(iii) How items not dealt with by an IFRS for SMEs should be treated. (5 marks)
题目
(iii) How items not dealt with by an IFRS for SMEs should be treated. (5 marks)
相似考题
更多“(iii) How items not dealt with by an IFRS for SMEs should be treated. (5 marks)”相关问题
-
第1题:
3 The directors of Panel, a public limited company, are reviewing the procedures for the calculation of the deferred tax
provision for their company. They are quite surprised at the impact on the provision caused by changes in accounting
standards such as IFRS1 ‘First time adoption of International Financial Reporting Standards’ and IFRS2 ‘Share-based
Payment’. Panel is adopting International Financial Reporting Standards for the first time as at 31 October 2005 and
the directors are unsure how the deferred tax provision will be calculated in its financial statements ended on that
date including the opening provision at 1 November 2003.
Required:
(a) (i) Explain how changes in accounting standards are likely to have an impact on the provision for deferred
taxation under IAS12 ‘Income Taxes’. (5 marks)
正确答案:(a) (i) IAS12 ‘Income Taxes’ adopts a balance sheet approach to accounting for deferred taxation. The IAS adopts a full
provision approach to accounting for deferred taxation. It is assumed that the recovery of all assets and the settlement
of all liabilities have tax consequences and that these consequences can be estimated reliably and are unavoidable.
IFRS recognition criteria are generally different from those embodied in tax law, and thus ‘temporary’ differences will
arise which represent the difference between the carrying amount of an asset and liability and its basis for taxation
purposes (tax base). The principle is that a company will settle its liabilities and recover its assets over time and at that
point the tax consequences will crystallise.Thus a change in an accounting standard will often affect the carrying value of an asset or liability which in turn will
affect the amount of the temporary difference between the carrying value and the tax base. This in turn will affect the
amount of the deferred taxation provision which is the tax rate multiplied by the amount of the temporary differences(assuming a net liability for deferred tax.) -
第2题:
(iii) Tyre has entered into two new long lease property agreements for two major retail outlets. Annual rentals are paid
under these agreements. Tyre has had to pay a premium to enter into these agreements because of the outlets’
location. Tyre feels that the premiums paid are justifiable because of the increase in revenue that will occur
because of the outlets’ location. Tyre has analysed the leases and has decided that one is a finance lease and
one is an operating lease but the company is unsure as to how to treat this premium. (5 marks)
Required:
Advise the directors of Tyre on how to treat the above items in the financial statements for the year ended
31 May 2006.
(The mark allocation is shown against each of the above items)
正确答案:
(iii) Retail outlets
The two new long lease agreements have been separately classified as an operating lease and a finance lease. The lease
premium paid for a finance lease should be capitalised and recognised as an asset under the lease. IAS17 ‘Leases’ says that
costs identified as directly attributable to a finance lease are added to the amount recognised as an asset. It will be included
in the present value calculation of the minimum lease payments. The finance lease will be recognised at its fair value or if
lower the present value of the minimum lease payments. The premium will be depreciated as part of the asset’s value over
the shorter of the lease term and the asset’s useful life. Initially, a finance lease liability will be set up which is equal to the
value of the leased asset.
The operating lease premium will be spread over the lease term on a straight line basis unless some other method is more
representative. The premium will be effectively treated as a prepayment of rent and is amortised over the life of the agreement. -
第3题:
(b) Describe with suitable calculations how the goodwill arising on the acquisition of Briars will be dealt with in
the group financial statements and how the loan to Briars should be treated in the financial statements of
Briars for the year ended 31 May 2006. (9 marks)
正确答案:(b) IAS21 ‘The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates’ requires goodwill arising on the acquisition of a foreign operation
and fair value adjustments to acquired assets and liabilities to be treated as belonging to the foreign operation. They should
be expressed in the functional currency of the foreign operation and translated at the closing rate at each balance sheet date.
Effectively goodwill is treated as a foreign currency asset which is retranslated at the closing rate. In this case the goodwillarising on the acquisition of Briars would be treated as follows:
At 31 May 2006, the goodwill will be retranslated at 2·5 euros to the dollar to give a figure of $4·4 million. Therefore this
will be the figure for goodwill in the balance sheet and an exchange loss of $1·4 million recorded in equity (translation
reserve). The impairment of goodwill will be expensed in profit or loss to the value of $1·2 million. (The closing rate has been
used to translate the impairment; however, there may be an argument for using the average rate.)
The loan to Briars will effectively be classed as a financial liability measured at amortised cost. It is the default category for
financial liabilities that do not meet the definition of financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss. For most entities,
most financial liabilities will fall into this category. When a financial liability is recognised initially in the balance sheet, the
liability is measured at fair value. Fair value is the amount for which a liability can be settled, between knowledgeable, willing
parties in an arm’s length transaction. In other words, fair value is an actual or estimated transaction price on the reporting
date for a transaction taking place between unrelated parties that have adequate information about the asset or liability being
measured.
Since fair value is a market transaction price, on initial recognition fair value generally is assumed to equal the amount of
consideration paid or received for the financial asset or financial liability. Accordingly, IAS39 specifies that the best evidence
of the fair value of a financial instrument at initial recognition generally is the transaction price. However for longer-term
receivables or payables that do not pay interest or pay a below-market interest, IAS39 does require measurement initially at
the present value of the cash flows to be received or paid.
Thus in Briars financial statements the following entries will be made: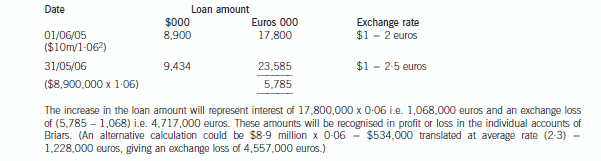
-
第4题:
(b) Discuss the nature of the following issues in developing IFRSs for SMEs.
(i) The purpose of the standards and the type of entity to whom they should apply. (7 marks)
正确答案:
(b) There are several issues which need to be addressed when developing IFRSs for SMEs:
(i) The purpose of the standards and type of entity
The principal aim of the development of an accounting framework for SMEs is to provide a framework which generates
relevant, reliable and useful information. The standards should provide high quality and understandable accounting
standards suitable for SMEs globally. Additionally they should meet the needs set out in (a) above. For example reduce
the financial reporting burden for SMEs. It is unlikely that one of the objectives would be to provide information for
management or meet the needs of the tax authorities as these bodies will have specific requirements which would be
difficult to meet in an accounting standard. However, it is likely that the standards for SMEs will be a modified version
of the full IFRSs and not an independently developed set of standards in order that they are based on the same
conceptual framework and will allow easier transition to full IFRS if the SME grows or decides to become a publicly listed
entity.
It is important to define the type of entity for which the standards are intended. Companies who have issued shares to
the public would be expected to use full IFRS. The question arises as to whether SME standards should apply to all
unlisted entities or just those listed entities below a certain size threshold. The difficulty with size criteria is that it would
have to apply worldwide and it would be very difficult to specify such criteria. Additionally some unlisted companies, for
example public utilities, have a reporting obligation that is equivalent to that of a listed company and should follow full
IFRS.
The main characteristic which distinguishes SMEs from other entities is the degree of public accountability. Thus the
definition of what constitutes an SME could revolve around those entities that do not have public accountability.
Indicators of public accountability will have to be developed. For example, a listed company or companies holding assets
in a fiduciary capacity (bank), or a public utility, or an entity with economic significance in its country. Thus all entities
that do not have public accountability may be considered as potential users of IFRSs for SMEs.
Size may not be the best way to determine what is an SME. SMEs could be defined by reference to ownership and themanagement of the entity. SMEs are not necessarily just smaller versions of public companies. -
第5题:
4 (a) Router, a public limited company operates in the entertainment industry. It recently agreed with a television
company to make a film which will be broadcast on the television company’s network. The fee agreed for the
film was $5 million with a further $100,000 to be paid every time the film is shown on the television company’s
channels. It is hoped that it will be shown on four occasions. The film was completed at a cost of $4 million and
delivered to the television company on 1 April 2007. The television company paid the fee of $5 million on
30 April 2007 but indicated that the film needed substantial editing before they were prepared to broadcast it,
the costs of which would be deducted from any future payments to Router. The directors of Router wish to
recognise the anticipated future income of $400,000 in the financial statements for the year ended 31 May
2007. (5 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above items should be dealt with in the group financial statements of Router for the year ended
31 May 2007.
正确答案:
(a) Under IAS18 ‘Revenue’, revenue on a service contract is recognised when the outcome of the transaction can be measured
reliably. For revenue arising from the rendering of services, provided that all of the following criteria are met, revenue should
be recognised by reference to the stage of completion of the transaction at the balance sheet date (the percentage-ofcompletion
method) (IAS18 para 20):
(a) the amount of revenue can be measured reliably;
(b) it is probable that the economic benefits will flow to the seller;
(c) the stage of completion at the balance sheet date can be measured reliably; and
(d) the costs incurred, or to be incurred, in respect of the transaction can be measured reliably.
When the above criteria are not met, revenue arising from the rendering of services should be recognised only to the extent
of the expenses recognised that are recoverable. Because the only revenue which can be measured reliably is the fee for
making the film ($5 million), this should therefore be recognised as revenue in the year to 31 May 2007 and matched against
the cost of the film of $4 million. Only when the television company shows the film should any further amounts of $100,000
be recognised as there is an outstanding ‘performance’ condition in the form. of the editing that needs to take place before the
television company will broadcast the film. The costs of the film should not be carried forward and matched against
anticipated future income unless they can be deemed to be an intangible asset under IAS 38 ‘Intangible Assets’. Additionally,
when assessing revenue to be recognised in future years, the costs of the editing and Router’s liability for these costs should
be assessed.
-
第6题:
(d) Additionally Router purchased 60% of the ordinary shares of a radio station, Playtime, a public limited company,
on 31 May 2007. The remaining 40% of the ordinary shares are owned by a competitor company who owns a
substantial number of warrants issued by Playtime which are currently exercisable. If these warrants are
exercised, they will result in Router only owning 35% of the voting shares of Playtime. (4 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above items should be dealt with in the group financial statements of Router for the year ended
31 May 2007.
正确答案:(d) IAS27 paragraph 14, ‘Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements’, states that warrants that have the potential to give
the holder voting power or reduce another party’s voting power over the financial and operating policies of the issuer should
be considered when existence of control is assessed. The warrants held by the competitor company, if exercised, would grant
that company control over Playtime. One party only can control Playtime and, therefore, the competitor company should
consolidate Playtime. In coming to this decision all the facts and circumstances that affect potential voting rights (except the
intention of management and the financial ability to exercise or convert) should be considered. It seems, however, that there
is a prima facie case for not consolidating Playtime but accounting for it under IAS28 or IAS39.
-
第7题:
(iii) A statement on the importance of confidentiality in the financing of the early stage working capital needs
and an explanation of how this conflicts with the duty of transparency in matters of corporate
governance. (6 marks)
Professional marks for layout, logical flow and persuasiveness of the statement. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(iii) Importance of confidentiality in the financing of the project and the normal duty of transparency.
I have been asked to include a statement in my remarks on the balance between our duty to be transparent whenever
possible and the need for discretion and confidentiality in some situations. In the case of our initial working capital needs
for the Giant Dam Project, the importance of confidentiality in financing is due to the potential for adverse publicity that
may arise for the lender. It is important that R&M have the project adequately financed, especially in the early stages
before the interim payments from the client become fully effective.
In general, of course, we at R&M attempt to observe the highest standards of corporate governance and this involves
adopting a default position of transparency rather than concealment wherever possible. We recognise that transparency
is important to underpin investor confidence and to provide investors with the information they need to make fund
allocation decisions.
Whilst it is normal to disclose the amount of debt we carry at any given point (on the balance sheet), it is rarely normal
practice to disclose the exact sources of those loans. In the case of the financing of initial working capital for the Giant
Dam Project, I’m sure you will realise that in this unique situation, disclosure of the lender’s identity could threaten the
progress of the project. For this reason we must resist any attempts to release this into the public domain. We are aware
of one pressure group that is actively seeking to discover this information in order to disrupt the project’s progress and
we shall be taking all internal measures necessary to ensure they do not obtain the information.
Thank you for listening. -
第8题:
(iii) Whether or not you agree with the statement of the marketing director in note (9) above. (5 marks)
Professional marks for appropriateness of format, style. and structure of the report. (4 marks)
正确答案:(iii) The marketing director is certainly correct in recognising that success is dependent on levels of service quality provided
by HFG to its clients. However, whilst the number of complaints is an important performance measure, it needs to be
used with caution. The nature of a complaint is, very often, far more indicative of the absence, or a lack, of service
quality. For example, the fact that 50 clients complained about having to wait for a longer time than they expected to
access gymnasium equipment is insignificant when compared to an accident arising from failure to maintain properly a
piece of gymnasium equipment. Moreover, the marketing director ought to be aware that the absolute number of
complaints may be misleading as much depends on the number of clients serviced during any given period. Thus, in
comparing the number of complaints received by the three centres then a relative measure of complaints received per
1,000 client days would be far more useful than the absolute number of complaints received.
The marketing director should also be advised that the number of complaints can give a misleading picture of the quality
of service provision since individuals have different levels of willingness to complain in similar situations.
The marketing director seems to accept the current level of complaints but is unwilling to accept any increase above this
level. This is not indicative of a quality-oriented organisation which would seek to reduce the number of complaints over
time via a programme of ‘continuous improvement’.
From the foregoing comments one can conclude that it would be myopic to focus on the number of client complaints
as being the only performance measure necessary to measure the quality of service provision. Other performance
measures which may indicate the level of service quality provided to clients by HFG are as follows:
– Staff responsiveness assumes critical significance in service industries. Hence the time taken to resolve client
queries by health centre staff is an important indicator of the level of service quality provided to clients.
– Staff appearance may be viewed as reflecting the image of the centres.
– The comfort of bedrooms and public rooms including facilities such as air-conditioning, tea/coffee-making and cold
drinks facilities, and office facilities such as e-mail, facsimile and photocopying.
– The availability of services such as the time taken to gain an appointment with a dietician or fitness consultant.
– The cleanliness of all areas within the centres will enhance the reputation of HFG. Conversely, unclean areas will
potentially deter clients from making repeat visits and/or recommendations to friends, colleagues etc.
– The presence of safety measures and the frequency of inspections made regarding gymnasium equipment within
the centres and compliance with legislation are of paramount importance in businesses like that of HFG.
– The achievement of target reductions in weight that have been agreed between centre consultants and clients.
(Other relevant measures would be acceptable.)
-
第9题:
(iii) State how your answer in (ii) would differ if the sale were to be delayed until August 2006. (3 marks)
正确答案:
-
第10题:
(iii) The extent to which Amy will be subject to income tax in the UK on her earnings in respect of duties
performed for Cutlass Inc and the travel costs paid for by that company. (5 marks)
Appropriateness of format and presentation of the report and the effectiveness with which its advice is
communicated. (2 marks)
Note:
You should assume that the income tax rates and allowances for the tax year 2006/07 and the corporation tax
rates and allowances for the financial year 2006 apply throughout this questio
正确答案:
(iii) Amy’s UK income tax position
Amy will remain UK resident and ordinarily resident as she is not leaving the UK permanently or for a complete tax year
under a full time contract of employment. Accordingly, she will continue to be subject to UK tax on her worldwide income
including her earnings in respect of the duties she performs for Cutlass Inc. The earnings from these duties will also be
taxable in Sharpenia as the income arises in that country.
The double tax treaty between the UK and Sharpenia will either exempt the employment income in one of the two
countries or give double tax relief for the tax paid in Sharpenia. The double tax relief will be the lower of the UK tax and
the Sharpenian tax on the income from Cutlass Inc.
Amy will not be subject to UK income tax on the expenses borne by Cutlass Inc in respect of her flights to and from
Sharpenia provided her journeys are wholly and exclusively for the purposes of performing her duties in Sharpenia.
The amounts paid by Cutlass Inc in respect of Amy’s family travelling to Sharpenia will be subject to UK income tax as
Amy will not be absent from the UK for a continuous period of at least 60 days. -
第11题:
向列表框中的最后填加一个新项目,正确的语句是()
AListBox1.Items.Add ("How are You")
BListBox1.Items.Insert ("How are You")
CListBox1.Items.Add (2, "How are You")
DListBox1.Items.Insert (2, "How are You")
A
略 -
第12题:
问答题TaskⅡ (20 marks) Write an article of no fewer than 120 words telling other students how you control stress about your courses.Take My Advice on How to Control Stress You should write the article on the answer sheet.正确答案:
Take My Advice on How to Control Stress As the competition between students increases, more and more students feel stressful about their courses. As far as I’m concerned, we can take the initiative to reduce the stress.
Firstly, make a plan for everyday study. For instance, you keep learning English for two hours every day, and within the two hours, you’ll learn 10 new words and read 2 articles. This way you can learn more than 1000 English words three months later and your reading ability will improve as well. Therefore, you don’t have to stay up late before the English examination. As long as you keep learning every day, you will find you are well prepared for the exams already.
Secondly, do something else to divert your mind before exams. For example, if you can play piano, play your favorite songs for one or two hours and you will feel relaxed.
To conclude, keep learning regularly and cultivate a hobby and you will find yourself relaxed about your courses.解析: 暂无解析 -
第13题:
(ii) Describe the basis for the calculation of the provision for deferred taxation on first time adoption of IFRS
including the provision in the opening IFRS balance sheet. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) A company has to apply IAS12 to the temporary differences between the carrying amount of the assets and liabilities in
its opening IFRS balance sheet (1 November 2003) and their tax bases (IFRS1 ‘First time adoption of IFRS’). The
deferred tax provision will be calculated using tax rates that have been enacted or substantially enacted by the balance
sheet date. The carrying values of the assets and liabilities at the opening balance sheet date will be determined by
reference to IFRS1 and will use the applicable IFRS in the first IFRS financial statements. Any adjustments required to
the deferred tax balance will be recognised directly in retained earnings.
Subsequent balance sheets (at 31 October 2004 and 31 October 2005) will be drawn up using the IFRS used in the
financial statements to 31 October 2005. The deferred tax provision will be adjusted as at 31 October 2004 and thenas at 31 October 2005 to reflect the temporary differences arising at those dates. -
第14题:
(iv) Tyre recently undertook a sales campaign whereby customers can obtain free car accessories, by presenting a
coupon, which has been included in an advertisement in a national newspaper, on the purchase of a vehicle.
The offer is valid for a limited time period from 1 January 2006 until 31 July 2006. The management are unsure
as to how to treat this offer in the financial statements for the year ended 31 May 2006.
(5 marks)
Required:
Advise the directors of Tyre on how to treat the above items in the financial statements for the year ended
31 May 2006.
(The mark allocation is shown against each of the above items)
正确答案:
(iv) Car accessories
An obligation should not be recognised for the coupons and no provision created under IAS37 ‘Provisions, Contingent
Liabilities and Contingent Assets’. A provision should only be recognised where there is an obligating event. There has to be
a present obligation (legal or constructive), the probability of an outflow of resources and the ability to make a reliable estimate
of the amount of the obligation. These conditions do not seem to have been met. Until the vehicle is purchased the
accessories cannot be obtained. That is the point at which the present obligation arises, the outflow of resources occurs and
an estimate of the amount of the obligation can be made. When the car is purchased, the accessories become part of the
cost of the sale. The revenue recognised will be the amount received from the customer (the sales price). The revenue will
not be grossed up to include the value of the accessories. -
第15题:
5 International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRSs) are primarily designed for use by publicly listed companies and
in many countries the majority of companies using IFRSs are listed companies. In other countries IFRSs are used as
national Generally Accepted Accounting Practices (GAAP) for all companies including unlisted entities. It has been
argued that the same IFRSs should be used by all entities or alternatively a different body of standards should apply
to small and medium entities (SMEs).
Required:
(a) Discuss whether there is a need to develop a set of IFRSs specifically for SMEs. (7 marks)
正确答案:
5 (a) IFRSs were not designed specifically for listed companies. However, in many countries the main users of IFRS are listed
companies. Currently SMEs who adopt IFRS have to follow all the requirements and not all SMEs take exception to applying
IFRS because it gives their financial statements enhanced reliability, relevance and credibility, and results in fair presentation.
However, other SMEs will wish to comply with IFRS for consistency and comparability purposes within their own country and
internationally but wish to apply simplified or different standards relevant to SMEs on the grounds that some IFRS are
unnecessarily demanding and some of the information produced is not used by users of SME financial statements.
The objectives of general purpose financial statements are basically appropriate for SMEs and publicly listed companies alike.
Therefore there is an argument that there is a need for only one set of IFRS which could be used nationally and internationally.
However, some SMEs require different financial information than listed companies. For example expanded related party
disclosures may be useful as SMEs often raise capital from shareholders, directors and suppliers. Additionally directors often
offer personal assets as security for bank finance.
The cost burden of applying the full set of IFRS may not be justified on the basis of user needs. The purpose and usage of
the financial statements, and the nature of the accounting expertise available to the SME, will not be the same as for listed
companies. These circumstances themselves may provide justification for a separate set of IFRSs for SMEs. A problem which
might arise is that users become familiar with IFRS as opposed to local GAAP thus creating a two tier system which could
lead to local GAAP being seen as an inferior or even a superior set of accounting rules.
One course of action would be for GAAP for SMEs to be developed on a national basis with IFRS being focused on accounting
for listed company activities. The main issue here would be that the practices developed for SMEs may not be consistent and
may lack comparability across national boundaries. This may mean that where SMEs wish to list their shares on a capital
market, the transition to IFRSs may be difficult. It seems that national standards setters are strongly supportive of thedevelopment of IFRSs for SMEs. -
第16题:
(ii) How existing standards could be modified to meet the needs of SMEs. (6 marks
正确答案:
(ii) The development of IFRSs for SMEs as a modification of existing IFRSs
Most SMEs have a narrower range of users than listed entities. The main groups of users are likely to be the owners,
suppliers and lenders. In deciding upon the modifications to make to IFRS, the needs of the users will need to be taken
into account as well as the costs and other burdens imposed upon SMEs by the IFRS. There will have to be a relaxation
of some of the measurement and recognition criteria in IFRS in order to achieve the reduction in the costs and the
burdens. Some disclosure requirements, such as segmental reports and earnings per share, are intended to meet the
needs of listed entities, or to assist users in making forecasts of the future. Users of financial statements of SMEs often
do not make such kinds of forecasts. Thus these disclosures may not be relevant to SMEs, and a review of all of the
disclosure requirements in IFRS will be required to assess their appropriateness for SMEs.
The difficulty is determining which information is relevant to SMEs without making the information disclosed
meaningless or too narrow/restricted. It may mean that measurement requirements of a complex nature may have to be
omitted.
There are, however, rational grounds for justifying different treatments because of the different nature of the entities and
the existence of established practices at the time of the issue of an IFRS.
-
第17题:
(c) At 1 June 2006, Router held a 25% shareholding in a film distribution company, Wireless, a public limited
company. On 1 January 2007, Router sold a 15% holding in Wireless thus reducing its investment to a 10%
holding. Router no longer exercises significant influence over Wireless. Before the sale of the shares the net asset
value of Wireless on 1 January 2007 was $200 million and goodwill relating to the acquisition of Wireless was
$5 million. Router received $40 million for its sale of the 15% holding in Wireless. At 1 January 2007, the fair
value of the remaining investment in Wireless was $23 million and at 31 May 2007 the fair value was
$26 million. (6 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above items should be dealt with in the group financial statements of Router for the year ended
31 May 2007.Required:
Discuss how the above items should be dealt with in the group financial statements of Router for the year ended
31 May 2007.
正确答案:
(c) The investment in Wireless is currently accounted for using the equity method of accounting under IAS28 ‘Investments in
Associates’. On the sale of a 15% holding, the investment in Wireless will be accounted for in accordance with IAS39. Router
should recognise a gain on the sale of the holding in Wireless of $7 million (Working 1). The gain comprises the following:
(i) the difference between the sale proceeds and the proportion of the net assets sold and
(ii) the goodwill disposed of.
The total gain is shown in the income statement.
The remaining 10 per cent investment will be classified as an ‘available for sale’ financial asset or at ‘fair value through profit
or loss’ financial asset. Changes in fair value for these categories are reported in equity or in the income statement respectively.
At 1 January 2007, the investment will be recorded at fair value and a gain of $1 million $(23 – 22) recorded. At 31 May
2007 a further gain of $(26 – 23) million, i.e. $3 million will be recorded. In order for the investment to be categorised as
at fair value through profit or loss, certain conditions have to be fulfilled. An entity may use this designation when doing so
results in more relevant information by eliminating or significantly reducing a measurement or recognition inconsistency (an
‘accounting mismatch’) or where a group of financial assets and/or financial liabilities is managed and its performance is
evaluated on a fair value basis, in accordance with a documented risk management or investment strategy, and information
about the assets and/ or liabilities is provided internally to the entity’s key management personnel.
-
第18题:
(b) Discuss how management’s judgement and the financial reporting infrastructure of a country can have a
significant impact on financial statements prepared under IFRS. (6 marks)
Appropriateness and quality of discussion. (2 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Management judgement may have a greater impact under IFRS than generally was the case under national GAAP. IFRS
utilises fair values extensively. Management have to use their judgement in selecting valuation methods and formulating
assumptions when dealing with such areas as onerous contracts, share-based payments, pensions, intangible assets acquired
in business combinations and impairment of assets. Differences in methods or assumptions can have a major impact on
amounts recognised in financial statements. IAS1 expects companies to disclose the sensitivity of carrying amounts to the
methods, assumptions and estimates underpinning their calculation where there is a significant risk of material adjustment
to their carrying amounts within the next financial year. Often management’s judgement is that there is no ‘significant risk’
and they often fail to disclose the degree of estimation or uncertainty and thus comparability is affected.
In addition to the IFRSs themselves, a sound financial reporting infrastructure is required. This implies effective corporate
governance practices, high quality auditing standards and practices, and an effective enforcement or oversight mechanism.
Therefore, consistency and comparability of IFRS financial statements will also depend on the robust nature of the other
elements of the financial reporting infrastructure.
Many preparers of financial statements will have been trained in national GAAP and may not have been trained in the
principles underlying IFRS and this can lead to unintended inconsistencies when implementing IFRS especially where the
accounting profession does not have a CPD requirement. Additionally where the regulatory system of a country is not well
developed, there may not be sufficient market information to utilise fair value measurements and thus this could lead to
hypothetical markets being created or the use of mathematical modelling which again can lead to inconsistencies because of
lack of experience in those countries of utilising these techniques. This problem applies to other assessments or estimates
relating to such things as actuarial valuations, investment property valuations, impairment testing, etc.
The transition to IFRS can bring significant improvement to the quality of financial performance and improve comparability
worldwide. However, there are issues still remaining which can lead to inconsistency and lack of comparability with those
financial statements. -
第19题:
(c) Explain how the introduction of an ERPS could impact on the role of management accountants. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(c) The introduction of ERPS has the potential to have a significant impact on the work of management accountants. The use of
ERPS causes a substantial reduction in the gathering and processing of routine information by management accountants.
Instead of relying on management accountants to provide them with information, managers are able to access the system to
obtain the information they require directly via a suitable electronic access medium.
ERPS integrate separate business functions in one system for the entire organisation and therefore co-ordination is usually
undertaken centrally by information management specialists who have a dual responsibility for the implementation and
operation of the system.
ERPS perform. routine tasks that not so long ago were seen as an essential part of the daily routines of management
accountants, for example perpetual inventory valuation. Therefore if the value of the role of management accountants is not
to be diminished then it is of necessity that management accountants should seek to expand their roles within their
organisations.
The management accountant will also control and audit the ERPS data input and analysis. Hence the implementation of ERPS
provides the management accountant with an opportunity to change the emphasis of their role from information gathering
and processing to that of the role of advisers and internal consultants to their organisations. This new role will require
management accountants to be involved in interpreting the information generated from the ERPS and to provide business
support for all levels of management within an organisation. -
第20题:
(iii) State any disadvantages to the relief in (i) that Sharon should be aware of, and identify and describe
another relief that she might use. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(iii) There are several disadvantages to incorporation relief as follows:
1. The requirement to transfer all business assets to the company means that it will not be possible to leave behind
certain assets, such as the property. This might lead to a double tax charge (sale of the property, then extraction
of sale proceeds) at a future date.
2. Taper relief is lost on the transfer of the business. This means that any disposal of chargeable business assets (the
shares) within two years of the incorporation will lead to a higher chargeable gain, as the full rate of business asset
taper relief will not be available.
3. The relief does not eliminate the tax charge, it merely defers the payment of tax until some future event. The
deferred gain will become taxable when Sharon sells her shares in the company.
Gift relief could be used instead of incorporation relief. The assets would be gifted to the company for no consideration,
with the base cost of the assets to the company being reduced by the deferred gain arising. Unlike incorporation relief,
gift relief applies to individual assets used in a trade and not to an entire business. This is particularly useful if the
transferor wishes to retain some assets, such as property outside the company, as not all assets have to be transferred.
Note: If the business was non-trading, incorporation relief would still be available, but gift relief would not. However,
this restriction should not apply to Sharon and gift relief remains an option in this case. -
第21题:
(iii) Explain the potential corporation tax (CT) implications of Tay Limited transferring work to Trent Limited,
and suggest how these can be minimised or eliminated. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(iii) Trading losses may not be carried forward where, within a period of three years there is both a change in the ownership
of a company and a major change in the nature or conduct of its trade. The transfer of work from Tay Limited to Trent
Limited is likely to constitute a major change in the nature or conduct of the latter’s trade. As a consequence, any tax
losses at the date of acquisition will be forfeited. Assuming losses were incurred uniformly in 2005, the tax losses at the
date of acquisition were £380,000 (300,000 + 2/3 x 120,000)). This is worth £114,000 assuming a corporation tax
rate of 30%.
Thus, Tay Limited should not consider transferring any trade to Trent Limited until after the third anniversary of the date
of the change of ownership i.e. not before 1 September 2008. As the trades are similar, there should be little problem
in transferring work from that date onwards. -
第22题:
There has been significant divergence in practice over recognition of revenue mainly because International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) have contained limited guidance in certain areas. The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) as a result of the joint project with the US Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) has issued IFRS 15 Revenue from Contracts with Customers. IFRS 15 sets out a five-step model, which applies to revenue earned from a contract with a customer with limited exceptions, regardless of the type of revenue transaction or the industry. Step one in the five-step model requires the identification of the contract with the customer and is critical for the purpose of applying the standard. The remaining four steps in the standard’s revenue recognition model are irrelevant if the contract does not fall within the scope of IFRS 15.
Required:
(a) (i) Discuss the criteria which must be met for a contract with a customer to fall within the scope of IFRS 15. (5 marks)
(ii) Discuss the four remaining steps which lead to revenue recognition after a contract has been identified as falling within the scope of IFRS 15. (8 marks)
(b) (i) Tang enters into a contract with a customer to sell an existing printing machine such that control of the printing machine vests with the customer in two years’ time. The contract has two payment options. The customer can pay $240,000 when the contract is signed or $300,000 in two years’ time when the customer gains control of the printing machine. The interest rate implicit in the contract is 11·8% in order to adjust for the risk involved in the delay in payment. However, Tang’s incremental borrowing rate is 5%. The customer paid $240,000 on 1 December 2014 when the contract was signed. (4 marks)
(ii) Tang enters into a contract on 1 December 2014 to construct a printing machine on a customer’s premises for a promised consideration of $1,500,000 with a bonus of $100,000 if the machine is completed within 24 months. At the inception of the contract, Tang correctly accounts for the promised bundle of goods and services as a single performance obligation in accordance with IFRS 15. At the inception of the contract, Tang expects the costs to be $800,000 and concludes that it is highly probable that a significant reversal in the amount of cumulative revenue recognised will occur. Completion of the printing machine is highly susceptible to factors outside of Tang’s influence, mainly issues with the supply of components.
At 30 November 2015, Tang has satisfied 65% of its performance obligation on the basis of costs incurred to date and concludes that the variable consideration is still constrained in accordance with IFRS 15. However, on 4 December 2015, the contract is modified with the result that the fixed consideration and expected costs increase by $110,000 and $60,000 respectively. The time allowable for achieving the bonus is extended by six months with the result that Tang concludes that it is highly probable that the bonus will be achieved and that the contract still remains a single performance obligation. Tang has an accounting year end of 30 November. (6 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above two contracts should be accounted for under IFRS 15. (In the case of (b)(i), the discussion should include the accounting treatment up to 30 November 2016 and in the case of (b)(ii), the accounting treatment up to 4 December 2015.)
Note: The mark allocation is shown against each of the items above.
Professional marks will be awarded in question 4 for clarity and quality of presentation. (2 marks)
正确答案:(a) (i) The definition of what constitutes a contract for the purpose of applying the standard is critical. The definition of contract is based on the definition of a contract in the USA and is similar to that in IAS 32 Financial Instruments: Presentation. A contract exists when an agreement between two or more parties creates enforceable rights and obligations between those parties. The agreement does not need to be in writing to be a contract but the decision as to whether a contractual right or obligation is enforceable is considered within the context of the relevant legal framework of a jurisdiction. Thus, whether a contract is enforceable will vary across jurisdictions. The performance obligation could include promises which result in a valid expectation that the entity will transfer goods or services to the customer even though those promises are not legally enforceable.
The first criteria set out in IFRS 15 is that the parties should have approved the contract and are committed to perform. their respective obligations. It would be questionable whether that contract is enforceable if this were not the case. In the case of oral or implied contracts, this may be difficult but all relevant facts and circumstances should be considered in assessing the parties’ commitment. The parties need not always be committed to fulfilling all of the obligations under a contract. IFRS 15 gives the example where a customer is required to purchase a minimum quantity of goods but past experience shows that the customer does not always do this and the other party does not enforce their contract rights. However, there needs to be evidence that the parties are substantially committed to the contract.
It is essential that each party’s rights and the payment terms can be identified regarding the goods or services to be transferred. This latter requirement is the key to determining the transaction price.
The contract must have commercial substance before revenue can be recognised, as without this requirement, entities might artificially inflate their revenue and it would be questionable whether the transaction has economic consequences. Further, it should be probable that the entity will collect the consideration due under the contract. An assessment of a customer’s credit risk is an important element in deciding whether a contract has validity but customer credit risk does not affect the measurement or presentation of revenue. The consideration may be different to the contract price because of discounts and bonus offerings. The entity should assess the ability of the customer to pay and the customer’s intention to pay the consideration. If a contract with a customer does not meet these criteria, the entity can continually re-assess the contract to determine whether it subsequently meets the criteria.
Two or more contracts which are entered into around the same time with the same customer may be combined and accounted for as a single contract, if they meet the specified criteria. The standard provides detailed requirements for contract modifications. A modification may be accounted for as a separate contract or a modification of the original contract, depending upon the circumstances of the case.
(ii) Step one in the five-step model requires the identification of the contract with the customer. After a contract has been determined to fall under IFRS 15, the following steps are required before revenue can be recognised.
Step two requires the identification of the separate performance obligations in the contract. This is often referred to as ’unbundling’, and is done at the beginning of a contract. The key factor in identifying a separate performance obligation is the distinctiveness of the good or service, or a bundle of goods or services. A good or service is distinct if the customer can benefit from the good or service on its own or together with other readily available resources and is separately identifiable from other elements of the contract. IFRS 15 requires a series of distinct goods or services which are substantially the same with the same pattern of transfer, to be regarded as a single performance obligation. A good or service, which has been delivered, may not be distinct if it cannot be used without another good or service which has not yet been delivered. Similarly, goods or services which are not distinct should be combined with other goods or services until the entity identifies a bundle of goods or services which is distinct. IFRS 15 provides indicators rather than criteria to determine when a good or service is distinct within the context of the contract. This allows management to apply judgement to determine the separate performance obligations which best reflect the economic substance of a transaction.
Step three requires the entity to determine the transaction price, which is the amount of consideration which an entity expects to be entitled to in exchange for the promised goods or services. This amount excludes amounts collected on behalf of a third party, for example, government taxes. An entity must determine the amount of consideration to which it expects to be entitled in order to recognise revenue.
The transaction price might include variable or contingent consideration. Variable consideration should be estimated as either the expected value or the most likely amount. Management should use the approach which it expects will best predict the amount of consideration and should be applied consistently throughout the contract. An entity can only include variable consideration in the transaction price to the extent that it is highly probable that a subsequent change in the estimated variable consideration will not result in a significant revenue reversal. If it is not appropriate to include all of the variable consideration in the transaction price, the entity should assess whether it should include part of the variable consideration. However, this latter amount still has to pass the ’revenue reversal’ test.
Additionally, an entity should estimate the transaction price taking into account non-cash consideration, consideration payable to the customer and the time value of money if a significant financing component is present. The latter is not required if the time period between the transfer of goods or services and payment is less than one year. If an entity anticipates that it may ultimately accept an amount lower than that initially promised in the contract due to, for example, past experience of discounts given, then revenue would be estimated at the lower amount with the collectability of that lower amount being assessed. Subsequently, if revenue already recognised is not collectable, impairment losses should be taken to profit or loss.
Step four requires the allocation of the transaction price to the separate performance obligations. The allocation is based on the relative standalone selling prices of the goods or services promised and is made at inception of the contract. It is not adjusted to reflect subsequent changes in the standalone selling prices of those goods or services. The best evidence of standalone selling price is the observable price of a good or service when the entity sells that good or service separately. If that is not available, an estimate is made by using an approach which maximises the use of observable inputs. For example, expected cost plus an appropriate margin or the assessment of market prices for similar goods or services adjusted for entity-specific costs and margins or in limited circumstances a residual approach. When a contract contains more than one distinct performance obligation, an entity allocates the transaction price to each distinct performance obligation on the basis of the standalone selling price.
Where the transaction price includes a variable amount and discounts, consideration needs to be given as to whether these amounts relate to all or only some of the performance obligations in the contract. Discounts and variable consideration will typically be allocated proportionately to all of the performance obligations in the contract. However, if certain conditions are met, they can be allocated to one or more separate performance obligations.
Step five requires revenue to be recognised as each performance obligation is satisfied. An entity satisfies a performance obligation by transferring control of a promised good or service to the customer, which could occur over time or at a point in time. The definition of control includes the ability to prevent others from directing the use of and obtaining the benefits from the asset. A performance obligation is satisfied at a point in time unless it meets one of three criteria set out in IFRS 15. Revenue is recognised in line with the pattern of transfer.
If an entity does not satisfy its performance obligation over time, it satisfies it at a point in time and revenue will be recognised when control is passed at that point in time. Factors which may indicate the passing of control include the present right to payment for the asset or the customer has legal title to the asset or the entity has transferred physical possession of the asset.
(b) (i) The contract contains a significant financing component because of the length of time between when the customer pays for the asset and when Tang transfers the asset to the customer, as well as the prevailing interest rates in the market. A contract with a customer which has a significant financing component should be separated into a revenue component (for the notional cash sales price) and a loan component. Consequently, the accounting for a sale arising from a contract which has a significant financing component should be comparable to the accounting for a loan with the same features. An entity should use the discount rate which would be reflected in a separate financing transaction between the entity and its customer at contract inception. The interest rate implicit in the transaction may be different from the rate to be used to discount the cash flows, which should be the entity’s incremental borrowing rate. IFRS 15 would therefore dictate that the rate which should be used in adjusting the promised consideration is 5%, which is the entity’s incremental borrowing rate, and not 11·8%.
Tang would account for the significant financing component as follows:
Recognise a contract liability for the $240,000 payment received on 1 December 2014 at the contract inception:
Dr Cash $240,000
Cr Contract liability $240,000During the two years from contract inception (1 December 2014) until the transfer of the printing machine, Tang adjusts the amount of consideration and accretes the contract liability by recognising interest on $240,000 at 5% for two years.
Year to 30 November 2015
Dr Interest expense $12,000
Cr Contract liability $12,000Contract liability would stand at $252,000 at 30 November 2015.
Year to 30 November 2016
Dr Interest expense $12,600
Cr Contract liability $12,600Recognition of contract revenue on transfer of printing machine at 30 November 2016 of $264,600 by debiting contract liability and crediting revenue with this amount.
(ii) Tang accounts for the promised bundle of goods and services as a single performance obligation satisfied over time in accordance with IFRS 15. At the inception of the contract, Tang expects the following:
Transaction price $1,500,000
Expected costs $800,000
Expected profit (46·7%) $700,000At contract inception, Tang excludes the $100,000 bonus from the transaction price because it cannot conclude that it is highly probable that a significant reversal in the amount of cumulative revenue recognised will not occur. Completion of the printing machine is highly susceptible to factors outside the entity’s influence. By the end of the first year, the entity has satisfied 65% of its performance obligation on the basis of costs incurred to date. Costs incurred to date are therefore $520,000 and Tang reassesses the variable consideration and concludes that the amount is still constrained. Therefore at 30 November 2015, the following would be recognised:
Revenue $975,000
Costs $520,000
Gross profit $455,000However, on 4 December 2015, the contract is modified. As a result, the fixed consideration and expected costs increase by $110,000 and $60,000, respectively. The total potential consideration after the modification is $1,710,000 which is $1,610,000 fixed consideration + $100,000 completion bonus. In addition, the allowable time for achieving the bonus is extended by six months with the result that Tang concludes that it is highly probable that including the bonus in the transaction price will not result in a significant reversal in the amount of cumulative revenue recognised in accordance with IFRS 15. Therefore the bonus of $100,000 can be included in the transaction price. Tang also concludes that the contract remains a single performance obligation. Thus,Tang accounts for the contract modification as if it were part of the original contract. Therefore, Tang updates its estimates of costs and revenue as follows:
Tang has satisfied 60·5% of its performance obligation ($520,000 actual costs incurred compared to $860,000 total expected costs). The entity recognises additional revenue of $59,550 [(60·5% of $1,710,000) – $975,000 revenue recognised to date] at the date of the modification as a cumulative catch-up adjustment. As the contract amendment took place after the year end, the additional revenue would not be treated as an adjusting event.
-
第23题:
向列表框中的最后填加一个新项目,正确的语句是()
- A、ListBox1.Items.Add ("How are You")
- B、ListBox1.Items.Insert ("How are You")
- C、ListBox1.Items.Add (2, "How are You")
- D、ListBox1.Items.Insert (2, "How are You")
正确答案:A
