(c) Describe the audit procedures you should perform. to determine the validity of the amortisation rate of fiveyears being applied to development costs in relation to Plummet. (5 marks)
题目
(c) Describe the audit procedures you should perform. to determine the validity of the amortisation rate of five
years being applied to development costs in relation to Plummet. (5 marks)
相似考题
更多“(c) Describe the audit procedures you should perform. to determine the validity of the amortisation rate of fiveyears being applied to development costs in relation to Plummet. (5 marks)”相关问题
-
第1题:
(b) Determine whether your decision in (a) would change if you were to use each of the Maximin and Minimax
regret decision criteria.
Your answer should be supported by relevant workings. (6 marks)
正确答案: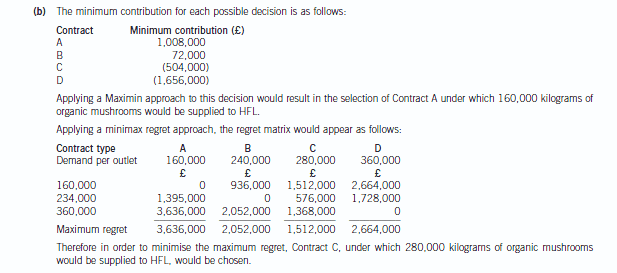
-
第2题:
(b) Describe the audit work to be performed in respect of the carrying amount of the following items in the
balance sheet of GVF as at 30 September 2005:
(i) goat herd; (4 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Audit work on carrying amounts
Tutorial note: This part concerns audit work to be undertaken in respect of non-current tangible assets (the production
animals in the goat herd and certain equipment) and inventories (the for-sale animals and cheese). One of the ‘tests’ for
assessing whether or not a point is worthy of a mark will be whether or not the asset to which it relates is apparent. Points
which are so vague that they could apply to ANY non-current asset for ANY entity, rather than those of GVF are unlikely to
attract many marks, if any, at this level.
(i) Goat herd
■ Physical inspection of the number and condition of animals in the herd and confirming, on a test basis, that they
are tagged (or otherwise ‘branded’ as being owned by GVF).
■ Tests of controls on management’s system of identifying and distinguishing held-for-sale animals (inventory) from
the production herd (depreciable non-current assets).
■ Comparison of GVF’s depreciation policies (including useful lives, depreciation methods and residual values) with
those used by other farming entities.
■ ‘Proof in total’, or other reasonableness check, of the depreciation charge for the herd for the year.
■ Observing test counts or total counts of animals held for sale.
■ Comparing carrying amounts of the kids, according to their weight and age, as at 30 September 2005 with their
market values. (These may approximate to actual invoiced selling prices obtained by GVF.)
Tutorial note: Market value of the production herd could also be compared with its carrying amount to assess possible
impairment. However, if value in use appears to be less than market value the herd should be sold rather than used
for production. -
第3题:
(b) A sale of industrial equipment to Deakin Co in May 2005 resulted in a loss on disposal of $0·3 million that has
been separately disclosed on the face of the income statement. The equipment cost $1·2 million when it was
purchased in April 1996 and was being depreciated on a straight-line basis over 20 years. (6 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Keffler Co for the year ended
31 March 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
(b) Sale of industrial equipment
(i) Matters
■ The industrial equipment was in use for nine years (from April 1996) and would have had a carrying value of
$660,000 at 31 March 2005 (11/20 × $1·2m – assuming nil residual value and a full year’s depreciation charge
in the year of acquisition and none in the year of disposal). Disposal proceeds were therefore only $360,000.
■ The $0·3m loss represents 15% of PBT (for the year to 31 March 2006) and is therefore material. The equipment
was material to the balance sheet at 31 March 2005 representing 2·6% of total assets ($0·66/$25·7 × 100).
■ Separate disclosure, of a material loss on disposal, on the face of the income statement is in accordance with
IAS 16 ‘Property, Plant and Equipment’. However, in accordance with IAS 1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’,
it should not be captioned in any way that might suggest that it is not part of normal operating activities (i.e. not
‘extraordinary’, ‘exceptional’, etc).
Tutorial note: However, note that if there is a prior period error to be accounted for (see later), there would be
no impact on the current period income statement requiring consideration of any disclosure.
■ The reason for the sale. For example, whether the equipment was:
– surplus to operating requirements (i.e. not being replaced); or
– being replaced with newer equipment (thereby contributing to the $8·1m increase (33·8 – 25·7) in total
assets).
■ The reason for the loss on sale. For example, whether:
– the sale was at an under-value (e.g. to a related party);
– the equipment had a bad maintenance history (or was otherwise impaired);
– the useful life of the equipment is less than 20 years;
– there is any deferred consideration not yet recorded;
– any non-cash disposal proceeds have been overlooked (e.g. if another asset was acquired in a part-exchange).
■ If the useful life was less than 20 years, tangible non-current assets may be materially overstated in respect of other
items of equipment that are still in use and being depreciated on the same basis.
■ If the sale was to a related party then additional disclosure should be required in a note to the financial statements
for the year to 31 March 2006 (IAS 24 ‘Related Party Disclosures’).
Tutorial note: Since there are no specific pointers to a related party transaction (RPT), this point is not expanded
on.
■ Whether the sale was identified in the prior year audit’s post balance sheet event review. If so:
– the disclosure made in the prior year’s financial statements (IAS 10 ‘Events After the Balance Sheet Date’);
– whether an impairment loss was recognised at 31 March 2005.
■ If not, and the equipment was impaired at 31 March 2005, a prior period error should be accounted for (IAS 8
‘Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors’). An impairment loss of $0·3m would have
been material to prior year profit (12·5%).
Tutorial note: Unless this was a RPT or the impairment arose after 31 March 2005 a prior period adjustment
should be made.
■ Failure to account for a prior period error (if any) would result in modification of the audit opinion ‘except for’ noncompliance
with IAS 8 (in the current year) and IAS 36 (in the prior period).
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Carrying amount ($0·66m as above) agreed to the non-current asset register balances at 31 March 2005 and
recalculation of the loss on disposal.
■ Cost and accumulated depreciation removed from the asset register in the year to 31 March 2006.
■ Receipt of proceeds per cash book agreed to bank statement.
■ Sales invoice transferring title to Deakin.
■ A review of maintenance expenses and records (e.g. to confirm reason for loss on sale).
■ Post balance sheet event review on prior year audit working papers file.
■ Management representation confirming that Deakin is not a related party (provided that there is no evidence to
suggest otherwise). -
第4题:
(c) Briefly describe the principal audit work to be performed in respect of the carrying amount of the following
items in the balance sheet:
(i) development expenditure on the Fox model; (3 marks)
正确答案:
(c) Principal audit work
(i) Development expenditure on the Fox model
■ Agree opening balance, $6·3 million, to prior year working papers.
■ Physically inspect assembly plant/factory where the Fox is being developed and any vehicles so far manufactured
(e.g. for testing).
■ Substantiate costs incurred during the year, for example:
– goods (e.g. components) and services (e.g. consultants) to purchase invoices;
– labour (e.g. design engineers/technicians, mechanics, test drivers) to the payroll analysis;
– overheads (e.g. depreciation of development buildings and equipment, power, consumables) to
management’s calculation of overhead absorption and underlying cost accounts.
■ Review of internal trials/test drive results (e.g. in reports to management and video recordings of events).
■ Reperform. management’s impairment test of development expenditure. In particular recalculate value in use.
Tutorial note: It is highly unlikely that a reasonable estimate of fair value less costs to sell could be made for so
unique an asset.
■ Substantiate the key assumptions made by management in calculating value in use. For example:
– the level of sales expected when the car is launched to advance orders (this may have fallen with the delay
in the launch);
– the discount rate used to Pavia’s cost of capital;
– projected growth in sales to actual sales growth seen last time a new model was launched. -
第5题:
(b) Explain the principal audit procedures to be performed during the final audit in respect of the estimated
warranty provision in the balance sheet of Island Co as at 30 November 2007. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(b) ISA 540 Audit of Accounting Estimates requires that auditors should obtain sufficient audit evidence as to whether an
accounting estimate, such as a warranty provision, is reasonable given the entity’s circumstances, and that disclosure is
appropriate. One, or a combination of the following approaches should be used:
Review and test the process used by management to develop the estimate
– Review contracts or orders for the terms of the warranty to gain an understanding of the obligation of Island Co
– Review correspondence with customers during the year to gain an understanding of claims already in progress at the
year end
– Perform. analytical procedures to compare the level of warranty provision year on year, and compare actual to budgeted
provisions. If possible disaggregate the data, for example, compare provision for specific types of machinery or customer
by customer
– Re-calculate the warranty provision
– Agree the percentage applied in the calculation to the stated accounting policy of Island Co
– Review board minutes for discussion of on-going warranty claims, and for approval of the amount provided
– Use management accounts to ascertain normal level of warranty rectification costs during the year
– Discuss with Kate Shannon the assumptions she used to determine the percentage used in her calculations
– Consider whether assumptions used are consistent with the auditors’ understanding of the business
– Compare prior year provision with actual expenditure on warranty claims in the accounting period
– Compare the current year provision with prior year and discuss any fluctuation with Kate Shannon.
Review subsequent events which confirm the estimate made
– Review any work carried out post year end on specific faults that have been provided for. Agree that all costs are included
in the year end provision.
– Agree cash expended on rectification work in the post balance sheet period to the cash book
– Agree cash expended on rectification work post year end to suppliers’ invoices, or to internal cost ledgers if work carried
out by employees of Island Co
– Read customer correspondence received post year end for any claims received since the year end. -
第6题:
(b) (i) Explain the matters you should consider to determine whether capitalised development costs are
appropriately recognised; and (5 marks)
正确答案:
(b) (i) Materiality
The net book value of capitalised development costs represent 7% of total assets in 2007 (2006 – 7·7%), and is
therefore material. The net book value has increased by 13%, a significant trend.
The costs capitalised during the year amount to $750,000. If it was found that the development cost had been
inappropriately capitalised, the cost should instead have been expensed. This would reduce profit before tax by
$750,000, representing 42% of the year’s profit. This is highly material. It is therefore essential to gather sufficient
evidence to support the assertion that development costs should be recognised as an asset.
In 2007, $750,000 capitalised development costs have been incurred, when added to $160,000 research costs
expensed, total research and development costs are $910,000 which represents 20·2% of total revenue, again
indicating a high level of materiality for this class of transaction.
Relevant accounting standard
Development costs should only be capitalised as an intangible asset if the recognition criteria of IAS 38 Intangible Assets
have been demonstrated in full:
– Intention to complete the intangible asset and use or sell it
– Technical feasibility and ability to use or sell
– Ability to generate future economic benefit
– Availability of technical, financial and other resources to complete
– Ability to measure the expenditure attributable to the intangible asset.
Research costs must be expensed, as should development costs which do not comply with the above criteria. The
auditors must consider how Sci-Tech Co differentiates between research and development costs.
There is risk that not all of the criteria have been demonstrated, especially due to the subjective nature of the
development itself:
– Pharmaceutical development is highly regulated. If the government does not license the product then the product
cannot be sold, and economic benefits will therefore not be received.
– Market research should justify the commercial viability of the product. The launch of a rival product to Flortex
means that market share is likely to be much lower than anticipated, and the ability to sell Flortex is reduced. This
could mean that Flortex will not generate an overall economic benefit if future sales will not recover the research
and development costs already suffered, and yet to be suffered, prior to launch. The existence of the rival product
could indicate that Flortex is no longer commercially viable, in which case the capitalised development costs
relating to Flortex should be immediately expensed.
– The funding on which development is dependent may be withdrawn, indicating that there are not adequate
resources to complete the development of the products. Sci-Tech has failed to meet one of its required key
performance indicators (KPI) in the year ended 30 November 2007, as products valued at 0·8% revenue have
been donated to charity, whereas the required KPI is 1% revenue.
Given that there is currently a breach of the target KPIs, this is likely to result in funding equivalent to 25% of
research and development expenditure being withdrawn. If Sci-Tech Co is unable to source alternative means of
finance, then it would seem that adequate resources may not be available to complete the development of new
products. -
第7题:
(ii) Describe the procedures to verify the number of serious accidents in the year ended 30 November 2007.
(4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Procedures to verify the number of serious accidents during 2007 could include the following:
Tutorial note: procedures should focus on the completeness of the disclosure as it is in the interest of Sci-Tech Co to
understate the number of serious accidents.
– Review the accident log book and count the total number of accidents during the year
– Discuss the definition of ‘serious accident’ with the directors and clarify exactly what criteria need to be met to
satisfy the definition
– For serious accidents identified:
? review HR records to determine the amount of time taken off work
? review payroll records to determine the financial amount of sick pay awarded to the employee
? review correspondence with the employee regarding the accident.
Tutorial note: the above will help to clarify that the accident was indeed serious.
– Review board minutes where the increase in the number of serious accidents has been discussed
– Review correspondence with Sci-Tech Co’s legal advisors to ascertain any legal claims made against the company
due to accidents at work
– Enquire as to whether any health and safety visits have been conducted during the year by regulatory bodies, and
review any documentation or correspondence issued to Sci-Tech Co after such visits.
Tutorial note: it is highly likely that in a regulated industry such as pharmaceutical research, any serious accident
would trigger a health and safety inspection from the appropriate regulatory body.
– Discuss the level of accidents with representatives of Sci-Tech Co’s employees to reach an understanding as to
whether accidents sometimes go unreported in the accident log book. -
第8题:
(b) Describe the potential benefits for Hugh Co in choosing to have a financial statement audit. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(b) There are several benefits for Hugh Co in choosing a voluntary financial statement audit.
An annual audit will ensure that any material mistakes made by the part-qualified accountant in preparing the year end
financial statements will be detected. This is important as the directors will be using the year end accounts to review their
progress in the first year of trading and will need reliable figures to assess performance. An audit will give the directors comfort
that the financial statements are a sound basis for making business decisions.
Accurate first year figures will also enable more effective budgeting and forecasting, which will be crucial if rapid growth is to
be achieved.
The auditors are likely to use the quarterly management accounts as part of normal audit procedures. The auditors will be
able to advise Monty Parkes of any improvements that could be made to the management accounts, for example, increased
level of detail, more frequent reporting. Better quality management accounts will help the day-to-day running of the business
and enable a speedier response to any problems arising during the year.
As a by-product of the audit, a management letter (report to those charged with governance) will be produced, identifying
weaknesses and making recommendations on areas such as systems and controls which will improve the smooth running of
the business.
It is likely that Hugh Co will require more bank funding in order to expand, and it is likely that the bank would like to see
audited figures for review, before deciding on further finance. It will be easier and potentially cheaper to raise finance from
other providers with an audited set of financial statements.
As the business deals in cash sales, and retails small, luxury items there is a high risk of theft of assets. The external audit
can act as both a deterrent and a detective control, thus reducing the risk of fraud and resultant detrimental impact on the
financial statements.
Accurate financial statements will be the best basis for tax assessment and tax planning. An audit opinion will enhance the
credibility of the figures.
If the business grows rapidly, then it is likely that at some point in the future, the audit exemption limit will be exceeded and
thus an audit will become mandatory.
Choosing to have an audit from the first year of incorporation will reduce potential errors carried down to subsequent periods
and thus avoid qualifications of opening balances. -
第9题:
(ii) Identify and explain the principal audit procedures to be performed on the valuation of the investment
properties. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Additional audit procedures
Audit procedures should focus on the appraisal of the work of the expert valuer. Procedures could include the following:
– Inspection of the written instructions provided by Poppy Co to the valuer, which should include matters such as
the objective and scope of the valuer’s work, the extent of the valuer’s access to relevant records and files, and
clarification of the intended use by the auditor of their work.
– Evaluation, using the valuation report, that any assumptions used by the valuer are in line with the auditor’s
knowledge and understanding of Poppy Co. Any documentation supporting assumptions used by the valuer should
be reviewed for consistency with the auditor’s business understanding, and also for consistency with any other
audit evidence.
– Assessment of the methodology used to arrive at the fair value and confirmation that the method is consistent with
that required by IAS 40.
– The auditor should confirm, using the valuation report, that a consistent method has been used to value each
property.
– It should also be confirmed that the date of the valuation report is reasonably close to the year end of Poppy Co.
– Physical inspection of the investment properties to determine the physical condition of the properties supports the
valuation.
– Inspect the purchase documentation of each investment property to ascertain the cost of each building. As the
properties were acquired during this accounting period, it would be reasonable to expect that the fair value at the
year end is not substantially different to the purchase price. Any significant increase or decrease in value should
alert the auditor to possible misstatement, and lead to further audit procedures.
– Review of forecasts of rental income from the properties – supporting evidence of the valuation.
– Subsequent events should be monitored for any additional evidence provided on the valuation of the properties.
For example, the sale of an investment property shortly after the year end may provide additional evidence relating
to the fair value measurement.
– Obtain a management representation regarding the reasonableness of any significant assumptions, where relevant,
to fair value measurements or disclosures. -
第10题:
(ii) State the principal audit procedures to be performed on the consolidation schedule of the Rosie Group.
(4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Audit procedures on the consolidation schedule of the Rosie Group:
– Agree correct extraction of individual company figures by reference to individual company audited financial
statements.
– Cast and cross cast all consolidation schedules.
– Recalculate all consolidation adjustments, including goodwill, elimination of pre acquisition reserves, cancellation
of intercompany balances, fair value adjustments and accounting policy adjustments.
– By reference to prior year audited consolidated accounts, agree accounting policies have been consistently applied.
– Agree brought down figures to prior year audited consolidated accounts and audit working papers (e.g. goodwill
figures for Timber Co and Ben Co, consolidated reserves).
– Agree that any post acquisition profits consolidated for Dylan Co arose since the date of acquisition by reference to
date of control passing per the purchase agreement.
– Reconcile opening and closing group reserves and agree reconciling items to group financial statements. -
第11题:
(c) In the context of a standard unmodified audit report, describe the content of a liability disclaimer paragraph,
and discuss the main arguments for and against the use of a liability disclaimer paragraph. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(c) It has become increasingly common for audit firms to include a disclaimer paragraph within the audit report. However, it is
not a requirement of auditing standards and individual audit firms need to assess the advantages and disadvantages of the
use of a disclaimer paragraph.
The wording is used to state the fact that the auditor’s report is intended solely for the use of the company’s members as a
body, and that no responsibility is accepted or assumed to anyone other than the company and the company’s members as
a body.
The main perceived advantage is that the disclaimer should help to reduce the exposure of the audit firm to liability claims
from anyone other than the company or the company’s body of shareholders. The disclaimer makes it clear that the audit
firm reports only to those who appointed the firm, i.e. the members of the company, and this may make it more difficult for
the audit firm to be sued by a third party.
It is also argued that the use of a disclaimer could help to bridge the ‘expectation gap’ by providing a clearer indication of the
responsibility of the auditor.
In this way the audit firm can manage its risk exposure in an increasingly litigious environment. Recent high profile legal cases
against audit firms, such as the Bannerman case in Scotland, illustrate that an audit firm’s duty of care can extend beyond
the company and its shareholders, and that audit firms should consider how to protect themselves against liability claims.
Tutorial note: It is appropriate here to quote recent cases such as the Bannerman case to illustrate the reason why audit
firms face increased potential exposure to claims from third parties. However, knowledge of specific legal cases is not
required to gain full marks for this requirement.
However, it can be argued that a disclaimer does not necessarily work to protect an audit firm. Each legal case has individual
circumstances, and while a disclaimer might protect the audit firm in one situation, equally it may not offer any protection
where the facts of the case are different.
In addition, it is often argued that if an audit firm conducts an audit using full due care and diligence, there is no need for a
disclaimer, as a high quality audit would be very unlikely to lead to any claims against the audit firm. Consequently, it could
be argued that the use of disclaimers as a means to limit liability could permit low quality audits to be performed, the auditors
being confident that legal cases against them are restricted due to the presence of a disclaimer within the audit report. -
第12题:
多选题You work as a database administrator for Certkiller .com. In your development environmentenvironment, the developers are responsible for modifying the table structure according to the application requirements. However, you want to keep track of the ALTER TABLE commands being executed by developers, so you enable auditing to achieve this objective. Which two views would you refer to find out the audit information?()ADBA_AUDIT_TRAIL
BDBA_AUDIT_SESSION
CDBA_FGA_AUDIT_TRAIL
DDBA_COMMON_AUDIT_TRAIL
正确答案: D,B解析: 暂无解析 -
第13题:
(b) Describe the principal audit work to be performed in respect of the useful lives of Shire Oil Co’s rig platforms.
(6 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Principal audit work – useful life of rig platforms
Tutorial notes: The platforms are just one item of each rig. Candidates should not be awarded marks here for the matters
to be considered in the assessment of useful lives (since this is illustrated in the scenario). No marks will be awarded for
criticising management for estimating useful lives on a per platform. basis or for audit work on depreciation charges/carrying
amounts unrelated to the determination of useful lives.
■ Review of management’s annual assessment of the useful life of each rig at 31 December 2005 and corroboration of
any information that has led to a change in previous estimates. For example, for the abandoned rig, where useful life
has been assessed to be at an end, obtain:
? weather reports;
? incident report supported by photographs;
? insurance claim, etc.
■ Consider management’s past experience and expertise in estimating useful lives. For example, if all lives initially
assessed as short (c. 15 years) are subsequently lengthened (or long lives consistently shortened) this would suggest
that management is being over (under) prudent in its initial estimates.
■ Review of industry comparatives as published in the annual reports of other oil producers.
■ Comparison of actual maintenance costs against budgeted to confirm that the investment needed in maintenance, to
achieve expected life expectancy, is being made.
■ Comparison of actual output (oil extracted) against budgeted. If actual output is less than budgeted the economic life
of the platform. may be:
? shorter (e.g. because there is less oil to be extracted than originally surveyed); or
? longer (e.g. because the rate of extraction is less than budgeted).
Tutorial note: An increase in actual output can be explained conversely.
■ A review of the results of management’s impairment testing of each rig (i.e. the cash-generating unit of which each
platform. is a part).
■ Recalculations of cash flow projections (based on reasonable and supportable assumptions) discounted at a suitable
pre-tax rate.
Tutorial note: As the rigs will not have readily determinable net selling prices (each one being unique and not available
for sale) any impairment will be assessed by a comparison of value in use against carrying amount.
■ Review of working papers of geologist/quantity surveyor(s) employed by Shire supporting estimations of reserves used
in the determination of useful lives of rigs. -
第14题:
(c) Explain the extent to which you should plan to place reliance on analytical procedures as audit evidence.
(6 marks)
正确答案:
(c) Extent of reliance on analytical procedures as audit evidence
Tutorial note: In the requirement ‘… reliance … as audit evidence’ is a direction to consider only substantive analytical
procedures. Answer points concerning planning and review stages were not asked for and earn no marks.
■ Although there is likely to be less reliance on analytical procedures than if this had been an existing audit client, the fact
that this is a new assignment does not preclude placing some reliance on such procedures.
■ Analytical procedures will not be relied on in respect of material items that require 100% testing. For example, additions
to property is likely to represent a very small number of transactions.
■ Analytical procedures alone may provide sufficient audit evidence on line items that are not individually material. For
example, inventory (less than 1/2% revenue and less than 1% total assets) may be shown to be materially correctly
stated through analytical procedures on consumable stores (i.e. fuel, lubricants, materials for servicing vehicles etc).
■ Substantive analytical procedures are best suited to large volume transactions (e.g. revenue, materials expense, staff
costs). If controls over the completeness, accuracy and validity of recording transactions in these areas are effective then
substantive analytical procedures showing that there are no unexpected fluctuations should reduce the need for
substantive detailed tests.
■ The extent of planned use will be dependent on the relationships expected between variables. (e.g. between items of
financial information and between items of financial and non-financial information). For example, if material costs rise
due to an increase in the level of business then a commensurate increase in revenue and staff costs might be expected
also.
■ ‘Proofs in total’ (or reasonableness tests) provide substantive evidence that income statement items are not materially
misstated. In the case of Yates these might be applied to staff costs (number of employees in each category ×
wage/salary rates, grossed up for social security, etc) and finance expense (interest rate × average monthly overdraft
balance).
■ However, such tests may have limited application, if any, if the population is not homogenous and cannot be subdivided.
For example, all the categories of non-current asset have a wide range of useful life. Therefore it would be
difficult/meaningless to apply an ‘average’ depreciation rate to all assets in the class to substantiate the total depreciation
expense for the year. (Although it might highlight a risk of potential over or understatement requiring further
investigation.)
■ Substantive analytical procedures are more likely to be used if there is relevant information available that is being used
by Yates. For example, as fuel costs will be significant, Yates may monitor consumption (e.g. miles per gallon (MPG)).
■ Analytical procedures may supplement alternative procedures that provide evidence regarding the same assertion. For
example, the review of after-date payments to confirm the completeness of trade payables may be supplemented by
calculations of average payment period on a monthly basis.
Tutorial note: Credit will be given for other relevant points drawn from the scenario. For example, the restructuring during
the previous year is likely to have caused fluctuations that may result in less reliance being placed on analytical procedures. -
第15题:
(b) Illustrate how you might use analytical procedures to provide audit evidence and reduce the level of detailed
substantive procedures. (7 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Illustration of use of analytical procedures as audit evidence
Tutorial note: Note that ‘as audit evidence’ requires consideration of substantive analytical procedures rather that the
identification of risks (relevant to part (a)).
Revenue
Analytical procedures may be used in testing revenue for completeness of recording (‘understatement’). The average selling
price of a vehicle in 2005 was $68,830 ($526·0 million ÷ 7,642 vehicles). Applying this to the number of vehicles sold
in 2006, might be projected to generate $698·8 million ($68,830 × 10,153) revenue from the sale of vehicles. The draft
financial statements therefore show a potential shortfall of $110·8 million ($(698·8 – 588·0) million) that is, 15·6%.
This should be investigated and substantiated through more detailed analytical procedures. For example, the number of
vehicles sold should be analysed into models and multiplied by the list price of each for a more accurate estimate of potential
revenue. The impact of discounts and other incentives (e.g. 0% finance) on the list prices should then be allowed for. If
recorded revenue for 2006 (as per draft income statement adjusted for cutoff and consignment inventories) is materially lower
than that calculated, detailed substantive procedures may be required in order to show that there is no material error.
‘Proof in total’/reasonableness tests
The material correctness, or otherwise, of income statement items (in particular) may be assessed through appropriate ‘proof
in total’ calculations (or ‘reasonableness’ tests). For example:
■ Employee benefits costs: the average number of employees by category (waged/salaried/apprenticed) × the average pay
rate for each might prove that in total $91·0 million (as adjusted to actual at 31 December 2006) is not materially
misstated. The average number of employees needs to be checked substantively (e.g. recalculated based on the number
of employees on each payroll) and the average pay rates (e.g. to rates agreed with employee representatives).
Tutorial note: An alternative reasonableness might be to take last year’s actual adjusted for 2006 numbers of
employees grossed-up for any pay increases during the year (pro-rated as necessary).
■ Depreciation: the cost (or net book value) of each category of asset × by the relevant straight-line (or reducing balance)
depreciation rate. If a ‘ballpark’ calculation for the year is materially different to the annual charge a more detailed
calculation can be made using monthly depreciation calculations. The cost (or net book value) on which depreciation
is calculated should be substantively tested, for example by agreeing brought forward balances to prior year working
papers and additions to purchase invoices (costings in respect of assets under construction).
Tutorial note: Alternatively, last year’s depreciation charge may be reconciled to this year’s by considering depreciation
rates applied to brought forward balances with adjustments for additions/disposals.
■ Interest income: an average interest rate for the year can be applied to the monthly balance invested (e.g. in deposit
accounts) and compared with the amount recognised for the year to 31 December 2006 (as adjusted for any accrued
interest per the bank letter for audit purposes). The monthly balances (or averages) on which the calculation is
performed should be substantiated to bank deposit statements.
■ Interest expense: if the cash balances do not go into overdraft then this may be similar expenses (e.g. prompt payment
discounts to customers). If this is to particular dealers then a proof in total might be to apply the discount rate to the
amounts invoiced to the dealer during the period.
Immaterial items
For immaterial items analytical procedures alone may provide sufficient audit evidence that amounts in the financial
statements are not materially misstated so that detailed substantive procedures are not required. For example, a comparison
of administration and distribution, maintenance and insurance costs for 2006 compared with 2005 may be sufficient to show
that material error is highly unlikely. If necessary, further reasonableness tests could be performed. For example, considering
insurance costs to value of assets insured or maintenance costs to costs of assets maintained.
Ratio analysis
Ratio analysis can provide substantive evidence that income statement and balance sheet items are not materially misstated
by considering their inter-relationships. For example:
■ Asset turnover: Based on the draft financial statements property, plant and equipment has turned over 5·2 times
($645·5/124·5) compared with 5·9 times in 2005. This again highlights that income may be overstated, or assets
overstated (e.g. if depreciation is understated).
■ Inventory turnover: Using cost of materials adjusted for changes in inventories this has remained stable at 10·9 times.
Tutorial note: This is to be expected as in (a) the cost in the income statement has increased by 9% and the value of
inventories by 8·5%.
Inventories represent the smallest asset value on the balance sheet at 31 December 2006 (7·8% of total assets).
Therefore substantive procedures may be limited to agreeing physical count of material items (vehicles) and agreeing
cutoff.
■ Average collection period: This has increased to 41 days (73·1/645·5 × 365) from 30 days. Further substantive analysis
is required, for example, separating out non-current amounts (for sales on 0% finance terms). Substantive procedures
may be limited to confirmation of amounts due from dealers (and/or receipt of after-date cash) and agreeing cutoff of
goods on consignment.
■ Payment periods: This has remained constant at 37 days (2005 – 38 days). Detailed substantive procedures may be
restricted to reconciling only major suppliers’ statements and agreeing the cutoff on parts purchased from them. -
第16题:
(c) Describe the examination procedures you should use to verify Cusiter Co’s prospective financial information.
(9 marks)
正确答案:
(c) Examination procedures
■ The arithmetic accuracy of the PFI should be confirmed, i.e. subtotals and totals should be recast and agreed.
■ The actual information for the year to 31 December 2006 that is shown as comparative information should be agreed
to the audited financial statements for that year to ensure consistency.
■ Balances and transaction totals for the quarter to 31 March 2007 should be agreed to general ledger account balances
at that date. The net book value of property, plant and equipment should be agreed to the non-current asset register;
accounts receivable/payable to control accounts and cash at bank to a bank reconciliation statement.
■ Tenders for the new equipment should be inspected to confirm the additional cost included in property, plant and
equipment included in the forecast for the year to 31 December 2008 and that it can be purchased with the funds being
lent by the bank.
■ The reasonableness of all new assumptions should be considered. For example, the expected useful life of the new
equipment, the capacity at which it will be operating, the volume of new product that can be sold, and at what price.
■ The forecast income statement should be reviewed for completeness of costs associated with the expansion. For
example, operating expenses should include salaries of additional equipment operatives or supervisors.
■ The consistency of accounting practices reflected in the forecast with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
should be considered. For example, the intangible asset might be expected to be less than $10,000 at 31 December
2008 as it should be carried at amortised cost.
■ The cost of property, plant and equipment at 31 December 2008 is $280,000 more than as at 31 December 2007.
Consideration should be given to the adequacy of borrowing $250,000 if the actual investment is $30,000 more.
■ The terms of existing borrowings (both non-current and short-term) should be reviewed to ensure that the forecast takes
full account of existing repayment schedules. For example, to confirm that only $23,000 of term borrowings will become
current by the end of 2007.
Trends should be reviewed and fluctuations explained, for example:
■ Revenue for the first quarter of 2007 is only 22% of revenue for 2006 and so may appear to be understated. However,
revenue may not be understated if sales are seasonal and the first quarter is traditionally ‘quieter’.
■ Forecast revenue for 2007 is 18% up on 2006. However, forecast revenue for 2008 is only 19% up on 2007. As the
growth in 2007 is before the investment in new plant and equipment it does not look as though the new investment
will be contributing significantly to increased growth in the first year.
■ The gross profit % is maintained at around 29% for the three years. However, the earnings before interest and tax (EBIT)
% is forecast to fall by 2% for 2008. Earnings after interest might be worrying to the potential lender as this is forecast
to rise from 12·2% in 2006 to 13·7% in 2007 but then fall to 7·6% in 2008.
The reasonableness of relationships between income statement and balance sheet items should be considered. For example:
■ The average collection period at each of the balance sheet dates presented is 66, 69, 66 and 66 days respectively (e.g.
71/394 × 365 = 66 days). Although it may be realistic to assume that the current average collection period may be
maintained in future it is possible that it could deteriorate if, for example, new customers taken on to launch the new
product are not as credit worthy as the existing customer base.
■ The number of days sales in inventory at each balance sheet date is 66, 88, 66 and 65 days respectively (e.g. 50/278
× 365 = 66 days). The reason for the increase to 88 at the end of the first quarter must be established and
management’s assertion that 66 days will be re-established as the ‘norm’ corroborated.
■ As the $42,000 movement on retained earnings from 2007 to 2008 is the earnings before income tax for 2008 it may
be that there is no tax in 2008 or that tax effects have not been forecast. (However, some deferred tax effect might be
expected if the investment in new plant and equipment is likely to attract accelerated capital allowances.) -
第17题:
(c) (i) Identify and describe FOUR quality control procedures that are applicable to the individual audit
engagement; and (8 marks)
正确答案:
(c) (i) ISQC 1 Quality Control for Firms That Perform. Audits and Reviews of Historical Financial Information and Other
Assurance and Related Services Engagements provides guidance on the overall quality control systems that should be
implemented by an audit firm. ISA 220 Quality Control for Audits of Historical Financial Information specifies the quality
control procedures that should be applied by the engagement team in individual audit assignments.
Procedures include the following:
Client acceptance procedures
There should be full documentation, and conclusion on, ethical and client acceptance issues in each audit assignment.
The engagement partner should consider whether members of the audit team have complied with ethical requirements,
for example, whether all members of the team are independent of the client. Additionally, the engagement partner should
conclude whether all acceptance procedures have been followed, for example, that the audit firm has considered the
integrity of the principal owners and key management of the client. Other procedures on client acceptance should
include:
– Obtaining professional clearance from previous auditors
– Consideration of any conflict of interest
– Money laundering (client identification) procedures.
Engagement team
Procedures should be followed to ensure that the engagement team collectively has the skills, competence and time to
perform. the audit engagement. The engagement partner should assess that the audit team, for example:
– Has the appropriate level of technical knowledge
– Has experience of audit engagements of a similar nature and complexity
– Has the ability to apply professional judgement
– Understands professional standards, and regulatory and legal requirements.
Direction
The engagement team should be directed by the engagement partner. Procedures such as an engagement planning
meeting should be undertaken to ensure that the team understands:
– Their responsibilities
– The objectives of the work they are to perform
– The nature of the client’s business
– Risk related issues
– How to deal with any problems that may arise; and
– The detailed approach to the performance of the audit.
The planning meeting should be led by the partner and should include all people involved with the audit. There should
be a discussion of the key issues identified at the planning stage.
Supervision
Supervision should be continuous during the engagement. Any problems that arise during the audit should be rectified
as soon as possible. Attention should be focused on ensuring that members of the audit team are carrying out their work
in accordance with the planned approach to the engagement. Significant matters should be brought to the attention of
senior members of the audit team. Documentation should be made of key decisions made during the audit engagement.
Review
The review process is one of the key quality control procedures. All work performed must be reviewed by a more senior
member of the audit team. Reviewers should consider for example whether:
– Work has been performed in accordance with professional standards
– The objectives of the procedures performed have been achieved
– Work supports conclusions drawn and is appropriately documented.
The review process itself must be evidenced.
Consultation
Finally the engagement partner should arrange consultation on difficult or contentious matters. This is a procedure
whereby the matter is discussed with a professional outside the engagement team, and sometimes outside the audit
firm. Consultations must be documented to show:
– The issue on which the consultation was sought; and
– The results of the consultation. -
第18题:
(ii) Describe the evidence you would seek to support the assertion that development costs are technically
feasible. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Evidence supporting the assertion that development costs are technically feasible would include the following:
– Review the results of scientific tests performed on the products, for example, the results of animal or human testing
of the products.
– Discuss any detrimental results of these tests, e.g. harmful side effects, with the scientists working on the project
to determine what corrective action is being taken.
– Enquire whether any licences necessary for continued development and/or commercial production have been
granted by the appropriate regulatory body.
– Compare expected to actual development costs incurred per product being developed. Where actual costs are in
excess of expected costs investigate whether the extra costs have been incurred in order to make good any problems
identified in the development process.
– Review board minutes for relevant discussion of the product development taking place during the year. -
第19题:
4 You are an audit manager in Nate & Co, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants. You are reviewing three situations,
which were recently discussed at the monthly audit managers’ meeting:
(1) Nate & Co has recently been approached by a potential new audit client, Fisher Co. Your firm is keen to take the
appointment and is currently carrying out client acceptance procedures. Fisher Co was recently incorporated by
Marcellus Fisher, with its main trade being the retailing of wooden storage boxes.
(2) Nate & Co provides the audit service to CF Co, a national financial services organisation. Due to a number of
errors in the recording of cash deposits from new customers that have been discovered by CF Co’s internal audit
team, the directors of CF Co have requested that your firm carry out a review of the financial information
technology systems. It has come to your attention that while working on the audit planning of CF Co, Jin Sayed,
one of the juniors on the audit team, who is a recent information technology graduate, spent three hours
providing advice to the internal audit team about how to improve the system. As far as you know, this advice has
not been used by the internal audit team.
(3) LA Shots Co is a manufacturer of bottled drinks, and has been an audit client of Nate & Co for five years. Two
audit juniors attended the annual inventory count last Monday. They reported that Brenda Mangle, the new
production manager of LA Shots Co, wanted the inventory count and audit procedures performed as quickly as
possible. As an incentive she offered the two juniors ten free bottles of ‘Super Juice’ from the end of the
production line. Brenda also invited them to join the LA Shots Co office party, which commenced at the end of
the inventory count. The inventory count and audit procedures were completed within two hours (the previous
year’s procedures lasted a full day), and the juniors then spent four hours at the office party.
Required:
(a) Define ‘money laundering’ and state the procedures specific to money laundering that should be considered
before, and on the acceptance of, the audit appointment of Fisher Co. (5 marks)
正确答案:
4 NATE & CO
(a) – Money laundering is the process by which criminals attempt to conceal the true origin and ownership of the proceeds
of criminal activity, allowing them to maintain control over the proceeds, and ultimately providing a legitimate cover for
their sources of income. The objective of money laundering is to break the connection between the money, and the crime
that it resulted from.
– It is widely defined, to include possession of, or concealment of, the proceeds of any crime.
– Examples include proceeds of fraud, tax evasion and benefits of bribery and corruption.
Client procedures should include the following:
– Client identification:
? Establish the identity of the entity and its business activity e.g. by obtaining a certificate of incorporation
? If the client is an individual, obtain official documentation including a name and address, e.g. by looking at
photographic identification such as passports and driving licences
? Consider whether the commercial activity makes business sense (i.e. it is not just a ‘front’ for illegal activities)
? Obtain evidence of the company’s registered address e.g. by obtaining headed letter paper
? Establish the current list of principal shareholders and directors.
– Client understanding:
? Pre-engagement communication may be considered, to explain to Marcellus Fisher and the other directors the
nature and reason for client acceptance procedures.
? Best practice recommends that the engagement letter should also include a paragraph outlining the auditor’s
responsibilities in relation to money laundering. -
第20题:
(b) Describe the principal audit procedures to be carried out in respect of the following:
(i) The measurement of the share-based payment expense; (6 marks)
正确答案:
(b) (i) Principal audit procedures – measurement of share-based payment expense
– Obtain management calculation of the expense and agree the following from the calculation to the contractual
terms of the scheme:
– Number of employees and executives granted options
– Number of options granted per employee
– The official grant date of the share options
– Vesting period for the scheme
– Required performance conditions attached to the options.
– Recalculate the expense and check that the fair value has been correctly spread over the stated vesting period.
– Agree fair value of share options to specialist’s report and calculation, and evaluate whether the specialist report is
a reliable source of evidence.
– Agree that the fair value calculated is at the grant date.
Tutorial note: A specialist such as a chartered financial analyst would commonly be used to calculate the fair value
of non-traded share options at the grant date, using models such as the Black-Scholes Model.
– Obtain and review a forecast of staffing levels or employee turnover rates for the duration of the vesting period, and
scrutinise the assumptions used to predict level of staff turnover.
– Discuss previous levels of staff turnover with a representative of the human resources department and query why
0% staff turnover has been predicted for the next three years.
– Check the sensitivity of the calculations to a change in the assumptions used in the valuation, focusing on the
assumption of 0% staff turnover.
– Obtain written representation from management confirming that the assumptions used in measuring the expense
are reasonable.
Tutorial note: A high degree of scepticism must be used by the auditor when conducting the final three procedures
due to the management assumption of 0% staff turnover during the vesting period. -
第21题:
5 (a) Compare and contrast the responsibilities of management, and of auditors, in relation to the assessment of
going concern. You should include a description of the procedures used in this assessment where relevant.
(7 marks)
正确答案:
5 Dexter Co
(a) Responsibilities of management and auditors
Responsibilities
ISA 570 Going Concern provides a clear framework for the assessment of the going concern status of an entity, and
differentiates between the responsibilities of management and of auditors. Management should assess going concern in order
to decide on the most appropriate basis for the preparation of the financial statements. IAS 1 Presentation of Financial
Statements (revised) requires that where there is significant doubt over an entity’s ability to continue as a going concern, the
uncertainties should be disclosed in a note to the financial statements. Where the directors intend to cease trading, or have
no realistic alternative but to do so, the financial statements should be prepared on a ‘break up’ basis.
Thus the main focus of the management’s assessment of going concern is to ensure that relevant disclosures are made where
necessary, and that the correct basis of preparation is used.
The auditor’s responsibility is to consider the appropriateness of the management’s use of the going concern assumption in
the preparation of the financial statements and to consider whether there are material uncertainties about the entity’s ability
to continue as a going concern that need to be disclosed in a note.
The auditor should also consider the length of the time period that management have looked at in their assessment of going
concern.
The auditor will therefore need to come to an opinion as to the going concern status of an entity but the focus of the auditor’s
evaluation of going concern is to see whether they agree with the assessment made by the management. Therefore whether
they agree with the basis of preparation of the financial statements, or the inclusion in a note to the financial statements, as
required by IAS 1, of any material uncertainty.
Evaluation techniques
In carrying out the going concern assessment, management will evaluate a wide variety of indicators, including operational
and financial. An entity employing good principles of corporate governance should be carrying out such an assessment as
part of the on-going management of the business.
Auditors will use a similar assessment technique in order to come to their own opinion as to the going concern status of an
entity. They will carry out an operational review of the business in order to confirm business understanding, and will conduct
a financial review as part of analytical procedures. Thus both management and auditors will use similar business risk
assessment techniques to discover any threats to the going concern status of the business.
Auditors should not see going concern as a ‘completion issue’, but be alert to issues affecting going concern throughout the
audit. In the same way that management should continually be managing risk (therefore minimising going concern risk),
auditors should be continually be alert to going concern problems throughout the duration of the audit.
However, one difference is that when going concern problems are discovered, the auditor is required by IAS 570 to carry out
additional procedures. Examples of such procedures would include:
– Analysing and discussing cash flow, profit and other relevant forecasts with management
– Analysing and discussing the entity’s latest available interim financial statements
– Reviewing events after the period end to identify those that either mitigate or otherwise affect the entity’s ability to
continue as a going concern, and
– Reading minutes of meetings of shareholders, those charged with governance and relevant committees for reference to
financing difficulties.
Management are not explicitly required to gather specific evidence about going concern, but as part of good governance would
be likely to investigate and react to problems discovered. -
第22题:
(ii) Recommend further audit procedures that should be carried out. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Further audit procedures:
Request from Peter Sheffield a written representation detailing:
– the exact nature of his control over Jarvis Co, i.e. if he is a shareholder then state his percentage shareholding, if
he is a member of senior management then state his exact position within the entity,
– a comment on whether in his opinion the balance is recoverable,
– a specific date by which the amount should be expected to be repaid, and
– a confirmation that there are no further balances outstanding from Jarvis Co, or any further transactions between
Jarvis Co and Pulp Co.
Tutorial note: Reference to the Exposure Draft ISA 550 Related Parties (Revised and Redrafted) requirement for both
general and specific management representations will be awarded credit.
Review the terms of any written confirmation of the amount, such as a signed agreement or invoice, checking whether
any interest is due to Pulp Co. The terms should be reviewed for details of any security offered, and the nature of the
consideration to be provided in settlement.
From discussion with Peter Sheffield, develop an understanding of the business purpose of the transaction, particularly
to understand whether the balance is a trade receivable or an investment.
Review the board minutes for evidence of any discussion of the transaction and the recoverability of the balance
outstanding.
Obtain the most recent audited financial statements of Jarvis Co and:
– ascertain whether Peter Sheffield is disclosed as the ultimate controlling party or disclosed as a member of key
management personnel,
– scrutinise the disclosure notes to find any disclosure of the transaction, where it should be described as a related
party liability, and
– perform. a liquidity analysis to establish whether the amount can be repaid from liquid assets. -
第23题:
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. All domain controllers and member servers run Windows Server 2008. All client computer run Windows 7. From a client computer, you create an audit policy by using the Advanced Audit Policy Configuration settings in the Default Domain Policy Group Policy object (GPO). You discover that the audit policy is not applied to the member servers. The audit policy is applied to the client computers. You need to ensure that the audit policy is applied to all member servers and all client computers. What should you do()
- A、Add a WMI filter to the Default Domain Policy GPO
- B、Modify the security settings of the Default Domain Policy GPO
- C、Configure a startup script that runs auditpol.exe on the member servers.
- D、Configure a startup script that runs auditpol.exe on the domain controllers.
正确答案:B
