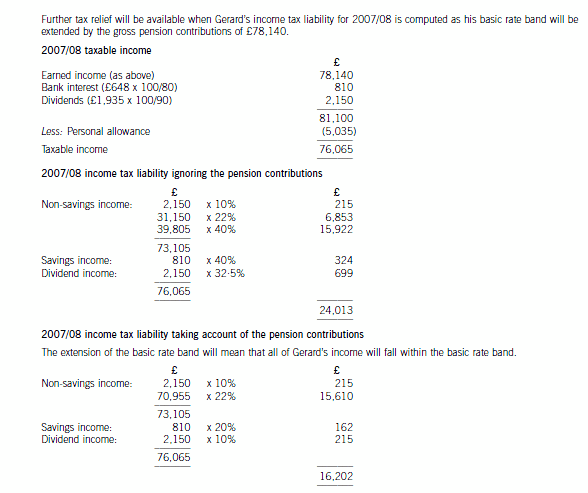
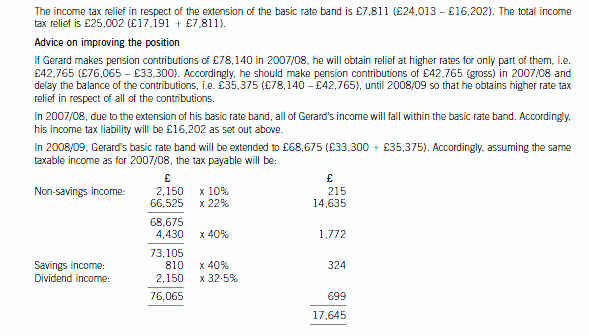
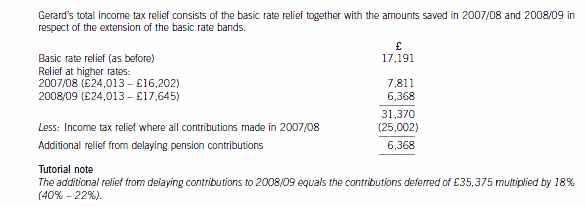
(c) Calculate and explain the amount of income tax relief that Gerard will obtain in respect of the pensioncontributions he proposes to make in the tax year 2007/08 and contrast this with how his position could beimproved by delaying some of the contribut
题目
(c) Calculate and explain the amount of income tax relief that Gerard will obtain in respect of the pension
contributions he proposes to make in the tax year 2007/08 and contrast this with how his position could be
improved by delaying some of the contributions that he could have made in 2007/08 until 2008/09. You
should include relevant supporting calculations and quantify the additional tax savings arising as a result of
your advice.
You should ignore the proposed changes to the bonus scheme for this part of this question and assume that
Gerard’s income will not change in 2008/09. (12 marks)
相似考题
参考答案和解析

更多“(c) Calculate and explain the amount of income tax relief that Gerard will obtain in respect of the pensioncontributions he proposes to make in the tax year 2007/08 and contrast this with how his position could beimproved by delaying some of the contribut”相关问题
-
第1题:
(ii) Advise Benny of the amount of tax he could save by delaying the sale of the shares by 30 days. For the
purposes of this part, you may assume that the benefit in respect of the furnished flat is £11,800 per
year. (3 marks)
正确答案:
-
第2题:
(ii) Calculate Paul’s tax liability if he exercises the share options in Memphis plc and subsequently sells the
shares in Memphis plc immediately, as proposed, and show how he may reduce this tax liability.
(4 marks)
正确答案:
-
第3题:
(b) Peter, one of Linden Limited’s non-executive directors, having lived and worked in the UK for most of his adult
life, sold his home near London on 22 March 2006 and, together with his wife (a French citizen), moved to live
in a villa which she owns in the south of France. Peter is now demanding that the tax deducted from his director’s
fees, for the board meetings held on 18 April and 16 May 2006, be refunded, on the grounds that, as he is no
longer resident in the UK, he is no longer liable to UK income tax. All of the company’s board meetings are held
at its offices in Cambridge.
Despite Peter’s assurance that none of the other companies of which he is a director has disputed his change of
tax status, Damian is uncertain whether he should make the refunds requested. However, as Peter is a friend of
the company’s founder, Linden Limited’s managing director is urging him to do so, stating that if the tax does
have to be paid, then Linden Limited could always bear the cost.
Required:
Advise Damian whether Peter is correct in his assertion regarding his tax position and in the case that there
is a UK tax liability the implications of the managing director’s suggestion. You are not required to consider
national insurance (NIC) issues. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Peter will have been resident and ordinarily resident in the UK. When such individuals leave the UK for a purpose other than
to take up full time employment abroad, they normally continue to still be so regarded unless their absence spans a complete
tax year. But, where someone intends to live permanently abroad or to do so for a period of at least three tax years, they may
be treated as non-resident and non-ordinarily resident from the day after the date of their departure, if they can provide
evidence to HMRC of that intention. Selling a residence in the UK and setting up home abroad will normally constitute such
evidence. However to retain non-resident status the intention must actually be fulfilled, and visits to the UK must not exceed
182 days in any tax year or average more than 90 days per year over a period of four tax years. Given that Peter would appear
to have several company directorships in the UK, it is possible that he might fail to satisfy the 90 day average ‘substantial
visits’ rule.
Even if Peter is classed as non-resident, any remuneration earned in the UK will still be liable to UK income tax, and subject
to PAYE, unless it is for duties incidental to an overseas employment, which is unlikely to be the case for fees paid to a nonexecutive
director for attending board meetings. Thus, income tax should still be deducted from the fees under PAYE. Where
PAYE should have been deducted from a director’s emoluments and it has not been, but the tax is nevertheless accounted
for by the company to HMRC, then to the extent that the tax is not reimbursed by the director, he will be treated as receiving
a benefit equivalent to the amount of tax. -
第4题:
(b) (i) Advise Andrew of the income tax (IT) and capital gains tax (CGT) reliefs available on his investment in
the ordinary share capital of Scalar Limited, together with any conditions which need to be satisfied.
Your answer should clearly identify any steps that should be taken by Andrew and the other investors
to obtain the maximum relief. (13 marks)
正确答案:
(b) (i) Andrew may be able to take advantage of tax reliefs under the enterprise investment scheme (EIS) provided the
necessary conditions are met. The conditions that have to be satisfied before full relief is available fall into three areas,
and broadly require that a ‘qualifying individual’ subscribes for ‘eligible shares’ in a ‘qualifying company’.
‘Qualifying Individual’
To be a qualifying individual, Andrew must not be connected with the EIS company. This means that he should not be
an employee (or, at the time the shares are issued, a director) or have an interest in (i.e. control) 30% or more of the
capital of the company. These conditions need to be satisfied throughout the period beginning two years before the share
issue and three years after the ‘relevant date’. Where the relevant date is defined as the later of the date the shares were
issued and the date on which the company commenced trading.
Andrew does not intend to become an employee (or director) of Scalar Limited, but he needs to exercise caution as to
how many shares he subscribes for. If only three investors subscribe for 100% of the shares, each will hold 33% of the
share capital. This exceeds the 30% limit and will mean that EIS relief (other than deferral relief) will not be available.
Therefore, Andrew and the other two investors should ensure not only that the potential fourth investor is recruited, but
that s/he subscribes for sufficient shares, such that none of them will hold 30% or more of the issued share capital, as
only then will they all attain qualifying individual status.
‘Eligible shares’
Qualifying shares need to be new ordinary shares which are subscribed for in cash and fully paid up at the time of issue.
The shares must not be redeemable for at least three years from the relevant date, and not carry any preferential rights
to dividends. On the basis of the information provided, the shares of Scalar Limited would qualify as eligible shares.
‘Qualifying Company’
The company must be unquoted, not controlled by another company, and engaged in qualifying business activities. The
latter requires that the company engage in a trading activity, which is carried on wholly or mainly in the UK, throughout
the three years following the relevant date. While certain trading activities, such as dealing in shares or trading in land,
are excluded, the manufacturing trade Scalar Limited proposes to carry on will qualify.
However, it is also necessary for at least 80% of the money raised to be used for the qualifying business activity within
12 months of the relevant date and the remaining 20% to be so used within the following 12 months. Andrew and the
other investors will thus have to ensure that Scalar Limited has not raised more funds than it is able to employ in the
business within the appropriate time periods.
Reliefs available:
Andrew can claim income tax relief at 20% income tax relief on the amount invested up to a maximum of £200,000
in any one tax year. The relief is given in the form. of a tax reducing allowance, which can reduce the investor’s income
tax liability to nil, but cannot be used to generate a tax refund. If the investment is made prior to 6 October in the tax
year, then 50% of the amount invested (up to a maximum of £25,000) can be treated as having been made in the
previous tax year.
Any capital gains arising on the sale of EIS shares will be fully exempt from capital gains tax provided that income tax
relief was given on the investment when made and has not been withdrawn. If the EIS shares are disposed of at a loss,
capital losses are still allowable, but reduced by the amount of any EIS relief attributable to the shares disposed of.
In addition, gains from the disposal of other assets can be deferred against the base cost of EIS shares acquired within
one year before and three years after their disposal. Such gains will, thus, not normally become chargeable until the EIS
shares themselves are disposed of. Further, for deferral relief to be available, it is not necessary for the investment to
qualify for EIS income tax relief, i.e. deferral is available even where the investor is not a qualifying individual. Thus,
Andrew could still defer the gain arising on the disposal of the residential property lease made in order to raise part of
the funds for his EIS investment, even if no fourth investor were to be found and his shareholding were to exceed 30%
of the issued share capital of Scalar Limited. Does not require the existence of income tax relief in order to be claimed.
Withdrawal of relief:
Any EIS relief claimed by Andrew will be withdrawn (partially or fully) if, within three year of the relevant date:
(1) he disposes of the shares;
(2) he receives value from the company;
(3) he ceases to be a qualifying individual; or
(4) Scalar Limited ceases to be a qualifying company.
With regard to receiving value from the company, the definition excludes dividends which do not exceed a normal rate
of return, but does include the repayment of any loans made to the company before the shares were issued, the provision
of benefits and the purchase of assets from the company at an undervalue. In this regard, Andrew and the other
subscribers should ensure that the £50,000 they are to invest in Scalar Limited as loan capital is appropriately timed
and structured relative to the issue of the EIS shares. -
第5题:
(ii) Analyse the effect of delaying the sale of the business of the Stiletto Partnership to Razor Ltd until
30 April 2007 on Clint’s income tax and national insurance position.
You are not required to prepare detailed calculations of his income tax or national insurance liabilities.
(4 marks)
正确答案:(ii) The implications of delaying the sale of the business
The implications of delaying the sale of the business until 30 April would have been as follows:
– Clint would have received an additional two months of profits amounting to £6,920 (£20,760 x 1/3).
– Clint’s trading income in 2006/07 would have been reduced by £13,015 (£43,723 – £30,708), much of which
would have been subject to income tax at 40%. His additional trading income in 2007/08 of £19,935 would all
have been taxed at 10% and 22%.
– Clint is entitled to the personal age allowance of £7,280 in both years. However, it is abated by £1 for every £2
by which his total income exceeds £20,100. Once Clint’s total income exceeds £24,590 (£20,100 + ((£7,280
– £5,035) x 2)), his personal allowance will be reduced to the standard amount of £5,035. Accordingly, the
increased personal allowance would not be available in 2006/07 regardless of the year in which the business was
sold. It is available in 2007/08 (although part of it is wasted) but would not have been if the sale of the business
had been delayed.
– Clint’s class 4 national insurance contributions in 2006/07 would have been reduced due to the fall in the level
of his trading income. However, much of the saving would be at 1% only. Clint is not liable to class 4 national
insurance contributions in 2007/08 as he is 65 at the start of the year.
– Changing the date on which the business was sold would have had no effect on Clint’s class 2 liability as he is
not required to make class 2 contributions once he is 65 years old.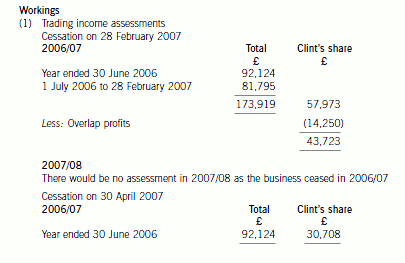
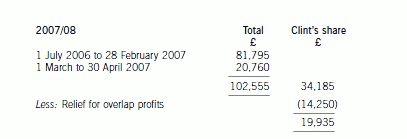
-
第6题:
6 Sergio and Gerard each inherited a half interest in a property, ‘Hilltop’, in October 2005. ‘Hilltop’ had a probate value
of £124,000, but in November 2005 it was badly damaged by fire. In January 2006 the insurance company made
a payment of £81,700 each to Sergio and Gerard. In February 2006 Sergio and Gerard each spent £55,500 of the
insurance proceeds on restoring the property. ‘Hilltop’ was worth £269,000 following the restoration work. In July
2006, Sergio and Gerard sold ‘Hilltop’ for £310,000.
Sergio is 69 years old and a widower with three adult children and seven grandchildren. His annual income consists
of a pension of £9,900 and interest of £300 on savings of £7,600 in a bank deposit account. Sergio owns his home
but no other significant assets. He plans to buy a domestic rental property with the proceeds from the sale of ‘Hilltop’,
such that on his death he will have a significant asset which can be sold and divided between the members of his
family.
Gerard is 34 years old. He is employed by Fizz plc on a salary of £66,500 per year together with a performance
related bonus. Gerard estimates that he will receive a bonus in December 2007 of £4,500, in line with previous
years, and that his taxable benefits in the tax year 2007/08 will amount to £7,140. He also expects to receive
dividends from UK companies of £1,935 and bank interest of £648 in the tax year 2007/08. Gerard intends to set
up a personal pension plan in August 2007. He has not made any pension contributions in the past and proposes to
use part of the proceeds from the sale of ‘Hilltop’ to make the maximum possible tax allowable contribution.
Fizz plc has announced that it intends to replace the performance related bonus scheme with a share incentive plan,
also linked to performance, with effect from 6 April 2008. Gerard estimates that Fizz plc will award him free shares
worth £2,100 each year. He will also purchase partnership shares worth £700 each year and, as a result, will be
awarded matching shares (further free shares) worth £1,400.
Required:
(a) Calculate the chargeable gains arising on the receipt of the insurance proceeds in January 2006 and the sale
of ‘Hilltop’ in July 2006. You should assume that any elections necessary to minimise the gain on the receipt
of the insurance proceeds have been submitted. (4 marks)
正确答案: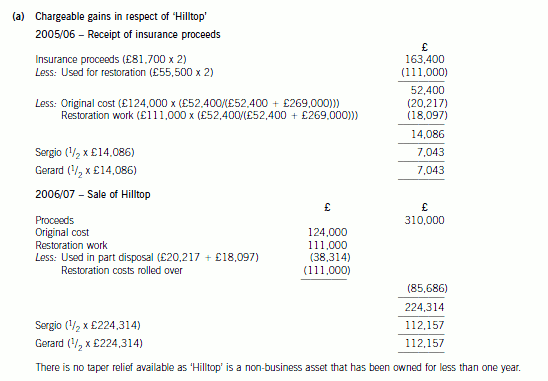
-
第7题:
(c) The inheritance tax payable by Adam in respect of the gift from his aunt. (4 marks)
Additional marks will be awarded for the appropriateness of the format and presentation of the memorandum and
the effectiveness with which the information is communicated. (2 marks)
Note: you should assume that the tax rates and allowances for the tax year 2006/07 will continue to apply for the
foreseeable future.
正确答案:
(c) Inheritance tax payable by Adam
The gift by AS’s aunt was a potentially exempt transfer. No tax will be due if she lives until 1 June 2014 (seven years after
the date of the gift).
The maximum possible liability, on the assumption that there are no annual exemptions or nil band available, is £35,216
(£88,040 x 40%). This will only arise if AS’s aunt dies before 1 June 2010.
The maximum liability will be reduced by taper relief of 20% for every full year after 31 May 2010 for which AS’s aunt lives.
The liability will also be reduced if the chargeable transfers made by the aunt in the seven years prior to 1 June 2007 are
less than £285,000 or if the annual exemption for 2006/07 and/or 2007/08 is/are available. -
第8题:
(b) (i) Explain, by reference to Coral’s residence, ordinary residence and domicile position, how the rental
income arising in respect of the property in the country of Kalania will be taxed in the UK in the tax year
2007/08. State the strategy that Coral should adopt in order to minimise the total income tax suffered
on the rental income. (7 marks)
正确答案:
(b) (i) UK tax on the rental income
Coral is UK resident in 2007/08 because she is present in the UK for more than 182 days. Accordingly, she will be
subject to UK income tax on her Kalanian rental income.
Coral is ordinarily resident in the UK in 2007/08 as she is habitually resident in the UK.
Coral will have acquired a domicile of origin in Kalania from her father. She has not acquired a domicile of choice in the
UK as she has not severed her ties with Kalania and does not intend to make her permanent home in the UK.
Accordingly, the rental income will be taxed in the UK on the remittance basis.
Any rental income remitted to the UK will fall into the basic rate band and will be subject to income tax at 22% on the
gross amount (before deduction of Kalanian tax). Unilateral double tax relief will be available in respect of the 8% tax
suffered in Kalania such that the effective rate of tax suffered by Coral in the UK on the grossed up amount of income
remitted will be 14%.
In order to minimise the total income tax suffered on the rental income Coral should ensure that it is not brought into or
used in the UK such that it will not be subject to income tax in the UK.
Coral should retain evidence, for example bank statements, to show that the rental income has not been removed from
Kalania. Coral can use the money whilst she is on holiday in Kalania with no UK tax implications. -
第9题:
5 Crusoe has contacted you following the death of his father, Noland. Crusoe has inherited the whole of his father’s
estate and is seeking advice on his father’s capital gains tax position and the payment of inheritance tax following his
death.
The following information has been extracted from client files and from telephone conversations with Crusoe.
Noland – personal information:
– Divorcee whose only other relatives are his sister, Avril, and two grandchildren.
– Died suddenly on 1 October 2007 without having made a will.
– Under the laws of intestacy, the whole of his estate passes to Crusoe.
Noland – income tax and capital gains tax:
– Has been a basic rate taxpayer since the tax year 2000/01.
– Sales of quoted shares resulted in:
– Chargeable gains of £7,100 and allowable losses of £17,800 in the tax year 2007/08.
– Chargeable gains of approximately £14,000 each tax year from 2000/01 to 2006/07.
– None of the shares were held for long enough to qualify for taper relief.
Noland – gifts made during lifetime:
– On 1 December 1999 Noland gave his house to Crusoe.
– Crusoe has allowed Noland to continue living in the house and has charged him rent of £120 per month
since 1 December 1999. The market rent for the house would be £740 per month.
– The house was worth £240,000 at the time of the gift and £310,000 on 1 October 2007.
– On 1 November 2004 Noland transferred quoted shares worth £232,000 to a discretionary trust for the benefit
of his grandchildren.
Noland – probate values of assets held at death: £
– Portfolio of quoted shares 370,000
Shares in Kurb Ltd 38,400
Chattels and cash 22,300
Domestic liabilities including income tax payable (1,900)
– It should be assumed that these values will not change for the foreseeable future.
Kurb Ltd:
– Unquoted trading company
– Noland purchased the shares on 1 December 2005.
Crusoe:
– Long-standing personal tax client of your firm.
– Married with two young children.
– Successful investment banker with very high net worth.
– Intends to gift the portfolio of quoted shares inherited from Noland to his aunt, Avril, who has very little personal
wealth.
Required:
(a) Prepare explanatory notes together with relevant supporting calculations in order to quantify the tax relief
potentially available in respect of Noland’s capital losses realised in 2007/08. (4 marks)
正确答案: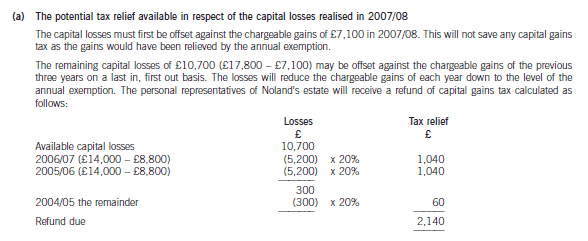
-
第10题:
(b) Calculate the amount of input tax that will be recovered by Vostok Ltd in respect of the new premises in the
year ending 31 March 2009 and explain, using illustrative calculations, how any additional recoverable input
tax will be calculated in future years. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Recoverable input tax in respect of new premises
Vostok Ltd will recover £47,880 (£446,500 x 7/47 x 72%) in the year ending 31 March 2009.
The capital goods scheme will apply to the purchase of the building because it is to cost more than £250,000. Under the
scheme, the total amount of input tax recovered reflects the use of the building over the period of ownership, up to a maximum
of ten years, rather than merely the year of purchase.
Further input tax will be recovered in future years as the percentage of exempt supplies falls. (If the percentage of exempt
supplies were to rise, Vostok Ltd would have to repay input tax to HMRC.)
The additional recoverable input tax will be computed by reference to the percentage of taxable supplies in each year including
the year of sale. For example, if the percentage of taxable supplies in a particular subsequent year were to be 80%, the
additional recoverable input tax would be computed as follows.
£446,500 x 7/47 x 1/10 x (80% – 72%) = £532.
Further input tax will be recovered in the year of sale as if Vostok Ltd’s supplies in the remaining years of the ten-year period
are fully vatable. For example, if the building is sold in year seven, the additional recoverable amount for the remaining three
years will be calculated as follows.
£446,500 x 7/47 x 1/10 x (100% – 72%) x 3 = £5,586. -
第11题:
The above chart shows individual income tax in China. The tax free threshold is 3,500 RMB per month. The tax rates are divided into 7 brackets. The lowest rate is 3% for income between 3,501 and 5,000, while the highest rate is 45% for income over 80,000. Therefore, the higher our income is, the more tax we should pay. Tax, which can be used in public services such as education, road construction, public health and so on, is very important to our country. As we all know, tax makes up a great part of our country’s revenue, and the development of our country depends on it. From what has been discussed above, we can see that it is everyone’s legal duty to pay tax because taxes contribute to the country and create benefits for everyone. Those who try to evade taxation are sure to be punished. In short, paying tax is our responsibility to society.Decide if each of the following statements is TRUE (T) or FALSE (F).
1. The purpose of the passage is to help people know the tips how to pay less tax.()
2. According to the chart, if a person’s monthly is 3600 yuan, he doesn’t need to pay tax.()
3. How much income tax a person pays each month depends on how much his/her income is.()
4. The underlined word “evade” in the last paragraph means increase.()
5. Personal income taxes are included in a government’s revenue.()
参考答案:FFTFT
-
第12题:
Income tax【个人所得税】
For many young Americans, graduating from college means finding a job, moving out of the dorm room and beginning to register one's annual earnings with the US government.
That last item is the law, though sometimes it's a hassle(难事)to obey.
Independent tax advisor Bob Gilbert calls the US income tax system "amazingly complicated". But he adds that "very little of the complicated tax law applies to young people who are just beginning their careers". According to Gilbert, 80 to 90 percent of Americans are not really burdened by the system's complications.
Still, all the numbers and forms can be a little confusing to those who are just starting their careers. Some pull out their calculators and try to do the math alone. Some use income tax software. Others just hand the whole responsibility over to tax firms like Gilbert's. According to income tax law expert Linda Beale, young people will often follow their parents' lead when filling their income forms.
"Young people who grow up in wealthy households typically use professional tax services because their parents have always done so," said Beale, a professor at Wayne State University in Michigan State.
"On the other hand, most poorer young people probably try to do their own taxes, unless they want a quick 'refund' with the help of a tax advisor".
In fact, obeying the law has its benefits. For one, many young people can expect a tax refund. This means that, over the course of the year, they have paid too much in monthly federal or state taxes and are entitled to the difference.
Bob Thalman, a 20-year-old university student, expects he will get a refund of about 100, which will probably go in the bank, or perhaps be used to pay for car insurance or credit card bills.
Thalman called the whole process a "hassle", but added that he didn't wat to test the law by not filling his income tax papers.
"I'm worried about what would happen if I failed to file," he said. "I know one individual who did not report his income tax for many years, and he's now in federal prison. I certainly don’t want that."
文章(16~22)
A college student with a part-time job is not required to file an income tax form.A.Right
B.Wrong
C.Not mentioned答案:C解析: -
第13题:
(ii) Assuming the relief in (i) is available, advise Sharon on the maximum amount of cash she could receive
on incorporation, without triggering a capital gains tax (CGT) liability. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) As Sharon is entitled to the full rate of business asset taper relief, any gain will be reduced by 75%. The position is
maximised where the chargeable gain equals Sharon’s unused capital gains tax annual exemption of £8,500. Thus,
before taper relief, the gain she requires is £34,000 (1/0·25 x £8,500).
The amount to be held over is therefore £46,000 (80,000 – 34,000). Where part of the consideration is in the form
of cash, the gain eligible for incorporation relief is calculated using the formula:
Gain deferred = Gain x value of shares issued/total consideration
The formula is manipulated on the following basis:
£46,000 = £80,000 x (shares/120,000)
Shares/120,000 = £46,000/80,000
Shares = £46,000 x 120,000/80,000
i.e. £69,000.
As the total consideration is £120,000, this means that Sharon can take £51,000 (£120,000 – £69,000) in cash
without any CGT consequences. -
第14题:
(c) Explain the capital gains tax (CGT) and income tax (IT) issues Paul and Sharon should consider in deciding
which form. of trust to set up for Gisella and Gavin. You are not required to consider inheritance tax (IHT) or
stamp duty land tax (SDLT) issues. (10 marks)
You should assume that the tax rates and allowances for the tax year 2005/06 apply throughout this question.
正确答案:
(c) As the trust is created in the settlors’ (Paul and Sharon’s) lifetime its creation will constitute a chargeable disposal for capital
gains tax. Also, as the settlors and trustees are connected persons, the disposal will be deemed to be at market value, resulting
in a chargeable gain of £80,000 (160,000 – 80,000). No taper relief will be available as the property is a non-business
asset, and has been held for less than three years, but annual exemptions of £17,000 (2 x £8,500) will be available.
However, in the case of a discretionary trust, gift hold over relief will be available. This is because the gift will constitute a
chargeable lifetime transfer and because there is an immediate charge to inheritance tax (even though no tax is payable due
to the nil rate band) relief is available if a specific accumulation and maintenance trust is used, as in this case the gift will
qualify as a potentially exempt transfer and so gift relief would only be available in respect of business assets. The use of a
basic discretionary trust will thus facilitate the deferral of an immediate capital gains tax charge of £25,200 (63,000 x 40%).
If/when the property is disposed of, however, the trustees will pay capital gains tax on the deferred gain at the trust income
tax rate of 40%, and have an annual exemption of only £4,250 (50% of the normal individual rate) available to them. The
40% rate of tax and lower annual exemption rate also apply to chargeable gains arising in a specific accumulation and
maintenance trust, as well as a basic discretionary trust.
A chargeable disposal between connected persons will also arise for the purposes of capital gains tax if/when the property
vests in a beneficiary, i.e. one or more of the beneficiaries becomes absolutely entitled to all or part of the income or capital
of the trust. Gift hold over relief will again be available on all assets in the case of a discretionary trust, but only on business
assets in the case of an accumulation and maintenance trust, except where a beneficiary becomes entitled to both income
and capital at the same time.
The trust will have taxable property income in the form. of net rents from its creation and in future years is also likely to have
other investment income, probably in the form. of interest, to the extent that monies are retained in the trust. Whichever form
of trust is used, the trustees will pay tax at the standard trust rate of 40% on income other than dividend income (32·5%),
except to the extent of (1) the first £500 of taxable income, which is taxed at the rate that would otherwise apply to such
income (i.e. 22% for non-savings (rental) income, 20% for savings income (interest) and 10% for dividends) but, only to the
extent that it is not distributed; and (2) the legitimate trust management expenses, which are offsettable for the purposes of
the higher trust tax rates against the income with the lowest rate(s) of normal tax and so bear tax only at that rate. The higher
trust tax rate always applies to income that is distributed, other than to the extent that it has been treated as the settlor’s
income, and taxed at that settlor’s marginal tax rate.
As Paul and Sharon intend to create a trust for their unmarried minor (under 18) children, then even if the trust specifically
excludes them from any benefit under the trust, the trust income will be treated as theirs for income tax purposes to the extent
that it constitutes income paid for on behalf (including maintenance payments) of Gisella and Gavin; except where (1) the
total income arising does not exceed £100 gross per annum, and (2) income is held for the benefit of a child under an
accumulation and maintenance settlement, to the extent that it is not paid out. -
第15题:
(b) For this part, assume today’s date is 1 May 2010.
Bill and Ben decided not to sell their company, and instead expanded the business themselves. Ben, however,
is now pursuing other interests, and is no longer involved with the day to day activities of Flower Limited. Bill
believes that the company would be better off without Ben as a voting shareholder, and wishes to buy Ben’s
shares. However, Bill does not have sufficient funds to buy the shares himself, and so is wondering if the
company could acquire the shares instead.
The proposed price for Ben’s shares would be £500,000. Both Bill and Ben pay income tax at the higher rate.
Required:
Write a letter to Ben:
(1) stating the income tax (IT) and/or capital gains tax (CGT) implications for Ben if Flower Limited were to
repurchase his 50% holding of ordinary shares, immediately in May 2010; and
(2) advising him of any available planning options that might improve this tax position. Clearly explain any
conditions which must be satisfied and quantify the tax savings which may result.
(13 marks)
Assume that the corporation tax rates for the financial year 2005 and the income tax rates and allowances
for the tax year 2005/06 apply throughout this question.
正确答案:(b) [Ben’s address] [Firm’s address]
Dear Ben [Date]
A company purchase of own shares can be subject to capital gains treatment if certain conditions are satisfied. However, one
of these conditions is that the shares in question must have been held for a minimum period of five years. As at 1 May 2010,
your shares in Flower Limited have only been held for four years and ten months. As a result, the capital gains treatment will
not apply.
In the absence of capital gains treatment, the position on a company repurchase of its own shares is that the payment will
be treated as an income distribution (i.e. a dividend) in the hands of the recipient. The distribution element is calculated as
the proceeds received for the shares less the price paid for them. On the basis that the purchase price is £500,000, then the
element of distribution will be £499,500 (500,000 – 500). This would be taxed as follows:
-
第16题:
(b) (i) Calculate Amanda’s income tax payable for the tax year 2006/07; (11 marks)
正确答案:

-
第17题:
(iii) The extent to which Amy will be subject to income tax in the UK on her earnings in respect of duties
performed for Cutlass Inc and the travel costs paid for by that company. (5 marks)
Appropriateness of format and presentation of the report and the effectiveness with which its advice is
communicated. (2 marks)
Note:
You should assume that the income tax rates and allowances for the tax year 2006/07 and the corporation tax
rates and allowances for the financial year 2006 apply throughout this questio
正确答案:
(iii) Amy’s UK income tax position
Amy will remain UK resident and ordinarily resident as she is not leaving the UK permanently or for a complete tax year
under a full time contract of employment. Accordingly, she will continue to be subject to UK tax on her worldwide income
including her earnings in respect of the duties she performs for Cutlass Inc. The earnings from these duties will also be
taxable in Sharpenia as the income arises in that country.
The double tax treaty between the UK and Sharpenia will either exempt the employment income in one of the two
countries or give double tax relief for the tax paid in Sharpenia. The double tax relief will be the lower of the UK tax and
the Sharpenian tax on the income from Cutlass Inc.
Amy will not be subject to UK income tax on the expenses borne by Cutlass Inc in respect of her flights to and from
Sharpenia provided her journeys are wholly and exclusively for the purposes of performing her duties in Sharpenia.
The amounts paid by Cutlass Inc in respect of Amy’s family travelling to Sharpenia will be subject to UK income tax as
Amy will not be absent from the UK for a continuous period of at least 60 days. -
第18题:
(d) Evaluate the effect on Gerard of the changes to be made by Fizz plc to its performance related bonus scheme.
You should ignore the effect of any pension contributions to be made by Gerard in the future, consider both
the value and timing of amounts received by Gerard and include relevant supporting calculations.
(5 marks)
Note: – You should assume that the income tax rates and allowances for the tax year 2006/07 apply throughout
this question.
正确答案:
(d) Implications for Gerard of the changes to Fizz plc’s bonus scheme
Value received
Under the existing scheme Gerard receives approximately £4,500 each year. This is subject to income tax at 40% and
national insurance contributions at 1% such that Gerard receives £2,655 (£4,500 x 59%) after all taxes.
Under the proposed share incentive plan (SIP), Gerard expects to receive free shares worth £3,500 (£2,100 + £1,400).
Provided the shares remain in the plan for at least five years there will be no income tax or national insurance contributions
in respect of the value received. Gerard’s base cost in the shares for the purposes of capital gains tax will be their value at
the time they are withdrawn from the scheme.
In addition, the amount he spends on partnership shares will be allowable for both income tax and national insurance such
that he will obtain shares with a value of £700 for a cost of only £413 (£700 x 59%).
Accordingly, Gerard will receive greater value under the SIP than he does under the existing bonus scheme. However, as noted
below, he will not be able to sell the free or matching shares until they have been in the scheme for at least three years by
which time they may have fallen in value.
Timing of receipt of benefit
Under the existing scheme Gerard receives a cash bonus each year.
The value of free and matching shares awarded under a SIP cannot be realised until the shares are withdrawn from the
scheme and sold. This withdrawal cannot take place until at least three years after the shares are awarded to Gerard.
Accordingly, Gerard will not have access to the value of the bonuses he receives under the SIP until the scheme has been in
operation for at least three years. In addition, if the shares are withdrawn within five years of being awarded, income tax and
national insurance contributions will become payable on the lower of their value at the time of the award and their value at
the time of withdrawal thus reducing the value of Gerard’s bonus. -
第19题:
4 Coral is the owner and managing director of Reef Ltd. She is considering the manner in which she will make her first
pension contributions. In November 2007 she inherited her mother’s house in the country of Kalania.
The following information has been extracted from client files and from telephone conversations with Coral.
Coral:
– 1972 – Born in the country of Kalania. Her father, who died in 2002, was domiciled in Kalania.
– 1999 – Moved to the UK and has lived and worked here since then.
– 2001 – Subscribed for 100% of the ordinary share capital of Reef Ltd.
– Intends to sell Reef Ltd and return to live in the country of Kalania in 2012.
– No income apart from that received from Reef Ltd.
Reef Ltd:
– A UK resident company with annual profits chargeable to corporation tax of approximately £70,000.
– Four employees including Coral.
– Provides scuba diving lessons to members of the public.
Payments from Reef Ltd to Coral in 2007/08:
– Director’s fees of £460 per month.
– Dividends paid of £14,250 in June 2007 and £14,250 in September 2007.
Pension contributions:
– Coral has not so far made any pension contributions in the tax year 2007/08 but wishes to make gross pension
contributions of £9,000.
– The contributions are to be made by Reef Ltd or Coral or a combination of the two in such a way as to minimise
the total after tax cost.
– Any contributions made by Coral will be funded by an additional dividend from Reef Ltd.
House in the country of Kalania:
– Beachfront property with potential rental income of £550 per month after deduction of allowable expenditure.
– Coral will use it for holidays for two months each year.
The tax system in the country of Kalania:
– No capital gains tax or inheritance tax.
– Income tax at 8% on income arising in the country of Kalania.
– No double tax treaty with the UK.
Required:
(a) With the objective of minimising the total after tax cost, advise Coral as to whether the gross pension
contributions of £9,000 should be made:
– wholly by Reef Ltd; or
– by Coral to the extent that they are tax allowable with the balance made by Reef Ltd.
Your answer should include supporting calculations where necessary. (9 marks)
正确答案:
-
第20题:
(ii) Explain how the inclusion of rental income in Coral’s UK income tax computation could affect the
income tax due on her dividend income. (2 marks)
You are not required to prepare calculations for part (b) of this question.
Note: you should assume that the tax rates and allowances for the tax year 2006/07 and for the financial year to
31 March 2007 will continue to apply for the foreseeable future.
正确答案:
(ii) The effect of taxable rental income on the tax due on Coral’s dividend income
Remitting rental income to the UK may cause some of Coral’s dividend income currently falling within the basic rate
band to fall within the higher rate band. The effect of this would be to increase the tax on the gross dividend income
from 0% (10% less the 10% tax credit) to 221/2% (321/2% less 10%).
Tutorial note
It would be equally acceptable to state that the effective rate of tax on the dividend income would increase from 0%
to 25%. -
第21题:
(c) (i) Explain how Messier Ltd can assist Galileo with the cost of relocating to the UK and/or provide him with
interest-free loan finance for this purpose without increasing his UK income tax liability; (3 marks)
正确答案:
(c) (i) Relocation costs
Direct assistance
Messier Ltd can bear the cost of certain qualifying relocation costs of Galileo up to a maximum of £8,000 without
increasing his UK income tax liability. Qualifying costs include the legal, professional and other fees in relation to the
purchase of a house, the costs of travelling to the UK and the cost of transporting his belongings. The costs must be
incurred before the end of the tax year following the year of the relocation, i.e. by 5 April 2010.
Assistance in the form. of a loan
Messier Ltd can provide Galileo with an interest-free loan of up to £5,000 without giving rise to any UK income tax. -
第22题:
(ii) Write a letter to Donald advising him on the most tax efficient manner in which he can relieve the loss
incurred in the year to 31 March 2007. Your letter should briefly outline the types of loss relief available
and explain their relative merits in Donald’s situation. Assume that Donald will have no source of income
other than the business in the year of assessment 2006/07 and that any income he earned on a parttime
basis while at university was always less than his annual personal allowance. (9 marks)
Assume that the corporation tax rates and allowances for the financial year 2004 and the income tax rates
and allowances for 2004/05 apply throughout this question.
Relevant retail price index figures are:
January 1998 159·5
April 1998 162·6
正确答案:(ii) [Donald’s address] [Firm’s address]
Dear Donald [Date]
I understand that you have incurred a tax loss in your first year of trading. The following options are available in respect
of this loss.
1. The first option is to use the trading loss against other forms of income in the same year. If such a claim is made,
losses are offset against income before personal allowances.
Any excess loss can still be offset against capital gains of the year. However, any offset against capital gains is
before both taper relief and annual exemptions.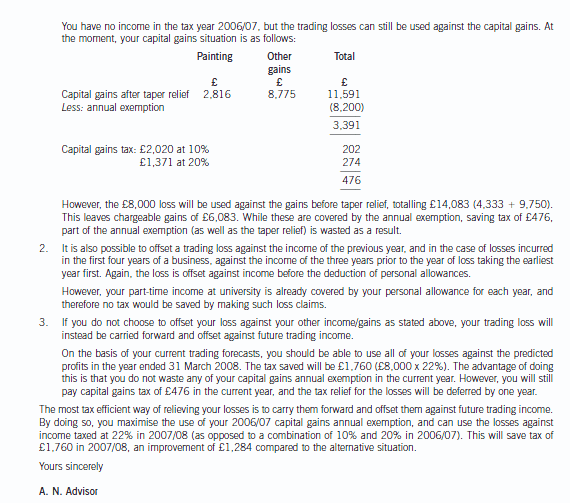
-
第23题:
James died on 22 January 2015. He had made the following gifts during his lifetime:
(1) On 9 October 2007, a cash gift of £35,000 to a trust. No lifetime inheritance tax was payable in respect of this gift.
(2) On 14 May 2013, a cash gift of £420,000 to his daughter.
(3) On 2 August 2013, a gift of a property valued at £260,000 to a trust. No lifetime inheritance tax was payable in respect of this gift because it was covered by the nil rate band. By the time of James’ death on 22 January 2015, the property had increased in value to £310,000.
On 22 January 2015, James’ estate was valued at £870,000. Under the terms of his will, James left his entire estate to his children.
The nil rate band of James’ wife was fully utilised when she died ten years ago.
The nil rate band for the tax year 2007–08 is £300,000, and for the tax year 2013–14 it is £325,000.
Required:
(a) Calculate the inheritance tax which will be payable as a result of James’ death, and state who will be responsible for paying the tax. (6 marks)
(b) Explain why it might have been beneficial for inheritance tax purposes if James had left a portion of his estate to his grandchildren rather than to his children. (2 marks)
(c) Explain why it might be advantageous for inheritance tax purposes for a person to make lifetime gifts even when such gifts are made within seven years of death.
Notes:
1. Your answer should include a calculation of James’ inheritance tax saving from making the gift of property to the trust on 2 August 2013 rather than retaining the property until his death.
2. You are not expected to consider lifetime exemptions in this part of the question. (2 marks)
正确答案:(a) James – Inheritance tax arising on death
Lifetime transfers within seven years of death
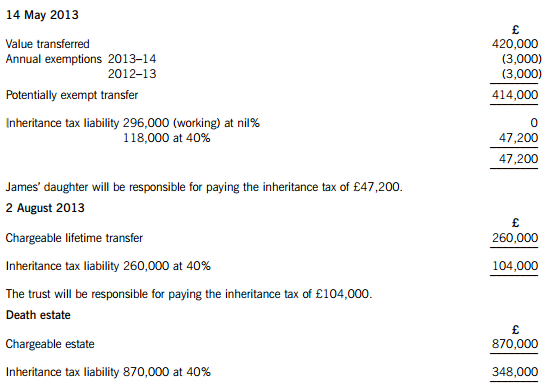
The personal representatives of James’ estate will be responsible for paying the inheritance tax of £348,000.
Working – Available nil rate band
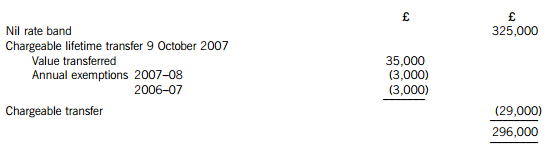
(b) Skipping a generation avoids a further charge to inheritance tax when the children die. Gifts will then only be taxed once before being inherited by the grandchildren, rather than twice.
(c) (1) Even if the donor does not survive for seven years, taper relief will reduce the amount of IHT payable after three years.
(2) The value of potentially exempt transfers and chargeable lifetime transfers are fixed at the time they are made.
(3) James therefore saved inheritance tax of £20,000 ((310,000 – 260,000) at 40%) by making the lifetime gift of property.
