5 The directors of Quapaw, a limited liability company, are reviewing the company’s draft financial statements for theyear ended 31 December 2004.The following material matters are under discussion:(a) During the year the company has begun selling a produ
题目
5 The directors of Quapaw, a limited liability company, are reviewing the company’s draft financial statements for the
year ended 31 December 2004.
The following material matters are under discussion:
(a) During the year the company has begun selling a product with a one-year warranty under which manufacturing
defects are remedied without charge. Some claims have already arisen under the warranty. (2 marks)
Required:
Advise the directors on the correct treatment of these matters, stating the relevant accounting standard which
justifies your answer in each case.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three matters
相似考题
更多“5 The directors of Quapaw, a limited liability company, are reviewing the company’s draft financial statements for theyear ended 31 December 2004.The following material matters are under discussion:(a) During the year the company has begun selling a produ”相关问题
-
第1题:
Additionally the directors wish to know how the provision for deferred taxation would be calculated in the following
situations under IAS12 ‘Income Taxes’:
(i) On 1 November 2003, the company had granted ten million share options worth $40 million subject to a two
year vesting period. Local tax law allows a tax deduction at the exercise date of the intrinsic value of the options.
The intrinsic value of the ten million share options at 31 October 2004 was $16 million and at 31 October 2005
was $46 million. The increase in the share price in the year to 31 October 2005 could not be foreseen at
31 October 2004. The options were exercised at 31 October 2005. The directors are unsure how to account
for deferred taxation on this transaction for the years ended 31 October 2004 and 31 October 2005.
(ii) Panel is leasing plant under a finance lease over a five year period. The asset was recorded at the present value
of the minimum lease payments of $12 million at the inception of the lease which was 1 November 2004. The
asset is depreciated on a straight line basis over the five years and has no residual value. The annual lease
payments are $3 million payable in arrears on 31 October and the effective interest rate is 8% per annum. The
directors have not leased an asset under a finance lease before and are unsure as to its treatment for deferred
taxation. The company can claim a tax deduction for the annual rental payment as the finance lease does not
qualify for tax relief.
(iii) A wholly owned overseas subsidiary, Pins, a limited liability company, sold goods costing $7 million to Panel on
1 September 2005, and these goods had not been sold by Panel before the year end. Panel had paid $9 million
for these goods. The directors do not understand how this transaction should be dealt with in the financial
statements of the subsidiary and the group for taxation purposes. Pins pays tax locally at 30%.
(iv) Nails, a limited liability company, is a wholly owned subsidiary of Panel, and is a cash generating unit in its own
right. The value of the property, plant and equipment of Nails at 31 October 2005 was $6 million and purchased
goodwill was $1 million before any impairment loss. The company had no other assets or liabilities. An
impairment loss of $1·8 million had occurred at 31 October 2005. The tax base of the property, plant and
equipment of Nails was $4 million as at 31 October 2005. The directors wish to know how the impairment loss
will affect the deferred tax provision for the year. Impairment losses are not an allowable expense for taxation
purposes.
Assume a tax rate of 30%.
Required:
(b) Discuss, with suitable computations, how the situations (i) to (iv) above will impact on the accounting for
deferred tax under IAS12 ‘Income Taxes’ in the group financial statements of Panel. (16 marks)
(The situations in (i) to (iv) above carry equal marks)
正确答案:(b) (i) The tax deduction is based on the option’s intrinsic value which is the difference between the market price and exercise
price of the share option. It is likely that a deferred tax asset will arise which represents the difference between the tax
base of the employee’s service received to date and the carrying amount which will effectively normally be zero.
The recognition of the deferred tax asset should be dealt with on the following basis:
(a) if the estimated or actual tax deduction is less than or equal to the cumulative recognised expense then the
associated tax benefits are recognised in the income statement
(b) if the estimated or actual tax deduction exceeds the cumulative recognised compensation expense then the excess
tax benefits are recognised directly in a separate component of equity.
As regards the tax effects of the share options, in the year to 31 October 2004, the tax effect of the remuneration expensewill be in excess of the tax benefit.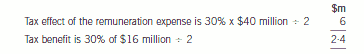
The company will have to estimate the amount of the tax benefit as it is based on the share price at 31 October 2005.
The information available at 31 October 2004 indicates a tax benefit based on an intrinsic value of $16 million.
As a result, the tax benefit of $2·4 million will be recognised within the deferred tax provision. At 31 October 2005,
the options have been exercised. Tax receivable will be 30% x $46 million i.e. $13·8 million. The deferred tax asset
of $2·4 million is no longer recognised as the tax benefit has crystallised at the date when the options were exercised.
For a tax benefit to be recognised in the year to 31 October 2004, the provisions of IAS12 should be complied with as
regards the recognition of a deferred tax asset.
(ii) Plant acquired under a finance lease will be recorded as property, plant and equipment and a corresponding liability for
the obligation to pay future rentals. Rents payable are apportioned between the finance charge and a reduction of the
outstanding obligation. A temporary difference will effectively arise between the value of the plant for accounting
purposes and the equivalent of the outstanding obligation as the annual rental payments qualify for tax relief. The tax
base of the asset is the amount deductible for tax in future which is zero. The tax base of the liability is the carrying
amount less any future tax deductible amounts which will give a tax base of zero. Thus the net temporary differencewill be: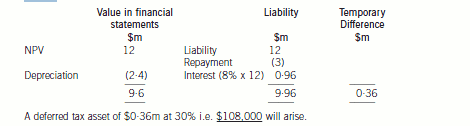
(iii) The subsidiary, Pins, has made a profit of $2 million on the transaction with Panel. These goods are held in inventory
at the year end and a consolidation adjustment of an equivalent amount will be made against profit and inventory. Pins
will have provided for the tax on this profit as part of its current tax liability. This tax will need to be eliminated at the
group level and this will be done by recognising a deferred tax asset of $2 million x 30%, i.e. $600,000. Thus any
consolidation adjustments that have the effect of deferring or accelerating tax when viewed from a group perspective will
be accounted for as part of the deferred tax provision. Group profit will be different to the sum of the profits of the
individual group companies. Tax is normally payable on the profits of the individual companies. Thus there is a need
to account for this temporary difference. IAS12 does not specifically address the issue of which tax rate should be used
calculate the deferred tax provision. IAS12 does generally say that regard should be had to the expected recovery or
settlement of the tax. This would be generally consistent with using the rate applicable to the transferee company (Panel)
rather than the transferor (Pins).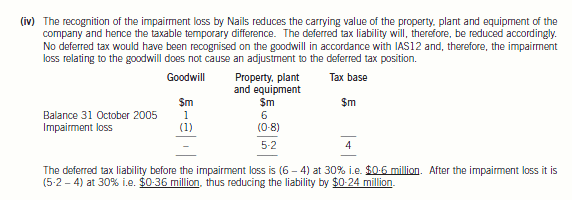
-
第2题:
(ii) The property of the former administrative centre of Tyre is owned by the company. Tyre had decided in the year
that the property was surplus to requirements and demolished the building on 10 June 2006. After demolition,
the company will have to carry out remedial environmental work, which is a legal requirement resulting from the
demolition. It was intended that the land would be sold after the remedial work had been carried out. However,
land prices are currently increasing in value and, therefore, the company has decided that it will not sell the land
immediately. Tyres uses the ‘cost model’ in IAS16 ‘Property, plant and equipment’ and has owned the property
for many years. (7 marks)
Required:
Advise the directors of Tyre on how to treat the above items in the financial statements for the year ended
31 May 2006.
(The mark allocation is shown against each of the above items)
正确答案:
(ii) Former administrative building
The land and buildings of the former administrative centre are accounted for as separate elements. The demolition of the
building is an indicator of the impairment of the property under IAS36. The building will not generate any future cash flows
and its recoverable amount is zero. Therefore, the carrying value of the building will be written down to zero and the loss
charged to profit or loss in the year to 31 May 2006 when the decision to demolish the building was made. The land value
will be in excess of its carrying amount as the company uses the cost model and land prices are rising. Thus no impairment
charge is recognised in respect of the land.
The demolition costs will be expensed when incurred and a provision for environmental costs recognised when an obligation
arises, i.e. in the financial year to 31 May 2007. It may be that some of these costs could be recognised as site preparation
costs and be capitalised under IAS16.
The land will not meet the criteria set out in IFRS5 ‘Non-current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations’ as a noncurrent
asset which is held for sale. IFRS5 says that a non-current asset should be classified as ‘held for sale’ if its carrying
amount will be recovered principally through a sale transaction rather than through continuing use. However, the non-current
asset must be available for immediate sale and must be actively marketed at its current fair value (amongst other criteria) and
these criteria have not been met in this case.
When the building has been demolished and the site prepared, the land could be considered to be an investment property
and accounted for under IAS40 ‘Investment Property’ where the fair value model allows gains (or losses) to be recognised inprofit or loss for the period. -
第3题:
3 (a) Leigh, a public limited company, purchased the whole of the share capital of Hash, a limited company, on 1 June
2006. The whole of the share capital of Hash was formerly owned by the five directors of Hash and under the
terms of the purchase agreement, the five directors were to receive a total of three million ordinary shares of $1
of Leigh on 1 June 2006 (market value $6 million) and a further 5,000 shares per director on 31 May 2007,
if they were still employed by Leigh on that date. All of the directors were still employed by Leigh at 31 May
2007.
Leigh granted and issued fully paid shares to its own employees on 31 May 2007. Normally share options issued
to employees would vest over a three year period, but these shares were given as a bonus because of the
company’s exceptional performance over the period. The shares in Leigh had a market value of $3 million
(one million ordinary shares of $1 at $3 per share) on 31 May 2007 and an average fair value of
$2·5 million (one million ordinary shares of $1 at $2·50 per share) for the year ended 31 May 2007. It is
expected that Leigh’s share price will rise to $6 per share over the next three years. (10 marks)
Required:
Discuss with suitable computations how the above share based transactions should be accounted for in the
financial statements of Leigh for the year ended 31 May 2007.
正确答案:
(a) The shares issued to the management of Hash by Leigh (three million ordinary shares of $1) for the purchase of the company
would not be accounted for under IFRS2 ‘Share-based payment’ but would be dealt with under IFRS3 ‘Business
Combinations’.
The cost of the business combination will be the total of the fair values of the consideration given by the acquirer plus any
attributable cost. In this case the shares of Leigh will be fair valued at $6 million with $3 million being shown as share capital
and $3million as share premium. However, the shares issued as contingent consideration may be accounted for under IFRS2.
The terms of the issuance of shares will need to be examined. Where part of the consideration may be reliant on uncertain
future events, and it is probable that the additional consideration is payable and can be measured reliably, then it is included
in the cost of the business consideration at the acquisition date. However, the question to be answered in the case of the
additional 5,000 shares per director is whether the shares are compensation or part of the purchase price. There is a need
to understand why the acquisition agreement includes a provision for a contingent payment. It is possible that the price paid
initially by Leigh was quite low and, therefore, this then represents a further purchase consideration. However, in this instance
the additional payment is linked to continuing employment and, therefore, it would be argued that because of the link between
the contingent consideration and continuing employment that it represents a compensation arrangement which should be
included within the scope of IFRS2.
Thus as there is a performance condition, (the performance condition will apply as it is not a market condition) the substance
of the agreement is that the shares are compensation, then they will be fair valued at the grant date and not when the shares
vest. Therefore, the share price of $2 per share will be used to give compensation of $50,000 (5 x 5,000 x $2). (Under
IFRS3, fair value is measured at the date the consideration is provided and discounted to presented value. No guidance is
provided on what the appropriate discount rate might be. Thus the fair value used would have been $3 per share at 31 May
2007.) The compensation will be charged to the income statement and included in equity.
The shares issued to the employees of Leigh will be accounted for under IFRS2. The issuance of fully paid shares will be
presumed to relate to past service. The normal vesting period for share options is irrelevant, as is the average fair value of the
shares during the period. The shares would be expensed at a value of $3 million with a corresponding increase in equity.
Goods or services acquired in a share based payment transaction should be recognised when they are received. In the case
of goods then this will be when this occurs. However, it is somewhat more difficult sometimes to determine when services
are received. In a case of goods the vesting date is not really relevant, however, it is highly relevant for employee services. If
shares are issued that vest immediately then there is a presumption that these are a consideration for past employee services. -
第4题:
(d) Additionally Router purchased 60% of the ordinary shares of a radio station, Playtime, a public limited company,
on 31 May 2007. The remaining 40% of the ordinary shares are owned by a competitor company who owns a
substantial number of warrants issued by Playtime which are currently exercisable. If these warrants are
exercised, they will result in Router only owning 35% of the voting shares of Playtime. (4 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above items should be dealt with in the group financial statements of Router for the year ended
31 May 2007.
正确答案:(d) IAS27 paragraph 14, ‘Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements’, states that warrants that have the potential to give
the holder voting power or reduce another party’s voting power over the financial and operating policies of the issuer should
be considered when existence of control is assessed. The warrants held by the competitor company, if exercised, would grant
that company control over Playtime. One party only can control Playtime and, therefore, the competitor company should
consolidate Playtime. In coming to this decision all the facts and circumstances that affect potential voting rights (except the
intention of management and the financial ability to exercise or convert) should be considered. It seems, however, that there
is a prima facie case for not consolidating Playtime but accounting for it under IAS28 or IAS39.
-
第5题:
13 At 1 January 2005 a company had an allowance for receivables of $18,000
At 31 December 2005 the company’s trade receivables were $458,000.
It was decided:
(a) To write off debts totalling $28,000 as irrecoverable;
(b) To adjust the allowance for receivables to the equivalent of 5% of the remaining receivables based on past
experience.
What figure should appear in the company’s income statement for the total of debts written off as irrecoverable
and the movement in the allowance for receivables for the year ended 31 December 2005?
A $49,500
B $31,500
C $32,900
D $50,900
正确答案:B
430,000 x 5% = 21,500 – 18,000 + 28,000 -
第6题:
(b) You are the audit manager of Jinack Co, a private limited liability company. You are currently reviewing two
matters that have been left for your attention on the audit working paper file for the year ended 30 September
2005:
(i) Jinack holds an extensive range of inventory and keeps perpetual inventory records. There was no full
physical inventory count at 30 September 2005 as a system of continuous stock checking is operated by
warehouse personnel under the supervision of an internal audit department.
A major systems failure in October 2005 caused the perpetual inventory records to be corrupted before the
year-end inventory position was determined. As data recovery procedures were found to be inadequate,
Jinack is reconstructing the year-end quantities through a physical count and ‘rollback’. The reconstruction
exercise is expected to be completed in January 2006. (6 marks)
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of the above matters for the auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Jinack Co for the year ended 30 September 2005 and, where appropriate, the year ending
30 September 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the matters.
正确答案:
(b) Implications for the auditor’s report
(i) Corruption of perpetual inventory records
■ The loss of data (of physical inventory quantities at the balance sheet date) gives rise to a limitation on scope.
Tutorial note: It is the records of the asset that have been destroyed – not the physical asset.
■ The systems failure in October 2005 is clearly a non-adjusting post balance sheet event (IAS 10). If it is material
(such that non-disclosure could influence the economic decisions of users) Jinack should disclose:
– the nature of the event (i.e. systems failure); and
– an estimate of its financial effect (i.e. the cost of disruption and reconstruction of data to the extent that it is
not covered by insurance).
Tutorial note: The event has no financial effect on the realisability of inventory, only on its measurement for the
purpose of reporting it in the financial statements.
■ If material this disclosure could be made in the context of explaining how inventory has been estimated at
30 September 2005 (see later). If such disclosure, that the auditor considers to be necessary, is not made, the
audit opinion should be qualified ‘except for’ disagreement (over lack of disclosure).
Tutorial note: Such qualifications are extremely rare since management should be persuaded to make necessary
disclosure in the notes to the financial statements rather than have users’ attention drawn to the matter through
a qualification of the audit opinion.
■ The limitation on scope of the auditor’s work has been imposed by circumstances. Jinack’s accounting records
(for inventory) are inadequate (non-existent) for the auditor to perform. tests on them.
■ An alternative procedure to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence of inventory quantities at a year end is
subsequent count and ‘rollback’. However, the extent of ‘roll back’ testing is limited as records are still under
reconstruction.
■ The auditor may be able to obtain sufficient evidence that there is no material misstatement through a combination
of procedures:
– testing management’s controls over counting inventory after the balance sheet date and recording inventory
movements (e.g. sales and goods received);
– reperforming the reconstruction for significant items on a sample basis;
– analytical procedures such as a review of profit margins by inventory category.
■ ‘An extensive range of inventory’ is clearly material. The matter (i.e. systems failure) is not however pervasive, as
only inventory is affected.
■ Unless the reconstruction is substantially completed (i.e. inventory items not accounted for are insignificant) the
auditor cannot determine what adjustment, if any, might be determined to be necessary. The auditor’s report
should then be modified, ‘except for’, limitation on scope.
■ However, if sufficient evidence is obtained the auditor’s report should be unmodified.
■ An ‘emphasis of matter’ paragraph would not be appropriate because this matter is not one of significant
uncertainty.
Tutorial note: An uncertainty in this context is a matter whose outcome depends on future actions or events not
under the direct control of Jinack.
2006
■ If the 2005 auditor’s report is qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of limitation on scope there are two possibilities for
the inventory figure as at 30 September 2005 determined on completion of the reconstruction exercise:
(1) it is not materially different from the inventory figure reported; or
(2) it is materially different.
■ In (1), with the limitation now removed, the need for qualification is removed and the 2006 auditor’s report would
be unmodified (in respect of this matter).
■ In (2) the opening position should be restated and the comparatives adjusted in accordance with IAS 8 ‘Accounting
Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors’. The 2006 auditor’s report would again be unmodified.
Tutorial note: If the error was not corrected in accordance with IAS 8 it would be a different matter and the
auditor’s report would be modified (‘except for’ qualification) disagreement on accounting treatment. -
第7题:
(b) You are an audit manager with specific responsibility for reviewing other information in documents containing
audited financial statements before your firm’s auditor’s report is signed. The financial statements of Hegas, a
privately-owned civil engineering company, show total assets of $120 million, revenue of $261 million, and profit
before tax of $9·2 million for the year ended 31 March 2005. Your review of the Annual Report has revealed
the following:
(i) The statement of changes in equity includes $4·5 million under a separate heading of ‘miscellaneous item’
which is described as ‘other difference not recognized in income’. There is no further reference to this
amount or ‘other difference’ elsewhere in the financial statements. However, the Management Report, which
is required by statute, is not audited. It discloses that ‘changes in shareholders’ equity not recognized in
income includes $4·5 million arising on the revaluation of investment properties’.
The notes to the financial statements state that the company has implemented IAS 40 ‘Investment Property’
for the first time in the year to 31 March 2005 and also that ‘the adoption of this standard did not have a
significant impact on Hegas’s financial position or its results of operations during 2005’.
(ii) The chairman’s statement asserts ‘Hegas has now achieved a position as one of the world’s largest
generators of hydro-electricity, with a dedicated commitment to accountable ethical professionalism’. Audit
working papers show that 14% of revenue was derived from hydro-electricity (2004: 12%). Publicly
available information shows that there are seven international suppliers of hydro-electricity in Africa alone,
which are all at least three times the size of Hegas in terms of both annual turnover and population supplied.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of the above matters for the auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Hegas for the year ended 31 March 2005. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Implications for the auditor’s report
(i) Management Report
■ $4·5 million represents 3·75% of total assets, 1·7% of revenue and 48·9% profit before tax. As this is material
by any criteria (exceeding all of 2% of total assets, 1/2% revenue and 5% PBT), the specific disclosure requirements
of IASs need to be met (IAS 1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’).
■ The Management Report discloses the amount and the reason for a material change in equity whereas the financial
statements do not show the reason for the change and suggest that it is immaterial. As the increase in equity
attributable to this adjustment is nearly half as much as that attributable to PBT there is a material inconsistency
between the Management Report and the audited financial statements.
■ Amendment to the Management Report is not required.
Tutorial note: Marks will be awarded for arguing, alternatively, that the Management Report disclosure needs to
be amended to clarify that the revaluation arises from the first time implementation.
■ Amendment to the financial statements is required because the disclosure is:
– incorrect – as, on first adoption of IAS 40, the fair value adjustment should be against the opening balance
of retained earnings; and
– inadequate – because it is being ‘supplemented’ by additional disclosure in a document which is not within
the scope of the audit of financial statements.
■ Whilst it is true that the adoption of IAS 40 did not have a significant impact on results of operations, Hegas’s
financial position has increased by nearly 4% in respect of the revaluation (to fair value) of just one asset category
(investment properties). As this is significant, the statement in the notes should be redrafted.
■ If the financial statements are not amended, the auditor’s report should be qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of
disagreement (non-compliance with IAS 40) as the matter is material but not pervasive. Additional disclosure
should also be given (e.g. that the ‘other difference’ is a fair value adjustment).
■ However, it is likely that when faced with the prospect of a qualified auditor’s report Hegas’s management will
rectify the financial statements so that an unmodified auditor’s report can be issued.
Tutorial note: Marks will be awarded for other relevant points e.g. citing IAS 8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in
Accounting Estimates and Errors’.
(ii) Chairman’s statement
Tutorial note: Hegas is privately-owned therefore IAS 14 ‘Segment Reporting’ does not apply and the proportion of
revenue attributable to hydro-electricity will not be required to be disclosed in the financial statements. However, credit
will be awarded for discussing the implications for the auditor’s report if it is regarded as a material inconsistency on
the assumption that segment revenue (or similar) is reported in the financial statements.
■ The assertion in the chairman’s statement, which does not fall within the scope of the audit of the financial
statements, claims two things, namely that the company:
(1) is ‘one of the world’s largest generators of hydro-electricity’; and
(2) has ‘a dedicated commitment to accountable ethical professionalism’.
■ To the extent that this information does not relate to matters disclosed in the financial statements it may give rise
to a material misstatement of fact. In particular, the first statement presents a misleading impression of the
company’s size. In misleading a user of the financial statements with this statement, the second statement is not
true (as it is not ethical or professional to mislead the reader and potentially undermine the credibility of the
financial statements).
■ The first statement is a material misstatement of fact because, for example:
– the company is privately-owned, and publicly-owned international/multi-nationals are larger;
– the company’s main activity is civil engineering not electricity generation (only 14% of revenue is derived from
HEP);
– as the company ranks at best eighth against African companies alone it ranks much lower globally.
■ Hegas should be asked to reconsider the wording of the chairman’s statement (i.e. removing these assertions) and
consult, as necessary, the company’s legal advisor.
■ If the statement is not changed there will be no grounds for qualification of the opinion on the audited financial
statements. The audit firm should therefore take legal advice on how the matter should be reported.
■ However, an emphasis of matter paragraph may be used to report on matters other than those affecting the audited
financial statements. For example, to explain the misstatement of fact if management refuses to make the
amendment.
Tutorial note: Marks will also be awarded for relevant comments about the chairman’s statement being perceived by
many readers to be subject to audit and therefore that the unfounded statement might undermine the credibility of the
financial statements. Shareholders tend to rely on the chairman’s statement, even though it is not regulated or audited,
because modern financial statements are so complex. -
第8题:
(c) Pinzon, a limited liability company and audit client, is threatening to sue your firm in respect of audit fees charged
for the year ended 31 December 2004. Pinzon is alleging that Bartolome billed the full rate on air fares for audit
staff when substantial discounts had been obtained by Bartolome. (4 marks)
Required:
Comment on the ethical and other professional issues raised by each of the above matters and their implications,
if any, for the continuation of each assignment.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
(c) Threatened legal action
Ethical and professional issues
■ An advocacy threat has arisen as Bartolome and Pinzon are in opposition concerning the fee note for the 2004 audit.
■ If Pinzon’s allegations are true this may cast serious doubt on the integrity of Bartolome. Pinzon should be advised to
take their claims first to ACCA’s Disciplinary Committee.
■ If Bartolome has indeed charged full air fares when substantial discounts had been obtained this could be due to:
– Bartolome incorrectly believing this to be an acceptable industry practice; or
– a billing error/oversight.
In either case Bartolome should issue a credit note, although this may be insufficient to make amends and salvage the
auditor-client relationship.
■ Bartolome may have legitimately claimed for full airfares if this was agreed in its contract (i.e. the terms of engagement)
with Pinzon.
Implications for continuation with assignment
Unless the threat of legal action is amicably resolved very quickly (which is perhaps unlikely) Pinzon and Bartolome are in
conflict. Bartolome cannot therefore be seen to be independent and so should tender their resignation as auditor for the year
ending 31 December 2005 (assuming they were re-appointed and have not already been removed from office). -
第9题:
(b) You are the audit manager of Johnston Co, a private company. The draft consolidated financial statements for
the year ended 31 March 2006 show profit before taxation of $10·5 million (2005 – $9·4 million) and total
assets of $55·2 million (2005 – $50·7 million).
Your firm was appointed auditor of Tiltman Co when Johnston Co acquired all the shares of Tiltman Co in March
2006. Tiltman’s draft financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2006 show profit before taxation of
$0·7 million (2005 – $1·7 million) and total assets of $16·1 million (2005 – $16·6 million). The auditor’s
report on the financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2005 was unmodified.
You are currently reviewing two matters that have been left for your attention on the audit working paper files for
the year ended 31 March 2006:
(i) In December 2004 Tiltman installed a new computer system that properly quantified an overvaluation of
inventory amounting to $2·7 million. This is being written off over three years.
(ii) In May 2006, Tiltman’s head office was relocated to Johnston’s premises as part of a restructuring.
Provisions for the resulting redundancies and non-cancellable lease payments amounting to $2·3 million
have been made in the financial statements of Tiltman for the year ended 31 March 2006.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of these two matters for your auditor’s reports on the financial
statements of Johnston Co and Tiltman Co for the year ended 31 March 2006. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Tiltman Co
Tiltman’s total assets at 31 March 2006 represent 29% (16·1/55·2 × 100) of Johnston’s total assets. The subsidiary is
therefore material to Johnston’s consolidated financial statements.
Tutorial note: Tiltman’s profit for the year is not relevant as the acquisition took place just before the year end and will
therefore have no impact on the consolidated income statement. Calculations of the effect on consolidated profit before
taxation are therefore inappropriate and will not be awarded marks.
(i) Inventory overvaluation
This should have been written off to the income statement in the year to 31 March 2005 and not spread over three
years (contrary to IAS 2 ‘Inventories’).
At 31 March 2006 inventory is overvalued by $0·9m. This represents all Tiltmans’s profit for the year and 5·6% of
total assets and is material. At 31 March 2005 inventory was materially overvalued by $1·8m ($1·7m reported profit
should have been a $0·1m loss).
Tutorial note: 1/3 of the overvaluation was written off in the prior period (i.e. year to 31 March 2005) instead of $2·7m.
That the prior period’s auditor’s report was unmodified means that the previous auditor concurred with an incorrect
accounting treatment (or otherwise gave an inappropriate audit opinion).
As the matter is material a prior period adjustment is required (IAS 8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting
Estimates and Errors’). $1·8m should be written off against opening reserves (i.e. restated as at 1 April 2005).
(ii) Restructuring provision
$2·3m expense has been charged to Tiltman’s profit and loss in arriving at a draft profit of $0·7m. This is very material.
(The provision represents 14·3% of Tiltman’s total assets and is material to the balance sheet date also.)
The provision for redundancies and onerous contracts should not have been made for the year ended 31 March 2006
unless there was a constructive obligation at the balance sheet date (IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and
Contingent Assets’). So, unless the main features of the restructuring plan had been announced to those affected (i.e.
redundancy notifications issued to employees), the provision should be reversed. However, it should then be disclosed
as a non-adjusting post balance sheet event (IAS 10 ‘Events After the Balance Sheet Date’).
Given the short time (less than one month) between acquisition and the balance sheet it is very possible that a
constructive obligation does not arise at the balance sheet date. The relocation in May was only part of a restructuring
(and could be the first evidence that Johnston’s management has started to implement a restructuring plan).
There is a risk that goodwill on consolidation of Tiltman may be overstated in Johnston’s consolidated financial
statements. To avoid the $2·3 expense having a significant effect on post-acquisition profit (which may be negligible
due to the short time between acquisition and year end), Johnston may have recognised it as a liability in the
determination of goodwill on acquisition.
However, the execution of Tiltman’s restructuring plan, though made for the year ended 31 March 2006, was conditional
upon its acquisition by Johnston. It does not therefore represent, immediately before the business combination, a
present obligation of Johnston. Nor is it a contingent liability of Johnston immediately before the combination. Therefore
Johnston cannot recognise a liability for Tiltman’s restructuring plans as part of allocating the cost of the combination
(IFRS 3 ‘Business Combinations’).
Tiltman’s auditor’s report
The following adjustments are required to the financial statements:
■ restructuring provision, $2·3m, eliminated;
■ adequate disclosure of relocation as a non-adjusting post balance sheet event;
■ current period inventory written down by $0·9m;
■ prior period inventory (and reserves) written down by $1·8m.
Profit for the year to 31 March 2006 should be $3·9m ($0·7 + $0·9 + $2·3).
If all these adjustments are made the auditor’s report should be unmodified. Otherwise, the auditor’s report should be
qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of disagreement. If none of the adjustments are made, the qualification should still be
‘except for’ as the matters are not pervasive.
Johnston’s auditor’s report
If Tiltman’s auditor’s report is unmodified (because the required adjustments are made) the auditor’s report of Johnston
should be similarly unmodified. As Tiltman is wholly-owned by Johnston there should be no problem getting the
adjustments made.
If no adjustments were made in Tiltman’s financial statements, adjustments could be made on consolidation, if
necessary, to avoid modification of the auditor’s report on Johnston’s financial statements.
The effect of these adjustments on Tiltman’s net assets is an increase of $1·4m. Goodwill arising on consolidation (if
any) would be reduced by $1·4m. The reduction in consolidated total assets required ($0·9m + $1·4m) is therefore
the same as the reduction in consolidated total liabilities (i.e. $2·3m). $2·3m is material (4·2% consolidated total
assets). If Tiltman’s financial statements are not adjusted and no adjustments are made on consolidation, the
consolidated financial position (balance sheet) should be qualified ‘except for’. The results of operations (i.e. profit for
the period) should be unqualified (if permitted in the jurisdiction in which Johnston reports).
Adjustment in respect of the inventory valuation may not be required as Johnston should have consolidated inventory
at fair value on acquisition. In this case, consolidated total liabilities should be reduced by $2·3m and goodwill arising
on consolidation (if any) reduced by $2·3m.
Tutorial note: The effect of any possible goodwill impairment has been ignored as the subsidiary has only just been
acquired and the balance sheet date is very close to the date of acquisition. -
第10题:
(b) You are the audit manager of Petrie Co, a private company, that retails kitchen utensils. The draft financial
statements for the year ended 31 March 2007 show revenue $42·2 million (2006 – $41·8 million), profit before
taxation of $1·8 million (2006 – $2·2 million) and total assets of $30·7 million (2006 – $23·4 million).
You are currently reviewing two matters that have been left for your attention on Petrie’s audit working paper file
for the year ended 31 March 2007:
(i) Petrie’s management board decided to revalue properties for the year ended 31 March 2007 that had
previously all been measured at depreciated cost. At the balance sheet date three properties had been
revalued by a total of $1·7 million. Another nine properties have since been revalued by $5·4 million. The
remaining three properties are expected to be revalued later in 2007. (5 marks)
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of these two matters for your auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Petrie Co for the year ended 31 March 2007.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the matters above.
正确答案:
(b) Implications for auditor’s report
(i) Selective revaluation of premises
The revaluations are clearly material to the balance sheet as $1·7 million and $5·4 million represent 5·5% and 17·6%
of total assets, respectively (and 23·1% in total). As the effects of the revaluation on line items in the financial statements
are clearly identified (e.g. revalued amount, depreciation, surplus in statement of changes in equity) the matter is not
pervasive.
The valuations of the nine properties after the year end provide additional evidence of conditions existing at the year end
and are therefore adjusting events per IAS 10 Events After the Balance Sheet Date.
Tutorial note: It is ‘now’ still less than three months after the year end so these valuations can reasonably be expected
to reflect year end values.
However, IAS 16 Property, Plant and Equipment does not permit the selective revaluation of assets thus the whole class
of premises would need to have been revalued for the year to 31 March 2007 to change the measurement basis for this
reporting period.
The revaluation exercise is incomplete. Unless the remaining three properties are revalued before the auditor’s report on
the financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2007 is signed off:
(1) the $7·1 revaluation made so far must be reversed to show all premises at depreciated cost as in previous years;
OR
(2) the auditor’s report would be qualified ‘except for’ disagreement regarding non-compliance with IAS 16.
When it is appropriate to adopt the revaluation model (e.g. next year) the change in accounting policy (from a cost model
to a revaluation model) should be accounted for in accordance with IAS 16 (i.e. as a revaluation).
Tutorial note: IAS 8 Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors does not apply to the initial
application of a policy to revalue assets in accordance with IAS 16.
Assuming the revaluation is written back, before giving an unmodified opinion, the auditor should consider why the three
properties were not revalued. In particular if there are any indicators of impairment (e.g. physical dilapidation) there
should be sufficient evidence on the working paper file to show that the carrying amount of these properties is not
materially greater than their recoverable amount (i.e. the higher of value in use and fair value less costs to sell).
If there is insufficient evidence to confirm that the three properties are not impaired (e.g. if the auditor was prevented
from inspecting the properties) the auditor’s report would be qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of limitation on scope.
If there is evidence of material impairment but management fail to write down the carrying amount to recoverable
amount the auditor’s report would be qualified ‘except for’ disagreement regarding non-compliance with IAS 36
Impairment of Assets.
-
第11题:
Boston Company, an electing S corporation, has an operating loss of $400,000 for the current year. Hank owns a 40% interest in the company and is a material participant. At the beginning of the year, Hank's adjusted basis in the stock is $30,000. During the year the company borrows $100,000 with a recourse note. How much of the loss can Hank deduct on his current-year income tax return?()
A.$0
B.$30,000
C.$70,000
D.$160,000
E.$200,000
答案:B
-
第12题:
For the year just ended, N company had an earnings of$ 2 per share and paid a dividend of $ 1. 2 on its stock. The growth rate in net income and dividend are both expected to be a constant 7 percent per year, indefinitely. N company has a Beta of 0. 8, the risk - free interest rate is 6 percent, and the market risk premium is 8 percent.
P Company is very similar to N company in growth rate, risk and dividend. payout ratio. It had 20 million shares outstanding and an earnings of $ 36 million for the year just ended. The earnings will increase to $ 38. 5 million the next year.
Requirement :
A. Calculate the expected rate of return on N company 's equity.
B. Calculate N Company 's current price-earning ratio and prospective price - earning ratio.
C. Using N company 's current price-earning ratio, value P company 's stock price.
D. Using N company 's prospective price - earning ratio, value P company 's stock price.
答案:解析:A. The expected rate of return on N company's equity =6% +0. 8*8% =12.4%
B. Current price -earning ratio = (1. 2/2) * (1 +7% )/ (12.4% -7% ) =11. 89
Prospective price - earning ratio = (1. 2/2) / (12. 4% - 70% ) =11. 11
C. P company's stock = 11. 89* 36/20 = 21. 4
D. P company's stock = 11. 11* 38. 5/20 = 21. 39
-
第13题:
4 Ryder, a public limited company, is reviewing certain events which have occurred since its year end of 31 October
2005. The financial statements were authorised on 12 December 2005. The following events are relevant to the
financial statements for the year ended 31 October 2005:
(i) Ryder has a good record of ordinary dividend payments and has adopted a recent strategy of increasing its
dividend per share annually. For the last three years the dividend per share has increased by 5% per annum.
On 20 November 2005, the board of directors proposed a dividend of 10c per share for the year ended
31 October 2005. The shareholders are expected to approve it at a meeting on 10 January 2006, and a
dividend amount of $20 million will be paid on 20 February 2006 having been provided for in the financial
statements at 31 October 2005. The directors feel that a provision should be made because a ‘valid expectation’
has been created through the company’s dividend record. (3 marks)
(ii) Ryder disposed of a wholly owned subsidiary, Krup, a public limited company, on 10 December 2005 and made
a loss of $9 million on the transaction in the group financial statements. As at 31 October 2005, Ryder had no
intention of selling the subsidiary which was material to the group. The directors of Ryder have stated that there
were no significant events which have occurred since 31 October 2005 which could have resulted in a reduction
in the value of Krup. The carrying value of the net assets and purchased goodwill of Krup at 31 October 2005
were $20 million and $12 million respectively. Krup had made a loss of $2 million in the period 1 November
2005 to 10 December 2005. (5 marks)
(iii) Ryder acquired a wholly owned subsidiary, Metalic, a public limited company, on 21 January 2004. The
consideration payable in respect of the acquisition of Metalic was 2 million ordinary shares of $1 of Ryder plus
a further 300,000 ordinary shares if the profit of Metalic exceeded $6 million for the year ended 31 October
2005. The profit for the year of Metalic was $7 million and the ordinary shares were issued on 12 November
2005. The annual profits of Metalic had averaged $7 million over the last few years and, therefore, Ryder had
included an estimate of the contingent consideration in the cost of the acquisition at 21 January 2004. The fair
value used for the ordinary shares of Ryder at this date including the contingent consideration was $10 per share.
The fair value of the ordinary shares on 12 November 2005 was $11 per share. Ryder also made a one for four
bonus issue on 13 November 2005 which was applicable to the contingent shares issued. The directors are
unsure of the impact of the above on earnings per share and the accounting for the acquisition. (7 marks)
(iv) The company acquired a property on 1 November 2004 which it intended to sell. The property was obtained
as a result of a default on a loan agreement by a third party and was valued at $20 million on that date for
accounting purposes which exactly offset the defaulted loan. The property is in a state of disrepair and Ryder
intends to complete the repairs before it sells the property. The repairs were completed on 30 November 2005.
The property was sold after costs for $27 million on 9 December 2005. The property was classified as ‘held for
sale’ at the year end under IFRS5 ‘Non-current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations’ but shown at
the net sale proceeds of $27 million. Property is depreciated at 5% per annum on the straight-line basis and no
depreciation has been charged in the year. (5 marks)
(v) The company granted share appreciation rights (SARs) to its employees on 1 November 2003 based on ten
million shares. The SARs provide employees at the date the rights are exercised with the right to receive cash
equal to the appreciation in the company’s share price since the grant date. The rights vested on 31 October
2005 and payment was made on schedule on 1 December 2005. The fair value of the SARs per share at
31 October 2004 was $6, at 31 October 2005 was $8 and at 1 December 2005 was $9. The company has
recognised a liability for the SARs as at 31 October 2004 based upon IFRS2 ‘Share-based Payment’ but the
liability was stated at the same amount at 31 October 2005. (5 marks)
Required:
Discuss the accounting treatment of the above events in the financial statements of the Ryder Group for the year
ended 31 October 2005, taking into account the implications of events occurring after the balance sheet date.
(The mark allocations are set out after each paragraph above.)
(25 marks)
正确答案:
4 (i) Proposed dividend
The dividend was proposed after the balance sheet date and the company, therefore, did not have a liability at the balance
sheet date. No provision for the dividend should be recognised. The approval by the directors and the shareholders are
enough to create a valid expectation that the payment will be made and give rise to an obligation. However, this occurred
after the current year end and, therefore, will be charged against the profits for the year ending 31 October 2006.
The existence of a good record of dividend payments and an established dividend policy does not create a valid expectation
or an obligation. However, the proposed dividend will be disclosed in the notes to the financial statements as the directors
approved it prior to the authorisation of the financial statements.
(ii) Disposal of subsidiary
It would appear that the loss on the sale of the subsidiary provides evidence that the value of the consolidated net assets of
the subsidiary was impaired at the year end as there has been no significant event since 31 October 2005 which would have
caused the reduction in the value of the subsidiary. The disposal loss provides evidence of the impairment and, therefore,
the value of the net assets and goodwill should be reduced by the loss of $9 million plus the loss ($2 million) to the date of
the disposal, i.e. $11 million. The sale provides evidence of a condition that must have existed at the balance sheet date
(IAS10). This amount will be charged to the income statement and written off goodwill of $12 million, leaving a balance of
$1 million on that account. The subsidiary’s assets are impaired because the carrying values are not recoverable. The net
assets and goodwill of Krup would form. a separate income generating unit as the subsidiary is being disposed of before the
financial statements are authorised. The recoverable amount will be the sale proceeds at the date of sale and represents the
value-in-use to the group. The impairment loss is effectively taking account of the ultimate loss on sale at an earlier point in
time. IFRS5, ‘Non-current assets held for sale and discontinued operations’, will not apply as the company had no intention
of selling the subsidiary at the year end. IAS10 would require disclosure of the disposal of the subsidiary as a non-adjusting
event after the balance sheet date.
(iii) Issue of ordinary shares
IAS33 ‘Earnings per share’ states that if there is a bonus issue after the year end but before the date of the approval of the
financial statements, then the earnings per share figure should be based on the new number of shares issued. Additionally
a company should disclose details of all material ordinary share transactions or potential transactions entered into after the
balance sheet date other than the bonus issue or similar events (IAS10/IAS33). The principle is that if there has been a
change in the number of shares in issue without a change in the resources of the company, then the earnings per share
calculation should be based on the new number of shares even though the number of shares used in the earnings per share
calculation will be inconsistent with the number shown in the balance sheet. The conditions relating to the share issue
(contingent) have been met by the end of the period. Although the shares were issued after the balance sheet date, the issue
of the shares was no longer contingent at 31 October 2005, and therefore the relevant shares will be included in the
computation of both basic and diluted EPS. Thus, in this case both the bonus issue and the contingent consideration issue
should be taken into account in the earnings per share calculation and disclosure made to that effect. Any subsequent change
in the estimate of the contingent consideration will be adjusted in the period when the revision is made in accordance with
IAS8.
Additionally IFRS3 ‘Business Combinations’ requires the fair value of all types of consideration to be reflected in the cost of
the acquisition. The contingent consideration should be included in the cost of the business combination at the acquisition
date if the adjustment is probable and can be measured reliably. In the case of Metalic, the contingent consideration has
been paid in the post-balance sheet period and the value of such consideration can be determined ($11 per share). Thus
an accurate calculation of the goodwill arising on the acquisition of Metalic can be made in the period to 31 October 2005.
Prior to the issue of the shares on 12 November 2005, a value of $10 per share would have been used to value the
contingent consideration. The payment of the contingent consideration was probable because the average profits of Metalic
averaged over $7 million for several years. At 31 October 2005 the value of the contingent shares would be included in a
separate category of equity until they were issued on 12 November 2005 when they would be transferred to the share capital
and share premium account. Goodwill will increase by 300,000 x ($11 – $10) i.e. $300,000.
(iv) Property
IFRS5 (paragraph 7) states that for a non-current asset to be classified as held for sale, the asset must be available for
immediate sale in its present condition subject to the usual selling terms, and its sale must be highly probable. The delay in
this case in the selling of the property would indicate that at 31 October 2005 the property was not available for sale. The
property was not to be made available for sale until the repairs were completed and thus could not have been available for
sale at the year end. If the criteria are met after the year end (in this case on 30 November 2005), then the non-current
asset should not be classified as held for sale in the previous financial statements. However, disclosure of the event should
be made if it meets the criteria before the financial statements are authorised (IFRS5 paragraph 12). Thus in this case,
disclosure should be made.
The property on the application of IFRS5 should have been carried at the lower of its carrying amount and fair value less
costs to sell. However, the company has simply used fair value less costs to sell as the basis of valuation and shown the
property at $27 million in the financial statements.
The carrying amount of the property would have been $20 million less depreciation $1 million, i.e. $19 million. Because
the property is not held for sale under IFRS5, then its classification in the balance sheet will change and the property will be
valued at $19 million. Thus the gain of $7 million on the wrong application of IFRS5 will be deducted from reserves, and
the property included in property, plant and equipment. Total equity will therefore be reduced by $8 million.
(v) Share appreciation rights
IFRS2 ‘Share-based payment’ (paragraph 30) requires a company to re-measure the fair value of a liability to pay cash-settled
share based payment transactions at each reporting date and the settlement date, until the liability is settled. An example of
such a transaction is share appreciation rights. Thus the company should recognise a liability of ($8 x 10 million shares),
i.e. $80 million at 31 October 2005, the vesting date. The liability recognised at 31 October 2005 was in fact based on the
share price at the previous year end and would have been shown at ($6 x 1/2) x 10 million shares, i.e. $30 million. This
liability at 31 October 2005 had not been changed since the previous year end by the company. The SARs vest over a twoyear
period and thus at 31 October 2004 there would be a weighting of the eventual cost by 1 year/2 years. Therefore, an
additional liability and expense of $50 million should be accounted for in the financial statements at 31 October 2005. The
SARs would be settled on 1 December 2005 at $9 x 10 million shares, i.e. $90 million. The increase in the value of the
SARs since the year end would not be accrued in the financial statements but charged to profit or loss in the year ended31 October 2006. -
第14题:
(iv) Tyre recently undertook a sales campaign whereby customers can obtain free car accessories, by presenting a
coupon, which has been included in an advertisement in a national newspaper, on the purchase of a vehicle.
The offer is valid for a limited time period from 1 January 2006 until 31 July 2006. The management are unsure
as to how to treat this offer in the financial statements for the year ended 31 May 2006.
(5 marks)
Required:
Advise the directors of Tyre on how to treat the above items in the financial statements for the year ended
31 May 2006.
(The mark allocation is shown against each of the above items)
正确答案:
(iv) Car accessories
An obligation should not be recognised for the coupons and no provision created under IAS37 ‘Provisions, Contingent
Liabilities and Contingent Assets’. A provision should only be recognised where there is an obligating event. There has to be
a present obligation (legal or constructive), the probability of an outflow of resources and the ability to make a reliable estimate
of the amount of the obligation. These conditions do not seem to have been met. Until the vehicle is purchased the
accessories cannot be obtained. That is the point at which the present obligation arises, the outflow of resources occurs and
an estimate of the amount of the obligation can be made. When the car is purchased, the accessories become part of the
cost of the sale. The revenue recognised will be the amount received from the customer (the sales price). The revenue will
not be grossed up to include the value of the accessories. -
第15题:
4 (a) Router, a public limited company operates in the entertainment industry. It recently agreed with a television
company to make a film which will be broadcast on the television company’s network. The fee agreed for the
film was $5 million with a further $100,000 to be paid every time the film is shown on the television company’s
channels. It is hoped that it will be shown on four occasions. The film was completed at a cost of $4 million and
delivered to the television company on 1 April 2007. The television company paid the fee of $5 million on
30 April 2007 but indicated that the film needed substantial editing before they were prepared to broadcast it,
the costs of which would be deducted from any future payments to Router. The directors of Router wish to
recognise the anticipated future income of $400,000 in the financial statements for the year ended 31 May
2007. (5 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above items should be dealt with in the group financial statements of Router for the year ended
31 May 2007.
正确答案:
(a) Under IAS18 ‘Revenue’, revenue on a service contract is recognised when the outcome of the transaction can be measured
reliably. For revenue arising from the rendering of services, provided that all of the following criteria are met, revenue should
be recognised by reference to the stage of completion of the transaction at the balance sheet date (the percentage-ofcompletion
method) (IAS18 para 20):
(a) the amount of revenue can be measured reliably;
(b) it is probable that the economic benefits will flow to the seller;
(c) the stage of completion at the balance sheet date can be measured reliably; and
(d) the costs incurred, or to be incurred, in respect of the transaction can be measured reliably.
When the above criteria are not met, revenue arising from the rendering of services should be recognised only to the extent
of the expenses recognised that are recoverable. Because the only revenue which can be measured reliably is the fee for
making the film ($5 million), this should therefore be recognised as revenue in the year to 31 May 2007 and matched against
the cost of the film of $4 million. Only when the television company shows the film should any further amounts of $100,000
be recognised as there is an outstanding ‘performance’ condition in the form. of the editing that needs to take place before the
television company will broadcast the film. The costs of the film should not be carried forward and matched against
anticipated future income unless they can be deemed to be an intangible asset under IAS 38 ‘Intangible Assets’. Additionally,
when assessing revenue to be recognised in future years, the costs of the editing and Router’s liability for these costs should
be assessed.
-
第16题:
The following information is relevant for questions 9 and 10
A company’s draft financial statements for 2005 showed a profit of $630,000. However, the trial balance did not agree,
and a suspense account appeared in the company’s draft balance sheet.
Subsequent checking revealed the following errors:
(1) The cost of an item of plant $48,000 had been entered in the cash book and in the plant account as $4,800.
Depreciation at the rate of 10% per year ($480) had been charged.
(2) Bank charges of $440 appeared in the bank statement in December 2005 but had not been entered in the
company’s records.
(3) One of the directors of the company paid $800 due to a supplier in the company’s payables ledger by a personal
cheque. The bookkeeper recorded a debit in the supplier’s ledger account but did not complete the double entry
for the transaction. (The company does not maintain a payables ledger control account).
(4) The payments side of the cash book had been understated by $10,000.
9 Which of the above items would require an entry to the suspense account in correcting them?
A All four items
B 3 and 4 only
C 2 and 3 only
D 1, 2 and 4 only
正确答案:B
-
第17题:
2 The draft financial statements of Rampion, a limited liability company, for the year ended 31 December 2005
included the following figures:
$
Profit 684,000
Closing inventory 116,800
Trade receivables 248,000
Allowance for receivables 10,000
No adjustments have yet been made for the following matters:
(1) The company’s inventory count was carried out on 3 January 2006 leading to the figure shown above. Sales
between the close of business on 31 December 2005 and the inventory count totalled $36,000. There were no
deliveries from suppliers in that period. The company fixes selling prices to produce a 40% gross profit on sales.
The $36,000 sales were included in the sales records in January 2006.
(2) $10,000 of goods supplied on sale or return terms in December 2005 have been included as sales and
receivables. They had cost $6,000. On 10 January 2006 the customer returned the goods in good condition.
(3) Goods included in inventory at cost $18,000 were sold in January 2006 for $13,500. Selling expenses were
$500.
(4) $8,000 of trade receivables are to be written off.
(5) The allowance for receivables is to be adjusted to the equivalent of 5% of the trade receivables after allowing for
the above matters, based on past experience.
Required:
(a) Prepare a statement showing the effect of the adjustments on the company’s net profit for the year ended
31 December 2005. (5 marks)
正确答案:
-
第18题:
5 You are an audit manager in Dedza, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants. Recently, you have been assigned
specific responsibility for undertaking annual reviews of existing clients. The following situations have arisen in
connection with three client companies:
(a) Dedza was appointed auditor and tax advisor to Kora Co, a limited liability company, last year and has recently
issued an unmodified opinion on the financial statements for the year ended 30 June 2005. To your surprise,
the tax authority has just launched an investigation into the affairs of Kora on suspicion of underdeclaring income.
(7 marks)
Required:
Identify and comment on the ethical and other professional issues raised by each of these matters and state what
action, if any, Dedza should now take.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three situations.
正确答案:
5 DEDZA CO
(a) Tax investigation
■ Kora is a relatively new client. Before accepting the assignment(s) Dedza should have carried out customer due
diligence (CDD). Dedza should therefore have a sufficient knowledge and understanding of Kora to be aware of any
suspicions that the tax authority might have.
■ As the investigation has come as a surprise it is possible that, for example:
– the tax authority’s suspicions are unfounded;
– Dedza has failed to recognise suspicious circumstances.
Tutorial note: In either case, Dedza should seek clarification on the period of suspicion and review relevant procedures.
■ Dedza should review any communication from the predecessor auditor obtained in response to its ‘professional inquiry’
(for any professional reasons why the appointment should not have been accepted).
■ A quality control for new audits is that the audit opinion should be subject to a second partner review before it is issued.
It should be considered now whether or not such a review took place. If it did, then it should be sufficiently well
documented to evidence that the review was thorough and not a mere formality.
■ Criminal property includes the proceeds of tax evasion. If Kora is found to be guilty of under-declaring income that is a
money laundering offence.
■ Dedza’s reputational risk will be increased if implicated because it knew (or ought to have known) about Kora’s activities.
(Dedza may also be liable if found to have been negligent in failing to detect any material misstatement arising in the
2004/05 financial statements as a result.)
■ Kora’s audit working paper files and tax returns should be reviewed for any suspicion of fraud being committed by Kora
or error overlooked by Dedza. Tax advisory work should have been undertaken and/or reviewed by a manager/partner
not involved in the audit work.
■ As tax advisor, Dedza could soon be making disclosures of misstatements to the tax authority on behalf of Kora. Dedza
should encourage Kora to make necessary disclosure voluntarily.
■ Dedza will not be in breach of its duty of confidentiality to Kora if Kora gives Dedza permission to disclose information
to the tax authority (or Dedza is legally required to do so).
■ If Dedza finds reasonable grounds to know or suspect that potential disclosures to the tax authority relate to criminal
conduct, then a suspicious transaction report (STR) should be made to the financial intelligence unit (FIU) also.
Tutorial note: Though not the main issue credit will be awarded for other ethical issues such as the potential selfinterest/
self-review threat arising from the provision of other services. -
第19题:
(b) Chatam, a limited liability company, is a long-standing client. One of its subsidiaries, Ayora, has made losses
for several years. At your firm’s request, Chatam’s management has made a written representation that goodwill
arising on the acquisition of Ayora is not impaired. Your firm’s auditor’s report on the consolidated financial
statements of Chatam for the year ended 31 March 2005 is unmodified. Your firm’s auditor’s report on the
financial statements of Ayora is similarly unmodified. Chatam’s Chief Executive, Charles Barrington, is due to
retire in 2006 when his share options mature. (6 marks)
Required:
Comment on the ethical and other professional issues raised by each of the above matters and their implications,
if any, for the continuation of each assignment.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
(b) Unmodified auditor’s reports
Ethical and professional issues
■ An unmodified opinion means, inter alia, that:
– there are no material matters giving rise to disagreement with the auditor; and
– the auditor’s report does not include an emphasis of matter paragraph (e.g. regarding going concern).
■ By implication the auditor must have obtained sufficient appropriate evidence that notwithstanding the losses:
– the going concern basis is appropriate to Ayora’s financial statements and any related matters (e.g. parental
support) are adequately disclosed therein;
– goodwill in Chatam’s consolidated financial statements is not materially impaired.
■ Management’s written representation (that the goodwill is not impaired) must have been necessary (otherwise it should
not have been asked for). This means that Bartolome does not have sufficient other audit evidence. This seems dubious
as management should have carried out an impairment test to satisfy themselves that goodwill is not impaired. This
test should similarly have satisfied Bartolome.
■ If there is evidence that goodwill is impaired management’s refusal to write it down might be considered a fraud.
■ The matter may cast doubt on the quality of audit evidence obtained in other areas. All other matters on which
management representations have been obtained should be reviewed by another audit partner/manager.
■ Charles Barrington is retiring next year and his share options would presumably be worth less if goodwill were written
down. His position in this long-standing client suggests a familiarity threat.
■ Bartolome may be threatened by self-interest to accept the representation as sufficient in order to retain the client.
■ Bartolome may be unduly influenced by a combination of factors (familiarity and previous experience) and failing to
exercise the necessary degree of professional scepticism.
Implications for continuation with assignment
There is no reason why the audit should not be continued. However, a change in senior audit staff and audit manager may
be overdue. The unmodified auditor’s reports should be subject to a cold review and any quality control issues raised with
the staff who conducted the audit. -
第20题:
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Keffler Co, a private limited company engaged in the manufacture of
plastic products. The draft financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2006 show revenue of $47·4 million
(2005 – $43·9 million), profit before taxation of $2 million (2005 – $2·4 million) and total assets of $33·8 million
(2005 – $25·7 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) In April 2005, Keffler bought the right to use a landfill site for a period of 15 years for $1·1 million. Keffler
expects that the amount of waste that it will need to dump will increase annually and that the site will be
completely filled after just ten years. Keffler has charged the following amounts to the income statement for the
year to 31 March 2006:
– $20,000 licence amortisation calculated on a sum-of-digits basis to increase the charge over the useful life
of the site; and
– $100,000 annual provision for restoring the land in 15 years’ time. (9 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Keffler Co for the year ended
31 March 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
3 KEFFLER CO
Tutorial note: None of the issues have any bearing on revenue. Therefore any materiality calculations assessed on revenue are
inappropriate and will not be awarded marks.
(a) Landfill site
(i) Matters
■ $1·1m cost of the right represents 3·3% of total assets and is therefore material.
■ The right should be amortised over its useful life, that is just 10 years, rather than the 15-year period for which
the right has been granted.
Tutorial note: Recalculation on the stated basis (see audit evidence) shows that a 10-year amortisation has been
correctly used.
■ The amortisation charge represents 1% of profit before tax (PBT) and is not material.
■ The amortisation method used should reflect the pattern in which the future economic benefits of the right are
expected to be consumed by Keffler. If that pattern cannot be determined reliably, the straight-line method must
be used (IAS 38 ‘Intangible Assets’).
■ Using an increasing sum-of-digits will ‘end-load’ the amortisation charge (i.e. least charge in the first year, highest
charge in the last year). However, according to IAS 38 there is rarely, if ever, persuasive evidence to support an
amortisation method that results in accumulated amortisation lower than that under the straight-line method.
Tutorial note: Over the first half of the asset’s life, depreciation will be lower than under the straight-line basis
(and higher over the second half of the asset’s life).
■ On a straight line basis the annual amortisation charge would be $0·11m, an increase of $90,000. Although this
difference is just below materiality (4·5% PBT) the cumulative effect (of undercharging amortisation) will become
material.
■ Also, when account is taken of the understatement of cost (see below), the undercharging of amortisation will be
material.
■ The sum-of-digits method might be suitable as an approximation to the unit-of-production method if Keffler has
evidence to show that use of the landfill site will increase annually.
■ However, in the absence of such evidence, the audit opinion should be qualified ‘except for’ disagreement with the
amortisation method (resulting in intangible asset overstatement/amortisation expense understatement).
■ The annual restoration provision represents 5% of PBT and 0·3% of total assets. Although this is only borderline
material (in terms of profit), there will be a cumulative impact.
■ Annual provisioning is contrary to IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets’.
■ The estimate of the future restoration cost is (presumably) $1·5m (i.e. $0·1 × 15). The present value of this
amount should have been provided in full in the current year and included in the cost of the right.
■ Thus the amortisation being charged on the cost of the right (including the restoration cost) is currently understated
(on any basis).
Tutorial note: A 15-year discount factor at 10% (say) is 0·239. $1·5m × 0·239 is approximately $0·36m. The
resulting present value (of the future cost) would be added to the cost of the right. Amortisation over 10 years
on a straight-line basis would then be increased by $36,000, increasing the difference between amortisation
charged and that which should be charged. The lower the discount rate, the greater the understatement of
amortisation expense.
Total amount expensed ($120k) is less than what should have been expensed (say $146k amortisation + $36k
unwinding of discount). However, this is not material.
■ Whether Keffler will wait until the right is about to expire before restoring the land or might restore earlier (if the
site is completely filled in 10 years).
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Written agreement for purchase of right and contractual terms therein (e.g. to make restoration in 15 years’ time).
■ Cash book/bank statement entries in April 2005 for $1·1m payment.
■ Physical inspection of the landfill site to confirm Keffler’s use of it.
■ Annual dump budget/projection over next 10 years and comparison with sum-of-digits proportions.
■ Amount actually dumped in the year (per dump records) compared with budget and as a percentage/proportion of
the total available.
■ Recalculation of current year’s amortisation based on sum-of-digits. That is, $1·1m ÷ 55 = $20,000.
Tutorial note: The sum-of-digits from 1 to 10 may be calculated long-hand or using the formula n(n+1)/2 i.e.
(10 × 11)/2 = 55.
■ The basis of the calculation of the estimated restoration costs and principal assumptions made.
■ If estimated by a quantity surveyor/other expert then a copy of the expert’s report.
■ Written management representation confirming the planned timing of the restoration in 15 years (or sooner). -
第21题:
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Lamont Co. The company’s principal activity is wholesaling frozen
fish. The draft consolidated financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2007 show revenue of $67·0 million
(2006 – $62·3 million), profit before taxation of $11·9 million (2006 – $14·2 million) and total assets of
$48·0 million (2006 – $36·4 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) In early 2007 a chemical leakage from refrigeration units owned by Lamont caused contamination of some of its
property. Lamont has incurred $0·3 million in clean up costs, $0·6 million in modernisation of the units to
prevent future leakage and a $30,000 fine to a regulatory agency. Apart from the fine, which has been expensed,
these costs have been capitalised as improvements. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Lamont Co for the year ended
31 March 2007.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
3 LAMONT CO
(a) Chemical leakage
(i) Matters
■ $30,000 fine is very immaterial (just 1/4% profit before tax). This is revenue expenditure and it is correct that it
has been expensed to the income statement.
■ $0·3 million represents 0·6% total assets and 2·5% profit before tax and is not material on its own. $0·6 million
represents 1·2% total assets and 5% profit before tax and is therefore material to the financial statements.
■ The $0·3 million clean-up costs should not have been capitalised as the condition of the property is not improved
as compared with its condition before the leakage occurred. Although not material in isolation this amount should
be adjusted for and expensed, thereby reducing the aggregate of uncorrected misstatements.
■ It may be correct that $0·6 million incurred in modernising the refrigeration units should be capitalised as a major
overhaul (IAS 16 Property, Plant and Equipment). However, any parts scrapped as a result of the modernisation
should be treated as disposals (i.e. written off to the income statement).
■ The carrying amount of the refrigeration units at 31 March 2007, including the $0·6 million for modernisation,
should not exceed recoverable amount (i.e. the higher of value in use and fair value less costs to sell). If it does,
an allowance for the impairment loss arising must be recognised in accordance with IAS 36 Impairment of Assets.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ A breakdown/analysis of costs incurred on the clean-up and modernisation amounting to $0·3 million and
$0·6 million respectively.
■ Agreement of largest amounts to invoices from suppliers/consultants/sub-contractors, etc and settlement thereof
traced from the cash book to the bank statement.
■ Physical inspection of the refrigeration units to confirm their modernisation and that they are in working order. (Do
they contain frozen fish?)
■ Sample of components selected from the non-current asset register traced to the refrigeration units and inspected
to ensure continuing existence.
■ $30,000 penalty notice from the regulatory agency and corresponding cash book payment/payment per the bank
statement.
■ Written management representation that there are no further penalties that should be provided for or disclosed other
than the $30,000 that has been accounted for. -
第22题:
(ii) On 1 July 2006 Petrie introduced a 10-year warranty on all sales of its entire range of stainless steel
cookware. Sales of stainless steel cookware for the year ended 31 March 2007 totalled $18·2 million. The
notes to the financial statements disclose the following:
‘Since 1 July 2006, the company’s stainless steel cookware is guaranteed to be free from defects in
materials and workmanship under normal household use within a 10-year guarantee period. No provision
has been recognised as the amount of the obligation cannot be measured with sufficient reliability.’
(4 marks)
Your auditor’s report on the financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2006 was unmodified.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of these two matters for your auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Petrie Co for the year ended 31 March 2007.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the matters above.
正确答案:
(ii) 10-year guarantee
$18·2 million stainless steel cookware sales amount to 43·1% of revenue and are therefore material. However, the
guarantee was only introduced three months into the year, say in respect of $13·6 million (3/4 × 18·2 million) i.e.
approximately 32% of revenue.
The draft note disclosure could indicate that Petrie’s management believes that Petrie has a legal obligation in respect
of the guarantee, that is not remote and likely to be material (otherwise no disclosure would have been required).
A best estimate of the obligation amounting to 5% profit before tax (or more) is likely to be considered material, i.e.
$90,000 (or more). Therefore, if it is probable that 0·66% of sales made under guarantee will be returned for refund,
this would require a warranty provision that would be material.
Tutorial note: The return of 2/3% of sales over a 10-year period may well be probable.
Clearly there is a present obligation as a result of a past obligating event for sales made during the nine months to
31 March 2007. Although the likelihood of outflow under the guarantee is likely to be insignificant (even remote) it is
probable that some outflow will be needed to settle the class of such obligations.
The note in the financial statements is disclosing this matter as a contingent liability. This term encompasses liabilities
that do not meet the recognition criteria (e.g. of reliable measurement in accordance with IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent
Liabilities and Contingent Assets).
However, it is extremely rare that no reliable estimate can be made (IAS 37) – the use of estimates being essential to
the preparation of financial statements. Petrie’s management must make a best estimate of the cost of refunds/repairs
under guarantee taking into account, for example:
■ the proportion of sales during the nine months to 31 March 2007 that have been returned under guarantee at the
balance sheet date (and in the post balance sheet event period);
■ the average age of cookware showing a defect;
■ the expected cost of a replacement item (as a refund of replacement is more likely than a repair, say).
If management do not make a provision for the best estimate of the obligation the audit opinion should be qualified
‘except for’ non-compliance with IAS 37 (no provision made). The disclosure made in the note to the financial
statements, however detailed, is not a substitute for making the provision.
Tutorial note: No marks will be awarded for suggesting that an emphasis of matter of paragraph would be appropriate
(drawing attention to the matter more fully explained in the note).
Management’s claim that the obligation cannot be measured with sufficient reliability does not give rise to a limitation
on scope on the audit. The auditor has sufficient evidence of the non-compliance with IAS 37 and disagrees with it. -
第23题:
You are an audit manager at Rockwell & Co, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants. You are responsible for the audit of the Hopper Group, a listed audit client which supplies ingredients to the food and beverage industry worldwide.
The audit work for the year ended 30 June 2015 is nearly complete, and you are reviewing the draft audit report which has been prepared by the audit senior. During the year the Hopper Group purchased a new subsidiary company, Seurat Sweeteners Co, which has expertise in the research and design of sugar alternatives. The draft financial statements of the Hopper Group for the year ended 30 June 2015 recognise profit before tax of $495 million (2014 – $462 million) and total assets of $4,617 million (2014: $4,751 million). An extract from the draft audit report is shown below:
Basis of modified opinion (extract)
In their calculation of goodwill on the acquisition of the new subsidiary, the directors have failed to recognise consideration which is contingent upon meeting certain development targets. The directors believe that it is unlikely that these targets will be met by the subsidiary company and, therefore, have not recorded the contingent consideration in the cost of the acquisition. They have disclosed this contingent liability fully in the notes to the financial statements. We do not feel that the directors’ treatment of the contingent consideration is correct and, therefore, do not believe that the criteria of the relevant standard have been met. If this is the case, it would be appropriate to adjust the goodwill balance in the statement of financial position.
We believe that any required adjustment may materially affect the goodwill balance in the statement of financial position. Therefore, in our opinion, the financial statements do not give a true and fair view of the financial position of the Hopper Group and of the Hopper Group’s financial performance and cash flows for the year then ended in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards.
Emphasis of Matter Paragraph
We draw attention to the note to the financial statements which describes the uncertainty relating to the contingent consideration described above. The note provides further information necessary to understand the potential implications of the contingency.
Required:
(a) Critically appraise the draft audit report of the Hopper Group for the year ended 30 June 2015, prepared by the audit senior.
Note: You are NOT required to re-draft the extracts from the audit report. (10 marks)
(b) The audit of the new subsidiary, Seurat Sweeteners Co, was performed by a different firm of auditors, Fish Associates. During your review of the communication from Fish Associates, you note that they were unable to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence with regard to the breakdown of research expenses. The total of research costs expensed by Seurat Sweeteners Co during the year was $1·2 million. Fish Associates has issued a qualified audit opinion on the financial statements of Seurat Sweeteners Co due to this inability to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence.
Required:
Comment on the actions which Rockwell & Co should take as the auditor of the Hopper Group, and the implications for the auditor’s report on the Hopper Group financial statements. (6 marks)
(c) Discuss the quality control procedures which should be carried out by Rockwell & Co prior to the audit report on the Hopper Group being issued. (4 marks)
正确答案:(a) Critical appraisal of the draft audit report
Type of opinion
When an auditor issues an opinion expressing that the financial statements ‘do not give a true and fair view’, this represents an adverse opinion. The paragraph explaining the modification should, therefore, be titled ‘Basis of Adverse Opinion’ rather than simply ‘Basis of Modified Opinion’.
An adverse opinion means that the auditor considers the misstatement to be material and pervasive to the financial statements of the Hopper Group. According to ISA 705 Modifications to Opinions in the Independent Auditor’s Report, pervasive matters are those which affect a substantial proportion of the financial statements or fundamentally affect the users’ understanding of the financial statements. It is unlikely that the failure to recognise contingent consideration is pervasive; the main effect would be to understate goodwill and liabilities. This would not be considered a substantial proportion of the financial statements, neither would it be fundamental to understanding the Hopper Group’s performance and position.
However, there is also some uncertainty as to whether the matter is even material. If the matter is determined to be material but not pervasive, then a qualified opinion would be appropriate on the basis of a material misstatement. If the matter is not material, then no modification would be necessary to the audit opinion.
Wording of opinion/report
The auditor’s reference to ‘the acquisition of the new subsidiary’ is too vague; the Hopper Group may have purchased a number of subsidiaries which this phrase could relate to. It is important that the auditor provides adequate description of the event and in these circumstances it would be appropriate to name the subsidiary referred to.
The auditor has not quantified the amount of the contingent element of the consideration. For the users to understand the potential implications of any necessary adjustments, they need to know how much the contingent consideration will be if it becomes payable. It is a requirement of ISA 705 that the auditor quantifies the financial effects of any misstatements, unless it is impracticable to do so.
In addition to the above point, the auditor should provide more description of the financial effects of the misstatement, including full quantification of the effect of the required adjustment to the assets, liabilities, incomes, revenues and equity of the Hopper Group.
The auditor should identify the note to the financial statements relevant to the contingent liability disclosure rather than just stating ‘in the note’. This will improve the understandability and usefulness of the contents of the audit report.
The use of the term ‘we do not feel that the treatment is correct’ is too vague and not professional. While there may be some interpretation necessary when trying to apply financial reporting standards to unique circumstances, the expression used is ambiguous and may be interpreted as some form. of disclaimer by the auditor with regard to the correct accounting treatment. The auditor should clearly explain how the treatment applied in the financial statements has departed from the requirements of the relevant standard.
Tutorial note: As an illustration to the above point, an appropriate wording would be: ‘Management has not recognised the acquisition-date fair value of contingent consideration as part of the consideration transferred in exchange for the acquiree, which constitutes a departure from International Financial Reporting Standards.’
The ambiguity is compounded by the use of the phrase ‘if this is the case, it would be appropriate to adjust the goodwill’. This once again suggests that the correct treatment is uncertain and perhaps open to interpretation.
If the auditor wishes to refer to a specific accounting standard they should refer to its full title. Therefore instead of referring to ‘the relevant standard’ they should refer to International Financial Reporting Standard 3 Business Combinations.
The opinion paragraph requires an appropriate heading. In this case the auditors have issued an adverse opinion and the paragraph should be headed ‘Adverse Opinion’.
As with the basis paragraph, the opinion paragraph lacks authority; suggesting that the required adjustments ‘may’ materially affect the financial statements implies that there is a degree of uncertainty. This is not the case; the amount of the contingent consideration will be disclosed in the relevant purchase agreement, so the auditor should be able to determine whether the required adjustments are material or not. Regardless, the sentence discussing whether the balance is material or not is not required in the audit report as to warrant inclusion in the report the matter must be considered material. The disclosure of the nature and financial effect of the misstatement in the basis paragraph is sufficient.
Finally, the emphasis of matter paragraph should not be included in the audit report. An emphasis of matter paragraph is only used to draw attention to an uncertainty/matter of fundamental importance which is correctly accounted for and disclosed in the financial statements. An emphasis of matter is not required in this case for the following reasons:
– Emphasis of matter is only required to highlight matters which the auditor believes are fundamental to the users’ understanding of the business. An example may be where a contingent liability exists which is so significant it could lead to the closure of the reporting entity. That is not the case with the Hopper Group; the contingent liability does not appear to be fundamental.
– Emphasis of matter is only used for matters where the auditor has obtained sufficient appropriate evidence that the matter is not materially misstated in the financial statements. If the financial statements are materially misstated, in this regard the matter would be fully disclosed by the auditor in the basis of qualified/adverse opinion paragraph and no emphasis of matter is necessary.
(b) Communication from the component auditor
The qualified opinion due to insufficient evidence may be a significant matter for the Hopper Group audit. While the possible adjustments relating to the current year may not be material to the Hopper Group, the inability to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence with regard to a material matter in Seurat Sweeteners Co’s financial statements may indicate a control deficiency which the auditor was not aware of at the planning stage and it could indicate potential problems with regard to the integrity of management, which could also indicate a potential fraud. It could also indicate an unwillingness of management to provide information, which could create problems for future audits, particularly if research and development costs increase in future years. If the group auditor suspects that any of these possibilities are true, they may need to reconsider their risk assessment and whether the audit procedures performed are still appropriate.
If the detail provided in the communication from the component auditor is insufficient, the group auditor should first discuss the matter with the component auditor to see whether any further information can be provided. The group auditor can request further working papers from the component auditor if this is necessary. However, if Seurat Sweeteners has not been able to provide sufficient appropriate evidence, it is unlikely that this will be effective.
If the discussions with the component auditor do not provide satisfactory responses to evaluate the potential impact on the Hopper Group, the group auditor may need to communicate with either the management of Seurat Sweeteners or the Hopper Group to obtain necessary clarification with regard to the matter.
Following these procedures, the group auditor needs to determine whether they have sufficient appropriate evidence to draw reasonable conclusions on the Hopper Group’s financial statements. If they believe the lack of information presents a risk of material misstatement in the group financial statements, they can request that further audit procedures be performed, either by the component auditor or by themselves.
Ultimately the group engagement partner has to evaluate the effect of the inability to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence on the audit opinion of the Hopper Group. The matter relates to research expenses totalling $1·2 million, which represents 0·2% of the profit for the year and 0·03% of the total assets of the Hopper Group. It is therefore not material to the Hopper Group’s financial statements. For this reason no modification to the audit report of the Hopper Group would be required as this does not represent a lack of sufficient appropriate evidence with regard to a matter which is material to the Group financial statements.
Although this may not have an impact on the Hopper Group audit opinion, this may be something the group auditor wishes to bring to the attention of those charged with governance. This would be particularly likely if the group auditor believed that this could indicate some form. of fraud in Seurat Sweeteners Co, a serious deficiency in financial reporting controls or if this could create problems for accepting future audits due to management’s unwillingness to provide access to accounting records.
(c) Quality control procedures prior to issuing the audit report
ISA 220 Quality Control for an Audit of Financial Statements and ISQC 1 Quality Control for Firms that Perform. Audits and Reviews of Historical Financial Information, and Other Assurance and Related Services Agreements require that an engagement quality control reviewer shall be appointed for audits of financial statements of listed entities. The audit engagement partner then discusses significant matters arising during the audit engagement with the engagement quality control reviewer.
The engagement quality control reviewer and the engagement partner should discuss the failure to recognise the contingent consideration and its impact on the auditor’s report. The engagement quality control reviewer must review the financial statements and the proposed auditor’s report, in particular focusing on the conclusions reached in formulating the auditor’s report and consideration of whether the proposed auditor’s opinion is appropriate. The audit documentation relating to the acquisition of Seurat Sweeteners Co will be carefully reviewed, and the reviewer is likely to consider whether procedures performed in relation to these balances were appropriate.
Given the listed status of the Hopper Group, any modification to the auditor’s report will be scrutinised, and the firm must be sure of any decision to modify the report, and the type of modification made. Once the engagement quality control reviewer has considered the necessity of a modification, they should consider whether a qualified or an adverse opinion is appropriate in the circumstances. This is an important issue, given that it requires judgement as to whether the matters would be material or pervasive to the financial statements.
The engagement quality control reviewer should ensure that there is adequate documentation regarding the judgements used in forming the final audit opinion, and that all necessary matters have been brought to the attention of those charged with governance.
The auditor’s report must not be signed and dated until the completion of the engagement quality control review.
Tutorial note: In the case of the Hopper Group’s audit, the lack of evidence in respect of research costs is unlikely to be discussed unless the audit engagement partner believes that the matter could be significant, for example, if they suspected the lack of evidence is being used to cover up a financial statements fraud.
