(b) Comment (with relevant calculations) on the performance of the business of Quicklink Ltd and CelerTransport during the year ended 31 May 2005 and, insofar as the information permits, its projectedperformance for the year ending 31 May 2006. Your answe
题目
(b) Comment (with relevant calculations) on the performance of the business of Quicklink Ltd and Celer
Transport during the year ended 31 May 2005 and, insofar as the information permits, its projected
performance for the year ending 31 May 2006. Your answer should specifically consider:
(i) Revenue generation per vehicle
(ii) Vehicle utilisation and delivery mix
(iii) Service quality. (14 marks)
相似考题
更多“(b) Comment (with relevant calculations) on the performance of the business of Quicklink Ltd and CelerTransport during the year ended 31 May 2005 and, insofar as the information permits, its projectedperformance for the year ending 31 May 2006. Your answe”相关问题
-
第1题:
(b) Describe with suitable calculations how the goodwill arising on the acquisition of Briars will be dealt with in
the group financial statements and how the loan to Briars should be treated in the financial statements of
Briars for the year ended 31 May 2006. (9 marks)
正确答案:(b) IAS21 ‘The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates’ requires goodwill arising on the acquisition of a foreign operation
and fair value adjustments to acquired assets and liabilities to be treated as belonging to the foreign operation. They should
be expressed in the functional currency of the foreign operation and translated at the closing rate at each balance sheet date.
Effectively goodwill is treated as a foreign currency asset which is retranslated at the closing rate. In this case the goodwillarising on the acquisition of Briars would be treated as follows:
At 31 May 2006, the goodwill will be retranslated at 2·5 euros to the dollar to give a figure of $4·4 million. Therefore this
will be the figure for goodwill in the balance sheet and an exchange loss of $1·4 million recorded in equity (translation
reserve). The impairment of goodwill will be expensed in profit or loss to the value of $1·2 million. (The closing rate has been
used to translate the impairment; however, there may be an argument for using the average rate.)
The loan to Briars will effectively be classed as a financial liability measured at amortised cost. It is the default category for
financial liabilities that do not meet the definition of financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss. For most entities,
most financial liabilities will fall into this category. When a financial liability is recognised initially in the balance sheet, the
liability is measured at fair value. Fair value is the amount for which a liability can be settled, between knowledgeable, willing
parties in an arm’s length transaction. In other words, fair value is an actual or estimated transaction price on the reporting
date for a transaction taking place between unrelated parties that have adequate information about the asset or liability being
measured.
Since fair value is a market transaction price, on initial recognition fair value generally is assumed to equal the amount of
consideration paid or received for the financial asset or financial liability. Accordingly, IAS39 specifies that the best evidence
of the fair value of a financial instrument at initial recognition generally is the transaction price. However for longer-term
receivables or payables that do not pay interest or pay a below-market interest, IAS39 does require measurement initially at
the present value of the cash flows to be received or paid.
Thus in Briars financial statements the following entries will be made: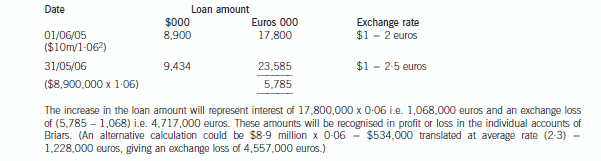
-
第2题:
3 (a) Leigh, a public limited company, purchased the whole of the share capital of Hash, a limited company, on 1 June
2006. The whole of the share capital of Hash was formerly owned by the five directors of Hash and under the
terms of the purchase agreement, the five directors were to receive a total of three million ordinary shares of $1
of Leigh on 1 June 2006 (market value $6 million) and a further 5,000 shares per director on 31 May 2007,
if they were still employed by Leigh on that date. All of the directors were still employed by Leigh at 31 May
2007.
Leigh granted and issued fully paid shares to its own employees on 31 May 2007. Normally share options issued
to employees would vest over a three year period, but these shares were given as a bonus because of the
company’s exceptional performance over the period. The shares in Leigh had a market value of $3 million
(one million ordinary shares of $1 at $3 per share) on 31 May 2007 and an average fair value of
$2·5 million (one million ordinary shares of $1 at $2·50 per share) for the year ended 31 May 2007. It is
expected that Leigh’s share price will rise to $6 per share over the next three years. (10 marks)
Required:
Discuss with suitable computations how the above share based transactions should be accounted for in the
financial statements of Leigh for the year ended 31 May 2007.
正确答案:
(a) The shares issued to the management of Hash by Leigh (three million ordinary shares of $1) for the purchase of the company
would not be accounted for under IFRS2 ‘Share-based payment’ but would be dealt with under IFRS3 ‘Business
Combinations’.
The cost of the business combination will be the total of the fair values of the consideration given by the acquirer plus any
attributable cost. In this case the shares of Leigh will be fair valued at $6 million with $3 million being shown as share capital
and $3million as share premium. However, the shares issued as contingent consideration may be accounted for under IFRS2.
The terms of the issuance of shares will need to be examined. Where part of the consideration may be reliant on uncertain
future events, and it is probable that the additional consideration is payable and can be measured reliably, then it is included
in the cost of the business consideration at the acquisition date. However, the question to be answered in the case of the
additional 5,000 shares per director is whether the shares are compensation or part of the purchase price. There is a need
to understand why the acquisition agreement includes a provision for a contingent payment. It is possible that the price paid
initially by Leigh was quite low and, therefore, this then represents a further purchase consideration. However, in this instance
the additional payment is linked to continuing employment and, therefore, it would be argued that because of the link between
the contingent consideration and continuing employment that it represents a compensation arrangement which should be
included within the scope of IFRS2.
Thus as there is a performance condition, (the performance condition will apply as it is not a market condition) the substance
of the agreement is that the shares are compensation, then they will be fair valued at the grant date and not when the shares
vest. Therefore, the share price of $2 per share will be used to give compensation of $50,000 (5 x 5,000 x $2). (Under
IFRS3, fair value is measured at the date the consideration is provided and discounted to presented value. No guidance is
provided on what the appropriate discount rate might be. Thus the fair value used would have been $3 per share at 31 May
2007.) The compensation will be charged to the income statement and included in equity.
The shares issued to the employees of Leigh will be accounted for under IFRS2. The issuance of fully paid shares will be
presumed to relate to past service. The normal vesting period for share options is irrelevant, as is the average fair value of the
shares during the period. The shares would be expensed at a value of $3 million with a corresponding increase in equity.
Goods or services acquired in a share based payment transaction should be recognised when they are received. In the case
of goods then this will be when this occurs. However, it is somewhat more difficult sometimes to determine when services
are received. In a case of goods the vesting date is not really relevant, however, it is highly relevant for employee services. If
shares are issued that vest immediately then there is a presumption that these are a consideration for past employee services. -
第3题:
(c) At 1 June 2006, Router held a 25% shareholding in a film distribution company, Wireless, a public limited
company. On 1 January 2007, Router sold a 15% holding in Wireless thus reducing its investment to a 10%
holding. Router no longer exercises significant influence over Wireless. Before the sale of the shares the net asset
value of Wireless on 1 January 2007 was $200 million and goodwill relating to the acquisition of Wireless was
$5 million. Router received $40 million for its sale of the 15% holding in Wireless. At 1 January 2007, the fair
value of the remaining investment in Wireless was $23 million and at 31 May 2007 the fair value was
$26 million. (6 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above items should be dealt with in the group financial statements of Router for the year ended
31 May 2007.Required:
Discuss how the above items should be dealt with in the group financial statements of Router for the year ended
31 May 2007.
正确答案:
(c) The investment in Wireless is currently accounted for using the equity method of accounting under IAS28 ‘Investments in
Associates’. On the sale of a 15% holding, the investment in Wireless will be accounted for in accordance with IAS39. Router
should recognise a gain on the sale of the holding in Wireless of $7 million (Working 1). The gain comprises the following:
(i) the difference between the sale proceeds and the proportion of the net assets sold and
(ii) the goodwill disposed of.
The total gain is shown in the income statement.
The remaining 10 per cent investment will be classified as an ‘available for sale’ financial asset or at ‘fair value through profit
or loss’ financial asset. Changes in fair value for these categories are reported in equity or in the income statement respectively.
At 1 January 2007, the investment will be recorded at fair value and a gain of $1 million $(23 – 22) recorded. At 31 May
2007 a further gain of $(26 – 23) million, i.e. $3 million will be recorded. In order for the investment to be categorised as
at fair value through profit or loss, certain conditions have to be fulfilled. An entity may use this designation when doing so
results in more relevant information by eliminating or significantly reducing a measurement or recognition inconsistency (an
‘accounting mismatch’) or where a group of financial assets and/or financial liabilities is managed and its performance is
evaluated on a fair value basis, in accordance with a documented risk management or investment strategy, and information
about the assets and/ or liabilities is provided internally to the entity’s key management personnel.
-
第4题:
(c) Comment on four reasons why the Managing Director of Quicklink Ltd might consider the acquisition of the
Celer Transport business to be a ‘good strategic move’ insofar as may be determined from the information
provided. (5 marks)
正确答案: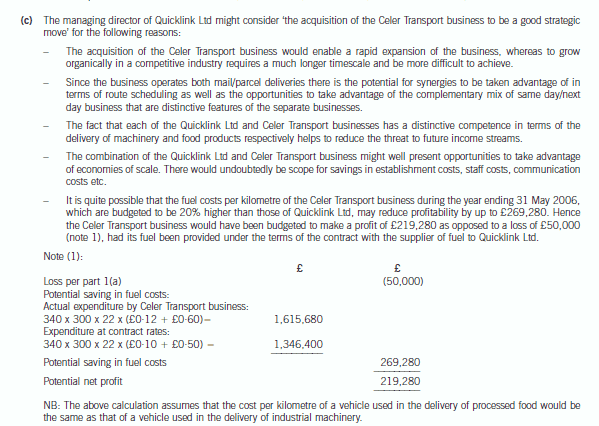
-
第5题:
(b) The marketing director of CTC has suggested the introduction of a new toy ‘Nellie the Elephant’ for which the
following estimated information is available:
1. Sales volumes and selling prices per unit
Year ending, 31 May 2009 2010 2011
Sales units (000) 80 180 100
Selling price per unit ($) 50 50 50
2. Nellie will generate a contribution to sales ratio of 50% throughout the three year period.
3. Product specific fixed overheads during the year ending 31 May 2009 are estimated to be $1·6 million. It
is anticipated that these fixed overheads would decrease by 10% per annum during each of the years ending
31 May 2010 and 31 May 2011.
4. Capital investment amounting to $3·9 million would be required in June 2008. The investment would have
no residual value at 31 May 2011.
5. Additional working capital of $500,000 would be required in June 2008. A further $200,000 would be
required on 31 May 2009. These amounts would be recovered in full at the end of the three year period.
6. The cost of capital is expected to be 12% per annum.
Assume all cash flows (other than where stated) arise at the end of the year.
Required:
(i) Determine whether the new product is viable purely on financial grounds. (4 marks)
正确答案:
-
第6题:
3 On 1 January 2007 Dovedale Ltd, a company with no subsidiaries, intends to purchase 65% of the ordinary share
capital of Hira Ltd from Belgrove Ltd. Belgrove Ltd currently owns 100% of the share capital of Hira Ltd and has no
other subsidiaries. All three companies have their head offices in the UK and are UK resident.
Hira Ltd had trading losses brought forward, as at 1 April 2006, of £18,600 and no income or gains against which
to offset losses in the year ended 31 March 2006. In the year ending 31 March 2007 the company expects to make
further tax adjusted trading losses of £55,000 before deduction of capital allowances, and to have no other income
or gains. The tax written down value of Hira Ltd’s plant and machinery as at 31 March 2006 was £96,000 and
there will be no fixed asset additions or disposals in the year ending 31 March 2007. In the year ending 31 March
2008 a small tax adjusted trading loss is anticipated. Hira Ltd will surrender the maximum possible trading losses
to Belgrove Ltd and Dovedale Ltd.
The tax adjusted trading profit of Dovedale Ltd for the year ending 31 March 2007 is expected to be £875,000 and
to continue at this level in the future. The profits chargeable to corporation tax of Belgrove Ltd are expected to be
£38,000 for the year ending 31 March 2007 and to increase in the future.
On 1 February 2007 Dovedale Ltd will sell a small office building to Hira Ltd for its market value of £234,000.
Dovedale Ltd purchased the building in March 2005 for £210,000. In October 2004 Dovedale Ltd sold a factory
for £277,450 making a capital gain of £84,217. A claim was made to roll over the gain on the sale of the factory
against the acquisition cost of the office building.
On 1 April 2007 Dovedale Ltd intends to acquire the whole of the ordinary share capital of Atapo Inc, an unquoted
company resident in the country of Morovia. Atapo Inc sells components to Dovedale Ltd as well as to other
companies in Morovia and around the world.
It is estimated that Atapo Inc will make a profit before tax of £160,000 in the year ending 31 March 2008 and will
pay a dividend to Dovedale Ltd of £105,000. It can be assumed that Atapo Inc’s taxable profits are equal to its profit
before tax. The rate of corporation tax in Morovia is 9%. There is a withholding tax of 3% on dividends paid to
non-Morovian resident shareholders. There is no double tax agreement between the UK and Morovia.
Required:
(a) Advise Belgrove Ltd of any capital gains that may arise as a result of the sale of the shares in Hira Ltd. You
are not required to calculate any capital gains in this part of the question. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(a) Capital gains that may arise on the sale by Belgrove Ltd of shares in Hira Ltd
Belgrove Ltd will realise a capital gain on the sale of the shares unless the substantial shareholding exemption applies. The
exemption will be given automatically provided all of the following conditions are satisfied.
– Belgrove Ltd has owned at least 10% of Hira Ltd for a minimum of 12 months during the two years prior to the sale.
– Belgrove Ltd is a trading company or a member of a trading group during that 12-month period and immediately after
the sale.
– Hira Ltd is a trading company or the holding company of a trading group during that 12-month period and immediately
after the sale.
Hira Ltd will no longer be in a capital gains group with Belgrove Ltd after the sale. Accordingly, a capital gain, known as a
degrouping charge, may arise in Hira Ltd. A degrouping charge will arise if, at the time it leaves the Belgrove Ltd group, Hira
Ltd owns any capital assets which were transferred to it at no gain, no loss within the previous six years by a member of the
Belgrove Ltd capital gains group. -
第7题:
(c) Calculate the expected corporation tax liability of Dovedale Ltd for the year ending 31 March 2007 on the
assumption that all available reliefs are claimed by Dovedale Ltd but that Hira Ltd will not claim any capital
allowances in that year. (4 marks)
正确答案:

-
第8题:
(ii) The use of the trading loss of Tethys Ltd for the year ending 31 December 2008; (6 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Tethys Ltd – Use of trading loss
– The two companies will not be in a group relief group as Saturn Ltd will not own 75% of Tethys Ltd.
– For a consortium to exist, 75% of the ordinary share capital of Tethys Ltd must be held by companies which each
hold at least 5%. Accordingly, Tethys Ltd will be a consortium company if the balance of its share capital is owned
by Clangers Ltd but not if it is owned by Edith Clanger.
– If Tethys Ltd qualifies as a consortium company: 65% of its trading losses in the period from 1 August 2008 to
31 December 2008 can be surrendered to Saturn Ltd, i.e. £21,667 (£80,000 x 5/12 x 65%).
– If Tethys Ltd does not qualify as a consortium company: none of its loss can be surrendered to Saturn Ltd.
– The acquisition of 65% of Tethys Ltd is a change in ownership of the company. If there is a major change in the
nature or conduct of the trade of Tethys Ltd within three years of 1 August 2008, the loss arising prior to that date
cannot be carried forward for relief in the future.
Further information required:
– Ownership of the balance of the share capital of Tethys Ltd. -
第9题:
4 (a) Explain the auditor’s responsibilities in respect of subsequent events. (5 marks)
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of the above matters for the auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Jinack Co for the year ended 30 September 2005 and, where appropriate, the year ending
30 September 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the matters.
正确答案:
4 JINACK CO
(a) Auditor’s responsibilities for subsequent events
■ Auditors must consider the effect of subsequent events on:
– the financial statements;
– the auditor’s report.
■ Subsequent events are all events occurring after a period end (i.e. reporting date) i.e.:
– events after the balance sheet date (as defined in IAS 10); and
– events after the financial statements have been authorised for issue.
Events occurring up to date of auditor’s report
■ The auditor is responsible for carrying out procedures designed to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence that all
events up to the date of the auditor’s report that may require adjustment of, or disclosure in, the financial statements
have been identified.
■ These procedures are in addition to those applied to specific transactions occurring after the period end that provide
audit evidence of period-end account balances (e.g. inventory cut-off and receipts from trade receivables). Such
procedures should ordinarily include:
– reviewing minutes of board/audit committee meetings;
– scrutinising latest interim financial statements/budgets/cash flows, etc;
– making/extending inquiries to legal advisors on litigation matters;
– inquiring of management whether any subsequent events have occurred that might affect the financial statements
(e.g. commitments entered into).
■ When the auditor becomes aware of events that materially affect the financial statements, the auditor must consider
whether they have been properly accounted for and adequately disclosed in the financial statements.
Facts discovered after the date of the auditor’s report but before financial statements are issued
Tutorial note: After the date of the auditor’s report it is management’s responsibility to inform. the auditor of facts which
may affect the financial statements.
■ If the auditor becomes aware of such facts which may materially affect the financial statements, the auditor:
– considers whether the financial statements need amendment;
– discusses the matter with management; and
– takes appropriate action (e.g. audit any amendments to the financial statements and issue a new auditor’s report).
■ If management does not amend the financial statements (where the auditor believes they need to be amended) and the
auditor’s report has not been released to the entity, the auditor should express a qualified opinion or an adverse opinion
(as appropriate).
■ If the auditor’s report has been released to the entity, the auditor must notify those charged with governance not to issue
the financial statements (and the auditor’s report thereon) to third parties.
Tutorial note: The auditor would seek legal advice if the financial statements and auditor’s report were subsequently issued.
Facts discovered after the financial statements have been issued
■ The auditor has no obligation to make any inquiry regarding financial statements that have been issued.
■ However, if the auditor becomes aware of a fact which existed at the date of the auditor’s report and which, if known
at that date, may have caused the auditor’s report to be modified, the auditor should:
– consider whether the financial statements need revision;
– discuss the matter with management; and
– take appropriate action (e.g. issuing a new report on revised financial statements). -
第10题:
(c) In October 2004, Volcan commenced the development of a site in a valley of ‘outstanding natural beauty’ on
which to build a retail ‘megastore’ and warehouse in late 2005. Local government planning permission for the
development, which was received in April 2005, requires that three 100-year-old trees within the valley be
preserved and the surrounding valley be restored in 2006. Additions to property, plant and equipment during
the year include $4·4 million for the estimated cost of site restoration. This estimate includes a provision of
$0·4 million for the relocation of the 100-year-old trees.
In March 2005 the trees were chopped down to make way for a car park. A fine of $20,000 per tree was paid
to the local government in May 2005. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Volcan for the year ended
31 March 2005.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
(c) Site restoration
(i) Matters
■ The provision for site restoration represents nearly 2·5% of total assets and is therefore material if it is not
warranted.
■ The estimated cost of restoring the site is a cost directly attributable to the initial measurement of the tangible fixed
asset to the extent that it is recognised as a provision under IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and
Contingent Assets’ (IAS 16 ‘Property, Plant and Equipment’).
■ A provision should not be recognised for site restoration unless it meets the definition of a liability, i.e:
– a present obligation;
– arising from past events;
– the settlement of which is expected to result in an outflow of resources embodying economic benefits.
■ The provision is overstated by nearly $0·34m since Volcan is not obliged to relocate the trees and de facto has
only an obligation of $60,000 as at 31 March 2005 (being the penalty for having felled them). When considered
in isolation, this overstatement is immaterial (representing only 0·2% of total assets and 3·6% of PBT).
■ It seems that even if there are local government regulations calling for site restoration there is no obligation unless
the penalties for non-compliance are prohibitive (unlike the fines for the trees).
■ It is unlikely that commencement of site development has given rise to a constructive obligation, since past actions
(disregarding the preservation of the trees) must dispel any expectation that Volcan will honour any pledge to
restore the valley.
■ Whether commencing development of the site, and destroying the trees, conflicts with any statement of socioenvironmental
responsibility in the annual report.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ A copy of the planning application and permission granted setting out the penalties for non-compliance.
■ Payment of $60,000 to local government in May 2005 agreed to the bank statement.
■ The present value calculation of the future cash expenditure making up the $4·0m provision.
Tutorial note: Evidence supporting the calculation of $0·4m is irrelevant as there is no liability to be provided for.
■ Agreement that the pre-tax discount rate used reflects current market assessments of the time value of money (as
for (a)).
■ Asset inspection at the site as at 31 March 2005.
■ Any contracts entered into which might confirm or dispute management’s intentions to restore the site. For
example, whether plant hire (bulldozers, etc) covers only the period over which the warehouse will be constructed
– or whether it extends to the period in which the valley would be ‘made good’. -
第11题:
(b) You are the audit manager of Johnston Co, a private company. The draft consolidated financial statements for
the year ended 31 March 2006 show profit before taxation of $10·5 million (2005 – $9·4 million) and total
assets of $55·2 million (2005 – $50·7 million).
Your firm was appointed auditor of Tiltman Co when Johnston Co acquired all the shares of Tiltman Co in March
2006. Tiltman’s draft financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2006 show profit before taxation of
$0·7 million (2005 – $1·7 million) and total assets of $16·1 million (2005 – $16·6 million). The auditor’s
report on the financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2005 was unmodified.
You are currently reviewing two matters that have been left for your attention on the audit working paper files for
the year ended 31 March 2006:
(i) In December 2004 Tiltman installed a new computer system that properly quantified an overvaluation of
inventory amounting to $2·7 million. This is being written off over three years.
(ii) In May 2006, Tiltman’s head office was relocated to Johnston’s premises as part of a restructuring.
Provisions for the resulting redundancies and non-cancellable lease payments amounting to $2·3 million
have been made in the financial statements of Tiltman for the year ended 31 March 2006.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of these two matters for your auditor’s reports on the financial
statements of Johnston Co and Tiltman Co for the year ended 31 March 2006. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Tiltman Co
Tiltman’s total assets at 31 March 2006 represent 29% (16·1/55·2 × 100) of Johnston’s total assets. The subsidiary is
therefore material to Johnston’s consolidated financial statements.
Tutorial note: Tiltman’s profit for the year is not relevant as the acquisition took place just before the year end and will
therefore have no impact on the consolidated income statement. Calculations of the effect on consolidated profit before
taxation are therefore inappropriate and will not be awarded marks.
(i) Inventory overvaluation
This should have been written off to the income statement in the year to 31 March 2005 and not spread over three
years (contrary to IAS 2 ‘Inventories’).
At 31 March 2006 inventory is overvalued by $0·9m. This represents all Tiltmans’s profit for the year and 5·6% of
total assets and is material. At 31 March 2005 inventory was materially overvalued by $1·8m ($1·7m reported profit
should have been a $0·1m loss).
Tutorial note: 1/3 of the overvaluation was written off in the prior period (i.e. year to 31 March 2005) instead of $2·7m.
That the prior period’s auditor’s report was unmodified means that the previous auditor concurred with an incorrect
accounting treatment (or otherwise gave an inappropriate audit opinion).
As the matter is material a prior period adjustment is required (IAS 8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting
Estimates and Errors’). $1·8m should be written off against opening reserves (i.e. restated as at 1 April 2005).
(ii) Restructuring provision
$2·3m expense has been charged to Tiltman’s profit and loss in arriving at a draft profit of $0·7m. This is very material.
(The provision represents 14·3% of Tiltman’s total assets and is material to the balance sheet date also.)
The provision for redundancies and onerous contracts should not have been made for the year ended 31 March 2006
unless there was a constructive obligation at the balance sheet date (IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and
Contingent Assets’). So, unless the main features of the restructuring plan had been announced to those affected (i.e.
redundancy notifications issued to employees), the provision should be reversed. However, it should then be disclosed
as a non-adjusting post balance sheet event (IAS 10 ‘Events After the Balance Sheet Date’).
Given the short time (less than one month) between acquisition and the balance sheet it is very possible that a
constructive obligation does not arise at the balance sheet date. The relocation in May was only part of a restructuring
(and could be the first evidence that Johnston’s management has started to implement a restructuring plan).
There is a risk that goodwill on consolidation of Tiltman may be overstated in Johnston’s consolidated financial
statements. To avoid the $2·3 expense having a significant effect on post-acquisition profit (which may be negligible
due to the short time between acquisition and year end), Johnston may have recognised it as a liability in the
determination of goodwill on acquisition.
However, the execution of Tiltman’s restructuring plan, though made for the year ended 31 March 2006, was conditional
upon its acquisition by Johnston. It does not therefore represent, immediately before the business combination, a
present obligation of Johnston. Nor is it a contingent liability of Johnston immediately before the combination. Therefore
Johnston cannot recognise a liability for Tiltman’s restructuring plans as part of allocating the cost of the combination
(IFRS 3 ‘Business Combinations’).
Tiltman’s auditor’s report
The following adjustments are required to the financial statements:
■ restructuring provision, $2·3m, eliminated;
■ adequate disclosure of relocation as a non-adjusting post balance sheet event;
■ current period inventory written down by $0·9m;
■ prior period inventory (and reserves) written down by $1·8m.
Profit for the year to 31 March 2006 should be $3·9m ($0·7 + $0·9 + $2·3).
If all these adjustments are made the auditor’s report should be unmodified. Otherwise, the auditor’s report should be
qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of disagreement. If none of the adjustments are made, the qualification should still be
‘except for’ as the matters are not pervasive.
Johnston’s auditor’s report
If Tiltman’s auditor’s report is unmodified (because the required adjustments are made) the auditor’s report of Johnston
should be similarly unmodified. As Tiltman is wholly-owned by Johnston there should be no problem getting the
adjustments made.
If no adjustments were made in Tiltman’s financial statements, adjustments could be made on consolidation, if
necessary, to avoid modification of the auditor’s report on Johnston’s financial statements.
The effect of these adjustments on Tiltman’s net assets is an increase of $1·4m. Goodwill arising on consolidation (if
any) would be reduced by $1·4m. The reduction in consolidated total assets required ($0·9m + $1·4m) is therefore
the same as the reduction in consolidated total liabilities (i.e. $2·3m). $2·3m is material (4·2% consolidated total
assets). If Tiltman’s financial statements are not adjusted and no adjustments are made on consolidation, the
consolidated financial position (balance sheet) should be qualified ‘except for’. The results of operations (i.e. profit for
the period) should be unqualified (if permitted in the jurisdiction in which Johnston reports).
Adjustment in respect of the inventory valuation may not be required as Johnston should have consolidated inventory
at fair value on acquisition. In this case, consolidated total liabilities should be reduced by $2·3m and goodwill arising
on consolidation (if any) reduced by $2·3m.
Tutorial note: The effect of any possible goodwill impairment has been ignored as the subsidiary has only just been
acquired and the balance sheet date is very close to the date of acquisition. -
第12题:
(ii) On 1 July 2006 Petrie introduced a 10-year warranty on all sales of its entire range of stainless steel
cookware. Sales of stainless steel cookware for the year ended 31 March 2007 totalled $18·2 million. The
notes to the financial statements disclose the following:
‘Since 1 July 2006, the company’s stainless steel cookware is guaranteed to be free from defects in
materials and workmanship under normal household use within a 10-year guarantee period. No provision
has been recognised as the amount of the obligation cannot be measured with sufficient reliability.’
(4 marks)
Your auditor’s report on the financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2006 was unmodified.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of these two matters for your auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Petrie Co for the year ended 31 March 2007.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the matters above.
正确答案:
(ii) 10-year guarantee
$18·2 million stainless steel cookware sales amount to 43·1% of revenue and are therefore material. However, the
guarantee was only introduced three months into the year, say in respect of $13·6 million (3/4 × 18·2 million) i.e.
approximately 32% of revenue.
The draft note disclosure could indicate that Petrie’s management believes that Petrie has a legal obligation in respect
of the guarantee, that is not remote and likely to be material (otherwise no disclosure would have been required).
A best estimate of the obligation amounting to 5% profit before tax (or more) is likely to be considered material, i.e.
$90,000 (or more). Therefore, if it is probable that 0·66% of sales made under guarantee will be returned for refund,
this would require a warranty provision that would be material.
Tutorial note: The return of 2/3% of sales over a 10-year period may well be probable.
Clearly there is a present obligation as a result of a past obligating event for sales made during the nine months to
31 March 2007. Although the likelihood of outflow under the guarantee is likely to be insignificant (even remote) it is
probable that some outflow will be needed to settle the class of such obligations.
The note in the financial statements is disclosing this matter as a contingent liability. This term encompasses liabilities
that do not meet the recognition criteria (e.g. of reliable measurement in accordance with IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent
Liabilities and Contingent Assets).
However, it is extremely rare that no reliable estimate can be made (IAS 37) – the use of estimates being essential to
the preparation of financial statements. Petrie’s management must make a best estimate of the cost of refunds/repairs
under guarantee taking into account, for example:
■ the proportion of sales during the nine months to 31 March 2007 that have been returned under guarantee at the
balance sheet date (and in the post balance sheet event period);
■ the average age of cookware showing a defect;
■ the expected cost of a replacement item (as a refund of replacement is more likely than a repair, say).
If management do not make a provision for the best estimate of the obligation the audit opinion should be qualified
‘except for’ non-compliance with IAS 37 (no provision made). The disclosure made in the note to the financial
statements, however detailed, is not a substitute for making the provision.
Tutorial note: No marks will be awarded for suggesting that an emphasis of matter of paragraph would be appropriate
(drawing attention to the matter more fully explained in the note).
Management’s claim that the obligation cannot be measured with sufficient reliability does not give rise to a limitation
on scope on the audit. The auditor has sufficient evidence of the non-compliance with IAS 37 and disagrees with it. -
第13题:
(c) Wader is reviewing the accounting treatment of its buildings. The company uses the ‘revaluation model’ for its
buildings. The buildings had originally cost $10 million on 1 June 2005 and had a useful economic life of
20 years. They are being depreciated on a straight line basis to a nil residual value. The buildings were revalued
downwards on 31 May 2006 to $8 million which was the buildings’ recoverable amount. At 31 May 2007 the
value of the buildings had risen to $11 million which is to be included in the financial statements. The company
is unsure how to treat the above events. (7 marks)
Required:
Discuss the accounting treatments of the above items in the financial statements for the year ended 31 May
2007.
Note: a discount rate of 5% should be used where necessary. Candidates should show suitable calculations where
necessary.
正确答案: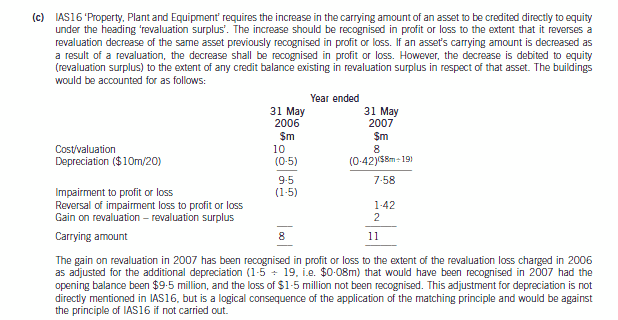
-
第14题:
(b) On 31 May 2007, Leigh purchased property, plant and equipment for $4 million. The supplier has agreed to
accept payment for the property, plant and equipment either in cash or in shares. The supplier can either choose
1·5 million shares of the company to be issued in six months time or to receive a cash payment in three months
time equivalent to the market value of 1·3 million shares. It is estimated that the share price will be $3·50 in
three months time and $4 in six months time.
Additionally, at 31 May 2007, one of the directors recently appointed to the board has been granted the right to
choose either 50,000 shares of Leigh or receive a cash payment equal to the current value of 40,000 shares at
the settlement date. This right has been granted because of the performance of the director during the year and
is unconditional at 31 May 2007. The settlement date is 1 July 2008 and the company estimates the fair value
of the share alternative is $2·50 per share at 31 May 2007. The share price of Leigh at 31 May 2007 is $3 per
share, and if the director chooses the share alternative, they must be kept for a period of four years. (9 marks)
Required:
Discuss with suitable computations how the above share based transactions should be accounted for in the
financial statements of Leigh for the year ended 31 May 2007.
正确答案:(b) Transactions that allow choice of settlement are accounted for as cash-settled to the extent that the entity has incurred a
liability (IFRS2 para 34). The share based transaction is treated as the issuance of a compound financial instrument. IFRS2
applies similar measurement principles to determine the value of the constituent parts of a compound instrument as that
required by IAS32 ‘Financial Instruments: Disclosure and Presentation’. The purchase of the property, plant and equipment
(PPE) and the grant to the director, both fall under this section of IFRS2 as the supplier and the director have a choice of
settlement. The fair value of the goods can be measured directly as regards the purchase of the PPE and therefore this fact
determines that the transaction is treated in a certain way. In the case of the director, the fair value of the service rendered
will be determined by the fair value of the equity instruments given and IFRS2 says that this type of share based transaction
should be dealt with in a certain way. Under IFRS2, if the fair value of the goods or services received can be measured directly
and easily then the equity element is determined by taking the fair value of the goods or services less the fair value of the
debt element of this instrument. The debt element is essentially the cash payment that will occur. If the fair value of the goods
or services is measured by reference to the fair value of the equity instruments given then the whole of the compound
instrument should be fair valued. The equity element becomes the difference between the fair value of the equity instruments
granted less the fair value of the debt component. It should take into account the fact that the counterparty must forfeit its
right to receive cash in order to receive the equity instrument.
When Leigh received the property, plant and equipment it should have recorded a liability of $4 million and an increase in
equity of $0·55 million being the difference between the value of the property, plant and equipment and the fair value of theliability. The fair value of the liability is the cash payment of $3·50 x 1·3 million shares, i.e. $4·55 million.
The accounting entry would be:
-
第15题:
Required:
(iii) A firm of consultants has offered to undertake a study on behalf of Envico Ltd which will provide perfect
information regarding seminar attendance during the forthcoming year.
Advise the management of Envico Ltd with regard to the maximum amount that they should pay to
consultants for perfect information regarding seminar attendance and comment briefly on the use of
perfect information in such decisions. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(iii) If attendance = 100 then management would opt for room size A which would produce a contribution of £832,000 x
0·2 = £166,400.
If attendance = 200 then management would opt for room size B which would produce a contribution of £2,163,200
x 0·5 = £1,081,600.
If attendance = 400 then management would opt for room size D which would produce a contribution of £6,656,000
x 0·3 = £1,996,800.
Therefore the expected value of perfect information would be the sum of the expected values of the three possible
outcomes which amounts to £3,244,800. Thus, if the information is correct then management should be willing to pay
up to £3,244,800 – £1,497,600 = £1,747,200 for the information. In practice, it is unlikely that perfect information
is obtainable. The management of Envico Ltd are really buying an information system that will provide them with a signal
which may prove to be correct or incorrect! For example, the consultants may predict that demand will be for 300
seminar places, however there still remains the fact that there is a likelihood of actual demand being for either 100,
200 or 400 seminar places. One should be mindful that imperfect information which may be, say only 75% reliable,
might still be worth obtaining. Other than when the value of imperfect and perfect information are equal to zero, the
value of perfect information will always be greater than the value of imperfect information. -
第16题:
(ii) The percentage change in revenue, total costs and net assets during the year ended 31 May 2008 that
would have been required in order to have achieved a target ROI of 20% by the Beetown centre. Your
answer should consider each of these three variables in isolation. State any assumptions that you make.
(6 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) The ROI of Beetown is currently 13·96%. In order to obtain an ROI of 20%, operating profit would need to increase to
(20% x $3,160,000) = $632,000, based on the current level of net assets. Three alternative ways in which a target
ROI of 20% could be achieved for the Beetown centre are as follows:
(1) Attempts could be made to increase revenue by attracting more clients while keeping invested capital and operating
profit per $ of revenue constant. Revenue would have to increase to $2,361,644, assuming that the current level
of profitability is maintained and fixed costs remain unchanged. The current rate of contribution to revenue is
$2,100,000 – $567,000 = $1,533,000/$2,100,000 = 73%. Operating profit needs to increase by $191,000
in order to achieve an ROI of 20%. Therefore, revenue needs to increase by $191,000/0·73 = $261,644 =
12·46%.
(2) Attempts could be made to decrease the level of operating costs by, for example, increasing the efficiency of
maintenance operations. This would have the effect of increasing operating profit per $ of revenue. This would
require that revenue and invested capital were kept constant. Total operating costs would need to fall by $191,000
in order to obtain an ROI of 20%. This represents a percentage decrease of 191,000/1,659,000 = 11·5%. If fixed
costs were truly fixed, then variable costs would need to fall to a level of $376,000, which represents a decrease
of 33·7%.
(3) Attempts could be made to decrease the net asset base of HFG by, for example, reducing debtor balances and/or
increasing creditor balances, while keeping turnover and operating profit per $ of revenue constant. Net assets
would need to fall to a level of ($441,000/0·2) = $2,205,000, which represents a percentage decrease
amounting to $3,160,000 – $2,205,000 = 955,000/3,160,000 = 30·2%. -
第17题:
(b) Calculate the corporation tax (CT) liabilities for Alantech Ltd, Boron Ltd and Bubble Ltd for the year ending
31 December 2004 on the assumption that loss reliefs are taken as early as possible. (9 marks)
正确答案:(b) Schedule D Case I calculation
The three companies form. a group for both group relief and capital gains purposes as all shareholdings pass the 75%
ownership test. The calculation of the corporation tax liabilities is as follows:
-
第18题:
(b) Explain by reference to Hira Ltd’s loss position why it may be beneficial for it not to claim any capital
allowances for the year ending 31 March 2007. Support your explanation with relevant calculations.
(6 marks)
正确答案:
(b) The advantage of Hira Ltd not claiming any capital allowances
In the year ending 31 March 2007 Hira Ltd expects to make a tax adjusted trading loss, before deduction of capital
allowances, of £55,000 and to surrender the maximum amount possible of trading losses to Belgrove Ltd and Dovedale Ltd.
For the first nine months of the year from 1 April 2006 to 31 December 2006 Hira Ltd is in a loss relief group with Belgrove
Ltd. The maximum surrender to Belgrove Ltd for this period is the lower of:
– the available loss of £41,250 (£55,000 x 9/12); and
– the profits chargeable to corporation tax of Belgrove of £28,500 (£38,000 x 9/12).
i.e. £28,500. This leaves losses of £12,750 (£41,250 – £28,500) unrelieved.
For the remaining three months from 1 January 2007 to 31 March 2007 Hira Ltd is a consortium company because at least
75% of its share capital is owned by companies, each of which own at least 5%. It can surrender £8,938 (£55,000 x 3/12
x 65%) to Dovedale Ltd and £4,812 (£55,000 x 3/12 x 35%) to Belgrove Ltd as both companies have sufficient taxable
profits to offset the losses. Accordingly, there are no losses remaining from the three-month period.
The unrelieved losses from the first nine months must be carried forward as Hira Ltd has no income or gains in that year or
the previous year. However, the losses cannot be carried forward beyond 1 January 2007 (the date of the change of
ownership of Hira Ltd) if there is a major change in the nature or conduct of the trade of Hira Ltd. Even if the losses can be
carried forward, the earliest year in which they can be relieved is the year ending 31 March 2009 as Hira Ltd is expected to
make a trading loss in the year ending 31 March 2008.
Any capital allowances claimed by Hira Ltd in the year ending 31 March 2007 would increase the tax adjusted trading loss
for that year and consequently the unrelieved losses arising in the first nine months.
If the capital allowances are not claimed, the whole of the tax written down value brought forward of £96,000 would be
carried forward to the year ending 31 March 2008 thus increasing the capital allowances and the tax adjusted trading loss,
for that year. By not claiming any capital allowances, Hira Ltd can effectively transfer a current period trading loss, which
would be created by capital allowances, of £24,000 (25% x £96,000) from the year ending 31 March 2007 to the following
year where it can be surrendered to the two consortium members. -
第19题:
3 Palm plc recently acquired 100% of the ordinary share capital of Nikau Ltd from Facet Ltd. Palm plc intends to use
Nikau Ltd to develop a new product range, under the name ‘Project Sabal’. Nikau Ltd owns shares in a non-UK
resident company, Date Inc.
The following information has been extracted from client files and from a meeting with the Finance Director of Palm
plc.
Palm plc:
– Has more than 40 wholly owned subsidiaries such that all group companies pay corporation tax at 30%.
– All group companies prepare accounts to 31 March.
– Acquired Nikau Ltd on 1 November 2007 from Facet Ltd, an unrelated company.
Nikau Ltd:
– UK resident company that manufactures domestic electronic appliances for sale in the European Union (EU).
– Large enterprise for the purposes of the enhanced relief available for research and development expenditure.
– Trading losses brought forward as at 1 April 2007 of £195,700.
– Budgeted taxable trading profit of £360,000 for the year ending 31 March 2008 before taking account of ‘Project
Sabal’.
– Dividend income of £38,200 will be received in the year ending 31 March 2008 in respect of the shares in Date
Inc.
‘Project Sabal’:
– Development of a range of electronic appliances, for sale in North America.
– Project Sabal will represent a significant advance in the technology of domestic appliances.
– Nikau Ltd will spend £70,000 on staffing costs and consumables researching and developing the necessary
technology between now and 31 March 2008. Further costs will be incurred in the following year.
– Sales to North America will commence in 2009 and are expected to generate significant profits from that year.
Shares in Date Inc:
– Nikau Ltd owns 35% of the ordinary share capital of Date Inc.
– The shares were purchased from Facet Ltd on 1 June 2003 for their market value of £338,000.
– The sale was a no gain, no loss transfer for the purposes of corporation tax.
– Facet Ltd purchased the shares in Date Inc on 1 March 1994 for £137,000.
Date Inc:
– A controlled foreign company resident in the country of Palladia.
– Annual chargeable profits arising out of property investment activities are approximately £120,000, of which
approximately £115,000 is distributed to its shareholders each year.
The tax system in Palladia:
– No taxes on income or capital profits.
– 4% withholding tax on dividends paid to shareholders resident outside Palladia.
Required:
(a) Prepare detailed explanatory notes, including relevant supporting calculations, on the effect of the following
issues on the amount of corporation tax payable by Nikau Ltd for the year ending 31 March 2008.
(i) The costs of developing ‘Project Sabal’ and the significant commercial changes to the company’s
activities arising out of its implementation. (8 marks)
正确答案:
(a) Nikau Ltd – Effect on corporation tax payable for the year ending 31 March 2008
(i) Project Sabal
Research and development expenditure
The expenditure incurred in respect of research and development will give rise to an enhanced deduction for the
purposes of computing the taxable trading profits of Nikau Ltd. The enhanced deduction is 125% of the qualifying
expenditure as Nikau Ltd is a large enterprise for this purpose.
The expenditure will reduce the profits chargeable to corporation tax of Nikau Ltd by £87,500 (£70,000 x 1·25) and
its corporation tax liability by £26,250 (£87,500 x 30%).
The budgeted expenditure will qualify for the enhanced deduction because it appears to satisfy the following conditions.
– It is likely to qualify as research and development expenditure within generally accepted accounting principles as
it will result in new technical knowledge and the production of a substantially improved device for use in the
industry.
– It exceeds £10,000 in Nikau Ltd’s accounting period.
– It relates to staff costs, consumable items or other qualifying expenditure as opposed to capital items.
– It will result in further trading activities for Nikau Ltd.
Use of brought forward trading losses
The development of products for the North American market is likely to represent a major change in the nature and
conduct of the trade of Nikau Ltd. This is because the company is developing new products and intends to sell them in
a new market. It is a major change as sales to North America are expected to generate significant additional profits.
Because this change will occur within three years of the change in the ownership of Nikau Ltd on 1 November 2007,
any trading losses arising prior to that date cannot be carried forward beyond that date.
Accordingly, the trading losses brought forward may only be offset against £158,958 ((£360,000 – £87,500) x 7/12)
of the company’s trading profits for the year. The remainder of the trading losses £36,742 (£195,700 – £158,958) will
be lost resulting in lost tax relief of £11,023 (£36,742 x 30%).
Tutorial note
The profits for the year ending 31 March 2008 will be apportioned to the periods pre and post 1 November 2007 on
either a time basis or some other basis that is just and reasonable. -
第20题:
(b) Using the information provided, state the financial statement risks arising and justify an appropriate audit
approach for Indigo Co for the year ending 31 December 2005. (14 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Financial statement risks
Assets
■ There is a very high risk that inventory could be materially overstated in the balance sheet (thereby overstating profit)
because:
? there is a high volume of metals (hence material);
? valuable metals are made more portable;
? subsidy gives an incentive to overstate purchases (and hence inventory);
? inventory may not exist due to lack of physical controls (e.g. aluminium can blow away);
? scrap metal in the stockyard may have zero net realisable value (e.g. iron is rusty and slow-moving);
? quantities per counts not attended by an auditor have increased by a third.
■ Inventory could be otherwise misstated (over or under) due to:
? the weighbridge being inaccurate;
? metal qualities being estimated;
? different metals being mixed up; and
? the lack of an independent expert to identify/measure/value metals.
■ Tangible non-current assets are understated as the parts of the furnaces that require replacement (the linings) are not
capitalised (and depreciated) as separate items but treated as repairs/maintenance/renewals and expensed.
■ Cash may be understated due to incomplete recording of sales.
■ Recorded cash will be overstated if it does not exist (e.g. if it has been stolen).
■ Trade receivables may be understated if cash receipts from credit customers have been misappropriated.
Liabilities
■ The provision for the replacement of the furnace linings is overstated by the amount provided in the current and previous
year (i.e. in its entirety).
Tutorial note: Last replacement was two years ago.
Income statement
■ Revenue will be understated in respect of unrecorded cash sales of salvaged metals and ‘clinker’.
■ Scrap metal purchases (for cash) are at risk of overstatement:
? to inflate the 15% subsidy;
? to conceal misappropriated cash.
■ The income subsidy will be overstated if quantities purchased are overstated and/or overvalued (on the quarterly returns)
to obtain the amount of the subsidy.
■ Cash receipts/payments that were recorded only in the cash book in November are at risk of being unrecorded (in the
absence of cash book postings for November), especially if they are of a ‘one-off’ nature.
Tutorial note: Cash purchases of scrap and sales of salvaged metal should be recorded elsewhere (i.e. in the manual
inventory records). However, a one-off expense (of a capital or revenue nature) could be omitted in the absence of
another record.
■ Expenditure is overstated in respect of the 25% provision for replacing the furnace linings. However, as depreciation
will be similarly understated (as the furnace linings have not been capitalised) there is no risk of material misstatement
to the income statement overall.
Disclosure risk
■ A going concern (‘failure’) risk may arise through the loss of:
? sales revenue (e.g. through misappropriation of salvaged metals and/or cash);
? the subsidy (e.g. if returns are prepared fraudulently);
? cash (e.g. if material amounts stolen).
Any significant doubts about going concern must be suitably disclosed in the notes to the financial statements.
Disclosure risk arises if the requirements of IAS 1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’ are not met.
■ Disclosure risk arises if contingent liabilities in connection with the dumping of ‘clinker’ (e.g. for fines and penalties) are
not adequately disclosed in accordance with IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets’.
Appropriate audit approach
Tutorial note: In explaining why AN audit approach is appropriate for Indigo it can be relevant to comment on the
unsuitability of other approaches.
■ A risk-based approach is suitable because:
? inherent risk is high at the entity and financial assertion levels;
? material errors are likely to arise in inventory where a high degree of subjectivity will be involved (regarding quality
of metals, quantities, net realisable value, etc);
? it directs the audit effort to inventory, purchases, income (sales and subsidy) and other risk areas (e.g. contingent
liabilities).
■ A systems-based/compliance approach is not suited to the risk areas identified because controls are lacking/ineffective
(e.g. over inventory and cash). Also, as the audit appointment was not more than three months ago and no interim
audit has been conducted (and the balance sheet date is only three weeks away) testing controls is likely to be less
efficient than a substantive approach.
■ A detailed substantive/balance sheet approach would be suitable to direct audit effort to the appropriate valuation of
assets (and liabilities) existing at balance sheet date. Principal audit work would include:
? attendance at a full physical inventory count at 31 December 2005;
? verifying cash at bank (through bank confirmation and reconciliation) and in hand (through physical count);
? confirming the accuracy of the quarterly returns to the local authority.
■ A cyclical approach/directional testing is unlikely to be suitable as cycles are incomplete. For example the purchases
cycle for metals is ‘purchase/cash’ rather than ‘purchase/payable/cash’ and there is no independent third party evidence
to compensate for that which would be available if there were trade payables (i.e. suppliers’ statements). Also the cycles
are inextricably inter-related to cash and inventory – amounts of which are subject to high inherent risk.
■ Analytical procedures may be of limited use for substantive purposes. Factors restricting the use of substantive analytical
procedures include:
? fluctuating margins (e.g. as many factors will influence the price at which scrap is purchased and subsequently
sold, when salvaged, sometime later);
? a lack of reliable/historic information on which to make comparisons. -
第21题:
(b) You are the audit manager of Jinack Co, a private limited liability company. You are currently reviewing two
matters that have been left for your attention on the audit working paper file for the year ended 30 September
2005:
(i) Jinack holds an extensive range of inventory and keeps perpetual inventory records. There was no full
physical inventory count at 30 September 2005 as a system of continuous stock checking is operated by
warehouse personnel under the supervision of an internal audit department.
A major systems failure in October 2005 caused the perpetual inventory records to be corrupted before the
year-end inventory position was determined. As data recovery procedures were found to be inadequate,
Jinack is reconstructing the year-end quantities through a physical count and ‘rollback’. The reconstruction
exercise is expected to be completed in January 2006. (6 marks)
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of the above matters for the auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Jinack Co for the year ended 30 September 2005 and, where appropriate, the year ending
30 September 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the matters.
正确答案:
(b) Implications for the auditor’s report
(i) Corruption of perpetual inventory records
■ The loss of data (of physical inventory quantities at the balance sheet date) gives rise to a limitation on scope.
Tutorial note: It is the records of the asset that have been destroyed – not the physical asset.
■ The systems failure in October 2005 is clearly a non-adjusting post balance sheet event (IAS 10). If it is material
(such that non-disclosure could influence the economic decisions of users) Jinack should disclose:
– the nature of the event (i.e. systems failure); and
– an estimate of its financial effect (i.e. the cost of disruption and reconstruction of data to the extent that it is
not covered by insurance).
Tutorial note: The event has no financial effect on the realisability of inventory, only on its measurement for the
purpose of reporting it in the financial statements.
■ If material this disclosure could be made in the context of explaining how inventory has been estimated at
30 September 2005 (see later). If such disclosure, that the auditor considers to be necessary, is not made, the
audit opinion should be qualified ‘except for’ disagreement (over lack of disclosure).
Tutorial note: Such qualifications are extremely rare since management should be persuaded to make necessary
disclosure in the notes to the financial statements rather than have users’ attention drawn to the matter through
a qualification of the audit opinion.
■ The limitation on scope of the auditor’s work has been imposed by circumstances. Jinack’s accounting records
(for inventory) are inadequate (non-existent) for the auditor to perform. tests on them.
■ An alternative procedure to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence of inventory quantities at a year end is
subsequent count and ‘rollback’. However, the extent of ‘roll back’ testing is limited as records are still under
reconstruction.
■ The auditor may be able to obtain sufficient evidence that there is no material misstatement through a combination
of procedures:
– testing management’s controls over counting inventory after the balance sheet date and recording inventory
movements (e.g. sales and goods received);
– reperforming the reconstruction for significant items on a sample basis;
– analytical procedures such as a review of profit margins by inventory category.
■ ‘An extensive range of inventory’ is clearly material. The matter (i.e. systems failure) is not however pervasive, as
only inventory is affected.
■ Unless the reconstruction is substantially completed (i.e. inventory items not accounted for are insignificant) the
auditor cannot determine what adjustment, if any, might be determined to be necessary. The auditor’s report
should then be modified, ‘except for’, limitation on scope.
■ However, if sufficient evidence is obtained the auditor’s report should be unmodified.
■ An ‘emphasis of matter’ paragraph would not be appropriate because this matter is not one of significant
uncertainty.
Tutorial note: An uncertainty in this context is a matter whose outcome depends on future actions or events not
under the direct control of Jinack.
2006
■ If the 2005 auditor’s report is qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of limitation on scope there are two possibilities for
the inventory figure as at 30 September 2005 determined on completion of the reconstruction exercise:
(1) it is not materially different from the inventory figure reported; or
(2) it is materially different.
■ In (1), with the limitation now removed, the need for qualification is removed and the 2006 auditor’s report would
be unmodified (in respect of this matter).
■ In (2) the opening position should be restated and the comparatives adjusted in accordance with IAS 8 ‘Accounting
Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors’. The 2006 auditor’s report would again be unmodified.
Tutorial note: If the error was not corrected in accordance with IAS 8 it would be a different matter and the
auditor’s report would be modified (‘except for’ qualification) disagreement on accounting treatment. -
第22题:
(b) You are an audit manager with specific responsibility for reviewing other information in documents containing
audited financial statements before your firm’s auditor’s report is signed. The financial statements of Hegas, a
privately-owned civil engineering company, show total assets of $120 million, revenue of $261 million, and profit
before tax of $9·2 million for the year ended 31 March 2005. Your review of the Annual Report has revealed
the following:
(i) The statement of changes in equity includes $4·5 million under a separate heading of ‘miscellaneous item’
which is described as ‘other difference not recognized in income’. There is no further reference to this
amount or ‘other difference’ elsewhere in the financial statements. However, the Management Report, which
is required by statute, is not audited. It discloses that ‘changes in shareholders’ equity not recognized in
income includes $4·5 million arising on the revaluation of investment properties’.
The notes to the financial statements state that the company has implemented IAS 40 ‘Investment Property’
for the first time in the year to 31 March 2005 and also that ‘the adoption of this standard did not have a
significant impact on Hegas’s financial position or its results of operations during 2005’.
(ii) The chairman’s statement asserts ‘Hegas has now achieved a position as one of the world’s largest
generators of hydro-electricity, with a dedicated commitment to accountable ethical professionalism’. Audit
working papers show that 14% of revenue was derived from hydro-electricity (2004: 12%). Publicly
available information shows that there are seven international suppliers of hydro-electricity in Africa alone,
which are all at least three times the size of Hegas in terms of both annual turnover and population supplied.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of the above matters for the auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Hegas for the year ended 31 March 2005. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Implications for the auditor’s report
(i) Management Report
■ $4·5 million represents 3·75% of total assets, 1·7% of revenue and 48·9% profit before tax. As this is material
by any criteria (exceeding all of 2% of total assets, 1/2% revenue and 5% PBT), the specific disclosure requirements
of IASs need to be met (IAS 1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’).
■ The Management Report discloses the amount and the reason for a material change in equity whereas the financial
statements do not show the reason for the change and suggest that it is immaterial. As the increase in equity
attributable to this adjustment is nearly half as much as that attributable to PBT there is a material inconsistency
between the Management Report and the audited financial statements.
■ Amendment to the Management Report is not required.
Tutorial note: Marks will be awarded for arguing, alternatively, that the Management Report disclosure needs to
be amended to clarify that the revaluation arises from the first time implementation.
■ Amendment to the financial statements is required because the disclosure is:
– incorrect – as, on first adoption of IAS 40, the fair value adjustment should be against the opening balance
of retained earnings; and
– inadequate – because it is being ‘supplemented’ by additional disclosure in a document which is not within
the scope of the audit of financial statements.
■ Whilst it is true that the adoption of IAS 40 did not have a significant impact on results of operations, Hegas’s
financial position has increased by nearly 4% in respect of the revaluation (to fair value) of just one asset category
(investment properties). As this is significant, the statement in the notes should be redrafted.
■ If the financial statements are not amended, the auditor’s report should be qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of
disagreement (non-compliance with IAS 40) as the matter is material but not pervasive. Additional disclosure
should also be given (e.g. that the ‘other difference’ is a fair value adjustment).
■ However, it is likely that when faced with the prospect of a qualified auditor’s report Hegas’s management will
rectify the financial statements so that an unmodified auditor’s report can be issued.
Tutorial note: Marks will be awarded for other relevant points e.g. citing IAS 8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in
Accounting Estimates and Errors’.
(ii) Chairman’s statement
Tutorial note: Hegas is privately-owned therefore IAS 14 ‘Segment Reporting’ does not apply and the proportion of
revenue attributable to hydro-electricity will not be required to be disclosed in the financial statements. However, credit
will be awarded for discussing the implications for the auditor’s report if it is regarded as a material inconsistency on
the assumption that segment revenue (or similar) is reported in the financial statements.
■ The assertion in the chairman’s statement, which does not fall within the scope of the audit of the financial
statements, claims two things, namely that the company:
(1) is ‘one of the world’s largest generators of hydro-electricity’; and
(2) has ‘a dedicated commitment to accountable ethical professionalism’.
■ To the extent that this information does not relate to matters disclosed in the financial statements it may give rise
to a material misstatement of fact. In particular, the first statement presents a misleading impression of the
company’s size. In misleading a user of the financial statements with this statement, the second statement is not
true (as it is not ethical or professional to mislead the reader and potentially undermine the credibility of the
financial statements).
■ The first statement is a material misstatement of fact because, for example:
– the company is privately-owned, and publicly-owned international/multi-nationals are larger;
– the company’s main activity is civil engineering not electricity generation (only 14% of revenue is derived from
HEP);
– as the company ranks at best eighth against African companies alone it ranks much lower globally.
■ Hegas should be asked to reconsider the wording of the chairman’s statement (i.e. removing these assertions) and
consult, as necessary, the company’s legal advisor.
■ If the statement is not changed there will be no grounds for qualification of the opinion on the audited financial
statements. The audit firm should therefore take legal advice on how the matter should be reported.
■ However, an emphasis of matter paragraph may be used to report on matters other than those affecting the audited
financial statements. For example, to explain the misstatement of fact if management refuses to make the
amendment.
Tutorial note: Marks will also be awarded for relevant comments about the chairman’s statement being perceived by
many readers to be subject to audit and therefore that the unfounded statement might undermine the credibility of the
financial statements. Shareholders tend to rely on the chairman’s statement, even though it is not regulated or audited,
because modern financial statements are so complex. -
第23题:
(b) You are the audit manager of Petrie Co, a private company, that retails kitchen utensils. The draft financial
statements for the year ended 31 March 2007 show revenue $42·2 million (2006 – $41·8 million), profit before
taxation of $1·8 million (2006 – $2·2 million) and total assets of $30·7 million (2006 – $23·4 million).
You are currently reviewing two matters that have been left for your attention on Petrie’s audit working paper file
for the year ended 31 March 2007:
(i) Petrie’s management board decided to revalue properties for the year ended 31 March 2007 that had
previously all been measured at depreciated cost. At the balance sheet date three properties had been
revalued by a total of $1·7 million. Another nine properties have since been revalued by $5·4 million. The
remaining three properties are expected to be revalued later in 2007. (5 marks)
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of these two matters for your auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Petrie Co for the year ended 31 March 2007.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the matters above.
正确答案:
(b) Implications for auditor’s report
(i) Selective revaluation of premises
The revaluations are clearly material to the balance sheet as $1·7 million and $5·4 million represent 5·5% and 17·6%
of total assets, respectively (and 23·1% in total). As the effects of the revaluation on line items in the financial statements
are clearly identified (e.g. revalued amount, depreciation, surplus in statement of changes in equity) the matter is not
pervasive.
The valuations of the nine properties after the year end provide additional evidence of conditions existing at the year end
and are therefore adjusting events per IAS 10 Events After the Balance Sheet Date.
Tutorial note: It is ‘now’ still less than three months after the year end so these valuations can reasonably be expected
to reflect year end values.
However, IAS 16 Property, Plant and Equipment does not permit the selective revaluation of assets thus the whole class
of premises would need to have been revalued for the year to 31 March 2007 to change the measurement basis for this
reporting period.
The revaluation exercise is incomplete. Unless the remaining three properties are revalued before the auditor’s report on
the financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2007 is signed off:
(1) the $7·1 revaluation made so far must be reversed to show all premises at depreciated cost as in previous years;
OR
(2) the auditor’s report would be qualified ‘except for’ disagreement regarding non-compliance with IAS 16.
When it is appropriate to adopt the revaluation model (e.g. next year) the change in accounting policy (from a cost model
to a revaluation model) should be accounted for in accordance with IAS 16 (i.e. as a revaluation).
Tutorial note: IAS 8 Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors does not apply to the initial
application of a policy to revalue assets in accordance with IAS 16.
Assuming the revaluation is written back, before giving an unmodified opinion, the auditor should consider why the three
properties were not revalued. In particular if there are any indicators of impairment (e.g. physical dilapidation) there
should be sufficient evidence on the working paper file to show that the carrying amount of these properties is not
materially greater than their recoverable amount (i.e. the higher of value in use and fair value less costs to sell).
If there is insufficient evidence to confirm that the three properties are not impaired (e.g. if the auditor was prevented
from inspecting the properties) the auditor’s report would be qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of limitation on scope.
If there is evidence of material impairment but management fail to write down the carrying amount to recoverable
amount the auditor’s report would be qualified ‘except for’ disagreement regarding non-compliance with IAS 36
Impairment of Assets.
