The tax written down value of Hira Ltd’s plant and machinery as at 31 March 2006 was £96,000 and
there will be no fixed asset additions or disposals in the year ending 31 March 2007. In the year ending 31 March
2008 a small tax adjusted trading loss is anticipated. Hira Ltd will surrender the maximum possible trading losses
to Belgrove Ltd and Dovedale Ltd.
The tax adjusted trading profit of Dovedale Ltd for the year ending 31 March 2007 is expected to be £875,000 and
to continue at this level in the future. The profits chargeable to corporation tax of Belgrove Ltd are expected to be
£38,000 for the year ending 31 March 2007 and to increase in the future.
On 1 February 2007 Dovedale Ltd will sell a small office building to Hira Ltd for its market value of £234,000.
Dovedale Ltd purchased the building in March 2005 for £210,000. In October 2004 Dovedale Ltd sold a factory
for £277,450 making a capital gain of £84,217. A claim was made to roll over the gain on the sale of the factory
against the acquisition cost of the office building.
On 1 April 2007 Dovedale Ltd intends to acquire the whole of the ordinary share capital of Atapo Inc, an unquoted
company resident in the country of Morovia. Atapo Inc sells components to Dovedale Ltd as well as to other
companies in Morovia and around the world.
It is estimated that Atapo Inc will make a profit before tax of £160,000 in the year ending 31 March 2008 and will
pay a dividend to Dovedale Ltd of £105,000. It can be assumed that Atapo Inc’s taxable profits are equal to its profit
before tax. The rate of corporation tax in Morovia is 9%. There is a withholding tax of 3% on dividends paid to
non-Morovian resident shareholders. There is no double tax agreement between the UK and Morovia.
Required:
(a) Advise Belgrove Ltd of any capital gains that may arise as a result of the sale of the shares in Hira Ltd. You
are not required to calculate any capital gains in this part of the question. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(a) Capital gains that may arise on the sale by Belgrove Ltd of shares in Hira Ltd
Belgrove Ltd will realise a capital gain on the sale of the shares unless the substantial shareholding exemption applies. The
exemption will be given automatically provided all of the following conditions are satisfied.
– Belgrove Ltd has owned at least 10% of Hira Ltd for a minimum of 12 months during the two years prior to the sale.
– Belgrove Ltd is a trading company or a member of a trading group during that 12-month period and immediately after
the sale.
– Hira Ltd is a trading company or the holding company of a trading group during that 12-month period and immediately
after the sale.
Hira Ltd will no longer be in a capital gains group with Belgrove Ltd after the sale. Accordingly, a capital gain, known as a
degrouping charge, may arise in Hira Ltd. A degrouping charge will arise if, at the time it leaves the Belgrove Ltd group, Hira
Ltd owns any capital assets which were transferred to it at no gain, no loss within the previous six years by a member of the
Belgrove Ltd capital gains group. -
第5题:
(b) Explain the advantages from a tax point of view of operating the new business as a partnership rather than
as a company whilst it is making losses. You should calculate the tax adjusted trading loss for the year
ending 31 March 2008 for both situations and indicate the years in which the loss relief will be obtained.
You are not required to prepare any other supporting calculations. (10 marks)
正确答案:(b) The new business
There are two tax advantages to operating the business as a partnership.
(i) Reduction in taxable income
If the new business is operated as a company, Cindy and Arthur would both be taxed at 40% on their salaries. In
addition, employer and employee national insurance contributions would be due on £105 (£5,000 – £4,895) in respect
of each of them.
If the new business is operated as a partnership, the partners would have no taxable trading income because the
partnership has made a loss; any salaries paid to the partners would be appropriations of the profit or loss of the
business and not employment income. They would, however, each have to pay Class 2 national insurance contributions
of £2·10 each per week.
(ii) Earlier relief for trading losses
If the new business is operated as a company, its tax adjusted trading loss in the year ending 31 March 2008 would
be as follows:
-
第6题:
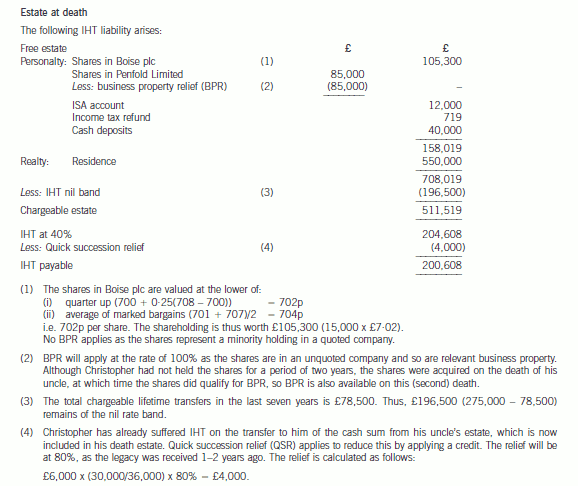
(b) Calculate the inheritance tax (IHT) liability arising as a result of Christopher’s death. (11 marks)
正确答案:

-
第7题:
(ii) Assuming the new structure is implemented with effect from 1 August 2006, calculate the level of
management charge that should be made by Bold plc to Linden Limited for the year ended 31 July
2007, so as to minimise the group’s overall corporation tax (CT) liability for that year. (2 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) For the year ended 31 July 2007, there will be two associated companies in the group. Bold plc will count as an
associated company as it is not dormant throughout the period in question. As a result, the corporation tax limits will be
divided by two (i.e. the number of associates) giving an upper limit of £750,000 (£1·5 million/2). As Linden Limited
is anticipated to make profits of £1·4 million in the year to 31 July 2007 it will pay corporation tax at the rate of 30%.
Bold plc can earn trading profits up to £150,000 (£300,000/2) and pay tax at the rate of 19%. It will therefore
minimise the group’s corporation tax liability if maximum use is made of this small companies rate band, as it will save
£16,500 (150,000 x (30% – 19%)) of corporation tax for the year to 31 July 2007. Bold plc should therefore make
a management charge of sufficient size to give it profits for that year equal to £150,000.
While the transfer pricing legislation no longer applies to small and medium sized enterprises, Bold plc should
nevertheless ensure that there is evidence to support the actual charge made in terms of the services provided. -
第8题:
(b) Calculate Alvaro Pelorus’s capital gains tax liability for the tax year 2006/07 on the assumption that all
available reliefs are claimed. (8 marks)
正确答案:

-
第9题:
3 Palm plc recently acquired 100% of the ordinary share capital of Nikau Ltd from Facet Ltd. Palm plc intends to use
Nikau Ltd to develop a new product range, under the name ‘Project Sabal’. Nikau Ltd owns shares in a non-UK
resident company, Date Inc.
The following information has been extracted from client files and from a meeting with the Finance Director of Palm
plc.
Palm plc:
– Has more than 40 wholly owned subsidiaries such that all group companies pay corporation tax at 30%.
– All group companies prepare accounts to 31 March.
– Acquired Nikau Ltd on 1 November 2007 from Facet Ltd, an unrelated company.
Nikau Ltd:
– UK resident company that manufactures domestic electronic appliances for sale in the European Union (EU).
– Large enterprise for the purposes of the enhanced relief available for research and development expenditure.
– Trading losses brought forward as at 1 April 2007 of £195,700.
– Budgeted taxable trading profit of £360,000 for the year ending 31 March 2008 before taking account of ‘Project
Sabal’.
– Dividend income of £38,200 will be received in the year ending 31 March 2008 in respect of the shares in Date
Inc.
‘Project Sabal’:
– Development of a range of electronic appliances, for sale in North America.
– Project Sabal will represent a significant advance in the technology of domestic appliances.
– Nikau Ltd will spend £70,000 on staffing costs and consumables researching and developing the necessary
technology between now and 31 March 2008. Further costs will be incurred in the following year.
– Sales to North America will commence in 2009 and are expected to generate significant profits from that year.
Shares in Date Inc:
– Nikau Ltd owns 35% of the ordinary share capital of Date Inc.
– The shares were purchased from Facet Ltd on 1 June 2003 for their market value of £338,000.
– The sale was a no gain, no loss transfer for the purposes of corporation tax.
– Facet Ltd purchased the shares in Date Inc on 1 March 1994 for £137,000.
Date Inc:
– A controlled foreign company resident in the country of Palladia.
– Annual chargeable profits arising out of property investment activities are approximately £120,000, of which
approximately £115,000 is distributed to its shareholders each year.
The tax system in Palladia:
– No taxes on income or capital profits.
– 4% withholding tax on dividends paid to shareholders resident outside Palladia.
Required:
(a) Prepare detailed explanatory notes, including relevant supporting calculations, on the effect of the following
issues on the amount of corporation tax payable by Nikau Ltd for the year ending 31 March 2008.
(i) The costs of developing ‘Project Sabal’ and the significant commercial changes to the company’s
activities arising out of its implementation. (8 marks)
正确答案:
(a) Nikau Ltd – Effect on corporation tax payable for the year ending 31 March 2008
(i) Project Sabal
Research and development expenditure
The expenditure incurred in respect of research and development will give rise to an enhanced deduction for the
purposes of computing the taxable trading profits of Nikau Ltd. The enhanced deduction is 125% of the qualifying
expenditure as Nikau Ltd is a large enterprise for this purpose.
The expenditure will reduce the profits chargeable to corporation tax of Nikau Ltd by £87,500 (£70,000 x 1·25) and
its corporation tax liability by £26,250 (£87,500 x 30%).
The budgeted expenditure will qualify for the enhanced deduction because it appears to satisfy the following conditions.
– It is likely to qualify as research and development expenditure within generally accepted accounting principles as
it will result in new technical knowledge and the production of a substantially improved device for use in the
industry.
– It exceeds £10,000 in Nikau Ltd’s accounting period.
– It relates to staff costs, consumable items or other qualifying expenditure as opposed to capital items.
– It will result in further trading activities for Nikau Ltd.
Use of brought forward trading losses
The development of products for the North American market is likely to represent a major change in the nature and
conduct of the trade of Nikau Ltd. This is because the company is developing new products and intends to sell them in
a new market. It is a major change as sales to North America are expected to generate significant additional profits.
Because this change will occur within three years of the change in the ownership of Nikau Ltd on 1 November 2007,
any trading losses arising prior to that date cannot be carried forward beyond that date.
Accordingly, the trading losses brought forward may only be offset against £158,958 ((£360,000 – £87,500) x 7/12)
of the company’s trading profits for the year. The remainder of the trading losses £36,742 (£195,700 – £158,958) will
be lost resulting in lost tax relief of £11,023 (£36,742 x 30%).
Tutorial note
The profits for the year ending 31 March 2008 will be apportioned to the periods pre and post 1 November 2007 on
either a time basis or some other basis that is just and reasonable. -
第10题:
4 (a) Explain the auditor’s responsibilities in respect of subsequent events. (5 marks)
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of the above matters for the auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Jinack Co for the year ended 30 September 2005 and, where appropriate, the year ending
30 September 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the matters.
正确答案:
4 JINACK CO
(a) Auditor’s responsibilities for subsequent events
■ Auditors must consider the effect of subsequent events on:
– the financial statements;
– the auditor’s report.
■ Subsequent events are all events occurring after a period end (i.e. reporting date) i.e.:
– events after the balance sheet date (as defined in IAS 10); and
– events after the financial statements have been authorised for issue.
Events occurring up to date of auditor’s report
■ The auditor is responsible for carrying out procedures designed to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence that all
events up to the date of the auditor’s report that may require adjustment of, or disclosure in, the financial statements
have been identified.
■ These procedures are in addition to those applied to specific transactions occurring after the period end that provide
audit evidence of period-end account balances (e.g. inventory cut-off and receipts from trade receivables). Such
procedures should ordinarily include:
– reviewing minutes of board/audit committee meetings;
– scrutinising latest interim financial statements/budgets/cash flows, etc;
– making/extending inquiries to legal advisors on litigation matters;
– inquiring of management whether any subsequent events have occurred that might affect the financial statements
(e.g. commitments entered into).
■ When the auditor becomes aware of events that materially affect the financial statements, the auditor must consider
whether they have been properly accounted for and adequately disclosed in the financial statements.
Facts discovered after the date of the auditor’s report but before financial statements are issued
Tutorial note: After the date of the auditor’s report it is management’s responsibility to inform. the auditor of facts which
may affect the financial statements.
■ If the auditor becomes aware of such facts which may materially affect the financial statements, the auditor:
– considers whether the financial statements need amendment;
– discusses the matter with management; and
– takes appropriate action (e.g. audit any amendments to the financial statements and issue a new auditor’s report).
■ If management does not amend the financial statements (where the auditor believes they need to be amended) and the
auditor’s report has not been released to the entity, the auditor should express a qualified opinion or an adverse opinion
(as appropriate).
■ If the auditor’s report has been released to the entity, the auditor must notify those charged with governance not to issue
the financial statements (and the auditor’s report thereon) to third parties.
Tutorial note: The auditor would seek legal advice if the financial statements and auditor’s report were subsequently issued.
Facts discovered after the financial statements have been issued
■ The auditor has no obligation to make any inquiry regarding financial statements that have been issued.
■ However, if the auditor becomes aware of a fact which existed at the date of the auditor’s report and which, if known
at that date, may have caused the auditor’s report to be modified, the auditor should:
– consider whether the financial statements need revision;
– discuss the matter with management; and
– take appropriate action (e.g. issuing a new report on revised financial statements). -
第11题:
(b) You are an audit manager in a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants currently assigned to the audit of Cleeves
Co for the year ended 30 September 2006. During the year Cleeves acquired a 100% interest in Howard Co.
Howard is material to Cleeves and audited by another firm, Parr & Co. You have just received Parr’s draft
auditor’s report for the year ended 30 September 2006. The wording is that of an unmodified report except for
the opinion paragraph which is as follows:
Audit opinion
As more fully explained in notes 11 and 15 impairment losses on non-current assets have not been
recognised in profit or loss as the directors are unable to quantify the amounts.
In our opinion, provision should be made for these as required by International Accounting Standard 36
(Impairment). If the provision had been so recognised the effect would have been to increase the loss before
and after tax for the year and to reduce the value of tangible and intangible non-current assets. However,
as the directors are unable to quantify the amounts we are unable to indicate the financial effect of such
omissions.
In view of the failure to provide for the impairments referred to above, in our opinion the financial statements
do not present fairly in all material respects the financial position of Howard Co as of 30 September 2006
and of its loss and its cash flows for the year then ended in accordance with International Financial Reporting
Standards.
Your review of the prior year auditor’s report shows that the 2005 audit opinion was worded identically.
Required:
(i) Critically appraise the appropriateness of the audit opinion given by Parr & Co on the financial
statements of Howard Co, for the years ended 30 September 2006 and 2005. (7 marks)
正确答案:(b) (i) Appropriateness of audit opinion given
Tutorial note: The answer points suggested by the marking scheme are listed in roughly the order in which they might
be extracted from the information presented in the question. The suggested answer groups together some of these
points under headings to give the analysis of the situation a possible structure.
Heading
■ The opinion paragraph is not properly headed. It does not state the form. of the opinion that has been given nor
the grounds for qualification.
■ The opinion ‘the financial statements do not give a true and fair view’ is an ‘adverse’ opinion.
■ That ‘provision should be made’, but has not, is a matter of disagreement that should be clearly stated as noncompliance
with IAS 36. The title of IAS 36 Impairment of Assets should be given in full.
■ The opinion should be headed ‘Disagreement on Accounting Policies – Inappropriate Accounting Method – Adverse
Opinion’.
1 ISA 250 does not specify with whom agreement should be reached but presumably with those charged with corporate governance (e.g audit committee or
2 other supervisory board).
20
6D–INTBA
Paper 3.1INT
Content
■ It is appropriate that the opinion paragraph should refer to the note(s) in the financial statements where the matter
giving rise to the modification is more fully explained. However, this is not an excuse for the audit opinion being
‘light’ on detail. For example, the reason for impairment could be summarised in the auditor’s report.
■ The effects have not been quantified, but they should be quantifiable. The maximum possible loss would be the
carrying amount of the non-current assets identified as impaired.
■ It is not clear why the directors have been ‘unable to quantify the amounts’. Since impairments should be
quantifiable any ‘inability’ suggest a limitation in scope of the audit, in which case the opinion should be disclaimed
(or ‘except for’) on grounds of lack of evidence rather than disagreement.
■ The wording is confusing. ‘Failure to provide’ suggests disagreement. However, there must be sufficient evidence
to support any disagreement. Although the directors cannot quantify the amounts it seems the auditors must have
been able to (estimate at least) in order to form. an opinion that the amounts involved are sufficiently material to
warrant a qualification.
■ The first paragraph refers to ‘non-current assets’. The second paragraph specifies ‘tangible and intangible assets’.
There is no explanation why or how both tangible and intangible assets are impaired.
■ The first paragraph refers to ‘profit or loss’ and the second and third paragraphs to ‘loss’. It may be clearer if the
first paragraph were to refer to recognition in the income statement.
■ It is not clear why the failure to recognise impairment warrants an adverse opinion rather than ‘except for’. The
effects of non-compliance with IAS 36 are to overstate the carrying amount(s) of non-current assets (that can be
specified) and to understate the loss. The matter does not appear to be pervasive and so an adverse opinion looks
unsuitable as the financial statements as a whole are not incomplete or misleading. A loss is already being reported
so it is not that a reported profit would be turned into a loss (which is sometimes judged to be ‘pervasive’).
Prior year
■ As the 2005 auditor’s report, as previously issued, included an adverse opinion and the matter that gave rise to
the modification:
– is unresolved; and
– results in a modification of the 2006 auditor’s report,
the 2006 auditor’s report should also be modified regarding the corresponding figures (ISA 710 Comparatives).
■ The 2006 auditor’s report does not refer to the prior period modification nor highlight that the matter resulting in
the current period modification is not new. For example, the report could say ‘As previously reported and as more
fully explained in notes ….’ and state ‘increase the loss by $x (2005 – $y)’. -
第12题:
(a) The following figures have been calculated from the financial statements (including comparatives) of Barstead for
the year ended 30 September 2009:
increase in profit after taxation 80%
increase in (basic) earnings per share 5%
increase in diluted earnings per share 2%
Required:
Explain why the three measures of earnings (profit) growth for the same company over the same period can
give apparently differing impressions. (4 marks)
(b) The profit after tax for Barstead for the year ended 30 September 2009 was $15 million. At 1 October 2008 the company had in issue 36 million equity shares and a $10 million 8% convertible loan note. The loan note will mature in 2010 and will be redeemed at par or converted to equity shares on the basis of 25 shares for each $100 of loan note at the loan-note holders’ option. On 1 January 2009 Barstead made a fully subscribed rights issue of one new share for every four shares held at a price of $2·80 each. The market price of the equity shares of Barstead immediately before the issue was $3·80. The earnings per share (EPS) reported for the year ended 30 September 2008 was 35 cents.
Barstead’s income tax rate is 25%.
Required:
Calculate the (basic) EPS figure for Barstead (including comparatives) and the diluted EPS (comparatives not required) that would be disclosed for the year ended 30 September 2009. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(a)Whilstprofitaftertax(anditsgrowth)isausefulmeasure,itmaynotgiveafairrepresentationofthetrueunderlyingearningsperformance.Inthisexample,userscouldinterpretthelargeannualincreaseinprofitaftertaxof80%asbeingindicativeofanunderlyingimprovementinprofitability(ratherthanwhatitreallyis:anincreaseinabsoluteprofit).Itispossible,evenprobable,that(someof)theprofitgrowthhasbeenachievedthroughtheacquisitionofothercompanies(acquisitivegrowth).Wherecompaniesareacquiredfromtheproceedsofanewissueofshares,orwheretheyhavebeenacquiredthroughshareexchanges,thiswillresultinagreaternumberofequitysharesoftheacquiringcompanybeinginissue.ThisiswhatappearstohavehappenedinthecaseofBarsteadastheimprovementindicatedbyitsearningspershare(EPS)isonly5%perannum.ThisexplainswhytheEPS(andthetrendofEPS)isconsideredamorereliableindicatorofperformancebecausetheadditionalprofitswhichcouldbeexpectedfromthegreaterresources(proceedsfromthesharesissued)ismatchedwiththeincreaseinthenumberofshares.Simplylookingatthegrowthinacompany’sprofitaftertaxdoesnottakeintoaccountanyincreasesintheresourcesusedtoearnthem.Anyincreaseingrowthfinancedbyborrowings(debt)wouldnothavethesameimpactonprofit(asbeingfinancedbyequityshares)becausethefinancecostsofthedebtwouldacttoreduceprofit.ThecalculationofadilutedEPStakesintoaccountanypotentialequitysharesinissue.Potentialordinarysharesarisefromfinancialinstruments(e.g.convertibleloannotesandoptions)thatmayentitletheirholderstoequitysharesinthefuture.ThedilutedEPSisusefulasitalertsexistingshareholderstothefactthatfutureEPSmaybereducedasaresultofsharecapitalchanges;inasenseitisawarningsign.InthiscasethelowerincreaseinthedilutedEPSisevidencethatthe(higher)increaseinthebasicEPShas,inpart,beenachievedthroughtheincreaseduseofdilutingfinancialinstruments.Thefinancecostoftheseinstrumentsislessthantheearningstheirproceedshavegeneratedleadingtoanincreaseincurrentprofits(andbasicEPS);however,inthefuturetheywillcausemoresharestobeissued.ThiscausesadilutionwherethefinancecostperpotentialnewshareislessthanthebasicEPS. -
第13题:
For this part, assume today’s date is 15 August 2005.
5 (a) Donald is aged 22, single, and about to finish his university education. He has plans to start up a business selling
computer games, and intends to start trading on 1 April 2006, making up accounts to 31 March annually.
He believes that his business will generate cash (equal to taxable profits) of £47,500 in the first year. He
originally intended to operate as a sole trader, but he has recently discovered that as an alternative, he could
operate through a company. He has been advised that if this is the case, he can take a maximum gross salary
of £42,648 out of the company.
Required:
(i) Advise Donald on the income tax (IT), national insurance (NIC) and corporation tax (CT) liabilities he
will incur for the year ended 31 March 2007 trading under each of the two alternative business
structures (sole trade/company). Your advice should be supported by calculations of disposable income
for both alternatives assuming that in the company case, he draws the maximum salary stated.
(7 marks)
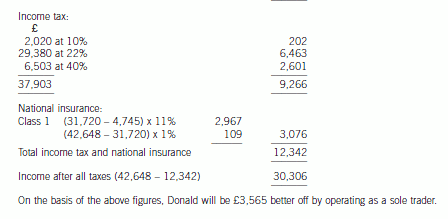
正确答案: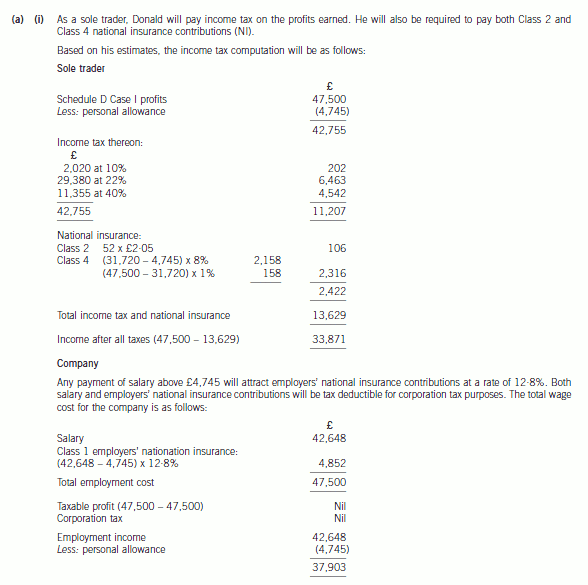
-
第14题:
3 Assume that today’s date is 10 May 2005.
You have recently been approached by Fred Flop. Fred is the managing director and 100% shareholder of Flop
Limited, a UK trading company with one wholly owned subsidiary. Both companies have a 31 March year-end.
Fred informs you that he is experiencing problems in dealing with aspects of his company tax returns. The company
accountant has been unable to keep up to date with matters, and Fred also believes that mistakes have been made
in the past. Fred needs assistance and tells you the following:
Year ended 31 March 2003
The corporation tax return for this period was not submitted until 2 November 2004, and corporation tax of £123,500
was paid at the same time. Profits chargeable to corporation tax were stated as £704,300.
A formal notice (CT203) requiring the company to file a self-assessment corporation tax return (dated 1 February
2004) had been received by the company on 4 February 2004.
A detailed examination of the accounts and tax computation has revealed the following.
– Computer equipment totalling £50,000 had been expensed in the accounts. No adjustment has been made in
the tax computation.
– A provision of £10,000 was made for repairs, but there is no evidence of supporting information.
– Legal and professional fees totalling £46,500 were allowed in full without any explanation. Fred has
subsequently produced the following analysis:
Analysis of legal & professional fees
£
Legal fees on a failed attempt to secure a trading loan 15,000
Debt collection agency fees 12,800
Obtaining planning consent for building extension 15,700
Accountant’s fees for preparing accounts 14,000
Legal fees relating to a trade dispute 19,000
– No enquiry has yet been raised by the Inland Revenue.
– Flop Ltd was a large company in terms of the Companies Act definition for the year in question.
– Flop Ltd had taxable profits of £595,000 in the previous year.
Year ended 31 March 2004
The corporation tax return has not yet been submitted for this year. The accounts are late and nearing completion,
with only one change still to be made. A notice requiring the company to file a self-assessment corporation tax return
(CT203) dated 27 July 2004 was received on 1 August 2004. No corporation tax has yet been paid.
1 – The computation currently shows profits chargeable to corporation tax of £815,000 before accounting
adjustments, and any adjustments for prior years.
– A company owing Flop Ltd £50,000 (excluding VAT) has gone into liquidation, and it is unlikely that any of this
money will be paid. The money has been outstanding since 3 September 2003, and the bad debt will need to
be included in the accounts.
1 Fred also believes there are problems in relation to the company’s VAT administration. The VAT return for the quarter
ended 31 March 2005 was submitted on 5 May 2005, and VAT of £24,000 was paid at the same time. The previous
return to 31 December 2004 was also submitted late. In addition, no account has been made for the VAT on the bad
debt. The VAT return for 30 June 2005 may also be late. Fred estimates the VAT liability for that quarter to be £8,250.
Required:
(a) (i) Calculate the revised corporation tax (CT) payable for the accounting periods ending 31 March 2003
and 2004 respectively. Your answer should include an explanation of the adjustments made as a result
of the information which has now come to light. (7 marks)
(ii) State, giving reasons, the due payment date of the corporation tax (CT) and the filing date of the
corporation tax return for each period, and identify any interest and penalties which may have arisen to
date. (8 marks)
正确答案:(a) Calculation of corporation tax
Year ended 31 March 2003
Corporation tax payable
There are three adjusting items:.
(i) The computers are capital items, as they have an enduring benefit. These need to be added back in the Schedule D
Case I calculation, and capital allowances claimed instead. The company is not small or medium by Companies Act
definitions and therefore no first year allowances are available. Allowances of £12,500 (50,000 x 25%) can be claimed,
leaving a TWDV of £37,500.
(ii) The provision appears to be general in nature. In addition there is insufficient information to justify the provision and it
should be disallowed until such times as it is released or utilised.
(iii) Costs relating to trading loan relationships are allowable, as are costs relating to the trade (debt collection, trade disputes
and accounting work). Costs relating to capital items (£5,700) are not allowable so will have to be added back.
Total profit chargeable to corporation tax is therefore £704,300 + 50,000 – 12,500 + 10,000 + 5,700 = 757,500. There are two associates, and therefore the 30% tax rate starts at £1,500,000/2 = £750,000. Corporation tax payable is 30% x£757,500 = £227,250.
Payment date
Although the rate of tax is 30% and the company ‘large’, quarterly payments will not apply, as the company was not large in the previous year. The due date for payment of tax is therefore nine months and one day after the end of the tax accounting period (31 March 2003) i.e. 1 January 2004.
Filing date
This is the later of:
– 12 months after the end of the period of account: 31 March 2004
– 3 months after the date of the notice requiring the return 1 May 2004
i.e. 1 May 2004.
-
第15题:
(b) Calculate the corporation tax (CT) liabilities for Alantech Ltd, Boron Ltd and Bubble Ltd for the year ending
31 December 2004 on the assumption that loss reliefs are taken as early as possible. (9 marks)
正确答案:(b) Schedule D Case I calculation
The three companies form. a group for both group relief and capital gains purposes as all shareholdings pass the 75%
ownership test. The calculation of the corporation tax liabilities is as follows:
-
第16题:
(c) Calculate the expected corporation tax liability of Dovedale Ltd for the year ending 31 March 2007 on the
assumption that all available reliefs are claimed by Dovedale Ltd but that Hira Ltd will not claim any capital
allowances in that year. (4 marks)
正确答案:

-
第17题:
(b) (i) Compute the corporation tax liability of Speak Write Ltd for its first trading period on the assumption
that the IR 35 legislation applies to all of its income. (2 marks)
正确答案: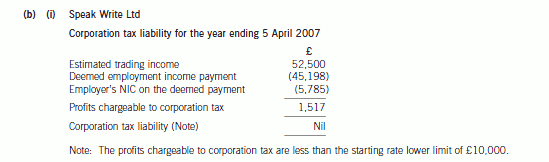
-
第18题:
(ii) Assuming the relief in (i) is available, advise Sharon on the maximum amount of cash she could receive
on incorporation, without triggering a capital gains tax (CGT) liability. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) As Sharon is entitled to the full rate of business asset taper relief, any gain will be reduced by 75%. The position is
maximised where the chargeable gain equals Sharon’s unused capital gains tax annual exemption of £8,500. Thus,
before taper relief, the gain she requires is £34,000 (1/0·25 x £8,500).
The amount to be held over is therefore £46,000 (80,000 – 34,000). Where part of the consideration is in the form
of cash, the gain eligible for incorporation relief is calculated using the formula:
Gain deferred = Gain x value of shares issued/total consideration
The formula is manipulated on the following basis:
£46,000 = £80,000 x (shares/120,000)
Shares/120,000 = £46,000/80,000
Shares = £46,000 x 120,000/80,000
i.e. £69,000.
As the total consideration is £120,000, this means that Sharon can take £51,000 (£120,000 – £69,000) in cash
without any CGT consequences. -
第19题:
(ii) Calculate the corporation tax (CT) payable by Tay Limited for the year ended 31 March 2006, taking
advantage of all available reliefs. (3 marks)
正确答案:
-
第20题:
(ii) Any increase or decrease in the group’s budgeted corporation tax liability for the year ending 30 June
2008 due to the restructuring on the assumption that trading losses will be used as efficiently as
possible. (8 marks)
正确答案:(ii) The budgeted corporation tax liability for the year ending 30 June 2008
Following the proposed restructuring, Rapier Ltd will be carrying on four separate trades. The current year loss arising
in the Dirk trade can be offset against its total profits. Its three subsidiaries will be dormant and will not be associates
for the purpose of determining the rate of corporation tax.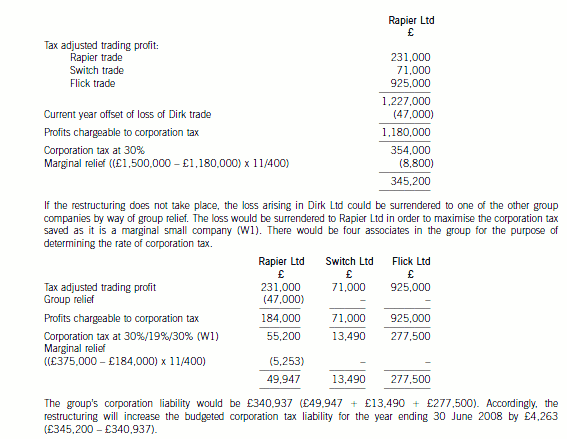
-
第21题:
(ii) The use of the trading loss of Tethys Ltd for the year ending 31 December 2008; (6 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Tethys Ltd – Use of trading loss
– The two companies will not be in a group relief group as Saturn Ltd will not own 75% of Tethys Ltd.
– For a consortium to exist, 75% of the ordinary share capital of Tethys Ltd must be held by companies which each
hold at least 5%. Accordingly, Tethys Ltd will be a consortium company if the balance of its share capital is owned
by Clangers Ltd but not if it is owned by Edith Clanger.
– If Tethys Ltd qualifies as a consortium company: 65% of its trading losses in the period from 1 August 2008 to
31 December 2008 can be surrendered to Saturn Ltd, i.e. £21,667 (£80,000 x 5/12 x 65%).
– If Tethys Ltd does not qualify as a consortium company: none of its loss can be surrendered to Saturn Ltd.
– The acquisition of 65% of Tethys Ltd is a change in ownership of the company. If there is a major change in the
nature or conduct of the trade of Tethys Ltd within three years of 1 August 2008, the loss arising prior to that date
cannot be carried forward for relief in the future.
Further information required:
– Ownership of the balance of the share capital of Tethys Ltd. -
第22题:
(b) You are the audit manager of Jinack Co, a private limited liability company. You are currently reviewing two
matters that have been left for your attention on the audit working paper file for the year ended 30 September
2005:
(i) Jinack holds an extensive range of inventory and keeps perpetual inventory records. There was no full
physical inventory count at 30 September 2005 as a system of continuous stock checking is operated by
warehouse personnel under the supervision of an internal audit department.
A major systems failure in October 2005 caused the perpetual inventory records to be corrupted before the
year-end inventory position was determined. As data recovery procedures were found to be inadequate,
Jinack is reconstructing the year-end quantities through a physical count and ‘rollback’. The reconstruction
exercise is expected to be completed in January 2006. (6 marks)
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of the above matters for the auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Jinack Co for the year ended 30 September 2005 and, where appropriate, the year ending
30 September 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the matters.
正确答案:
(b) Implications for the auditor’s report
(i) Corruption of perpetual inventory records
■ The loss of data (of physical inventory quantities at the balance sheet date) gives rise to a limitation on scope.
Tutorial note: It is the records of the asset that have been destroyed – not the physical asset.
■ The systems failure in October 2005 is clearly a non-adjusting post balance sheet event (IAS 10). If it is material
(such that non-disclosure could influence the economic decisions of users) Jinack should disclose:
– the nature of the event (i.e. systems failure); and
– an estimate of its financial effect (i.e. the cost of disruption and reconstruction of data to the extent that it is
not covered by insurance).
Tutorial note: The event has no financial effect on the realisability of inventory, only on its measurement for the
purpose of reporting it in the financial statements.
■ If material this disclosure could be made in the context of explaining how inventory has been estimated at
30 September 2005 (see later). If such disclosure, that the auditor considers to be necessary, is not made, the
audit opinion should be qualified ‘except for’ disagreement (over lack of disclosure).
Tutorial note: Such qualifications are extremely rare since management should be persuaded to make necessary
disclosure in the notes to the financial statements rather than have users’ attention drawn to the matter through
a qualification of the audit opinion.
■ The limitation on scope of the auditor’s work has been imposed by circumstances. Jinack’s accounting records
(for inventory) are inadequate (non-existent) for the auditor to perform. tests on them.
■ An alternative procedure to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence of inventory quantities at a year end is
subsequent count and ‘rollback’. However, the extent of ‘roll back’ testing is limited as records are still under
reconstruction.
■ The auditor may be able to obtain sufficient evidence that there is no material misstatement through a combination
of procedures:
– testing management’s controls over counting inventory after the balance sheet date and recording inventory
movements (e.g. sales and goods received);
– reperforming the reconstruction for significant items on a sample basis;
– analytical procedures such as a review of profit margins by inventory category.
■ ‘An extensive range of inventory’ is clearly material. The matter (i.e. systems failure) is not however pervasive, as
only inventory is affected.
■ Unless the reconstruction is substantially completed (i.e. inventory items not accounted for are insignificant) the
auditor cannot determine what adjustment, if any, might be determined to be necessary. The auditor’s report
should then be modified, ‘except for’, limitation on scope.
■ However, if sufficient evidence is obtained the auditor’s report should be unmodified.
■ An ‘emphasis of matter’ paragraph would not be appropriate because this matter is not one of significant
uncertainty.
Tutorial note: An uncertainty in this context is a matter whose outcome depends on future actions or events not
under the direct control of Jinack.
2006
■ If the 2005 auditor’s report is qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of limitation on scope there are two possibilities for
the inventory figure as at 30 September 2005 determined on completion of the reconstruction exercise:
(1) it is not materially different from the inventory figure reported; or
(2) it is materially different.
■ In (1), with the limitation now removed, the need for qualification is removed and the 2006 auditor’s report would
be unmodified (in respect of this matter).
■ In (2) the opening position should be restated and the comparatives adjusted in accordance with IAS 8 ‘Accounting
Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors’. The 2006 auditor’s report would again be unmodified.
Tutorial note: If the error was not corrected in accordance with IAS 8 it would be a different matter and the
auditor’s report would be modified (‘except for’ qualification) disagreement on accounting treatment. -
第23题:
3 The Stiletto Partnership consisted of three partners, Clint, Ben and Amy, who shared the profits of the business
equally. On 28 February 2007 the partners sold the business to Razor Ltd, in exchange for shares in Razor Ltd, with
each former partner owning one third of the new company.
The recent, tax adjusted, trading profits of the Stiletto Partnership have been as follows:
£
Year ended 30 June 2006 92,124
1 July 2006 to 28 February 2007 81,795
Clint, who was 65 on 5 October 2006, retired when the business was sold to Razor Ltd. He is now suggesting that
if the sale of the partnership, and his retirement, had been delayed until 30 April 2007, his total tax liability would
have been reduced. Clint’s only other income is gross pension income of £6,100 per year, which he began receiving
in the tax year 2005/06. Clint did not receive any salary or dividends from Razor Ltd. It is estimated that the
partnership’s tax adjusted trading profits for the period from 1 March 2007 to 30 April 2007 would have been
£20,760. Clint has overlap profits of £14,250 brought forward from when the partnership began trading.
Razor Ltd manufactures industrial cutting tools. On 1 July 2007, Razor Ltd will subscribe for the whole of the ordinary
share capital of Cutlass Inc, a company newly incorporated in the country of Sharpenia. It is intended that Cutlass
Inc will purchase partly finished tools from Razor Ltd and customise them in Sharpenia. It is anticipated that Cutlass
Inc’s annual profits chargeable to corporation tax will be approximately £120,000.
Ben and Amy will be the directors of Cutlass Inc, although Ben will not be involved in the company’s business on a
day-to-day basis. Amy intends to spend one or two weeks each month in the country of Sharpenia looking after the
company’s affairs. The remainder of her time will be spent in the UK. Amy has employment contracts with both Razor
Ltd and Cutlass Inc and her duties for Cutlass Inc will be carried out wholly in Sharpenia. Cutlass Inc will pay for
Amy’s flights to and from Sharpenia and for her husband and baby to visit her there twice a year. Amy is currently
UK resident and ordinarily resident.
The system of income tax and corporation tax in the country of Sharpenia is broadly similar to that in the UK although
the rate of corporation tax is 38% regardless of the level of profits. There is a double tax treaty between the UK and
Sharpenia based on the OECD model treaty. The clause in the treaty dealing with company residency states that a
company resident in both countries under domestic law will be regarded under the treaty as being resident only in the
country where it is effectively managed and controlled. Sharpenia is not a member of the European Union.
Required:
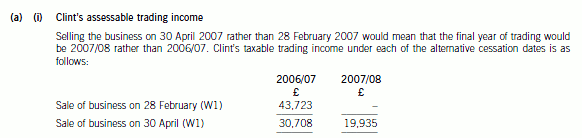
(a) (i) Calculate Clint’s taxable trading profits for the tax years 2006/07 and 2007/08 for both of the
alternative retirement dates (28 February 2007 and 30 April 2007). (3 marks)
正确答案: