(b) Explain by reference to Hira Ltd’s loss position why it may be beneficial for it not to claim any capitalallowances for the year ending 31 March 2007. Support your explanation with relevant calculations.(6 marks)
题目
(b) Explain by reference to Hira Ltd’s loss position why it may be beneficial for it not to claim any capital
allowances for the year ending 31 March 2007. Support your explanation with relevant calculations.
(6 marks)
相似考题
更多“(b) Explain by reference to Hira Ltd’s loss position why it may be beneficial for it not to claim any capitalallowances for the year ending 31 March 2007. Support your explanation with relevant calculations.(6 marks)”相关问题
-
第1题:
(b) Donald actually decided to operate as a sole trader. The first year’s results of his business were not as he had
hoped, and he made a trading loss of £8,000 in the year to 31 March 2007. However, trading is now improving,
and Donald has sufficient orders to ensure that the business will make profits of at least £30,000 in the year to
31 March 2008.
In order to raise funds to support his business over the last 15 months, Donald has sold a painting which was
given to him on the death of his grandmother in January 1998. The probate value of the painting was £3,200,
and Donald sold it for £8,084 (after deduction of 6% commission costs) in November 2006.
He also sold other assets in the year of assessment 2006/07, realising further chargeable gains of £8,775 (after
indexation of £249 and taper relief of £975).
Required:
(i) Calculate the chargeable gain on the disposal of the painting in November 2006. (4 marks)
正确答案: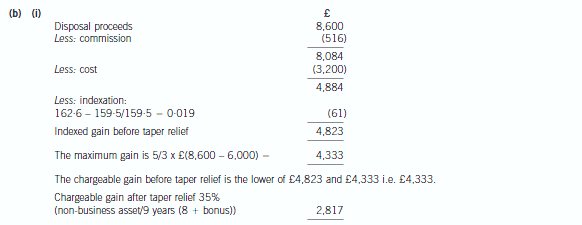
-
第2题:
(c) State any reliefs Bob could claim regarding the fall in value of his shares in Willis Ltd, and describe how the
operation of any such reliefs could reduce Bob’s taxable income. (4 marks)
Relevant retail price index figures are:
September 1990 129·3
April 1998 162·6
December 2004 189·9
正确答案:
(c) Claims for capital losses
Where the value of shares (a chargeable asset) has become negligible (defined as <5% of the original cost), a claim can be
made to treat the asset as though it was sold and then immediately reacquired for its current market value. This is known as
a negligible value claim.
The sale and reacquisition is treated as taking place at the time that the claim is made or at a specified time (up to 2 years
before the start of the tax year in which the claim was made) if the asset was of negligible value at that time.
As the loss is on unquoted shares, a further relief (s.574 ICTA 1988) allows the loss to be relieved against the total income
of the taxpayer for the year in which the loss arose, and/or against the total income of the previous year.
Losses are first relieved against current year income, with any excess being available for offset against the prior year’s income.
Bob can therefore make a negligible value claim as at 1 December 2004. This will give rise to a loss of £14,500
(£500 – £15,000) which will be deemed to arise in the year 2004/05. By doing so, his taxable income for that year will be
reduced from £36,875 to £22,375. -
第3题:
(c) Advise Alan on the proposed disposal of the shares in Mobile Ltd. Your answer should include calculations
of the potential capital gain, and explain any options available to Alan to reduce this tax liability. (7 marks)
正确答案:
However, an exemption from corporation tax exists for any gain arising when a trading company (or member of a trading
group) sells the whole or any part of a substantial shareholding in another trading company.
A substantial shareholding is one where the investing company holds 10% of the ordinary share capital and is beneficially
entitled to at least 10% of the
(i) profits available for distribution to equity holders and
(ii) assets of the company available for distribution to equity holders on a winding up.
In meeting the 10% test, shares owned by a chargeable gains group may be amalgamated. The 10% test must have been
met for a continuous 12 month period during the 2 years preceding the disposal.
The companies making the disposals must have been trading companies (or members of a trading group) throughout the
12 month period, as well as at the date of disposal. In addition, they must also be trading companies (or members of a trading
group) immediately after the disposal.
The exemption is given automatically, and acts to deny losses as well as eliminate gains.
While Alantech Ltd has owned its holding in Mobile Ltd for 33 months, its ownership of the Boron holding has only lasted
for 10 months (at 1 June 2005) since Boron was acquired on 1 July 2004. Selling the shares in June 2005 will fail the
12 month test, and the gain will become chargeable.
It would be better for the companies to wait for a further month until July 2005 before selling the amalgamated shareholding.
By doing so, they will both be able to take advantage of the substantial shareholdings relief, thereby saving tax of £29,625
assuming a corporation tax rate of 19%. -
第4题:
(c) Calculate the expected corporation tax liability of Dovedale Ltd for the year ending 31 March 2007 on the
assumption that all available reliefs are claimed by Dovedale Ltd but that Hira Ltd will not claim any capital
allowances in that year. (4 marks)
正确答案:

-
第5题:
(b) Explain the advantages from a tax point of view of operating the new business as a partnership rather than
as a company whilst it is making losses. You should calculate the tax adjusted trading loss for the year
ending 31 March 2008 for both situations and indicate the years in which the loss relief will be obtained.
You are not required to prepare any other supporting calculations. (10 marks)
正确答案:(b) The new business
There are two tax advantages to operating the business as a partnership.
(i) Reduction in taxable income
If the new business is operated as a company, Cindy and Arthur would both be taxed at 40% on their salaries. In
addition, employer and employee national insurance contributions would be due on £105 (£5,000 – £4,895) in respect
of each of them.
If the new business is operated as a partnership, the partners would have no taxable trading income because the
partnership has made a loss; any salaries paid to the partners would be appropriations of the profit or loss of the
business and not employment income. They would, however, each have to pay Class 2 national insurance contributions
of £2·10 each per week.
(ii) Earlier relief for trading losses
If the new business is operated as a company, its tax adjusted trading loss in the year ending 31 March 2008 would
be as follows:
-
第6题:
3 Palm plc recently acquired 100% of the ordinary share capital of Nikau Ltd from Facet Ltd. Palm plc intends to use
Nikau Ltd to develop a new product range, under the name ‘Project Sabal’. Nikau Ltd owns shares in a non-UK
resident company, Date Inc.
The following information has been extracted from client files and from a meeting with the Finance Director of Palm
plc.
Palm plc:
– Has more than 40 wholly owned subsidiaries such that all group companies pay corporation tax at 30%.
– All group companies prepare accounts to 31 March.
– Acquired Nikau Ltd on 1 November 2007 from Facet Ltd, an unrelated company.
Nikau Ltd:
– UK resident company that manufactures domestic electronic appliances for sale in the European Union (EU).
– Large enterprise for the purposes of the enhanced relief available for research and development expenditure.
– Trading losses brought forward as at 1 April 2007 of £195,700.
– Budgeted taxable trading profit of £360,000 for the year ending 31 March 2008 before taking account of ‘Project
Sabal’.
– Dividend income of £38,200 will be received in the year ending 31 March 2008 in respect of the shares in Date
Inc.
‘Project Sabal’:
– Development of a range of electronic appliances, for sale in North America.
– Project Sabal will represent a significant advance in the technology of domestic appliances.
– Nikau Ltd will spend £70,000 on staffing costs and consumables researching and developing the necessary
technology between now and 31 March 2008. Further costs will be incurred in the following year.
– Sales to North America will commence in 2009 and are expected to generate significant profits from that year.
Shares in Date Inc:
– Nikau Ltd owns 35% of the ordinary share capital of Date Inc.
– The shares were purchased from Facet Ltd on 1 June 2003 for their market value of £338,000.
– The sale was a no gain, no loss transfer for the purposes of corporation tax.
– Facet Ltd purchased the shares in Date Inc on 1 March 1994 for £137,000.
Date Inc:
– A controlled foreign company resident in the country of Palladia.
– Annual chargeable profits arising out of property investment activities are approximately £120,000, of which
approximately £115,000 is distributed to its shareholders each year.
The tax system in Palladia:
– No taxes on income or capital profits.
– 4% withholding tax on dividends paid to shareholders resident outside Palladia.
Required:
(a) Prepare detailed explanatory notes, including relevant supporting calculations, on the effect of the following
issues on the amount of corporation tax payable by Nikau Ltd for the year ending 31 March 2008.
(i) The costs of developing ‘Project Sabal’ and the significant commercial changes to the company’s
activities arising out of its implementation. (8 marks)
正确答案:
(a) Nikau Ltd – Effect on corporation tax payable for the year ending 31 March 2008
(i) Project Sabal
Research and development expenditure
The expenditure incurred in respect of research and development will give rise to an enhanced deduction for the
purposes of computing the taxable trading profits of Nikau Ltd. The enhanced deduction is 125% of the qualifying
expenditure as Nikau Ltd is a large enterprise for this purpose.
The expenditure will reduce the profits chargeable to corporation tax of Nikau Ltd by £87,500 (£70,000 x 1·25) and
its corporation tax liability by £26,250 (£87,500 x 30%).
The budgeted expenditure will qualify for the enhanced deduction because it appears to satisfy the following conditions.
– It is likely to qualify as research and development expenditure within generally accepted accounting principles as
it will result in new technical knowledge and the production of a substantially improved device for use in the
industry.
– It exceeds £10,000 in Nikau Ltd’s accounting period.
– It relates to staff costs, consumable items or other qualifying expenditure as opposed to capital items.
– It will result in further trading activities for Nikau Ltd.
Use of brought forward trading losses
The development of products for the North American market is likely to represent a major change in the nature and
conduct of the trade of Nikau Ltd. This is because the company is developing new products and intends to sell them in
a new market. It is a major change as sales to North America are expected to generate significant additional profits.
Because this change will occur within three years of the change in the ownership of Nikau Ltd on 1 November 2007,
any trading losses arising prior to that date cannot be carried forward beyond that date.
Accordingly, the trading losses brought forward may only be offset against £158,958 ((£360,000 – £87,500) x 7/12)
of the company’s trading profits for the year. The remainder of the trading losses £36,742 (£195,700 – £158,958) will
be lost resulting in lost tax relief of £11,023 (£36,742 x 30%).
Tutorial note
The profits for the year ending 31 March 2008 will be apportioned to the periods pre and post 1 November 2007 on
either a time basis or some other basis that is just and reasonable. -
第7题:
(b) (i) Explain, by reference to Coral’s residence, ordinary residence and domicile position, how the rental
income arising in respect of the property in the country of Kalania will be taxed in the UK in the tax year
2007/08. State the strategy that Coral should adopt in order to minimise the total income tax suffered
on the rental income. (7 marks)
正确答案:
(b) (i) UK tax on the rental income
Coral is UK resident in 2007/08 because she is present in the UK for more than 182 days. Accordingly, she will be
subject to UK income tax on her Kalanian rental income.
Coral is ordinarily resident in the UK in 2007/08 as she is habitually resident in the UK.
Coral will have acquired a domicile of origin in Kalania from her father. She has not acquired a domicile of choice in the
UK as she has not severed her ties with Kalania and does not intend to make her permanent home in the UK.
Accordingly, the rental income will be taxed in the UK on the remittance basis.
Any rental income remitted to the UK will fall into the basic rate band and will be subject to income tax at 22% on the
gross amount (before deduction of Kalanian tax). Unilateral double tax relief will be available in respect of the 8% tax
suffered in Kalania such that the effective rate of tax suffered by Coral in the UK on the grossed up amount of income
remitted will be 14%.
In order to minimise the total income tax suffered on the rental income Coral should ensure that it is not brought into or
used in the UK such that it will not be subject to income tax in the UK.
Coral should retain evidence, for example bank statements, to show that the rental income has not been removed from
Kalania. Coral can use the money whilst she is on holiday in Kalania with no UK tax implications. -
第8题:
(b) Provide the directors of Acrux Ltd with a detailed explanation of the maximum rate of tax that will be suffered
on both the distributed and non-distributed profits of the non-UK resident investee companies where:
(1) there is a double tax treaty between the UK and the country in which the individual companies are
resident; and
(2) there is no such double tax treaty.
Note: you are not required to explain the position of the overseas resident branches. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Rate of tax on profits of non-UK resident investee companies
Undistributed profits
The companies will be subject to tax in the countries in which they are resident; this is because of their residency status or
because they have a permanent establishment in that country. Undistributed profits will not be taxed in the UK.
The rate of tax on undistributed profits will therefore be the rate of tax in the country of residency of the respective companies.
Distributed profits with double tax treaty
The dividends received by Acrux Ltd from each of the overseas companies will be grossed up in respect of underlying tax (the
overseas corporation tax paid on the distributed profits) because Acrux Ltd will own at least 10% of the overseas companies.
The gross amount will then be included in Acrux Ltd’s profits chargeable to corporation tax.
The treaty will provide double tax relief in the UK for the overseas tax suffered in respect of each dividend up to a maximum
of the UK tax on the grossed up overseas dividend. As a result of the double tax relief, the overall rate of tax suffered will be
the higher of the UK rate paid by Acrux Ltd and the overseas tax rate borne by the overseas company.
Where the rate of overseas tax in respect of a particular dividend exceeds the rate of corporation tax in the UK, excess foreign
tax will arise. This can be relieved, via onshore pooling, against the UK tax due on those dividends where the rate of tax in
the UK exceeds the rate overseas. This will reduce the overall rate of tax suffered on the total overseas profits of the overseas
companies as a whole.
Distributed profits with no double tax treaty
Where there is no double tax treaty, unilateral double tax relief will be available in the UK. This relief will operate in the same
way as double tax relief under a double tax treaty such that the overall rate of tax on each dividend will be the higher of the
UK rate paid by Acrux Ltd and the overseas rate borne by the overseas company. Relief via onshore pooling will also be
available. -
第9题:
(b) Calculate the amount of input tax that will be recovered by Vostok Ltd in respect of the new premises in the
year ending 31 March 2009 and explain, using illustrative calculations, how any additional recoverable input
tax will be calculated in future years. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Recoverable input tax in respect of new premises
Vostok Ltd will recover £47,880 (£446,500 x 7/47 x 72%) in the year ending 31 March 2009.
The capital goods scheme will apply to the purchase of the building because it is to cost more than £250,000. Under the
scheme, the total amount of input tax recovered reflects the use of the building over the period of ownership, up to a maximum
of ten years, rather than merely the year of purchase.
Further input tax will be recovered in future years as the percentage of exempt supplies falls. (If the percentage of exempt
supplies were to rise, Vostok Ltd would have to repay input tax to HMRC.)
The additional recoverable input tax will be computed by reference to the percentage of taxable supplies in each year including
the year of sale. For example, if the percentage of taxable supplies in a particular subsequent year were to be 80%, the
additional recoverable input tax would be computed as follows.
£446,500 x 7/47 x 1/10 x (80% – 72%) = £532.
Further input tax will be recovered in the year of sale as if Vostok Ltd’s supplies in the remaining years of the ten-year period
are fully vatable. For example, if the building is sold in year seven, the additional recoverable amount for the remaining three
years will be calculated as follows.
£446,500 x 7/47 x 1/10 x (100% – 72%) x 3 = £5,586. -
第10题:
(b) Explain what effect the acquisition of Di Rollo Co will have on the planning of your audit of the consolidated
financial statements of Murray Co for the year ending 31 March 2008. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Effect of acquisition on planning the audit of Murray’s consolidated financial statements for the year ending 31 March
2008
Group structure
The new group structure must be ascertained to identify all entities that should be consolidated into the Murray group’s
financial statements for the year ending 31 March 2008.
Materiality assessment
Preliminary materiality for the group will be much higher, in monetary terms, than in the prior year. For example, if a % of
total assets is a determinant of the preliminary materiality, it may be increased by 10% (as the fair value of assets acquired,
including goodwill, is $2,373,000 compared with $21·5m in Murray’s consolidated financial statements for the year ended
31 March 2007).
The materiality of each subsidiary should be re-assessed, in terms of the enlarged group as at the planning stage. For
example, any subsidiary that was just material for the year ended 31 March 2007 may no longer be material to the group.
This assessment will identify, for example:
– those entities requiring an audit visit; and
– those entities for which substantive analytical procedures may suffice.
As Di Rollo’s assets are material to the group Ross should plan to inspect the South American operations. The visit may
include a meeting with Di Rollo’s previous auditors to discuss any problems that might affect the balances at acquisition and
a review of the prior year audit working papers, with their permission.
Di Rollo was acquired two months into the financial year therefore its post-acquisition results should be expected to be
material to the consolidated income statement.
Goodwill acquired
The assets and liabilities of Di Rollo at 31 March 2008 will be combined on a line-by-line basis into the consolidated financial
statements of Murray and goodwill arising on acquisition recognised.
Audit work on the fair value of the Di Rollo brand name at acquisition, $600,000, may include a review of a brand valuation
specialist’s working papers and an assessment of the reasonableness of assumptions made.
Significant items of plant are likely to have been independently valued prior to the acquisition. It may be appropriate to plan
to place reliance on the work of expert valuers. The fair value adjustment on plant and equipment is very high (441% of
carrying amount at the date of acquisition). This may suggest that Di Rollo’s depreciation policies are over-prudent (e.g. if
accelerated depreciation allowed for tax purposes is accounted for under local GAAP).
As the amount of goodwill is very material (approximately 50% of the cash consideration) it may be overstated if Murray has
failed to recognise any assets acquired in the purchase of Di Rollo in accordance with IFRS 3 Business Combinations. For
example, Murray may have acquired intangible assets such as customer lists or franchises that should be recognised
separately from goodwill and amortised (rather than tested for impairment).
Subsequent impairment
The audit plan should draw attention to the need to consider whether the Di Rollo brand name and goodwill arising have
suffered impairment as a result of the allegations against Di Rollo’s former chief executive.
Liabilities
Proceedings in the legal claim made by Di Rollo’s former chief executive will need to be reviewed. If the case is not resolved
at 31 March 2008, a contingent liability may require disclosure in the consolidated financial statements, depending on the
materiality of amounts involved. Legal opinion on the likelihood of Di Rollo successfully defending the claim may be sought.
Provision should be made for any actual liabilities, such as legal fees.
Group (related party) transactions and balances
A list of all the companies in the group (including any associates) should be included in group audit instructions to ensure
that intra-group transactions and balances (and any unrealised profits and losses on transactions with associates) are
identified for elimination on consolidation. Any transfer pricing policies (e.g. for clothes manufactured by Di Rollo for Murray
and sales of Di Rollo’s accessories to Murray’s retail stores) must be ascertained and any provisions for unrealised profit
eliminated on consolidation.
It should be confirmed at the planning stage that inter-company transactions are identified as such in the accounting systems
of all companies and that inter-company balances are regularly reconciled. (Problems are likely to arise if new inter-company
balances are not identified/reconciled. In particular, exchange differences are to be expected.)
Other auditors
If Ross plans to use the work of other auditors in South America (rather than send its own staff to undertake the audit of Di
Rollo), group instructions will need to be sent containing:
– proforma statements;
– a list of group and associated companies;
– a statement of group accounting policies (see below);
– the timetable for the preparation of the group accounts (see below);
– a request for copies of management letters;
– an audit work summary questionnaire or checklist;
– contact details (of senior members of Ross’s audit team).
Accounting policies
Di Rollo may have material accounting policies which do not comply with the rest of the Murray group. As auditor to Di Rollo,
Ross will be able to recalculate the effect of any non-compliance with a group accounting policy (that Murray’s management
would be adjusting on consolidation).
Timetable
The timetable for the preparation of Murray’s consolidated financial statements should be agreed with management as soon
as possible. Key dates should be planned for:
– agreement of inter-company balances and transactions;
– submission of proforma statements;
– completion of the consolidation package;
– tax review of group accounts;
– completion of audit fieldwork by other auditors;
– subsequent events review;
– final clearance on accounts of subsidiaries;
– Ross’s final clearance of consolidated financial statements.
Tutorial note: The order of dates is illustrative rather than prescriptive. -
第11题:
(b) You are the audit manager of Petrie Co, a private company, that retails kitchen utensils. The draft financial
statements for the year ended 31 March 2007 show revenue $42·2 million (2006 – $41·8 million), profit before
taxation of $1·8 million (2006 – $2·2 million) and total assets of $30·7 million (2006 – $23·4 million).
You are currently reviewing two matters that have been left for your attention on Petrie’s audit working paper file
for the year ended 31 March 2007:
(i) Petrie’s management board decided to revalue properties for the year ended 31 March 2007 that had
previously all been measured at depreciated cost. At the balance sheet date three properties had been
revalued by a total of $1·7 million. Another nine properties have since been revalued by $5·4 million. The
remaining three properties are expected to be revalued later in 2007. (5 marks)
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of these two matters for your auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Petrie Co for the year ended 31 March 2007.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the matters above.
正确答案:
(b) Implications for auditor’s report
(i) Selective revaluation of premises
The revaluations are clearly material to the balance sheet as $1·7 million and $5·4 million represent 5·5% and 17·6%
of total assets, respectively (and 23·1% in total). As the effects of the revaluation on line items in the financial statements
are clearly identified (e.g. revalued amount, depreciation, surplus in statement of changes in equity) the matter is not
pervasive.
The valuations of the nine properties after the year end provide additional evidence of conditions existing at the year end
and are therefore adjusting events per IAS 10 Events After the Balance Sheet Date.
Tutorial note: It is ‘now’ still less than three months after the year end so these valuations can reasonably be expected
to reflect year end values.
However, IAS 16 Property, Plant and Equipment does not permit the selective revaluation of assets thus the whole class
of premises would need to have been revalued for the year to 31 March 2007 to change the measurement basis for this
reporting period.
The revaluation exercise is incomplete. Unless the remaining three properties are revalued before the auditor’s report on
the financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2007 is signed off:
(1) the $7·1 revaluation made so far must be reversed to show all premises at depreciated cost as in previous years;
OR
(2) the auditor’s report would be qualified ‘except for’ disagreement regarding non-compliance with IAS 16.
When it is appropriate to adopt the revaluation model (e.g. next year) the change in accounting policy (from a cost model
to a revaluation model) should be accounted for in accordance with IAS 16 (i.e. as a revaluation).
Tutorial note: IAS 8 Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors does not apply to the initial
application of a policy to revalue assets in accordance with IAS 16.
Assuming the revaluation is written back, before giving an unmodified opinion, the auditor should consider why the three
properties were not revalued. In particular if there are any indicators of impairment (e.g. physical dilapidation) there
should be sufficient evidence on the working paper file to show that the carrying amount of these properties is not
materially greater than their recoverable amount (i.e. the higher of value in use and fair value less costs to sell).
If there is insufficient evidence to confirm that the three properties are not impaired (e.g. if the auditor was prevented
from inspecting the properties) the auditor’s report would be qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of limitation on scope.
If there is evidence of material impairment but management fail to write down the carrying amount to recoverable
amount the auditor’s report would be qualified ‘except for’ disagreement regarding non-compliance with IAS 36
Impairment of Assets.
-
第12题:
(ii) Write a letter to Donald advising him on the most tax efficient manner in which he can relieve the loss
incurred in the year to 31 March 2007. Your letter should briefly outline the types of loss relief available
and explain their relative merits in Donald’s situation. Assume that Donald will have no source of income
other than the business in the year of assessment 2006/07 and that any income he earned on a parttime
basis while at university was always less than his annual personal allowance. (9 marks)
Assume that the corporation tax rates and allowances for the financial year 2004 and the income tax rates
and allowances for 2004/05 apply throughout this question.
Relevant retail price index figures are:
January 1998 159·5
April 1998 162·6
正确答案:(ii) [Donald’s address] [Firm’s address]
Dear Donald [Date]
I understand that you have incurred a tax loss in your first year of trading. The following options are available in respect
of this loss.
1. The first option is to use the trading loss against other forms of income in the same year. If such a claim is made,
losses are offset against income before personal allowances.
Any excess loss can still be offset against capital gains of the year. However, any offset against capital gains is
before both taper relief and annual exemptions.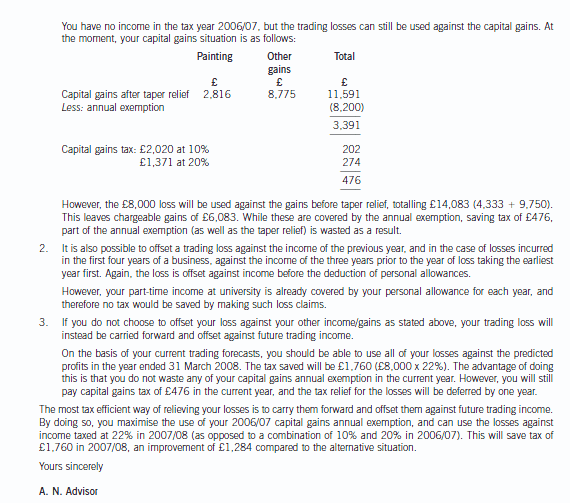
-
第13题:
(b) Assuming that the income from the sale of the books is not treated as trading income, calculate Bob’s taxable
income and gains for all relevant tax years, using any loss reliefs in the most tax-efficient manner. Your
answer should include an explanation of the loss reliefs available and your reasons for using (or not using)
them. (12 marks)
Assume that the rates and allowances for 2004/05 apply throughout this part of the question.
正确答案:
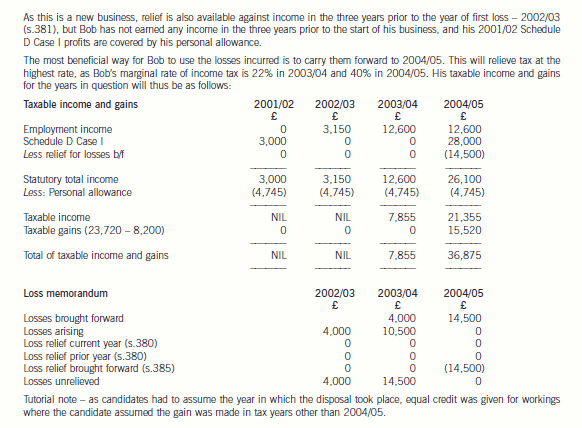
-
第14题:
(b) Calculate the corporation tax (CT) liabilities for Alantech Ltd, Boron Ltd and Bubble Ltd for the year ending
31 December 2004 on the assumption that loss reliefs are taken as early as possible. (9 marks)
正确答案:(b) Schedule D Case I calculation
The three companies form. a group for both group relief and capital gains purposes as all shareholdings pass the 75%
ownership test. The calculation of the corporation tax liabilities is as follows:
-
第15题:
3 On 1 January 2007 Dovedale Ltd, a company with no subsidiaries, intends to purchase 65% of the ordinary share
capital of Hira Ltd from Belgrove Ltd. Belgrove Ltd currently owns 100% of the share capital of Hira Ltd and has no
other subsidiaries. All three companies have their head offices in the UK and are UK resident.
Hira Ltd had trading losses brought forward, as at 1 April 2006, of £18,600 and no income or gains against which
to offset losses in the year ended 31 March 2006. In the year ending 31 March 2007 the company expects to make
further tax adjusted trading losses of £55,000 before deduction of capital allowances, and to have no other income
or gains. The tax written down value of Hira Ltd’s plant and machinery as at 31 March 2006 was £96,000 and
there will be no fixed asset additions or disposals in the year ending 31 March 2007. In the year ending 31 March
2008 a small tax adjusted trading loss is anticipated. Hira Ltd will surrender the maximum possible trading losses
to Belgrove Ltd and Dovedale Ltd.
The tax adjusted trading profit of Dovedale Ltd for the year ending 31 March 2007 is expected to be £875,000 and
to continue at this level in the future. The profits chargeable to corporation tax of Belgrove Ltd are expected to be
£38,000 for the year ending 31 March 2007 and to increase in the future.
On 1 February 2007 Dovedale Ltd will sell a small office building to Hira Ltd for its market value of £234,000.
Dovedale Ltd purchased the building in March 2005 for £210,000. In October 2004 Dovedale Ltd sold a factory
for £277,450 making a capital gain of £84,217. A claim was made to roll over the gain on the sale of the factory
against the acquisition cost of the office building.
On 1 April 2007 Dovedale Ltd intends to acquire the whole of the ordinary share capital of Atapo Inc, an unquoted
company resident in the country of Morovia. Atapo Inc sells components to Dovedale Ltd as well as to other
companies in Morovia and around the world.
It is estimated that Atapo Inc will make a profit before tax of £160,000 in the year ending 31 March 2008 and will
pay a dividend to Dovedale Ltd of £105,000. It can be assumed that Atapo Inc’s taxable profits are equal to its profit
before tax. The rate of corporation tax in Morovia is 9%. There is a withholding tax of 3% on dividends paid to
non-Morovian resident shareholders. There is no double tax agreement between the UK and Morovia.
Required:
(a) Advise Belgrove Ltd of any capital gains that may arise as a result of the sale of the shares in Hira Ltd. You
are not required to calculate any capital gains in this part of the question. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(a) Capital gains that may arise on the sale by Belgrove Ltd of shares in Hira Ltd
Belgrove Ltd will realise a capital gain on the sale of the shares unless the substantial shareholding exemption applies. The
exemption will be given automatically provided all of the following conditions are satisfied.
– Belgrove Ltd has owned at least 10% of Hira Ltd for a minimum of 12 months during the two years prior to the sale.
– Belgrove Ltd is a trading company or a member of a trading group during that 12-month period and immediately after
the sale.
– Hira Ltd is a trading company or the holding company of a trading group during that 12-month period and immediately
after the sale.
Hira Ltd will no longer be in a capital gains group with Belgrove Ltd after the sale. Accordingly, a capital gain, known as a
degrouping charge, may arise in Hira Ltd. A degrouping charge will arise if, at the time it leaves the Belgrove Ltd group, Hira
Ltd owns any capital assets which were transferred to it at no gain, no loss within the previous six years by a member of the
Belgrove Ltd capital gains group. -
第16题:
(d) Explain whether or not Dovedale Ltd, Hira Ltd and Atapo Inc can register as a group for the purposes of value
added tax. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(d) Dovedale Ltd and Hira Ltd can register as a group for the purposes of value added tax (VAT) because Dovedale Ltd controls
Hira Ltd and both companies are established in the UK in that their head offices are in the UK.
Dovedale Ltd will also control Atapo Inc. However, Atapo Inc cannot be part of a group registration unless it is established
in the UK or has a fixed establishment in the UK. It will be regarded as established in the UK if it is centrally managed and
controlled in the UK or if its head office is in the UK. A fixed establishment is a place where the company has staff and
equipment and where its business is carried on. -
第17题:
(b) Advise on the capital gains implications should Trent Limited’s old building be sold as proposed. Support your
advice with relevant calculations. (4 marks)
正确答案:
This gives a higher post-entry loss of £50,000 (150,000 – 100,000) and so it is advisable for Trent Limited to make
this election.
The £100,000 of pre-entry losses are still available, but can only be set against gains on assets which:
(i) Trent Limited sold prior to being acquired (subject to the normal carry back restrictions), or
(ii) Trent Limited already owned when it was acquired, or
(iii) Trent Limited acquired from outside the group and used in its trade after being bought by Tay Limited. -
第18题:
(b) Explain why making sales of Sabals in North America will have no effect on Nikau Ltd’s ability to recover its
input tax. (3 marks)
Notes: – you should assume that the corporation tax rates and allowances for the financial year to 31 March 2007
will continue to apply for the foreseeable future.
– you should ignore indexation allowance.
正确答案:
(b) Recoverability of input tax
Sales by Nikau Ltd of its existing products are subject to UK VAT at 17·5% because it is selling to domestic customers who
will not be registered for VAT. Accordingly, at present, Nikau Ltd can recover all of its input tax.
Sales to customers in North America will be zero rated because the goods are being exported from the EU. Zero rated supplies
are classified as taxable for the purposes of VAT and therefore Nikau Ltd will continue to be able to recover all of its input tax. -
第19题:
(ii) The use of the trading loss of Tethys Ltd for the year ending 31 December 2008; (6 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Tethys Ltd – Use of trading loss
– The two companies will not be in a group relief group as Saturn Ltd will not own 75% of Tethys Ltd.
– For a consortium to exist, 75% of the ordinary share capital of Tethys Ltd must be held by companies which each
hold at least 5%. Accordingly, Tethys Ltd will be a consortium company if the balance of its share capital is owned
by Clangers Ltd but not if it is owned by Edith Clanger.
– If Tethys Ltd qualifies as a consortium company: 65% of its trading losses in the period from 1 August 2008 to
31 December 2008 can be surrendered to Saturn Ltd, i.e. £21,667 (£80,000 x 5/12 x 65%).
– If Tethys Ltd does not qualify as a consortium company: none of its loss can be surrendered to Saturn Ltd.
– The acquisition of 65% of Tethys Ltd is a change in ownership of the company. If there is a major change in the
nature or conduct of the trade of Tethys Ltd within three years of 1 August 2008, the loss arising prior to that date
cannot be carried forward for relief in the future.
Further information required:
– Ownership of the balance of the share capital of Tethys Ltd. -
第20题:
(ii) Explain why Galileo is able to pay the inheritance tax due in instalments, state when the instalments are
due and identify any further issues relevant to Galileo relating to the payments. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Payment by instalments
The inheritance tax can be paid by instalments because Messier Ltd is an unquoted company controlled by Kepler at
the time of the gift and is still unquoted at the time of his death.
The tax is due in ten equal annual instalments starting on 30 November 2008.
Interest will be charged on any instalments paid late; otherwise the instalments will be interest free because Messier is
a trading company that does not deal in property or financial assets.
All of the outstanding inheritance tax will become payable if Galileo sells the shares in Messier Ltd.
Tutorial note
Candidates were also given credit for stating that payment by instalments is available because the shares represent at
least 10% of the company’s share capital and are valued at £20,000 or more. -
第21题:
(b) You are the audit manager of Johnston Co, a private company. The draft consolidated financial statements for
the year ended 31 March 2006 show profit before taxation of $10·5 million (2005 – $9·4 million) and total
assets of $55·2 million (2005 – $50·7 million).
Your firm was appointed auditor of Tiltman Co when Johnston Co acquired all the shares of Tiltman Co in March
2006. Tiltman’s draft financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2006 show profit before taxation of
$0·7 million (2005 – $1·7 million) and total assets of $16·1 million (2005 – $16·6 million). The auditor’s
report on the financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2005 was unmodified.
You are currently reviewing two matters that have been left for your attention on the audit working paper files for
the year ended 31 March 2006:
(i) In December 2004 Tiltman installed a new computer system that properly quantified an overvaluation of
inventory amounting to $2·7 million. This is being written off over three years.
(ii) In May 2006, Tiltman’s head office was relocated to Johnston’s premises as part of a restructuring.
Provisions for the resulting redundancies and non-cancellable lease payments amounting to $2·3 million
have been made in the financial statements of Tiltman for the year ended 31 March 2006.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of these two matters for your auditor’s reports on the financial
statements of Johnston Co and Tiltman Co for the year ended 31 March 2006. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Tiltman Co
Tiltman’s total assets at 31 March 2006 represent 29% (16·1/55·2 × 100) of Johnston’s total assets. The subsidiary is
therefore material to Johnston’s consolidated financial statements.
Tutorial note: Tiltman’s profit for the year is not relevant as the acquisition took place just before the year end and will
therefore have no impact on the consolidated income statement. Calculations of the effect on consolidated profit before
taxation are therefore inappropriate and will not be awarded marks.
(i) Inventory overvaluation
This should have been written off to the income statement in the year to 31 March 2005 and not spread over three
years (contrary to IAS 2 ‘Inventories’).
At 31 March 2006 inventory is overvalued by $0·9m. This represents all Tiltmans’s profit for the year and 5·6% of
total assets and is material. At 31 March 2005 inventory was materially overvalued by $1·8m ($1·7m reported profit
should have been a $0·1m loss).
Tutorial note: 1/3 of the overvaluation was written off in the prior period (i.e. year to 31 March 2005) instead of $2·7m.
That the prior period’s auditor’s report was unmodified means that the previous auditor concurred with an incorrect
accounting treatment (or otherwise gave an inappropriate audit opinion).
As the matter is material a prior period adjustment is required (IAS 8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting
Estimates and Errors’). $1·8m should be written off against opening reserves (i.e. restated as at 1 April 2005).
(ii) Restructuring provision
$2·3m expense has been charged to Tiltman’s profit and loss in arriving at a draft profit of $0·7m. This is very material.
(The provision represents 14·3% of Tiltman’s total assets and is material to the balance sheet date also.)
The provision for redundancies and onerous contracts should not have been made for the year ended 31 March 2006
unless there was a constructive obligation at the balance sheet date (IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and
Contingent Assets’). So, unless the main features of the restructuring plan had been announced to those affected (i.e.
redundancy notifications issued to employees), the provision should be reversed. However, it should then be disclosed
as a non-adjusting post balance sheet event (IAS 10 ‘Events After the Balance Sheet Date’).
Given the short time (less than one month) between acquisition and the balance sheet it is very possible that a
constructive obligation does not arise at the balance sheet date. The relocation in May was only part of a restructuring
(and could be the first evidence that Johnston’s management has started to implement a restructuring plan).
There is a risk that goodwill on consolidation of Tiltman may be overstated in Johnston’s consolidated financial
statements. To avoid the $2·3 expense having a significant effect on post-acquisition profit (which may be negligible
due to the short time between acquisition and year end), Johnston may have recognised it as a liability in the
determination of goodwill on acquisition.
However, the execution of Tiltman’s restructuring plan, though made for the year ended 31 March 2006, was conditional
upon its acquisition by Johnston. It does not therefore represent, immediately before the business combination, a
present obligation of Johnston. Nor is it a contingent liability of Johnston immediately before the combination. Therefore
Johnston cannot recognise a liability for Tiltman’s restructuring plans as part of allocating the cost of the combination
(IFRS 3 ‘Business Combinations’).
Tiltman’s auditor’s report
The following adjustments are required to the financial statements:
■ restructuring provision, $2·3m, eliminated;
■ adequate disclosure of relocation as a non-adjusting post balance sheet event;
■ current period inventory written down by $0·9m;
■ prior period inventory (and reserves) written down by $1·8m.
Profit for the year to 31 March 2006 should be $3·9m ($0·7 + $0·9 + $2·3).
If all these adjustments are made the auditor’s report should be unmodified. Otherwise, the auditor’s report should be
qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of disagreement. If none of the adjustments are made, the qualification should still be
‘except for’ as the matters are not pervasive.
Johnston’s auditor’s report
If Tiltman’s auditor’s report is unmodified (because the required adjustments are made) the auditor’s report of Johnston
should be similarly unmodified. As Tiltman is wholly-owned by Johnston there should be no problem getting the
adjustments made.
If no adjustments were made in Tiltman’s financial statements, adjustments could be made on consolidation, if
necessary, to avoid modification of the auditor’s report on Johnston’s financial statements.
The effect of these adjustments on Tiltman’s net assets is an increase of $1·4m. Goodwill arising on consolidation (if
any) would be reduced by $1·4m. The reduction in consolidated total assets required ($0·9m + $1·4m) is therefore
the same as the reduction in consolidated total liabilities (i.e. $2·3m). $2·3m is material (4·2% consolidated total
assets). If Tiltman’s financial statements are not adjusted and no adjustments are made on consolidation, the
consolidated financial position (balance sheet) should be qualified ‘except for’. The results of operations (i.e. profit for
the period) should be unqualified (if permitted in the jurisdiction in which Johnston reports).
Adjustment in respect of the inventory valuation may not be required as Johnston should have consolidated inventory
at fair value on acquisition. In this case, consolidated total liabilities should be reduced by $2·3m and goodwill arising
on consolidation (if any) reduced by $2·3m.
Tutorial note: The effect of any possible goodwill impairment has been ignored as the subsidiary has only just been
acquired and the balance sheet date is very close to the date of acquisition. -
第22题:
(b) While the refrigeration units were undergoing modernisation Lamont outsourced all its cold storage requirements
to Hogg Warehousing Services. At 31 March 2007 it was not possible to physically inspect Lamont’s inventory
held by Hogg due to health and safety requirements preventing unauthorised access to cold storage areas.
Lamont’s management has provided written representation that inventory held at 31 March 2007 was
$10·1 million (2006 – $6·7 million). This amount has been agreed to a costing of Hogg’s monthly return of
quantities held at 31 March 2007. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Lamont Co for the year ended
31 March 2007.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
(b) Outsourced cold storage
(i) Matters
■ Inventory at 31 March 2007 represents 21% of total assets (10·1/48·0) and is therefore a very material item in the
balance sheet.
■ The value of inventory has increased by 50% though revenue has increased by only 7·5%. Inventory may be
overvalued if no allowance has been made for slow-moving/perished items in accordance with IAS 2 Inventories.
■ Inventory turnover has fallen to 6·6 times per annum (2006 – 9·3 times). This may indicate a build up of
unsaleable items.
Tutorial note: In the absence of cost of sales information, this is calculated on revenue. It may also be expressed
as the number of days sales in inventory, having increased from 39 to 55 days.
■ Inability to inspect inventory may amount to a limitation in scope if the auditor cannot obtain sufficient audit
evidence regarding quantity and its condition. This would result in an ‘except for’ opinion.
■ Although Hogg’s monthly return provides third party documentary evidence concerning the quantity of inventory it
does not provide sufficient evidence with regard to its valuation. Inventory will need to be written down if, for
example, it was contaminated by the leakage (before being moved to Hogg’s cold storage) or defrosted during
transfer.
■ Lamont’s written representation does not provide sufficient evidence regarding the valuation of inventory as
presumably Lamont’s management did not have access to physically inspect it either. If this is the case this may
call into question the value of any other representations made by management.
■ Whether, since the balance sheet date, inventory has been moved back from Hogg’s cold storage to Lamont’s
refrigeration units. If so, a physical inspection and roll-back of the most significant fish lines should have been
undertaken.
Tutorial note: Credit will be awarded for other relevant accounting issues. For example a candidate may question
whether, for example, cold storage costs have been capitalised into the cost of inventory. Or whether inventory moves
on a FIFO basis in deep storage (rather than LIFO).
(ii) Audit evidence
■ A copy of the health and safety regulation preventing the auditor from gaining access to Hogg’s cold storage to
inspect Lamont’s inventory.
■ Analysis of Hogg’s monthly returns and agreement of significant movements to purchase/sales invoices.
■ Analytical procedures such as month-on-month comparison of gross profit percentage and inventory turnover to
identify any trend that may account for the increase in inventory valuation (e.g. if Lamont has purchased
replacement inventory but spoiled items have not been written off).
■ Physical inspection of any inventory in Lamont’s refrigeration units after the balance sheet date to confirm its
condition.
■ An aged-inventory analysis and recalculation of any allowance for slow-moving items.
■ A review of after-date sales invoices for large quantities of fish to confirm that fair value (less costs to sell) exceed
carrying amount.
■ A review of after-date credit notes for any returns of contaminated/perished or otherwise substandard fish. -
第23题:
(ii) On 1 July 2006 Petrie introduced a 10-year warranty on all sales of its entire range of stainless steel
cookware. Sales of stainless steel cookware for the year ended 31 March 2007 totalled $18·2 million. The
notes to the financial statements disclose the following:
‘Since 1 July 2006, the company’s stainless steel cookware is guaranteed to be free from defects in
materials and workmanship under normal household use within a 10-year guarantee period. No provision
has been recognised as the amount of the obligation cannot be measured with sufficient reliability.’
(4 marks)
Your auditor’s report on the financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2006 was unmodified.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of these two matters for your auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Petrie Co for the year ended 31 March 2007.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the matters above.
正确答案:
(ii) 10-year guarantee
$18·2 million stainless steel cookware sales amount to 43·1% of revenue and are therefore material. However, the
guarantee was only introduced three months into the year, say in respect of $13·6 million (3/4 × 18·2 million) i.e.
approximately 32% of revenue.
The draft note disclosure could indicate that Petrie’s management believes that Petrie has a legal obligation in respect
of the guarantee, that is not remote and likely to be material (otherwise no disclosure would have been required).
A best estimate of the obligation amounting to 5% profit before tax (or more) is likely to be considered material, i.e.
$90,000 (or more). Therefore, if it is probable that 0·66% of sales made under guarantee will be returned for refund,
this would require a warranty provision that would be material.
Tutorial note: The return of 2/3% of sales over a 10-year period may well be probable.
Clearly there is a present obligation as a result of a past obligating event for sales made during the nine months to
31 March 2007. Although the likelihood of outflow under the guarantee is likely to be insignificant (even remote) it is
probable that some outflow will be needed to settle the class of such obligations.
The note in the financial statements is disclosing this matter as a contingent liability. This term encompasses liabilities
that do not meet the recognition criteria (e.g. of reliable measurement in accordance with IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent
Liabilities and Contingent Assets).
However, it is extremely rare that no reliable estimate can be made (IAS 37) – the use of estimates being essential to
the preparation of financial statements. Petrie’s management must make a best estimate of the cost of refunds/repairs
under guarantee taking into account, for example:
■ the proportion of sales during the nine months to 31 March 2007 that have been returned under guarantee at the
balance sheet date (and in the post balance sheet event period);
■ the average age of cookware showing a defect;
■ the expected cost of a replacement item (as a refund of replacement is more likely than a repair, say).
If management do not make a provision for the best estimate of the obligation the audit opinion should be qualified
‘except for’ non-compliance with IAS 37 (no provision made). The disclosure made in the note to the financial
statements, however detailed, is not a substitute for making the provision.
Tutorial note: No marks will be awarded for suggesting that an emphasis of matter of paragraph would be appropriate
(drawing attention to the matter more fully explained in the note).
Management’s claim that the obligation cannot be measured with sufficient reliability does not give rise to a limitation
on scope on the audit. The auditor has sufficient evidence of the non-compliance with IAS 37 and disagrees with it.
