Additionally the directors wish to know how the provision for deferred taxation would be calculated in the followingsituations under IAS12 ‘Income Taxes’:(i) On 1 November 2003, the company had granted ten million share options worth $40 million subject t
题目
Additionally the directors wish to know how the provision for deferred taxation would be calculated in the following
situations under IAS12 ‘Income Taxes’:
(i) On 1 November 2003, the company had granted ten million share options worth $40 million subject to a two
year vesting period. Local tax law allows a tax deduction at the exercise date of the intrinsic value of the options.
The intrinsic value of the ten million share options at 31 October 2004 was $16 million and at 31 October 2005
was $46 million. The increase in the share price in the year to 31 October 2005 could not be foreseen at
31 October 2004. The options were exercised at 31 October 2005. The directors are unsure how to account
for deferred taxation on this transaction for the years ended 31 October 2004 and 31 October 2005.
(ii) Panel is leasing plant under a finance lease over a five year period. The asset was recorded at the present value
of the minimum lease payments of $12 million at the inception of the lease which was 1 November 2004. The
asset is depreciated on a straight line basis over the five years and has no residual value. The annual lease
payments are $3 million payable in arrears on 31 October and the effective interest rate is 8% per annum. The
directors have not leased an asset under a finance lease before and are unsure as to its treatment for deferred
taxation. The company can claim a tax deduction for the annual rental payment as the finance lease does not
qualify for tax relief.
(iii) A wholly owned overseas subsidiary, Pins, a limited liability company, sold goods costing $7 million to Panel on
1 September 2005, and these goods had not been sold by Panel before the year end. Panel had paid $9 million
for these goods. The directors do not understand how this transaction should be dealt with in the financial
statements of the subsidiary and the group for taxation purposes. Pins pays tax locally at 30%.
(iv) Nails, a limited liability company, is a wholly owned subsidiary of Panel, and is a cash generating unit in its own
right. The value of the property, plant and equipment of Nails at 31 October 2005 was $6 million and purchased
goodwill was $1 million before any impairment loss. The company had no other assets or liabilities. An
impairment loss of $1·8 million had occurred at 31 October 2005. The tax base of the property, plant and
equipment of Nails was $4 million as at 31 October 2005. The directors wish to know how the impairment loss
will affect the deferred tax provision for the year. Impairment losses are not an allowable expense for taxation
purposes.
Assume a tax rate of 30%.
Required:
(b) Discuss, with suitable computations, how the situations (i) to (iv) above will impact on the accounting for
deferred tax under IAS12 ‘Income Taxes’ in the group financial statements of Panel. (16 marks)
(The situations in (i) to (iv) above carry equal marks)
相似考题
参考答案和解析
(b) (i) The tax deduction is based on the option’s intrinsic value which is the difference between the market price and exercise
price of the share option. It is likely that a deferred tax asset will arise which represents the difference between the tax
base of the employee’s service received to date and the carrying amount which will effectively normally be zero.
The recognition of the deferred tax asset should be dealt with on the following basis:
(a) if the estimated or actual tax deduction is less than or equal to the cumulative recognised expense then the
associated tax benefits are recognised in the income statement
(b) if the estimated or actual tax deduction exceeds the cumulative recognised compensation expense then the excess
tax benefits are recognised directly in a separate component of equity.
As regards the tax effects of the share options, in the year to 31 October 2004, the tax effect of the remuneration expensewill be in excess of the tax benefit.
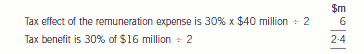
The company will have to estimate the amount of the tax benefit as it is based on the share price at 31 October 2005.
The information available at 31 October 2004 indicates a tax benefit based on an intrinsic value of $16 million.
As a result, the tax benefit of $2·4 million will be recognised within the deferred tax provision. At 31 October 2005,
the options have been exercised. Tax receivable will be 30% x $46 million i.e. $13·8 million. The deferred tax asset
of $2·4 million is no longer recognised as the tax benefit has crystallised at the date when the options were exercised.
For a tax benefit to be recognised in the year to 31 October 2004, the provisions of IAS12 should be complied with as
regards the recognition of a deferred tax asset.
(ii) Plant acquired under a finance lease will be recorded as property, plant and equipment and a corresponding liability for
the obligation to pay future rentals. Rents payable are apportioned between the finance charge and a reduction of the
outstanding obligation. A temporary difference will effectively arise between the value of the plant for accounting
purposes and the equivalent of the outstanding obligation as the annual rental payments qualify for tax relief. The tax
base of the asset is the amount deductible for tax in future which is zero. The tax base of the liability is the carrying
amount less any future tax deductible amounts which will give a tax base of zero. Thus the net temporary differencewill be:

(iii) The subsidiary, Pins, has made a profit of $2 million on the transaction with Panel. These goods are held in inventory
at the year end and a consolidation adjustment of an equivalent amount will be made against profit and inventory. Pins
will have provided for the tax on this profit as part of its current tax liability. This tax will need to be eliminated at the
group level and this will be done by recognising a deferred tax asset of $2 million x 30%, i.e. $600,000. Thus any
consolidation adjustments that have the effect of deferring or accelerating tax when viewed from a group perspective will
be accounted for as part of the deferred tax provision. Group profit will be different to the sum of the profits of the
individual group companies. Tax is normally payable on the profits of the individual companies. Thus there is a need
to account for this temporary difference. IAS12 does not specifically address the issue of which tax rate should be used
calculate the deferred tax provision. IAS12 does generally say that regard should be had to the expected recovery or
settlement of the tax. This would be generally consistent with using the rate applicable to the transferee company (Panel)
rather than the transferor (Pins).
更多“Additionally the directors wish to know how the provision for deferred taxation would be calculated in the followingsituations under IAS12 ‘Income Taxes’:(i) On 1 November 2003, the company had granted ten million share options worth $40 million subject t”相关问题
-
第1题:
(b) a discussion (with suitable calculations) as to how the directors’ share options would be accounted for in the
financial statements for the year ended 31 May 2005 including the adjustment to opening balances;
(9 marks)
正确答案:(b) Accounting in the financial statements for the year ended 31 May 2005
IFRS2 requires an expense to be recognised for the share options granted to the directors with a corresponding amount shown
in equity. Where options do not vest immediately but only after a period of service, then there is a presumption that the
services will be rendered over the ‘vesting period’. The fair value of the services rendered will be measured by reference to
the fair value of the equity instruments at the date that the equity instruments were granted. Fair value should be based on
market prices. The treatment of vesting conditions depends on whether or not the conditions relate to the market price of the
instruments. Market conditions are effectively taken into account in determining the fair value of the instruments and therefore
can be ignored for the purposes of estimating the number of equity instruments that will vest. For other conditions such as
remaining in the employment of the company, the calculations are carried out based on the best estimate of the number of
instruments that will vest. The estimate is revised when subsequent information is available.
The share options granted to J. Van Heflin on 1 June 2002 were before the date set in IFRS2 for accounting for such options
(7 November 2002). Therefore, no expense calculation is required. (Note: candidates calculating the expense for the latter
share options would be given credit if they stated that the company could apply IFRS2 to other options in certaincircumstances.) The remaining options are valued as follows:
-
第2题:
(b) Misson has purchased goods from a foreign supplier for 8 million euros on 31 July 2006. At 31 October 2006,
the trade payable was still outstanding and the goods were still held by Misson. Similarly Misson has sold goods
to a foreign customer for 4 million euros on 31 July 2006 and it received payment for the goods in euros on
31 October 2006. Additionally Misson had purchased an investment property on 1 November 2005 for
28 million euros. At 31 October 2006, the investment property had a fair value of 24 million euros. The company
uses the fair value model in accounting for investment properties.
Misson would like advice on how to treat these transactions in the financial statements for the year ended 31
October 2006. (7 marks)
Required:
Discuss the accounting treatment of the above transactions in accordance with the advice required by the
directors.
(Candidates should show detailed workings as well as a discussion of the accounting treatment used.)
正确答案:
(b) Inventory, Goods sold and Investment property
The inventory and trade payable initially would be recorded at 8 million euros ÷ 1·6, i.e. $5 million. At the year end, the
amount payable is still outstanding and is retranslated at 1 dollar = 1·3 euros, i.e. $6·2 million. An exchange loss of
$(6·2 – 5) million, i.e. $1·2 million would be reported in profit or loss. The inventory would be recorded at $5 million at the
year end unless it is impaired in value.
The sale of goods would be recorded at 4 million euros ÷ 1·6, i.e. $2·5 million as a sale and as a trade receivable. Payment
is received on 31 October 2006 in euros and the actual value of euros received will be 4 million euros ÷ 1·3,
i.e. $3·1 million.
Thus a gain on exchange of $0·6 million will be reported in profit or loss.
The investment property should be recognised on 1 November 2005 at 28 million euros ÷ 1·4, i.e. $20 million. At
31 October 2006, the property should be recognised at 24 million euros ÷ 1·3, i.e. $18·5 million. The decrease in fair value
should be recognised in profit and loss as a loss on investment property. The property is a non-monetary asset and any foreign
currency element is not recognised separately. When a gain or loss on a non-monetary item is recognised in profit or loss,
any exchange component of that gain or loss is also recognised in profit or loss. If any gain or loss is recognised in equity ona non-monetary asset, any exchange gain is also recognised in equity. -
第3题:
(c) Issue of bond
The club proposes to issue a 7% bond with a face value of $50 million on 1 January 2007 at a discount of 5%
that will be secured on income from future ticket sales and corporate hospitality receipts, which are approximately
$20 million per annum. Under the agreement the club cannot use the first $6 million received from corporate
hospitality sales and reserved tickets (season tickets) as this will be used to repay the bond. The money from the
bond will be used to pay for ground improvements and to pay the wages of players.
The bond will be repayable, both capital and interest, over 15 years with the first payment of $6 million due on
31 December 2007. It has an effective interest rate of 7·7%. There will be no active market for the bond and
the company does not wish to use valuation models to value the bond. (6 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above proposals would be dealt with in the financial statements of Seejoy for the year ending
31 December 2007, setting out their accounting treatment and appropriateness in helping the football club’s
cash flow problems.
(Candidates do not need knowledge of the football finance sector to answer this question.)
正确答案:(c) Issue of bond
This form. of financing a football club’s operations is known as ‘securitisation’. Often in these cases a special purpose vehicle
is set up to administer the income stream or assets involved. In this case, a special purpose vehicle has not been set up. The
benefit of securitisation of the future corporate hospitality sales and season ticket receipts is that there will be a capital
injection into the club and it is likely that the effective interest rate is lower because of the security provided by the income
from the receipts. The main problem with the planned raising of capital is the way in which the money is to be used. The
use of the bond for ground improvements can be commended as long term cash should be used for long term investment but
using the bond for players’ wages will cause liquidity problems for the club.
This type of securitisation is often called a ‘future flow’ securitisation. There is no existing asset transferred to a special purpose
vehicle in this type of transaction and, therefore, there is no off balance sheet effect. The bond is shown as a long term liability
and is accounted for under IAS39 ‘Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement’. There are no issues of
derecognition of assets as there can be in other securitisation transactions. In some jurisdictions there are legal issues in
assigning future receivables as they constitute an unidentifiable debt which does not exist at present and because of this
uncertainty often the bond holders will require additional security such as a charge on the football stadium.
The bond will be a financial liability and it will be classified in one of two ways:
(i) Financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss include financial liabilities that the entity either has incurred for
trading purposes and, where permitted, has designated to the category at inception. Derivative liabilities are always
treated as held for trading unless they are designated and effective as hedging instruments. An example of a liability held
for trading is an issued debt instrument that the entity intends to repurchase in the near term to make a gain from shortterm
movements in interest rates. It is unlikely that the bond will be classified in this category.
(ii) The second category is financial liabilities measured at amortised cost. It is the default category for financial liabilities
that do not meet the criteria for financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss. In most entities, most financial
liabilities will fall into this category. Examples of financial liabilities that generally would be classified in this category are
account payables, note payables, issued debt instruments, and deposits from customers. Thus the bond is likely to be
classified under this heading. When a financial liability is recognised initially in the balance sheet, the liability is
measured at fair value. Fair value is the amount for which a liability can be settled between knowledgeable, willing
parties in an arm’s length transaction. Since fair value is a market transaction price, on initial recognition fair value will
usually equal the amount of consideration received for the financial liability. Subsequent to initial recognition financial
liabilities are measured using amortised cost or fair value. In this case the company does not wish to use valuation
models nor is there an active market for the bond and, therefore, amortised cost will be used to measure the bond.
The bond will be shown initially at $50 million × 95%, i.e. $47·5 million as this is the consideration received. Subsequentlyat 31 December 2007, the bond will be shown as follows:
-
第4题:
(b) On 31 May 2007, Leigh purchased property, plant and equipment for $4 million. The supplier has agreed to
accept payment for the property, plant and equipment either in cash or in shares. The supplier can either choose
1·5 million shares of the company to be issued in six months time or to receive a cash payment in three months
time equivalent to the market value of 1·3 million shares. It is estimated that the share price will be $3·50 in
three months time and $4 in six months time.
Additionally, at 31 May 2007, one of the directors recently appointed to the board has been granted the right to
choose either 50,000 shares of Leigh or receive a cash payment equal to the current value of 40,000 shares at
the settlement date. This right has been granted because of the performance of the director during the year and
is unconditional at 31 May 2007. The settlement date is 1 July 2008 and the company estimates the fair value
of the share alternative is $2·50 per share at 31 May 2007. The share price of Leigh at 31 May 2007 is $3 per
share, and if the director chooses the share alternative, they must be kept for a period of four years. (9 marks)
Required:
Discuss with suitable computations how the above share based transactions should be accounted for in the
financial statements of Leigh for the year ended 31 May 2007.
正确答案:(b) Transactions that allow choice of settlement are accounted for as cash-settled to the extent that the entity has incurred a
liability (IFRS2 para 34). The share based transaction is treated as the issuance of a compound financial instrument. IFRS2
applies similar measurement principles to determine the value of the constituent parts of a compound instrument as that
required by IAS32 ‘Financial Instruments: Disclosure and Presentation’. The purchase of the property, plant and equipment
(PPE) and the grant to the director, both fall under this section of IFRS2 as the supplier and the director have a choice of
settlement. The fair value of the goods can be measured directly as regards the purchase of the PPE and therefore this fact
determines that the transaction is treated in a certain way. In the case of the director, the fair value of the service rendered
will be determined by the fair value of the equity instruments given and IFRS2 says that this type of share based transaction
should be dealt with in a certain way. Under IFRS2, if the fair value of the goods or services received can be measured directly
and easily then the equity element is determined by taking the fair value of the goods or services less the fair value of the
debt element of this instrument. The debt element is essentially the cash payment that will occur. If the fair value of the goods
or services is measured by reference to the fair value of the equity instruments given then the whole of the compound
instrument should be fair valued. The equity element becomes the difference between the fair value of the equity instruments
granted less the fair value of the debt component. It should take into account the fact that the counterparty must forfeit its
right to receive cash in order to receive the equity instrument.
When Leigh received the property, plant and equipment it should have recorded a liability of $4 million and an increase in
equity of $0·55 million being the difference between the value of the property, plant and equipment and the fair value of theliability. The fair value of the liability is the cash payment of $3·50 x 1·3 million shares, i.e. $4·55 million.
The accounting entry would be:
-
第5题:
(b) One of the hotels owned by Norman is a hotel complex which includes a theme park, a casino and a golf course,
as well as a hotel. The theme park, casino, and hotel were sold in the year ended 31 May 2008 to Conquest, a
public limited company, for $200 million but the sale agreement stated that Norman would continue to operate
and manage the three businesses for their remaining useful life of 15 years. The residual interest in the business
reverts back to Norman after the 15 year period. Norman would receive 75% of the net profit of the businesses
as operator fees and Conquest would receive the remaining 25%. Norman has guaranteed to Conquest that the
net minimum profit paid to Conquest would not be less than $15 million. (4 marks)
Norman has recently started issuing vouchers to customers when they stay in its hotels. The vouchers entitle the
customers to a $30 discount on a subsequent room booking within three months of their stay. Historical
experience has shown that only one in five vouchers are redeemed by the customer. At the company’s year end
of 31 May 2008, it is estimated that there are vouchers worth $20 million which are eligible for discount. The
income from room sales for the year is $300 million and Norman is unsure how to report the income from room
sales in the financial statements. (4 marks)
Norman has obtained a significant amount of grant income for the development of hotels in Europe. The grants
have been received from government bodies and relate to the size of the hotel which has been built by the grant
assistance. The intention of the grant income was to create jobs in areas where there was significant
unemployment. The grants received of $70 million will have to be repaid if the cost of building the hotels is less
than $500 million. (4 marks)
Appropriateness and quality of discussion (2 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above income would be treated in the financial statements of Norman for the year ended
31 May 2008.
正确答案:
(b) Property is sometimes sold with a degree of continuing involvement by the seller so that the risks and rewards of ownership
have not been transferred. The nature and extent of the buyer’s involvement will determine how the transaction is accounted
for. The substance of the transaction is determined by looking at the transaction as a whole and IAS18 ‘Revenue’ requires
this by stating that where two or more transactions are linked, they should be treated as a single transaction in order to
understand the commercial effect (IAS18 paragraph 13). In the case of the sale of the hotel, theme park and casino, Norman
should not recognise a sale as the company continues to enjoy substantially all of the risks and rewards of the businesses,
and still operates and manages them. Additionally the residual interest in the business reverts back to Norman. Also Norman
has guaranteed the income level for the purchaser as the minimum payment to Conquest will be $15 million a year. The
transaction is in substance a financing arrangement and the proceeds should be treated as a loan and the payment of profits
as interest.
The principles of IAS18 and IFRIC13 ‘Customer Loyalty Programmes’ require that revenue in respect of each separate
component of a transaction is measured at its fair value. Where vouchers are issued as part of a sales transaction and are
redeemable against future purchases, revenue should be reported at the amount of the consideration received/receivable less
the voucher’s fair value. In substance, the customer is purchasing both goods or services and a voucher. The fair value of the
voucher is determined by reference to the value to the holder and not the cost to the issuer. Factors to be taken into account
when estimating the fair value, would be the discount the customer obtains, the percentage of vouchers that would be
redeemed, and the time value of money. As only one in five vouchers are redeemed, then effectively the hotel has sold goods
worth ($300 + $4) million, i.e. $304 million for a consideration of $300 million. Thus allocating the discount between the
two elements would mean that (300 ÷ 304 x $300m) i.e. $296·1 million will be allocated to the room sales and the balance
of $3·9 million to the vouchers. The deferred portion of the proceeds is only recognised when the obligations are fulfilled.
The recognition of government grants is covered by IAS20 ‘Accounting for government grants and disclosure of government
assistance’. The accruals concept is used by the standard to match the grant received with the related costs. The relationship
between the grant and the related expenditure is the key to establishing the accounting treatment. Grants should not be
recognised until there is reasonable assurance that the company can comply with the conditions relating to their receipt and
the grant will be received. Provision should be made if it appears that the grant may have to be repaid.
There may be difficulties of matching costs and revenues when the terms of the grant do not specify precisely the expense
towards which the grant contributes. In this case the grant appears to relate to both the building of hotels and the creation of
employment. However, if the grant was related to revenue expenditure, then the terms would have been related to payroll or
a fixed amount per job created. Hence it would appear that the grant is capital based and should be matched against the
depreciation of the hotels by using a deferred income approach or deducting the grant from the carrying value of the asset
(IAS20). Additionally the grant is only to be repaid if the cost of the hotel is less than $500 million which itself would seem
to indicate that the grant is capital based. If the company feels that the cost will not reach $500 million, a provision should
be made for the estimated liability if the grant has been recognised. -
第6题:
6 Assume today’s date is 16 April 2005.
Henry, aged 48, is the managing director of Happy Home Ltd, an unquoted UK company specialising in interior
design. He is wealthy in his own right and is married to Helen, who is 45 years old. They have two children – Stephen,
who is 19, and Sally who is 17.
As part of his salary, Henry was given 3,000 shares in Happy Home Ltd with an option to acquire a further 10,000
shares. The options were granted on 15 July 2003, shortly after the company started trading, and were not part of
an approved share option scheme. The free shares were given to Henry on the same day.
The exercise price of the share options was set at the then market value of £1·00 per share. The options are not
capable of being exercised after 10 years from the date of grant. The company has been successful, and the current
value of the shares is now £14·00 per share. Another shareholder has offered to buy the shares at their market value,
so Henry exercised his share options on 14 April 2005 and will sell the shares next week, on 20 April 2005.
With the company growing in size, Henry wishes to recruit high quality staff, but the company lacks the funds to pay
them in cash. Henry believes that giving new employees the chance to buy shares in the company would help recruit
staff, as they could share in the growth in value of Happy Home Ltd. Henry has heard that there is a particular share
scheme that is suitable for small, fast growing companies. He would like to obtain further information on how such
a scheme would work.
Henry has accumulated substantial assets over the years. The family house is owned jointly with Helen, and is worth
£650,000. Henry has a £250,000 mortgage on the house. In addition, Henry has liquid assets worth £340,000
and Helen has shares in quoted companies currently worth £125,000. Henry has no forms of insurance, and believes
he should make sure that his wealth and family are protected. He is keen to find out what options he should be
considering.
Required:
(a) (i) State how the gift of the 3,000 shares in Happy Home Ltd was taxed. (1 mark)
正确答案:
(a) (i) Gift of shares
Shares, which are given free or sold at less than market value, are charged to income tax on the difference between the
market value and the amount paid (if any) for the shares. Henry was given 3,000 shares with a market value of £1 at
the time of gift, so he was assessed to income tax on £3,000, in the tax year 2003/04. -
第7题:
(b) (i) State the condition that would need to be satisfied for the exercise of Paul’s share options in Memphis
plc to be exempt from income tax and the tax implications if this condition is not satisfied.
(2 marks)
正确答案:
(b) (i) Paul has options in an HMRC approved share scheme. Under such schemes, no tax liabilities arise either on the grant
or exercise of the option. The excess of the proceeds over the price paid for the shares (the exercise price) is charged to
capital gains tax on their disposal.
However, in order to secure this treatment, one of the conditions to be satisfied is that the options cannot be exercised
within three years of the date of grant. If Paul were to exercise his options now (i.e. before the third anniversary of the
grant), the exercise would instead be treated as an unapproved exercise. At that date, income tax would be charged on
the difference between the market value of the shares on exercise and the price paid to exercise the option. -
第8题:
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Seymour Co. The company offers information, proprietary foods and
medical innovations designed to improve the quality of life. (Proprietary foods are marketed under and protected by
registered names.) The draft consolidated financial statements for the year ended 30 September 2006 show revenue
of $74·4 million (2005 – $69·2 million), profit before taxation of $13·2 million (2005 – $15·8 million) and total
assets of $53·3 million (2005 – $40·5 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) In 2001, Seymour had been awarded a 20-year patent on a new drug, Tournose, that was also approved for
food use. The drug had been developed at a cost of $4 million which is being amortised over the life of the
patent. The patent cost $11,600. In September 2006 a competitor announced the successful completion of
preliminary trials on an alternative drug with the same beneficial properties as Tournose. The alternative drug is
expected to be readily available in two years time. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Seymour Co for the year ended
30 September 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案: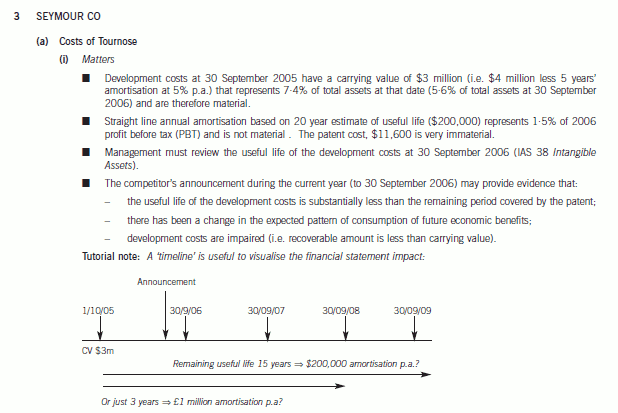
■ A change in the estimated useful life should be accounted for as a change in accounting estimate in accordance
with IAS 8 Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors. For example, if the development
costs have little, if any, useful life after the introduction of the alternative drug (‘worst case’ scenario), the carrying
value ($3 million) should be written off over the current and remaining years, i.e. $1 million p.a. The increase in
amortisation/decrease in carrying value ($800,000) is material to PBT (6%) and total assets (1·5%).
■ Similarly a change in the expected pattern of consumption of the future economic benefits should be accounted for
as a change in accounting estimate (IAS 8). For example, it may be that the useful life is still to 2020 but that
the economic benefits may reduce significantly in two years time.
■ After adjusting the carrying amount to take account of the change in accounting estimate(s) management should
have tested it for impairment and any impairment loss recognised in profit or loss.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ $3 million carrying amount of development costs brought forward agreed to prior year working papers and financial
statements.
■ A copy of the press release announcing the competitor’s alternative drug.
■ Management’s projections of future cashflows from Tournose-related sales as evidence of the useful life of the
development costs and pattern of consumption.
■ Reperformance of management’s impairment test on the development costs: Recalculation of management’s
calculation of the carrying amount after revising estimates of useful life and/or consumption of benefits compared
with management’s calculation of value in use.
■ Sensitivity analysis on management’s key assumptions (e.g. estimates of useful life, discount rate).
■ Written management representation on the key assumptions concerning the future that have a significant risk of
causing material adjustment to the carrying amount of the development costs. (These assumptions should be
disclosed in accordance with IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements.) -
第9题:
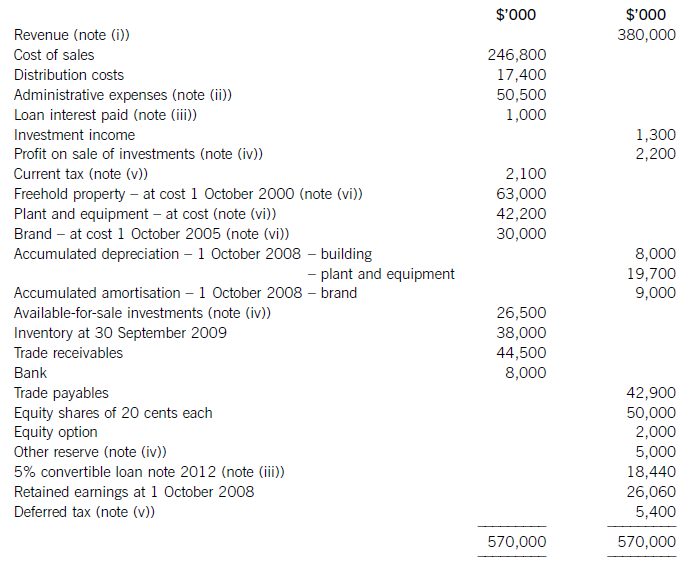
The following trial balance relates to Sandown at 30 September 2009:
The following notes are relevant:
(i) Sandown’s revenue includes $16 million for goods sold to Pending on 1 October 2008. The terms of the sale are that Sandown will incur ongoing service and support costs of $1·2 million per annum for three years after the sale. Sandown normally makes a gross profit of 40% on such servicing and support work. Ignore the time value of money.
(ii) Administrative expenses include an equity dividend of 4·8 cents per share paid during the year.
(iii) The 5% convertible loan note was issued for proceeds of $20 million on 1 October 2007. It has an effective interest rate of 8% due to the value of its conversion option.
(iv) During the year Sandown sold an available-for-sale investment for $11 million. At the date of sale it had a
carrying amount of $8·8 million and had originally cost $7 million. Sandown has recorded the disposal of the
investment. The remaining available-for-sale investments (the $26·5 million in the trial balance) have a fair value of $29 million at 30 September 2009. The other reserve in the trial balance represents the net increase in the value of the available-for-sale investments as at 1 October 2008. Ignore deferred tax on these transactions.
(v) The balance on current tax represents the under/over provision of the tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2008. The directors have estimated the provision for income tax for the year ended 30 September 2009 at $16·2 million. At 30 September 2009 the carrying amounts of Sandown’s net assets were $13 million in excess of their tax base. The income tax rate of Sandown is 30%.
(vi) Non-current assets:
The freehold property has a land element of $13 million. The building element is being depreciated on a
straight-line basis.
Plant and equipment is depreciated at 40% per annum using the reducing balance method.
Sandown’s brand in the trial balance relates to a product line that received bad publicity during the year which led to falling sales revenues. An impairment review was conducted on 1 April 2009 which concluded that, based on estimated future sales, the brand had a value in use of $12 million and a remaining life of only three years.
However, on the same date as the impairment review, Sandown received an offer to purchase the brand for
$15 million. Prior to the impairment review, it was being depreciated using the straight-line method over a
10-year life.
No depreciation/amortisation has yet been charged on any non-current asset for the year ended 30 September
2009. Depreciation, amortisation and impairment charges are all charged to cost of sales.
Required:
(a) Prepare the statement of comprehensive income for Sandown for the year ended 30 September 2009.
(13 marks)
(b) Prepare the statement of financial position of Sandown as at 30 September 2009. (12 marks)
Notes to the financial statements are not required.
A statement of changes in equity is not required.
正确答案:
(i)IAS18Revenuerequiresthatwheresalesrevenueincludesanamountforaftersalesservicingandsupportcoststhenaproportionoftherevenueshouldbedeferred.Theamountdeferredshouldcoverthecostandareasonableprofit(inthiscaseagrossprofitof40%)ontheservices.Astheservicingandsupportisforthreeyearsandthedateofthesalewas1October2008,revenuerelatingtotwoyears’servicingandsupportprovisionmustbedeferred:($1·2millionx2/0·6)=$4million.Thisisshownas$2millioninbothcurrentandnon-currentliabilities. -
第10题:
(a) The following figures have been calculated from the financial statements (including comparatives) of Barstead for
the year ended 30 September 2009:
increase in profit after taxation 80%
increase in (basic) earnings per share 5%
increase in diluted earnings per share 2%
Required:
Explain why the three measures of earnings (profit) growth for the same company over the same period can
give apparently differing impressions. (4 marks)
(b) The profit after tax for Barstead for the year ended 30 September 2009 was $15 million. At 1 October 2008 the company had in issue 36 million equity shares and a $10 million 8% convertible loan note. The loan note will mature in 2010 and will be redeemed at par or converted to equity shares on the basis of 25 shares for each $100 of loan note at the loan-note holders’ option. On 1 January 2009 Barstead made a fully subscribed rights issue of one new share for every four shares held at a price of $2·80 each. The market price of the equity shares of Barstead immediately before the issue was $3·80. The earnings per share (EPS) reported for the year ended 30 September 2008 was 35 cents.
Barstead’s income tax rate is 25%.
Required:
Calculate the (basic) EPS figure for Barstead (including comparatives) and the diluted EPS (comparatives not required) that would be disclosed for the year ended 30 September 2009. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(a)Whilstprofitaftertax(anditsgrowth)isausefulmeasure,itmaynotgiveafairrepresentationofthetrueunderlyingearningsperformance.Inthisexample,userscouldinterpretthelargeannualincreaseinprofitaftertaxof80%asbeingindicativeofanunderlyingimprovementinprofitability(ratherthanwhatitreallyis:anincreaseinabsoluteprofit).Itispossible,evenprobable,that(someof)theprofitgrowthhasbeenachievedthroughtheacquisitionofothercompanies(acquisitivegrowth).Wherecompaniesareacquiredfromtheproceedsofanewissueofshares,orwheretheyhavebeenacquiredthroughshareexchanges,thiswillresultinagreaternumberofequitysharesoftheacquiringcompanybeinginissue.ThisiswhatappearstohavehappenedinthecaseofBarsteadastheimprovementindicatedbyitsearningspershare(EPS)isonly5%perannum.ThisexplainswhytheEPS(andthetrendofEPS)isconsideredamorereliableindicatorofperformancebecausetheadditionalprofitswhichcouldbeexpectedfromthegreaterresources(proceedsfromthesharesissued)ismatchedwiththeincreaseinthenumberofshares.Simplylookingatthegrowthinacompany’sprofitaftertaxdoesnottakeintoaccountanyincreasesintheresourcesusedtoearnthem.Anyincreaseingrowthfinancedbyborrowings(debt)wouldnothavethesameimpactonprofit(asbeingfinancedbyequityshares)becausethefinancecostsofthedebtwouldacttoreduceprofit.ThecalculationofadilutedEPStakesintoaccountanypotentialequitysharesinissue.Potentialordinarysharesarisefromfinancialinstruments(e.g.convertibleloannotesandoptions)thatmayentitletheirholderstoequitysharesinthefuture.ThedilutedEPSisusefulasitalertsexistingshareholderstothefactthatfutureEPSmaybereducedasaresultofsharecapitalchanges;inasenseitisawarningsign.InthiscasethelowerincreaseinthedilutedEPSisevidencethatthe(higher)increaseinthebasicEPShas,inpart,beenachievedthroughtheincreaseduseofdilutingfinancialinstruments.Thefinancecostoftheseinstrumentsislessthantheearningstheirproceedshavegeneratedleadingtoanincreaseincurrentprofits(andbasicEPS);however,inthefuturetheywillcausemoresharestobeissued.ThiscausesadilutionwherethefinancecostperpotentialnewshareislessthanthebasicEPS. -
第11题:
I didn't attend the conference,but I wish I__there.A.had been
B.be
C.were
D.would be答案:A解析:wish后的宾语从句中,如表示过去不曾实现的愿望,则用过去完成时表示虚拟语气。 -
第12题:
单选题How much loss will the shutdown cause the government in royalties and taxes in a week?AAbout $44.8 million.
BAbout $2.8 million.
CAbout $28 million.
DAbout $4.48 million.
正确答案: C解析:
数字信息的找寻和判断。录音中指出油田的关闭导致每天损失40万桶油,以目前的油价来计算,也就意味着“the state is losing about $6.4 million a day in royalties and taxes”,即“该州每天损失大概$6. 4 million(640万美元),那么一周下来就会损失44. 8 million。因此选项A为正确答案。 -
第13题:
(c) the deferred tax implications (with suitable calculations) for the company which arise from the recognition
of a remuneration expense for the directors’ share options. (7 marks)
正确答案:
-
第14题:
3 Seejoy is a famous football club but has significant cash flow problems. The directors and shareholders wish to take
steps to improve the club’s financial position. The following proposals had been drafted in an attempt to improve the
cash flow of the club. However, the directors need advice upon their implications.
(a) Sale and leaseback of football stadium (excluding the land element)
The football stadium is currently accounted for using the cost model in IAS16, ‘Property, Plant, and Equipment’.
The carrying value of the stadium will be $12 million at 31 December 2006. The stadium will have a remaining
life of 20 years at 31 December 2006, and the club uses straight line depreciation. It is proposed to sell the
stadium to a third party institution on 1 January 2007 and lease it back under a 20 year finance lease. The sale
price and fair value are $15 million which is the present value of the minimum lease payments. The agreement
transfers the title of the stadium back to the football club at the end of the lease at nil cost. The rental is
$1·2 million per annum in advance commencing on 1 January 2007. The directors do not wish to treat this
transaction as the raising of a secured loan. The implicit interest rate on the finance in the lease is 5·6%.
(9 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above proposals would be dealt with in the financial statements of Seejoy for the year ending
31 December 2007, setting out their accounting treatment and appropriateness in helping the football club’s
cash flow problems.
(Candidates do not need knowledge of the football finance sector to answer this question.)
正确答案:

-
第15题:
3 (a) Leigh, a public limited company, purchased the whole of the share capital of Hash, a limited company, on 1 June
2006. The whole of the share capital of Hash was formerly owned by the five directors of Hash and under the
terms of the purchase agreement, the five directors were to receive a total of three million ordinary shares of $1
of Leigh on 1 June 2006 (market value $6 million) and a further 5,000 shares per director on 31 May 2007,
if they were still employed by Leigh on that date. All of the directors were still employed by Leigh at 31 May
2007.
Leigh granted and issued fully paid shares to its own employees on 31 May 2007. Normally share options issued
to employees would vest over a three year period, but these shares were given as a bonus because of the
company’s exceptional performance over the period. The shares in Leigh had a market value of $3 million
(one million ordinary shares of $1 at $3 per share) on 31 May 2007 and an average fair value of
$2·5 million (one million ordinary shares of $1 at $2·50 per share) for the year ended 31 May 2007. It is
expected that Leigh’s share price will rise to $6 per share over the next three years. (10 marks)
Required:
Discuss with suitable computations how the above share based transactions should be accounted for in the
financial statements of Leigh for the year ended 31 May 2007.
正确答案:
(a) The shares issued to the management of Hash by Leigh (three million ordinary shares of $1) for the purchase of the company
would not be accounted for under IFRS2 ‘Share-based payment’ but would be dealt with under IFRS3 ‘Business
Combinations’.
The cost of the business combination will be the total of the fair values of the consideration given by the acquirer plus any
attributable cost. In this case the shares of Leigh will be fair valued at $6 million with $3 million being shown as share capital
and $3million as share premium. However, the shares issued as contingent consideration may be accounted for under IFRS2.
The terms of the issuance of shares will need to be examined. Where part of the consideration may be reliant on uncertain
future events, and it is probable that the additional consideration is payable and can be measured reliably, then it is included
in the cost of the business consideration at the acquisition date. However, the question to be answered in the case of the
additional 5,000 shares per director is whether the shares are compensation or part of the purchase price. There is a need
to understand why the acquisition agreement includes a provision for a contingent payment. It is possible that the price paid
initially by Leigh was quite low and, therefore, this then represents a further purchase consideration. However, in this instance
the additional payment is linked to continuing employment and, therefore, it would be argued that because of the link between
the contingent consideration and continuing employment that it represents a compensation arrangement which should be
included within the scope of IFRS2.
Thus as there is a performance condition, (the performance condition will apply as it is not a market condition) the substance
of the agreement is that the shares are compensation, then they will be fair valued at the grant date and not when the shares
vest. Therefore, the share price of $2 per share will be used to give compensation of $50,000 (5 x 5,000 x $2). (Under
IFRS3, fair value is measured at the date the consideration is provided and discounted to presented value. No guidance is
provided on what the appropriate discount rate might be. Thus the fair value used would have been $3 per share at 31 May
2007.) The compensation will be charged to the income statement and included in equity.
The shares issued to the employees of Leigh will be accounted for under IFRS2. The issuance of fully paid shares will be
presumed to relate to past service. The normal vesting period for share options is irrelevant, as is the average fair value of the
shares during the period. The shares would be expensed at a value of $3 million with a corresponding increase in equity.
Goods or services acquired in a share based payment transaction should be recognised when they are received. In the case
of goods then this will be when this occurs. However, it is somewhat more difficult sometimes to determine when services
are received. In a case of goods the vesting date is not really relevant, however, it is highly relevant for employee services. If
shares are issued that vest immediately then there is a presumption that these are a consideration for past employee services. -
第16题:
4 (a) Router, a public limited company operates in the entertainment industry. It recently agreed with a television
company to make a film which will be broadcast on the television company’s network. The fee agreed for the
film was $5 million with a further $100,000 to be paid every time the film is shown on the television company’s
channels. It is hoped that it will be shown on four occasions. The film was completed at a cost of $4 million and
delivered to the television company on 1 April 2007. The television company paid the fee of $5 million on
30 April 2007 but indicated that the film needed substantial editing before they were prepared to broadcast it,
the costs of which would be deducted from any future payments to Router. The directors of Router wish to
recognise the anticipated future income of $400,000 in the financial statements for the year ended 31 May
2007. (5 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above items should be dealt with in the group financial statements of Router for the year ended
31 May 2007.
正确答案:
(a) Under IAS18 ‘Revenue’, revenue on a service contract is recognised when the outcome of the transaction can be measured
reliably. For revenue arising from the rendering of services, provided that all of the following criteria are met, revenue should
be recognised by reference to the stage of completion of the transaction at the balance sheet date (the percentage-ofcompletion
method) (IAS18 para 20):
(a) the amount of revenue can be measured reliably;
(b) it is probable that the economic benefits will flow to the seller;
(c) the stage of completion at the balance sheet date can be measured reliably; and
(d) the costs incurred, or to be incurred, in respect of the transaction can be measured reliably.
When the above criteria are not met, revenue arising from the rendering of services should be recognised only to the extent
of the expenses recognised that are recoverable. Because the only revenue which can be measured reliably is the fee for
making the film ($5 million), this should therefore be recognised as revenue in the year to 31 May 2007 and matched against
the cost of the film of $4 million. Only when the television company shows the film should any further amounts of $100,000
be recognised as there is an outstanding ‘performance’ condition in the form. of the editing that needs to take place before the
television company will broadcast the film. The costs of the film should not be carried forward and matched against
anticipated future income unless they can be deemed to be an intangible asset under IAS 38 ‘Intangible Assets’. Additionally,
when assessing revenue to be recognised in future years, the costs of the editing and Router’s liability for these costs should
be assessed.
-
第17题:
(c) On 1 May 2007 Sirus acquired another company, Marne plc. The directors of Marne, who were the only
shareholders, were offered an increased profit share in the enlarged business for a period of two years after the
date of acquisition as an incentive to accept the purchase offer. After this period, normal remuneration levels will
be resumed. Sirus estimated that this would cost them $5 million at 30 April 2008, and a further $6 million at
30 April 2009. These amounts will be paid in cash shortly after the respective year ends. (5 marks)
Required:
Draft a report to the directors of Sirus which discusses the principles and nature of the accounting treatment of
the above elements under International Financial Reporting Standards in the financial statements for the year
ended 30 April 2008.
正确答案:
(c) Acquisition of Marne
All business combinations within the scope of IFRS 3 ‘Business Combinations’ must be accounted for using the purchase
method. (IFRS 3.14) The pooling of interests method is prohibited. Under IFRS 3, an acquirer must be identified for all
business combinations. (IFRS 3.17) Sirus will be identified as the acquirer of Marne and must measure the cost of a business
combination at the sum of the fair values, at the date of exchange, of assets given, liabilities incurred or assumed, in exchange
for control of Marne; plus any costs directly attributable to the combination. (IFRS 3.24) If the cost is subject to adjustment
contingent on future events, the acquirer includes the amount of that adjustment in the cost of the combination at the
acquisition date if the adjustment is probable and can be measured reliably. (IFRS 3.32) However, if the contingent payment
either is not probable or cannot be measured reliably, it is not measured as part of the initial cost of the business combination.
If that adjustment subsequently becomes probable and can be measured reliably, the additional consideration is treated as
an adjustment to the cost of the combination. (IAS 3.34) The issue with the increased profit share payable to the directors
of Marne is whether the payment constitutes remuneration or consideration for the business acquired. Because the directors
of Marne fall back to normal remuneration levels after the two year period, it appears that this additional payment will
constitute part of the purchase consideration with the resultant increase in goodwill. It seems as though these payments can
be measured reliably and therefore the cost of the acquisition should be increased by the net present value of $11 million at
1 May 2007 being $5 million discounted for 1 year and $6 million for 2 years. -
第18题:
(b) (i) Advise Benny of the income tax implications of the grant and exercise of the share options in Summer
Glow plc on the assumption that the share price on 1 September 2007 and on the day he exercises the
options is £3·35 per share. Explain why the share option scheme is not free from risk by reference to
the rules of the scheme and the circumstances surrounding the company. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(b) (i) The share options
There are no income tax implications on the grant of the share options.
In the tax year in which Benny exercises the options and acquires the shares, the excess of the market value of the
shares over the price paid, i.e. £11,500 ((£3·35 – £2·20) x 10,000) will be subject to income tax.
Benny’s financial exposure is caused by the rule within the share option scheme obliging him to hold the shares for a
year before he can sell them. If the company’s expansion into Eastern Europe fails, such that its share price
subsequently falls to less than £2·20 before Benny has the chance to sell the shares, Benny’s financial position may be
summarised as follows:
– Benny will have paid £22,000 (£2·20 x 10,000) for shares which are now worth less than that.
– He will also have paid income tax of £4,600 (£11,500 x 40%). -
第19题:
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Keffler Co, a private limited company engaged in the manufacture of
plastic products. The draft financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2006 show revenue of $47·4 million
(2005 – $43·9 million), profit before taxation of $2 million (2005 – $2·4 million) and total assets of $33·8 million
(2005 – $25·7 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) In April 2005, Keffler bought the right to use a landfill site for a period of 15 years for $1·1 million. Keffler
expects that the amount of waste that it will need to dump will increase annually and that the site will be
completely filled after just ten years. Keffler has charged the following amounts to the income statement for the
year to 31 March 2006:
– $20,000 licence amortisation calculated on a sum-of-digits basis to increase the charge over the useful life
of the site; and
– $100,000 annual provision for restoring the land in 15 years’ time. (9 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Keffler Co for the year ended
31 March 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
3 KEFFLER CO
Tutorial note: None of the issues have any bearing on revenue. Therefore any materiality calculations assessed on revenue are
inappropriate and will not be awarded marks.
(a) Landfill site
(i) Matters
■ $1·1m cost of the right represents 3·3% of total assets and is therefore material.
■ The right should be amortised over its useful life, that is just 10 years, rather than the 15-year period for which
the right has been granted.
Tutorial note: Recalculation on the stated basis (see audit evidence) shows that a 10-year amortisation has been
correctly used.
■ The amortisation charge represents 1% of profit before tax (PBT) and is not material.
■ The amortisation method used should reflect the pattern in which the future economic benefits of the right are
expected to be consumed by Keffler. If that pattern cannot be determined reliably, the straight-line method must
be used (IAS 38 ‘Intangible Assets’).
■ Using an increasing sum-of-digits will ‘end-load’ the amortisation charge (i.e. least charge in the first year, highest
charge in the last year). However, according to IAS 38 there is rarely, if ever, persuasive evidence to support an
amortisation method that results in accumulated amortisation lower than that under the straight-line method.
Tutorial note: Over the first half of the asset’s life, depreciation will be lower than under the straight-line basis
(and higher over the second half of the asset’s life).
■ On a straight line basis the annual amortisation charge would be $0·11m, an increase of $90,000. Although this
difference is just below materiality (4·5% PBT) the cumulative effect (of undercharging amortisation) will become
material.
■ Also, when account is taken of the understatement of cost (see below), the undercharging of amortisation will be
material.
■ The sum-of-digits method might be suitable as an approximation to the unit-of-production method if Keffler has
evidence to show that use of the landfill site will increase annually.
■ However, in the absence of such evidence, the audit opinion should be qualified ‘except for’ disagreement with the
amortisation method (resulting in intangible asset overstatement/amortisation expense understatement).
■ The annual restoration provision represents 5% of PBT and 0·3% of total assets. Although this is only borderline
material (in terms of profit), there will be a cumulative impact.
■ Annual provisioning is contrary to IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets’.
■ The estimate of the future restoration cost is (presumably) $1·5m (i.e. $0·1 × 15). The present value of this
amount should have been provided in full in the current year and included in the cost of the right.
■ Thus the amortisation being charged on the cost of the right (including the restoration cost) is currently understated
(on any basis).
Tutorial note: A 15-year discount factor at 10% (say) is 0·239. $1·5m × 0·239 is approximately $0·36m. The
resulting present value (of the future cost) would be added to the cost of the right. Amortisation over 10 years
on a straight-line basis would then be increased by $36,000, increasing the difference between amortisation
charged and that which should be charged. The lower the discount rate, the greater the understatement of
amortisation expense.
Total amount expensed ($120k) is less than what should have been expensed (say $146k amortisation + $36k
unwinding of discount). However, this is not material.
■ Whether Keffler will wait until the right is about to expire before restoring the land or might restore earlier (if the
site is completely filled in 10 years).
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Written agreement for purchase of right and contractual terms therein (e.g. to make restoration in 15 years’ time).
■ Cash book/bank statement entries in April 2005 for $1·1m payment.
■ Physical inspection of the landfill site to confirm Keffler’s use of it.
■ Annual dump budget/projection over next 10 years and comparison with sum-of-digits proportions.
■ Amount actually dumped in the year (per dump records) compared with budget and as a percentage/proportion of
the total available.
■ Recalculation of current year’s amortisation based on sum-of-digits. That is, $1·1m ÷ 55 = $20,000.
Tutorial note: The sum-of-digits from 1 to 10 may be calculated long-hand or using the formula n(n+1)/2 i.e.
(10 × 11)/2 = 55.
■ The basis of the calculation of the estimated restoration costs and principal assumptions made.
■ If estimated by a quantity surveyor/other expert then a copy of the expert’s report.
■ Written management representation confirming the planned timing of the restoration in 15 years (or sooner). -
第20题:
Under her leadership, the group’s ______ grew from less than one million dollars to more than ten million.
A data
Bbudget
Citem
Dpiece
参考答案:B
-
第21题:
(a) The following information relates to Crosswire a publicly listed company.
Summarised statements of financial position as at:
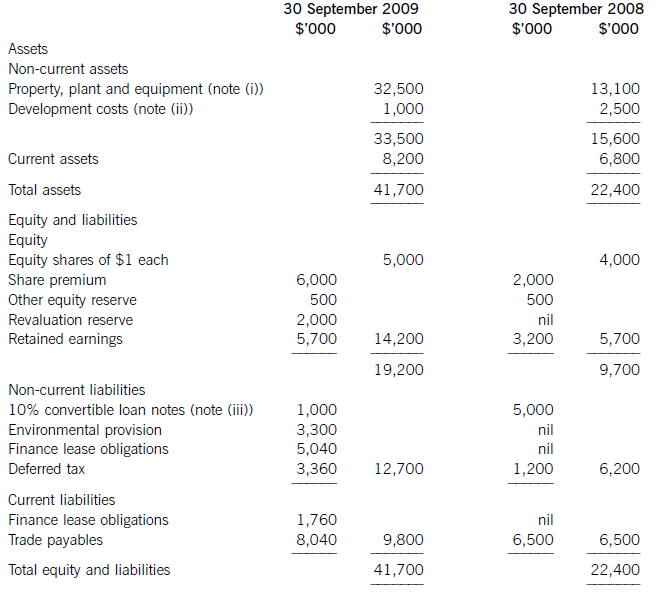
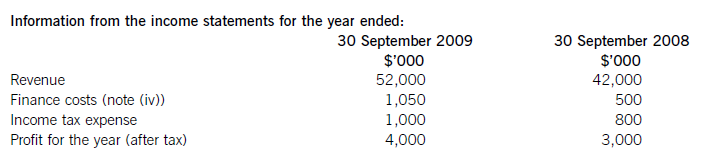
The following information is available:
(i) During the year to 30 September 2009, Crosswire embarked on a replacement and expansion programme for its non-current assets. The details of this programme are:
On 1 October 2008 Crosswire acquired a platinum mine at a cost of $5 million. A condition of mining the
platinum is a requirement to landscape the mining site at the end of its estimated life of ten years. The
present value of this cost at the date of the purchase was calculated at $3 million (in addition to the
purchase price of the mine of $5 million).
Also on 1 October 2008 Crosswire revalued its freehold land for the first time. The credit in the revaluation
reserve is the net amount of the revaluation after a transfer to deferred tax on the gain. The tax rate applicable to Crosswire for deferred tax is 20% per annum.
On 1 April 2009 Crosswire took out a finance lease for some new plant. The fair value of the plant was
$10 million. The lease agreement provided for an initial payment on 1 April 2009 of $2·4 million followed
by eight six-monthly payments of $1·2 million commencing 30 September 2009.
Plant disposed of during the year had a carrying amount of $500,000 and was sold for $1·2 million. The
remaining movement on the property, plant and equipment, after charging depreciation of $3 million, was
the cost of replacing plant.
(ii) From 1 October 2008 to 31 March 2009 a further $500,000 was spent completing the development
project at which date marketing and production started. The sales of the new product proved disappointing
and on 30 September 2009 the development costs were written down to $1 million via an impairment
charge.
(iii) During the year ended 30 September 2009, $4 million of the 10% convertible loan notes matured. The
loan note holders had the option of redemption at par in cash or to exchange them for equity shares on the
basis of 20 new shares for each $100 of loan notes. 75% of the loan-note holders chose the equity option.
Ignore any effect of this on the other equity reserve.
All the above items have been treated correctly according to International Financial Reporting Standards.
(iv) The finance costs are made up of:
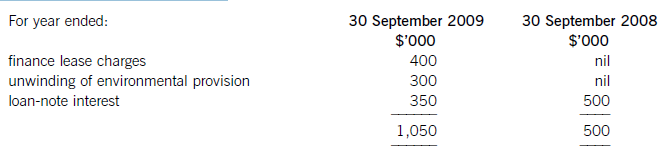
Required:
(i) Prepare a statement of the movements in the carrying amount of Crosswire’s non-current assets for the
year ended 30 September 2009; (9 marks)
(ii) Calculate the amounts that would appear under the headings of ‘cash flows from investing activities’
and ‘cash flows from financing activities’ in the statement of cash flows for Crosswire for the year ended
30 September 2009.
Note: Crosswire includes finance costs paid as a financing activity. (8 marks)
(b) A substantial shareholder has written to the directors of Crosswire expressing particular concern over the
deterioration of the company’s return on capital employed (ROCE)
Required:
Calculate Crosswire’s ROCE for the two years ended 30 September 2008 and 2009 and comment on the
apparent cause of its deterioration.
Note: ROCE should be taken as profit before interest on long-term borrowings and tax as a percentage of equity plus loan notes and finance lease obligations (at the year end). (8 marks)
正确答案:
(i)Thecashelementsoftheincreaseinproperty,plantandequipmentare$5millionforthemine(thecapitalisedenvironmentalprovisionisnotacashflow)and$2·4millionforthereplacementplantmakingatotalof$7·4million.(ii)Ofthe$4millionconvertibleloannotes(5,000–1,000)thatwereredeemedduringtheyear,75%($3million)ofthesewereexchangedforequitysharesonthebasisof20newsharesforeach$100inloannotes.Thiswouldcreate600,000(3,000/100x20)newsharesof$1eachandsharepremiumof$2·4million(3,000–600).As1million(5,000–4,000)newshareswereissuedintotal,400,000musthavebeenforcash.Theremainingincrease(aftertheeffectoftheconversion)inthesharepremiumof$1·6million(6,000–2,000b/f–2,400conversion)mustrelatetothecashissueofshares,thuscashproceedsfromtheissueofsharesis$2million(400nominalvalue+1,600premium).(iii)Theinitialleaseobligationis$10million(thefairvalueoftheplant).At30September2009totalleaseobligationsare$6·8million(5,040+1,760),thusrepaymentsintheyearwere$3·2million(10,000–6,800).(b)TakingthedefinitionofROCEfromthequestion:Fromtheaboveitcanbeclearlyseenthatthe2009operatingmarginhasimprovedbynearly1%point,despitethe$2millionimpairmentchargeonthewritedownofthedevelopmentproject.ThismeansthedeteriorationintheROCEisduetopoorerassetturnover.Thisimpliestherehasbeenadecreaseintheefficiencyintheuseofthecompany’sassetsthisyearcomparedtolastyear.Lookingatthemovementinthenon-currentassetsduringtheyearrevealssomemitigatingpoints:Thelandrevaluationhasincreasedthecarryingamountofproperty,plantandequipmentwithoutanyphysicalincreaseincapacity.Thisunfavourablydistortsthecurrentyear’sassetturnoverandROCEfigures.TheacquisitionoftheplatinummineappearstobeanewareaofoperationforCrosswirewhichmayhaveadifferent(perhapslower)ROCEtootherpreviousactivitiesoritmaybethatitwilltakesometimefortheminetocometofullproductioncapacity.Thesubstantialacquisitionoftheleasedplantwashalf-waythroughtheyearandcanonlyhavecontributedtotheyear’sresultsforsixmonthsatbest.Infutureperiodsafullyear’scontributioncanbeexpectedfromthisnewinvestmentinplantandthisshouldimprovebothassetturnoverandROCE.Insummary,thefallintheROCEmaybeduelargelytotheabovefactors(effectivelythereplacementandexpansionprogramme),ratherthantopooroperatingperformance,andinfutureperiodsthismaybereversed.ItshouldalsobenotedthathadtheROCEbeencalculatedontheaveragecapitalemployedduringtheyear(ratherthantheyearendcapitalemployed),whichisarguablymorecorrect,thenthedeteriorationintheROCEwouldnothavebeenaspronounced. -
第22题:
For the year just ended, N company had an earnings of$ 2 per share and paid a dividend of $ 1. 2 on its stock. The growth rate in net income and dividend are both expected to be a constant 7 percent per year, indefinitely. N company has a Beta of 0. 8, the risk - free interest rate is 6 percent, and the market risk premium is 8 percent.
P Company is very similar to N company in growth rate, risk and dividend. payout ratio. It had 20 million shares outstanding and an earnings of $ 36 million for the year just ended. The earnings will increase to $ 38. 5 million the next year.
Requirement :
A. Calculate the expected rate of return on N company 's equity.
B. Calculate N Company 's current price-earning ratio and prospective price - earning ratio.
C. Using N company 's current price-earning ratio, value P company 's stock price.
D. Using N company 's prospective price - earning ratio, value P company 's stock price.
答案:解析:A. The expected rate of return on N company's equity =6% +0. 8*8% =12.4%
B. Current price -earning ratio = (1. 2/2) * (1 +7% )/ (12.4% -7% ) =11. 89
Prospective price - earning ratio = (1. 2/2) / (12. 4% - 70% ) =11. 11
C. P company's stock = 11. 89* 36/20 = 21. 4
D. P company's stock = 11. 11* 38. 5/20 = 21. 39
-
第23题:
单选题Supposing 1 million leukemia cells were killed after 24 hours of exposure to radio waves, how many healthy cells would be killed under the same condition?A1.2 million.
B1.4 million.
C0.8 million.
D2 million.
正确答案: D解析:
数字的找寻和判断。录音中提到“In the Italian study, after 24 hours 20 percent mole leukemia cells died than healthy cells but longer exposure to the radio waves triggered…”,可知暴露在无线电波之下24小时,被杀死的白血病细胞比正常细胞数量多出20%。也就是说,如果有1 million(100万)个白血病细胞被杀死,同时也有0.8 million(80万)的正常细胞被杀死。因此选C。
