(c) Explain how the use of activity-based techniques may benefit Taliesin Ltd. (5 marks)
题目
(c) Explain how the use of activity-based techniques may benefit Taliesin Ltd. (5 marks)
相似考题
参考答案和解析
(c) The usefulness of activity-based techniques is accentuated in situations where overheads comprise a significant proportion of
product costs. Manufacturing overheads comprise 30·9% of turnover during the year ended 31 May 2005. Traditional
methods of allocating overheads to products might result in product cost information which is misleading and detrimental to
managerial decision-making. Calculations of product costs are more prone to error in situations where higher levels of
overhead exist. The consequences can prove disastrous as, for example, in the under-pricing or over-pricing of products.
Since Taliesin Ltd is going to confine its activities to its home country it must be prepared to face increased competition and
this increases the need for greater visibility and more accurate product cost information.
At present, Taliesin Ltd offers a range of products which is increasing in number and this may lead to the need for a more
detailed costing system. Traditional absorption systems might well be inadequate as the number of product variants increases.
One would expect that each new product developed is more complex than its predecessors. The company would probably
start with simple Vanilla, then a few basic flavours but as Taliesin Ltd has expanded one would expect it to take longer to
originate and test new products until they are ready to be introduced. It will probably take longer to mix the ingredients for a
run of each product.
These two, development and mixing ingredients, are examples of activities which arise when new products are considered.
If traditional absorption costing and budgeting are used based on machine-time in production then the effect of these activities
would be ignored.
In order to gain a full appreciation of the impact of new product introduction activity-based techniques should be used to
guide Taliesin Ltd into the easiest way to maintain its policy of growth. It may be a better decision to expand abroad or into
new markets at home with the existing products than pursue growth by introducing new products to a dwindling number of
customers.
We are not told of the composition of the customer base of Taliesin Ltd. However, one thing we do know is that the scope of
activity-based techniques extends beyond products and services. For example, the application of activity-based costing can
provide vital information that enables management to undertake customer profitability analysis, thereby further improving
management decision-making and operating performance.
更多“(c) Explain how the use of activity-based techniques may benefit Taliesin Ltd. (5 marks)”相关问题
-
第1题:
(b) Explain how the process of developing scenarios might help John better understand the macro-environmental
factors influencing Airtite’s future strategy. (8 marks)
正确答案:(b) Carrying out a systematic PESTEL analysis is a key step in developing alternative scenarios about the future. Johnson and
Scholes define scenarios as ‘detailed and plausible views of how the business environment of an organisation might develop
in the future based on groupings of key environmental influences and drivers of change about which there is a high level of
uncertainty’. In developing scenarios it is necessary to isolate the key drivers of change, which have the potential to have a
significant impact on the company and are associated with high levels of uncertainty. Development of scenarios enables
managers to share assumptions about the future and the key variables shaping that future. This provides an opportunity for
real organisational learning. They are then in a position to monitor these key variables and amend strategies accordingly. It
is important to note that different stakeholder groups will have different expectations about the future and each may provide
a key input to the process of developing scenarios. By their very nature scenarios should not attempt to allocate probabilities
to the key factors and in so doing creating ‘spurious accuracy’ about those factors. A positive scenario is shown below and
should provide a shared insight into the external factors most likely to have a significant impact on Airtite‘s future strategy.
For most companies operating in global environments the ability to respond flexibly and quickly to macro-environmental
change would seem to be a key capability.
The scenario as illustrated below, clearly could have a major impact on the success or otherwise of Airtite’s strategy for the
future. The key drivers for change would seem to be the link between technology and global emissions, fuel prices and the
stability of the global political environment. Through creating a process which considers the drivers which will have most
impact on Airtite and which are subject to the greatest uncertainty, Airtite will have a greater chance of its strategy adaptingto changing circumstances.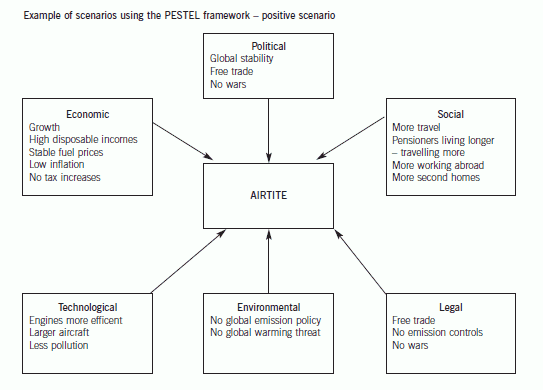
-
第2题:
(c) Explain how absolutist (dogmatic) and relativist (pragmatic) ethical assumptions would affect the outcome
of Anne’s decision. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(c) Absolutism and relativism
Absolutism and relativism represent two extreme positions of ethical assumptions.
Definitions
An absolutist assumption is one that believes that there are ‘eternal’ rules that should guide all ethical and moral decision
making in all situations. Accordingly, in any given situation, there is likely to be one right course of action regardless of the
outcome. An absolutist believes that this should be chosen regardless of the consequences or the cost. A dogmatic approach
to morality is an example of an absolutist approach to ethics. A dogmatic assumption is one that is accepted without
discussion or debate.
Relativist assumptions are ‘situational’ in nature. Rather than arguing that there is a single right choice, a relativist will tend
to adopt a pragmatic approach and decide, in the light of the situation being considered, which is the best outcome. This will
involve a decision on what outcome is the most favourable and that is a matter of personal judgment.
Outcomes
If Anne were to adopt absolutist/dogmatic assumptions, she would be likely to decide that she would need to pursue what
she perceives is the right course of action regardless of cost to herself or the relationship with the client or her manager. Given
that she unearthed a suspect and unaccounted-for payment, and that she received an inadequate explanation from the client,
she would probably recommend extension to the audit beyond the weekend.
If Ann were to adopt relativist or pragmatic assumptions, she would have a potentially much more complicated decision to
make. She would have to decide whether it was more important, ethically, to yield to the pressure from Zachary in the
interests of her short-term career interests or ‘hold out’ to protect the interests of the shareholders. Anne could recommend
sign off and trust the FD’s explanation but she is more likely to seek further evidence or assurance from the company before
she does so. -
第3题:
2 (a) Explain the term ‘backflush accounting’ and the circumstances in which its use would be appropriate.
(6 marks)
正确答案:
(a) Backflush accounting focuses upon output of an organisation and then works backwards when allocating costs between cost
of goods sold and inventories. It can be argued that backflush accounting simplifies costing since it ignores both labour
variances and work-in-progress. Whilst in a perfect just-in-time environment there would be no work-in-progress at all, there
will in practice be a small amount of work-in-progress in the system at any point in time. This amount, however, is likely to
be negligible in quantity and therefore not significant in terms of value. Thus, a backflush accounting system simplifies the
accounting records by avoiding the need to follow the movement of materials and work-in-progress through the manufacturing
process within the organisation.
The backflush accounting system is likely to involve the maintenance of a raw materials and work-in–progress account
together with a finished goods account. The use of standard costs and variances is likely to be incorporated into the
accounting entries. Transfers from raw materials and work-in-progress account to finished goods (or cost of sales) will probably
be made at standard cost. The difference between the actual inputs and the standard charges from the raw materials and
work-in-progress account will be recorded as a residual variance, which will be recorded in the profit and loss account. Thus,
it is essential that standard costs are a good surrogate for actual costs if large variances are to be avoided. Backflush
accounting is ideally suited to a just-in-time philosophy and is employed where the overall cycle time is relatively short and
inventory levels are low. Naturally, management will still be eager to ascertain the cause of any variances that arise from the
inefficient usage of materials, labour and overhead. However investigations are far more likely to be undertaken using nonfinancial
performance indicators as opposed to detailed cost variances. -
第4题:
(b) Explain how the use of SWOT analysis may be of assistance to the management of Diverse Holdings Plc.
(3 marks)
正确答案:
(b) The use of SWOT analysis will focus management attention on current strengths and weaknesses of each subsidiary company
which will be of assistance in the formulating of the business strategy of Diverse Holdings Plc. It will also enable management
to monitor trends and developments in the constantly changing environments of their subsidiaries. Each trend or development
may be classified as an opportunity or a threat that will provide a stimulus for an appropriate management response.
Management can make an assessment of the feasibility of required actions in order that the company may capitalise upon
opportunities whilst considering how best to negate or minimise the effect of any threats.
A SWOT analysis should assist the management of Diverse Holdings Plc as they must identify their strengths, weaknesses,
opportunities and threats. These may be classified as follows:
Strengths which appear to include both OFL and HTL.
Weaknesses which must include PSL and its limited outlets, which generate little growth and could collapse overnight. KAL
is also a weakness due to its declining profitability.
Opportunities where OFT, HTL and OPL are operating in growth markets.
Threats from which KAL is suffering.
If these four categories are identified and analysed then the group should be strengthened. -
第5题:
(b) Discuss FOUR factors that distinguish service from manufacturing organisations and explain how each of
these factors relates to the services provided by the Dental Health Partnership. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(b) The major characteristics of services which distinguish services from manufacturing are as follows:
– Intangibility.
When a dentist provides a service to a client there are many intangible factors involved such as for example the
appearance of the surgery, the personality of the dentist, the manner and efficiency of the dental assistant. The output
of the service is ‘performance’ by the dentist as opposed to tangible goods.
– Simultaneity.
The service provided by the dentist to the patient is created by the dentist at the same time as the patient consumed it
thus preventing any advance verification of quality.
– Heterogeneity.
Many service organisations face the problem of achieving consistency in the quality of its output. Whilst each of the
dentists within the Dental Health Partnership will have similar professional qualifications there will be differences in the
manner they provide services to clients.
– Perishability.
Many services are perishable. The services of a dentist are purchased only for the duration of an appointment. -
第6题:
(ii) Comment briefly on how divisional managers might respond to the results achieved and ONE potential
problem that might be experienced by Our Timbers Ltd. (2 marks)
正确答案:
-
第7题:
(c) Explain the term ‘target costing’ and how it may be applied by GWCC. Briefly discuss any potential
limitations in its application. (8 marks)
正确答案:
(c) Target costing should be viewed as an integral part of a strategic profit management system. The initial consideration in target
costing is the determination of an estimate of the selling price for a new product which will enable a firm to capture its required
share of the market. In this particular example, Superstores plc, which on the face of it looks a powerful commercial
organisation, wishes to apply a 35% mark-up on the purchase price of each cake from GWCC. Since Superstores plc has
already decided on a launch price of £20·25 then it follows that the maximum selling price that can be charged by GWCC
is (100/135) x £20·25 which is £15·00.
This is clearly a situation which lends itself to the application of target costing/pricing techniques as in essence GWCC can
see the extent to which they fall short of the required level of return with regard to a contract with Superstores plc which ends
after twelve months. Thus it is necessary to reduce the total costs by £556,029 to this figure in order to achieve the desired
level of profit, having regard to the rate of return required on new capital investment. The deduction of required profit from
the proposed selling price will produce a target price that must be met in order to ensure that the desired rate of return is
obtained. Thus the main theme that underpins target costing can be seen to be ‘what should a product cost in order to achieve
the desired level of return’.
Target costing will necessitate comparison of current estimated cost levels against the target level which must be achieved if
the desired levels of profitability, and hence return on investment, are to be achieved. Thus where a gap exists between the
current estimated cost levels and the target cost, it is essential that this gap be closed.
The Directors of GWCC plc should be aware of the fact that it is far easier to ‘design out’ cost during the pre-production phase
than to ‘control out’ cost during the production phase. Thus cost reduction at this stage of a product’s life cycle is of critical
significance to business success.
A number of techniques may be employed in order to help in the achievement and maintenance of the desired level of target
cost. Attention should be focussed upon the identification of value added and non-value added activities with the aim of the
elimination of the latter. The product should be developed in an atmosphere of ‘continuous improvement’. In this regard, total
quality techniques such as the use of Quality circles may be used in attempting to find ways of achieving reductions in product
cost.
Value engineering techniques can be used to evaluate necessary product features such as the quality of materials used. It is
essential that a collaborative approach is taken by the management of GWCC and that all interested parties such as suppliers
and customers are closely involved in order to engineer product enhancements at reduced cost.
The degree of success that will be achieved by GWCC via the application of target costing principles will be very much
dependent on the extent of ‘flexibility’ in variable costs. Also the accuracy of information gathered by GWCC will assume
critical importance because the use of inaccurate information will produce calculated ‘cost gaps’ which are meaningless and
render the application of target costing principles of little value. -
第8题:
(b) Explain how growth may be assessed, and critically discuss the advantages and issues that might arise as a
result of a decision by the directors of CSG to pursue the objective of growth. (8 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Growth may be measured in a number of ways which are as follows:
Cash flow
This is a very important measure of growth as it ultimately determines the amount of funds available for re-investment by any
business.
Sales revenue
Growth in sales revenues generated is only of real value to investors if it precipitates growth in profits.
Profitability
There are many measures relating to profit which include sales margin, earnings before interest, taxation, depreciation and
amortisation (EBITDA) and earnings per share. More sophisticated measures such as return on capital employed and residual
income consider the size of the investment relative to the level of profits earned. In general terms, measures of profitability
are only meaningful if they are used as a basis for comparisons over time or in conjunction with other measures of
performance. Growth rate in profitability are useful when compared with other companies and also with other industries.
Return on investment
A growing return upon invested capital suggests that capital is being used more and more productively. Indicators of a growing
return would be measured by reference to dividend payment and capital growth.
Market share
Growth in market share is generally seen as positive as it can generate economies of scale.
Number of products/service offerings
Growth is only regarded as useful if products and services are profitable.
Number of employees
Measures of productivity such as value added per employee and profit per employee are often used by shareholders in
assessing growth. Very often an increased headcount is a measure of success in circumstances where more people are
needed in order to deliver a service to a required standard. However it is incumbent on management to ensure that all
employees are utilised in an effective manner.
It is a widely held belief that growth requires profits and that growth produces profits. Profits are essential in order to prevent
a company which has achieved growth from becoming a target for a take-over or in a worse case scenario goes into
liquidation. Hence it is fundamental that a business is profitable throughout its existence. Growth accompanied by growth in
profits is also likely to aid the long-term survival of an organisation. CSG operates in Swingland which experiences fluctuations
in its economic climate and in this respect the exploitation of profitable growth opportunities will help CSG to survive at the
expense of its competitors who do not exploit such opportunities.
Note: Alternative relevant discussion and examples would be accepted. -
第9题:
(c) Discuss the practical problems that may be encountered in the implementation of an activity-based system
of product cost management. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(c) The benefits of an activity-based system as the basis for product cost/profit estimation may not be straightforward. A number
of problems may be identified.
The selection of relevant activities and cost drivers may be complicated where there are many activities and cost drivers in
complex business situations.
There may be difficulty in the collection of data to enable accurate cost driver rates to be calculated. This is also likely to
require an extensive data collection and analysis system.
The problem of ‘cost driver denominator level’ may also prove difficult. This is similar to the problem in a traditional volume
related system. This is linked to the problem of fixed/variable cost analysis. For example the cost per batch may be fixed. Its
impact may be reduced, however, where the batch size can be increased without a proportionate increase in cost.
The achievement of the required level of management skill and commitment to change may also detract from the
implementation of the new system. Management may feel that the activity based approach contains too many assumptions
and estimates about activities and cost drivers. There may be doubt as to the degree of increased accuracy which it provides.
(alternative relevant examples and discussion would be acceptable) -
第10题:
(c) Advise Alan on the proposed disposal of the shares in Mobile Ltd. Your answer should include calculations
of the potential capital gain, and explain any options available to Alan to reduce this tax liability. (7 marks)
正确答案:
However, an exemption from corporation tax exists for any gain arising when a trading company (or member of a trading
group) sells the whole or any part of a substantial shareholding in another trading company.
A substantial shareholding is one where the investing company holds 10% of the ordinary share capital and is beneficially
entitled to at least 10% of the
(i) profits available for distribution to equity holders and
(ii) assets of the company available for distribution to equity holders on a winding up.
In meeting the 10% test, shares owned by a chargeable gains group may be amalgamated. The 10% test must have been
met for a continuous 12 month period during the 2 years preceding the disposal.
The companies making the disposals must have been trading companies (or members of a trading group) throughout the
12 month period, as well as at the date of disposal. In addition, they must also be trading companies (or members of a trading
group) immediately after the disposal.
The exemption is given automatically, and acts to deny losses as well as eliminate gains.
While Alantech Ltd has owned its holding in Mobile Ltd for 33 months, its ownership of the Boron holding has only lasted
for 10 months (at 1 June 2005) since Boron was acquired on 1 July 2004. Selling the shares in June 2005 will fail the
12 month test, and the gain will become chargeable.
It would be better for the companies to wait for a further month until July 2005 before selling the amalgamated shareholding.
By doing so, they will both be able to take advantage of the substantial shareholdings relief, thereby saving tax of £29,625
assuming a corporation tax rate of 19%. -
第11题:
(b) Calculate the amount of input tax that will be recovered by Vostok Ltd in respect of the new premises in the
year ending 31 March 2009 and explain, using illustrative calculations, how any additional recoverable input
tax will be calculated in future years. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Recoverable input tax in respect of new premises
Vostok Ltd will recover £47,880 (£446,500 x 7/47 x 72%) in the year ending 31 March 2009.
The capital goods scheme will apply to the purchase of the building because it is to cost more than £250,000. Under the
scheme, the total amount of input tax recovered reflects the use of the building over the period of ownership, up to a maximum
of ten years, rather than merely the year of purchase.
Further input tax will be recovered in future years as the percentage of exempt supplies falls. (If the percentage of exempt
supplies were to rise, Vostok Ltd would have to repay input tax to HMRC.)
The additional recoverable input tax will be computed by reference to the percentage of taxable supplies in each year including
the year of sale. For example, if the percentage of taxable supplies in a particular subsequent year were to be 80%, the
additional recoverable input tax would be computed as follows.
£446,500 x 7/47 x 1/10 x (80% – 72%) = £532.
Further input tax will be recovered in the year of sale as if Vostok Ltd’s supplies in the remaining years of the ten-year period
are fully vatable. For example, if the building is sold in year seven, the additional recoverable amount for the remaining three
years will be calculated as follows.
£446,500 x 7/47 x 1/10 x (100% – 72%) x 3 = £5,586. -
第12题:
In relation to company law, explain:
(a) the limitations on the use of company names; (4 marks)
(b) the tort of ‘passing off’; (4 marks)
(c) the role of the company names adjudicators under the Companies Act 2006. (2 marks)
正确答案:(a) Except in relation to specifically exempted companies, such as those involved in charitable work, companies are required to indicate that they are operating on the basis of limited liability. Thus private companies are required to end their names, either with the word ‘limited’ or the abbreviation ‘ltd’, and public companies must end their names with the words ‘public limited company’ or the abbreviation ‘plc’. Welsh companies may use the Welsh language equivalents (Companies Act (CA)2006 ss.58, 59 & 60).
Companies Registry maintains a register of business names, and will refuse to register any company with a name that is the same as one already on that index (CA 2006 s.66).
Certain categories of names are, subject to the decision of the Secretary of State, unacceptable per se, as follows:
(i) names which in the opinion of the Secretary of State constitute a criminal offence or are offensive (CA 2006 s.53)
(ii) names which are likely to give the impression that the company is connected with either government or local government authorities (s.54).
(iii) names which include a word or expression specified under the Company and Business Names Regulations 1981 (s.26(2)(b)). This category requires the express approval of the Secretary of State for the use of any of the names or expressions contained on the list, and relates to areas which raise a matter of public concern in relation to their use.
Under s.67 of the Companies Act 2006 the Secretary of State has power to require a company to alter its name under the following circumstances:
(i) where it is the same as a name already on the Registrar’s index of company names.
(ii) where it is ‘too like’ a name that is on that index.
The name of a company can always be changed by a special resolution of the company so long as it continues to comply with the above requirements (s.77).(b) The tort of passing off was developed to prevent one person from using any name which is likely to divert business their way by suggesting that the business is actually that of some other person or is connected in any way with that other business. It thus enables people to protect the goodwill they have built up in relation to their business activity. In Ewing v Buttercup
Margarine Co Ltd (1917) the plaintiff successfully prevented the defendants from using a name that suggested a link with
his existing dairy company. It cannot be used, however, if there is no likelihood of the public being confused, where for example the companies are conducting different businesses (Dunlop Pneumatic Tyre Co Ltd v Dunlop Motor Co Ltd (1907)
and Stringfellow v McCain Foods GB Ltd (1984). Nor can it be used where the name consists of a word in general use (Aerators Ltd v Tollitt (1902)).
Part 41 of the Companies Act (CA) 2006, which repeals and replaces the Business Names Act 1985, still does not prevent one business from using the same, or a very similar, name as another business so the tort of passing off will still have an application in the wider business sector. However the Act introduced a new procedure to deal specifically with company names. As previously under the CA 1985, a company cannot register with a name that was the same as any already registered (s.665 Companies Act (CA) 2006) and under CA s.67 the Secretary of State may direct a company to change its name if it has been registered in a name that is the same as, or too like a name appearing on the registrar’s index of company names. In addition, however, a completely new system of complaint has been introduced.(c) Under ss.69–74 of CA 2006 a new procedure has been introduced to cover situations where a company has been registered with a name
(i) that it is the same as a name associated with the applicant in which he has goodwill, or
(ii) that it is sufficiently similar to such a name that its use in the United Kingdom would be likely to mislead by suggesting a connection between the company and the applicant (s.69).
Section 69 can be used not just by other companies but by any person to object to a company names adjudicator if a company’s name is similar to a name in which the applicant has goodwill. There is list of circumstances raising a presumption that a name was adopted legitimately, however even then, if the objector can show that the name was registered either, to obtain money from them, or to prevent them from using the name, then they will be entitled to an order to require the company to change its name.
Under s.70 the Secretary of State is given the power to appoint company names adjudicators and their staff and to finance their activities, with one person being appointed Chief Adjudicator.
Section 71 provides the Secretary of State with power to make rules for the proceedings before a company names adjudicator.
Section 72 provides that the decision of an adjudicator and the reasons for it, are to be published within 90 days of the decision.
Section 73 provides that if an objection is upheld, then the adjudicator is to direct the company with the offending name to change its name to one that does not similarly offend. A deadline must be set for the change. If the offending name is not changed, then the adjudicator will decide a new name for the company.
Under s.74 either party may appeal to a court against the decision of the company names adjudicator. The court can either uphold or reverse the adjudicator’s decision, and may make any order that the adjudicator might have made. -
第13题:
(b) What research techniques could Mark use to get an accurate assessment of staff attitudes to the proposed
changes? (8 marks)
正确答案:
(b) As the term internal marketing implies, the methods of ascertaining staff reactions to the proposed growth strategy have close
parallels with the ways you find out about customer reaction to the company or its products. The benefits of taking a
structured research approach are considerable and often firms may prefer that attitude surveys are carried out by outside
consultants in order to improve objectivity and to remove some of the problems with Mark’s power and position. As with
external market research you are looking to see whether staff will ‘buy into’ the proposed strategy and the accurate
measurement of attitudes and consequent behaviour is very important.
Creating the framework for undertaking the research involves defining the issue to be researched – in this case staff attitudes
towards the growth strategy, designing the research methods, including the use of questionnaires and interviews, determining
the sample of staff to be involved, the use or otherwise of focus groups and ways of ensuring the data collected gives an
accurate picture of staff attitudes. The data generated must be analysed and presented to Mark in an appropriate way. How
the insights into staff attitudes are gained through the research is important, as is the communication of the results to the
staff. Mark should be aware that such research will inevitably create expectations among staff and managing those
expectations will be a test of his leadership powers. -
第14题:
(d) Explain the term ‘environmental management accounting’ and the benefits that may accrue to organisations
which adopt it. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(d) Environmental management accounting (EMA) involves the generation and analysis of both financial and non-financial
information in order to support internal environmental management processes. It is complementary to the conventional
management accounting approach, with the aim to develop appropriate mechanisms that assist the management of
organisations in the identification and allocation of environmentally related costs.
Organisations that alter their management accounting practices to incorporate environmental concerns will have greater
awareness of the impact of environment-related activities on their profit and loss accounts and balance sheets. This is because
conventional management accounting systems tend to attribute many environmental costs to general overhead accounts with
the result that they are ‘hidden’ from management. It follows that organisations which adopt EMA are more likely to identify
and take advantage of cost reduction and other improvement opportunities. A concern with environmental costs will also
reduce the chances of employing incorrect pricing of products and services and taking the wrong options in terms of mix and
development decisions. This in turn may lead to enhanced customer value whilst reducing the risk profile attaching to
investments and other decisions which have long term consequences.
Reputational risk will also be reduced as a consequence of adopting (EMA) since management will be seen to be acting in
an environmentally responsible manner. Organisations can learn from the Shell Oil Company whose experience in the much
publicised Brent Spar incident cost the firm millions in terms of lost revenues as a result of a consumer boycott. -
第15题:
(c) Identify TWO QUALITATIVE benefits that might arise as a consequence of the investment in a new IT system
and explain how you would attempt to assess them. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(c) One of the main qualitative benefits that may arise from an investment in a new IT system by Moffat Ltd is the improved level
of service to its customers in the form. of reduced waiting times which may arise as a consequence of better scheduling of
appointments, inventory management etc. This could be assessed via the introduction of a questionnaire requiring customers
to rate the service that they have received from their recent visit to a location within Moffat Ltd according to specific criteria
such as adherence to appointment times, time taken to service the vehicle, cleanliness of the vehicle, attitude of staff etc.
Alternatively a follow-up telephone call from a centralised customer services department may be made by Moffat Ltd
personnel in order to gather such information.
Another qualitative benefit of the proposed investment may arise in the form. of competitive advantage. Improvements in
customer specific information and service levels may give Moffat Ltd a competitive advantage. Likewise, improved inventory
management may enable costs to be reduced thereby enabling a ‘win-win’ relationship to be enjoyed with its customers. -
第16题:
(b) Discuss ways in which the traditional budgeting process may be seen as a barrier to the achievement of the
aims of EACH of the following models for the implementation of strategic change:
(i) benchmarking;
(ii) balanced scorecard; and
(iii) activity-based models. (12 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Benchmarking
Benchmarks enable goals to be set that may be based on either external measures of ‘best practice’ organisations or internal
cross-functional comparisons which exhibit ‘best practice’. A primary aim of the traditional budgeting process is the setting of
realistic targets that can be achieved within the budget period. The setting of realistic targets means that the extent of
underperformance against ‘best practice’ standards loses visibility, and thus short-term financial targets remain the
predominant focus of the traditional budgeting process. It is arguable that because the budgetary reporting system purports
to give managers ‘control’, there is very little real incentive to seek out benchmarks which may be used to raise budgeted
performance targets. Much depends upon the prevailing organisational culture since benchmarking may be viewed as an
attempt by top management to impose impossible targets upon operational managers. The situation is further exacerbated
where organisations do not measure their success relative to their competition.
Balanced scorecard
The Balanced scorecard is often misunderstood as a consequence of the failure by top management to ensure that it is
implemented effectively within the organisation. Thus it may be viewed as the addition of a few non-financial measures to
the conventional budget. In an attempt to overcome this misperception many management teams now establish a
performance-rewards linkage based upon the achievement of Scorecard targets for the forthcoming budget period.
Unfortunately this can precipitate dysfunctional behaviour at every level within the organisation.
Even in situations where the Scorecard has been well-designed and well-implemented it is difficult for it to gain widespread
acceptance. This is because all too often there exists a culture which places a very high value upon the achievement of the
fixed annual targets in order to avoid the loss of status, recognition and rewards.
A well-constructed Scorecard contains a mix of long-term and short-term measures and therefore drives the company in the
direction of medium-term strategic goals which are supported by cross-functional initiatives. On the other hand, the budgeting
process focuses the organisation on the achievement of short-term financial goals supported by the initiatives of individual
departments. Budgets can also act as an impediment to the acceptance of responsibility by local managers for the
achievement of the Scorecard targets. This is often the case in situations where a continued emphasis exists on meeting shortterm
e.g. quarterly targets.
Activity-based models
Traditional budgets show the costs of functions and departments (e.g. staff costs and establishment costs) instead of the costs
of those activities that are performed by people (e.g. receipt of goods inwards, processing and dispatch of orders etc). Thus
managers have no visibility of the real ‘cost drivers’ of their business. In addition, it is probable that a traditional budget
contains a significant amount of non-value-added costs that are not visible to the managers. The annual budget also tends
to fix capacity for the forthcoming budget period thereby undermining the potential of Activity-based management (ABM)
analysis to determine required capacity from a customer demand perspective. Those experienced in the use of ABM
techniques are used to dealing with such problems, however their tasks would be much easier to perform. and their results
made more reliable if these problems were removed. -
第17题:
(b) (i) Explain how the use of Ansoff’s product-market matrix might assist the management of Vision plc to
reduce the profit-gap that is forecast to exist at 30 November 2009. (3 marks)
正确答案:
-
第18题:
(ii) Comment briefly on the use of its own tree plantations as a source of raw materials by Our Timbers Ltd.
(3 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) The use of its own tree plantations as a source of raw materials not only ensures available supplies of timber but may
also demonstrate that the directors of Our Timbers Ltd are mindful of the need for careful planning in the consumption
of natural resources. This concern with the need to protect the environment will enhance the reputation of Our Timbers
Ltd as an environmentally-conscious organisation which in turn may translate into a source of competitive advantage
since contemporary thought is very much focused on the environmental responsibilities of organisations with particular
regard to the use of natural resources such as timber.
-
第19题:
(ii) Briefly explain the extent to which the application of sensitivity analysis might be useful in deciding
which refrigeration system to purchase and discuss the limitations inherent in its use. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Sensitivity analysis could be used to assess how responsive the NPV calculated in part (a) in respect of each decision
option change is to changes in the variables used to calculate it. The application of sensitivity analysis requires that the
net present values are calculated under alternative assumptions in order to determine how sensitive they are to changing
conditions. In this particular example then a relatively small change in the forecast cash flows might lead to a change
in the investment decision. The application of sensitivity analysis can indicate those variables to which the NPV is most
sensitive and the extent to which these variables may change before an investment results in a negative NPV. Thus the
application of sensitivity analysis may provide management with an indication of why a particular project might fail. The
directors of Stay Cool Ltd should give consideration to the potential variations in the independent variables which feature
in the decision-making process such as:
– estimated revenues
– estimated operating costs
– estimated working lives
– estimated repair costs
– the estimated discount rate i.e. cost of capital of each alternative investment.
Sensitivity analysis has some serious limitations. The use of the method requires changes in each variable under
consideration are isolated. However management may be focused on what happens if changes occur in two or more
critical variables. Another problem relating to the use of sensitivity analysis to forecast outcomes lies in the fact that it
provides no indication of the likelihood of the occurrence of changes in critical variables. -
第20题:
(c) Explain how the introduction of an ERPS could impact on the role of management accountants. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(c) The introduction of ERPS has the potential to have a significant impact on the work of management accountants. The use of
ERPS causes a substantial reduction in the gathering and processing of routine information by management accountants.
Instead of relying on management accountants to provide them with information, managers are able to access the system to
obtain the information they require directly via a suitable electronic access medium.
ERPS integrate separate business functions in one system for the entire organisation and therefore co-ordination is usually
undertaken centrally by information management specialists who have a dual responsibility for the implementation and
operation of the system.
ERPS perform. routine tasks that not so long ago were seen as an essential part of the daily routines of management
accountants, for example perpetual inventory valuation. Therefore if the value of the role of management accountants is not
to be diminished then it is of necessity that management accountants should seek to expand their roles within their
organisations.
The management accountant will also control and audit the ERPS data input and analysis. Hence the implementation of ERPS
provides the management accountant with an opportunity to change the emphasis of their role from information gathering
and processing to that of the role of advisers and internal consultants to their organisations. This new role will require
management accountants to be involved in interpreting the information generated from the ERPS and to provide business
support for all levels of management within an organisation. -
第21题:
(c) Critically discuss the adoption of activity-based management (ABM) in companies such as TOC. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(c) Activity-based management (ABM) is a method of identifying and evaluating activities that a business performs using
activity-based costing to carry out a value chain analysis or a re-engineering initiative to improve strategic and operational
decisions in an organisation. Activity-based costing establishes relationships between overhead costs and activities so that
overhead costs can be more precisely allocated to products, services, or customer segments. Activity-based management
focuses on managing activities to reduce costs and improve customer value.
Kaplan and Cooper (1998) divide ABM into operational ABM and strategic ABM:
Operational ABM is about ‘doing things right’, using ABC information to improve efficiency. Those activities which add value
to the product can be identified and improved. Activities that don’t add value are the ones that need to be reduced to cut costs
without reducing product value.
Strategic ABM is about ‘doing the right things’, using ABC information to decide which products to develop and which
activities to use. This can also be used for customer profitability analysis, identifying which customers are the most profitable
and focusing on them more.
A risk with ABM is that some activities have an implicit value, not necessarily reflected in a financial value added to any
product. For instance a particularly pleasant workplace can help attract and retain the best staff, but may not be identified as
adding value in operational ABM. A customer that represents a loss based on committed activities, but that opens up leads
in a new market, may be identified as a low value customer by a strategic ABM process.
ABM can give middle managers an understanding of costs to other teams to help them make decisions that benefit the whole
organisation, not just their activities’ bottom line.
-
第22题:
(iii) Explain the potential corporation tax (CT) implications of Tay Limited transferring work to Trent Limited,
and suggest how these can be minimised or eliminated. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(iii) Trading losses may not be carried forward where, within a period of three years there is both a change in the ownership
of a company and a major change in the nature or conduct of its trade. The transfer of work from Tay Limited to Trent
Limited is likely to constitute a major change in the nature or conduct of the latter’s trade. As a consequence, any tax
losses at the date of acquisition will be forfeited. Assuming losses were incurred uniformly in 2005, the tax losses at the
date of acquisition were £380,000 (300,000 + 2/3 x 120,000)). This is worth £114,000 assuming a corporation tax
rate of 30%.
Thus, Tay Limited should not consider transferring any trade to Trent Limited until after the third anniversary of the date
of the change of ownership i.e. not before 1 September 2008. As the trades are similar, there should be little problem
in transferring work from that date onwards. -
第23题:
In relation to the law of contract, distinguish between and explain the effect of:
(a) a term and a mere representation; (3 marks)
(b) express and implied terms, paying particular regard to the circumstances under which terms may be implied in contracts. (7 marks)
正确答案:This question requires candidates to consider the law relating to terms in contracts. It specifically requires the candidates to distinguish between terms and mere representations and then to establish the difference between express and implied terms in contracts.
(a) As the parties to a contract will be bound to perform. any promise they have contracted to undertake, it is important to distinguish between such statements that will be considered part of the contract, i.e. terms, and those other pre-contractual statements which are not considered to be part of the contract, i.e. mere representations. The reason for distinguishing between them is that there are different legal remedies available if either statement turns out to be incorrect.
A representation is a statement that induces a contract but does not become a term of the contract. In practice it is sometimes difficult to distinguish between the two, but in attempting to do so the courts will focus on when the statement was made in relation to the eventual contract, the importance of the statement in relation to the contract and whether or not the party making the statement had specialist knowledge on which the other party relied (Oscar Chess v Williams (1957) and Dick
Bentley v Arnold Smith Motors (1965)).
(b) Express terms are statements actually made by one of the parties with the intention that they become part of the contract and
thus binding and enforceable through court action if necessary. It is this intention that distinguishes the contractual term from
the mere representation, which, although it may induce the contractual agreement, does not become a term of the contract.
Failure to comply with the former gives rise to an action for breach of contract, whilst failure to comply with the latter only gives rise to an action for misrepresentation.Such express statements may be made by word of mouth or in writing as long as they are sufficiently clear for them to be enforceable. Thus in Scammel v Ouston (1941) Ouston had ordered a van from the claimant on the understanding that the balance of the purchase price was to be paid ‘on hire purchase terms over two years’. When Scammel failed to deliver the van Ouston sued for breach of contract without success, the court holding that the supposed terms of the contract were too
uncertain to be enforceable. There was no doubt that Ouston wanted the van on hire purchase but his difficulty was that
Scammel operated a range of hire purchase terms and the precise conditions of his proposed hire purchase agreement were
never sufficiently determined.
Implied terms, however, are not actually stated or expressly included in the contract, but are introduced into the contract by implication. In other words the exact meaning and thus the terms of the contract are inferred from its context. Implied terms can be divided into three types.
Terms implied by statute
In this instance a particular piece of legislation states that certain terms have to be taken as constituting part of an agreement, even where the contractual agreement between the parties is itself silent as to that particular provision. For example, under s.5 of the Partnership Act 1890, every member of an ordinary partnership has the implied power to bind the partnership in a contract within its usual sphere of business. That particular implied power can be removed or reduced by the partnership agreement and any such removal or reduction of authority would be effective as long as the other party was aware of it. Some implied terms, however, are completely prescriptive and cannot be removed.
Terms implied by custom or usage
An agreement may be subject to terms that are customarily found in such contracts within a particular market, trade or locality. Once again this is the case even where it is not actually specified by the parties. For example, in Hutton v Warren (1836), it was held that customary usage permitted a farm tenant to claim an allowance for seed and labour on quitting his tenancy. It should be noted, however, that custom cannot override the express terms of an agreement (Les Affreteurs Reunnis SA v Walford (1919)).
Terms implied by the courts Generally, it is a matter for the parties concerned to decide the terms of a contract, but on occasion the court will presume that the parties intended to include a term which is not expressly stated. They will do so where it is necessary to give business efficacy to the contract.Whether a term may be implied can be decided on the basis of the officious bystander test. Imagine two parties, A and B, negotiating a contract, when a third party, C, interrupts to suggest a particular provision. A and B reply that that particular term is understood. In just such a way, the court will decide that a term should be implied into a contract.
In The Moorcock (1889), the appellants, owners of a wharf, contracted with the respondents to permit them to discharge their ship at the wharf. It was apparent to both parties that when the tide was out the ship would rest on the riverbed. When the tide was out, the ship sustained damage by settling on a ridge. It was held that there was an implied warranty in the contract that the place of anchorage should be safe for the ship. As a consequence, the ship owner was entitled to damages for breach of that term.
Alternatively the courts will imply certain terms into unspecific contracts where the parties have not reduced the general agreement into specific details. Thus in contracts of employment the courts have asserted the existence of implied terms to impose duties on both employers and employees, although such implied terms can be overridden by express contractual provision to the contrary.
