当执行下面的程序时,如果输入ABC,则输出结果是______。 #include "stdio.h" #include "string.h" main() { char ss[10]="12345"; gets(ss);strcat(ss,"6789"); printf("%s\n",ss); }A.ABC6789B.ABC67C.12345ABC6D.ABC456789
题目
当执行下面的程序时,如果输入ABC,则输出结果是______。 #include "stdio.h" #include "string.h" main() { char ss[10]="12345"; gets(ss);strcat(ss,"6789"); printf("%s\n",ss); }
A.ABC6789
B.ABC67
C.12345ABC6
D.ABC456789
相似考题
参考答案和解析
解析:sdtrcat(str1,str2)合并字符串函数的作用是把str2所指字符串的内容连接到str1字符串的后面,自动删去str1原来串中的'\0'。为了进行这项操作,要求str1所指的字符串后面有足够的空间来容纳str2所指字符串中的内容。函数值为str1所指第一个字符的地址。
更多“当执行下面的程序时,如果输入ABC,则输出结果是______。#include"stdio.h"#include"string.h"main( ”相关问题
-
第1题:
当执行下面的程序时,如果输入ABC,输出结果是 ______。includeinclude voi 当执行下面的程序时,如果输入ABC,输出结果是 ______。 #include<iostream.h> #include<string.h> void main(){ char ss[10]=“XYZWV”; cin>>ss; strcat(ss,”DEFG”); cout<<ss; }
A.ABCDEFG
B.ABCEF
C.XYZVO/ABCX
D.ABCXYZWVD
正确答案:A
-
第2题:
当执行以下程序时,输入1234567890<回车>,则其中while循环体将执行【 】次。includemain() 当执行以下程序时,输入1234567890<回车>,则其中while循环体将执行【 】次。
include<stdio.h>
main()
{ char ch;
while((ch=getchar())=='0')prinft("");
}
正确答案:×
0 解析:通过getchar()函数来取得从键盘输入的数据,再判断其是否是字符‘0’,如果是,则执行一次循环,因为从键盘输入的1234567890都是整型数,不是字符.所以while循环执行的条件始终不成立,循环体执行的次数为0。 -
第3题:
若执行下面的程序时,从键盘上输入5和2,则输出结果是includevoid main( ){int a,b,k 若执行下面的程序时,从键盘上输入5和2,则输出结果是 #include<iostream.h> void main( ) { int a,b,k; cin >> a >> b; k=a; if(a<b) k=a%b; else k=b%a; cout < < k < < endl;}
A.5
B.3
C.2
D.0
正确答案:C
解析:本题考查简单的if…else语句。先执行条件if(ab) ,显然不成立,则执行else语句。 -
第4题:
以下程序的输出结果是()。includeinclude main(){char str[12]={'s','t','r 以下程序的输出结果是( )。 #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> main() { char str[12]={'s','t','r','i','n','g'}; printf("%d\n",strlen(str) ); }
A.6
B.7
C.11
D.12
正确答案:A
解析:本题考查求字符串的长度。程序中定义字符串str时中请了12个字节的内存空间,对它赋初值后,函数strlen在求串长度时,以'\0'作为串结束符,所以,strlen(str)的值为6。 -
第5题:
若执行下述程序时,从键盘输入的数据是3和6,则程序的输出结果是()。includevoid main(){ 若执行下述程序时,从键盘输入的数据是3和6,则程序的输出结果是( )。 #include <stdio.h> void main() {int x,y,z; scanf("%d%d",&X,&y); z = y + x; if (x<y) z = y + x; printf("%d",z); }
A.9
B.3
C.0
D.有语法错误
正确答案:B
解析:变量x得到数据3,变量y得到数据6。z=6+3=9。xy即36关系表达式的值为1,执行z=y-x=6-3=3。最后输出z的值为3。 -
第6题:
若执行下列的程序时,从键盘上输入1和2,则输出结果是( )。 includemain(){ int a,b,s;s 若执行下列的程序时,从键盘上输入1和2,则输出结果是( )。 #include<stdio.h> main() { int a,b,s; scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); s=a; if(a<b) s=b; s=s*s; printf("%d\n",s); }
A.1
B.4
C.2
D.9
正确答案:B
解析:本题考查if语句。scanf函数通过键盘读入a、b的值,a=1,b=2。第一个if语句,先判断条件,发现ab条件成立,则s=b=2, s=s*s=4。 -
第7题:
下列程序的输出结果是()。 includeinclude main() {char a[]="\n123\\";pr 下列程序的输出结果是( )。 #include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> main() { char a[]="\n123\\"; printf ("%d,%d\n",strlen(a),sizeof(a)); }
A.5,6
B.5,5
C.6,6
D.6,5
正确答案:A
解析:转义字符'\n'表示换行,'\\'表示反斜杠,函数strlen()是计算字符串的长度,不包括文件结束标志('\0'),函数sizeof()统计字符串所占的字节数。 -
第8题:
执行下列程序时输入12345678,程序的运行结果是______。 includemain() { int x,y; sca 执行下列程序时输入12345678,程序的运行结果是______。 #include<stdio.h> main() { int x,y; scanf("%2d%2d"); printf("%d\n",x+y); }
A.17
B.46
C.15
D.9
正确答案:B
-
第9题:
以下程序 includeinclude main() { char*p1="abc",*p2="ABC",str[50]="xy 以下程序 #include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> main() { char*p1="abc",*p2="ABC",str[50]="xyz"; strcpy(ar+2,strcat(p1,p2)); printf("%s\n",str); } 的输出是______。
A.xyzabcABC
B.zabeABC
C.yzabcABC
D.xyabcABC
正确答案:D
解析:strcat(p1,p2)将字符串abcABC防到了*p1所指向的存储单元中:strcpy在本题将abcABC复制到str+2所指向的存储单元中,即覆盖原str数组中的字符z及其后的所有字符,故str的值为“xyabcABC”。 -
第10题:
当执行下面程序且输入a boy时,输出的结果是______。includeinclude main(){c 当执行下面程序且输入a boy时,输出的结果是______。 #include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> main() { char ss[81]="A BOY",hh[81],*pt; scanf("%s",hh); pt=strcat(ss,hh); puts(pt); printf("%s\n",hh); }
A.A BOY a a
B.A BOY a boy a boy
C.A BOY a boy a
D.A BOY a boy a boy
正确答案:A
解析:对于函数strcat(ss,hh),把字符串hh(若遇空格,舍去后面的部分,并重新赋给hh)连至字符串ss的后面。 -
第11题:
执行以下程序时输入1234567,则输出结果是【 】。 include main(){int a=1,b; scanf("%2 执行以下程序时输入1234567<CR>,则输出结果是【 】。
include <stdio.h>
main()
{ int a=1,b;
scanf("%2d%2d",&a,&b); prinff("%d %dhn",a,b);
}
正确答案:12 34
12 34 解析:本题考查的知识点是:Scanf()函数。 scanf()是标准输入函数;其第1个参数为格式控制字符串。其中“%2d”表示读入一个2个字符宽的整数。所以本题代码将连续读入2个2字符宽的整数分别存到变量a和b中。根据题目要求,输入数据1234567CR>,则scanf()读入的两个整数分别为 12和34,故输出结果为12 34。 -
第12题:
单选题当执行下面的程序时,如果输入ABC,则输出结果是()。 #include "stdio.h" #include "string.h" main() { char ss[10]="12345"; gets(ss); strcat(ss,"6789"); printf("%s/n",ss); }AABC6789
BABC67
C12345ABC6
DABC456789
正确答案: A解析: 暂无解析 -
第13题:
当执行下面的程序时,如果输入ABC,则输出结果是 ( ) includeinclude 当执行下面的程序时,如果输入ABC,则输出结果是 ( ) # include<stdio.h> # include<string.h> main( ) { char ss [10] ="12345"; gets(ss);strcat(ss"6789");printf("%s\n",ss); }
A.ABC6789
B.ABC67
C.12345ABC6
D.ABC456789
正确答案:A
-
第14题:
当执行下面的程序时,如果输入“ABC”,则输出结果是_____。#include"stdio.h"#include"string.h"main(){ char ss[10]="1,2,3,4,5"; gets(ss);strcat(ss,"6789");printf("%s\n",ss);}
A.ABC6789
B.ABC67
C.12345ABC6
D.ABC456789
正确答案:A
-
第15题:
若执行下列程序时从键盘上输入2,则输出结果是()。 inclUdemain() {int a; scanf("%d", 若执行下列程序时从键盘上输入2,则输出结果是( )。
#inclUde<stdio.h>
main()
{int a;
scanf("%d",&A);
if(a++<3)
printf("%d\n",A);
else printf("%d\n",a--);
}
A.1
B.3
C.2
D.4
正确答案:B
解析:本题考查if else语句。程序中首先使用函数scanf()通过键盘读入a的值,并通过第1个if语句,先判断条件,取a的值2和3比较,然后将a的值加1,发现条件成立,执行下列的printf语句,输出a的值3。 -
第16题:
下列程序的输出结果是( )。 includeinclude"string.h" void main() {char a[]="He 下列程序的输出结果是( )。 #include<iostream.h> #include"string.h" void main() {char a[]="Hello Test",b[]="Test"; strcpy(a,b); cout<<a<<end1; }
A.Hello
B.Test
C.Hello Test
D.Hello Test HelloTest
正确答案:B
解析:程序中首先定义字符数a和b,其值分别为“Hello Test”和“Test”。然后利用strcpy复制函数,将b的值复制给a,所以输出a的结果为Test。 -
第17题:
当执行下面的程序时,如果输入ABC,则输出结果是( )。
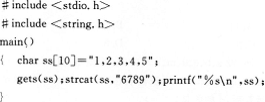
A.ABC6789
B.ABC67
C.12345ABC6
D.ABC456789
正确答案:A
当执行gets(ss)后,ss数组中的元素为ABC,再执行strcat(ss,″6789″),strcat的作用是把6789连接到ss数组后面,执行完后ss数组为ABC6789,故选择A选项。 -
第18题:
下面程序的运行结果是 ( ) includeinclude main( ) { char * a=" 下面程序的运行结果是 ( ) # include<stdio.h> # include<string.h> main( ) { char * a="AbcdEf",* b="aBcD" a + +;b + +; printf("%d\n",strcmp(a,b)); }
A.0
B.负数
C.正数
D.无确定值
正确答案:C
-
第19题:
下面程序的输出结果是 ( ) includeinclude { char * p1="abc" , * 下面程序的输出结果是 ( ) # include<stdio.h> # include<string.h> { char * p1="abc" , * p2=" ABC ",str[50]="xyz"; strcpy(str+2.strcat (pi,p2)); printf("%s\n",str);}
A.xyzabcAB
B.zabcABC
C.yzabcABC
D.xycbcABC
正确答案:D
-
第20题:
下面程序的输出结果是includeinclude main(){char *p1="abc",*p2="ABC",str 下面程序的输出结果是 #include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> main() { char *p1="abc",*p2="ABC",str[50]="xyz"; strcpy(str+2,strcat(p1,p2)); printf("%s\n",str);}
A.xyzabcABC
B.zabcABC
C.xyabcABC
D.yzabcABC
正确答案:C
解析:本题考查的重点是拷贝字符串——使用strcpy()函数,该函数的调用方式是:strcpy(字符数组,字符串)其中“字符串”可以是字符串常量,也可以是字符数组。函数的功能是:将“字符串”完整地复制到“字符数组”中,字符数组中原有内容被覆盖。使用该函数时注意:①字符数组必须定义得足够大,以便容纳复制过来的字符串。复制时,连同结束标志‘\0’一起复制。②不能用赋值运算符“=”将一个字符串直接赋值给一个字符数组,只能用strcpy()函数来处理。另外,本题还考查连接字符串的strcat()函数,其调用方式是:strcat(字符数组,字符串)功能是把“字符串”连接到“字符数组”中的字符串尾端,并存储于“字符数组”中。“字符数组”中原来的结束标志,被“字符串”的第一个字符覆盖,而“字符串”在操作中未被修改。使用该函数时注意:①由于没有边界检查,编程者要注意保证“字符数组”定义得足够大,以便容纳连接后的目标字符串;否则,会因长度不够而产生问题。③连接前两个字符串都有结束标志‘\0’,连接后“字符数组”中存储的字符串的结束标志‘\0’被舍弃,只在目标串的最后保留一个‘\0’。 -
第21题:
有以下程序:includeinclude main(){char *p[10]={"abc","aabdfg","dcdbe" 有以下程序: #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> main() { char *p[10]={"abc","aabdfg","dcdbe","abbd","cd"}; printf("%d\n",strlen(p[4])); } 执行后的输出结果是( )。
A.2
B.3
C.4
D.5
正确答案:A
解析:p是由10个指向字符型数据的指针元素组成的指针数组,其中前5个数组元素进行了初始化。p[4]="cd",strlen(str)是统计字符串str中字符的个数(不包括终止符'\0'),输出结果为2。 -
第22题:
下列程序执行后的输出结果是()。includeinclude main(){char arr[2][4]; str 下列程序执行后的输出结果是( )。 #include<stdio.h> #include <string.h> main() { char arr[2][4]; strcpy(arr[0],"you");strcpy(arr[1],"me"); arr[0][3]='&'; Printf("%s\n",arr); }
A.you&me
B.you
C.me
D.err
正确答案:A
解析:函数strcpy的功能是字符串拷贝,函数原型为char*strcpy(char*strl,char*str2),作用是将字符串2复制到字符串1中去。二维数组可以看做是一种特殊的一维数组,它的每一个元素又是一个一维数组。本题arr可看做是一个具有两个元素arr[0]和arr[1]的一维数组,每个元素又是一个包含四个元素的一维数组。 -
第23题:
当执行下面的程序时,如果输入ABC,则输出结果是()。 #include "stdio.h" #include "string.h" main() { char ss[10]="12345"; gets(ss); strcat(ss,"6789"); printf("%s/n",ss); }
- A、ABC6789
- B、ABC67
- C、12345ABC6
- D、ABC456789
正确答案:A
