(b) Using models where appropriate, what are likely to be the critical success factors (CSFs) as the businessgrows and develops? (10 marks)
题目
(b) Using models where appropriate, what are likely to be the critical success factors (CSFs) as the business
grows and develops? (10 marks)
相似考题
参考答案和解析
(b) David even at this early stage needs to identify the critical success factors and related performance indicators that will show
that the concept is turning into a business reality. Many of the success factors will be linked to customer needs and
expectations and therefore where David’s business must excel in order to outperform. the competition. As an innovator one of
the critical success factors will be the time taken to develop and launch the new vase. Being first-to-market will be critical for
success. His ability to generate sales from demanding corporate customers will be a real indicator of that success. David will
need to ensure that he has adequate patent protection for the product and recognise that it will have a product life cycle.
There look to be a number of alternative markets and the ability to customise the product may be a CSF. Greiner indicates
the different stages a growing business goes through and the different problems associated with each stage. One of David’s
key problems will be to decide what type of business he wants to be. From the scenario it looks as if he is aiming to carry
out most of the functions himself and there is a need to decide what he does and what he gets others to do for him. Indeed
the skills he has may be as an innovator rather than as someone who carries out manufacture, distribution, etc. Gift Designs
may develop most quickly as a firm that creates new products and then licences them to larger firms with the skills to
penetrate the many market opportunities that are present. It is important for David to recognise that turning the product
concept into a viable and growing business may result in a business and a business model very different to what he
anticipated. Gift Designs needs to have the flexibility and agility to take advantage of the opportunities that will emerge over
time.
更多“(b) Using models where appropriate, what are likely to be the critical success factors (CSFs) as the businessgrows and develops? (10 marks)”相关问题
-
第1题:
The twentieth century saw great change. In your opinion, what is one change that should be remembered about the twentieth century? Write an essay of about 400 words to state your opinion.
In the first part of your essay you should present your thesis statement, and in the second part you should support the thesis statement with appropriate details. In the last part you should bring what you have written to a natural conclusion or a summary.
You should supply an appropriate title for your essay.
Marks will be awarded for content, organization, grammar and appropriateness. Failure to follow the above instructions may result in a loss of marks.
正确答案:Computer The twentieth century witnessed great changes in the whole world: economic boom industrial development and raise in people's living standards to which technological evolution contributed a lot. Among all those inventions which was the greatest one? Different people have different views. Some think the greatest invention was television while others believe it should be atom energy. But as far as I am concerned in terms of the depth of influence no other inventions can be compared with computers which would remain unrivalled even for another one hundred years. First of all computers save a great deal of effort people spend on calculating. Before computers were invented people had to calculate manually. Sometimes it took scientists weeks even months to work out a result daring the course of which they might make mistakes and the accuracy of data was in turn affected. But with the help of computers people are freed from heavy calculation. It only takes seconds to have a result which used to take weeks in the past. Moreover not only the speed but also the accuracy is improved to a large extent. Computers can also simulate different environments that can't be created in real life. In the science research sometimes scientists need to have a simulation environment to improve their theories or as a basis of further research. Without computers it would be difficult to have accurate and reliable results. But computers can make everything easy. Just input programs and data everything will be done. With computers the storage of information has become easier which in turn has increased the whole world's efficiency. At banks post offices and supermarkets people no longer need to queue for a long time because computers help the working staff increase their work efficiency — files and data stored in computers can be located in a very short time and their chances of getting lost are lowered to a large extent. Computers' influence has been further reinforced with the appearance of Internet which was developed based on the local area network (LAN) of computers. Today Internet has become the fastest developing medium in the world and you can do almost everything you need on it: communicating with friends reading news watching movies listening to music etc. But you must do all the above things on a computer. Although many other inventions of the 20th century brought great convenience to human or changed people's lives computers have the most valuable contribution to human and it will have much more contribution in the future.
Computer The twentieth century witnessed great changes in the whole world: economic boom, industrial development and raise in people's living standards, to which technological evolution contributed a lot. Among all those inventions, which was the greatest one? Different people have different views. Some think the greatest invention was television, while others believe it should be atom energy. But as far as I am concerned, in terms of the depth of influence, no other inventions can be compared with computers, which would remain unrivalled even for another one hundred years. First of all, computers save a great deal of effort people spend on calculating. Before computers were invented, people had to calculate manually. Sometimes it took scientists weeks, even months to work out a result, daring the course of which they might make mistakes and the accuracy of data was in turn affected. But with the help of computers, people are freed from heavy calculation. It only takes seconds to have a result which used to take weeks in the past. Moreover, not only the speed but also the accuracy is improved to a large extent. Computers can also simulate different environments that can't be created in real life. In the science research, sometimes scientists need to have a simulation environment to improve their theories or as a basis of further research. Without computers it would be difficult to have accurate and reliable results. But computers can make everything easy. Just input programs and data, everything will be done. With computers, the storage of information has become easier, which in turn has increased the whole world's efficiency. At banks, post offices, and supermarkets, people no longer need to queue for a long time, because computers help the working staff increase their work efficiency — files and data stored in computers can be located in a very short time and their chances of getting lost are lowered to a large extent. Computers' influence has been further reinforced with the appearance of Internet, which was developed based on the local area network (LAN) of computers. Today, Internet has become the fastest developing medium in the world and you can do almost everything you need on it: communicating with friends, reading news, watching movies, listening to music etc. But you must do all the above things on a computer. Although many other inventions of the 20th century brought great convenience to human or changed people's lives, computers have the most valuable contribution to human, and it will have much more contribution in the future. 解析: 在上个世纪,世界发生了巨大的变化。题目要求考生自己命题,淡谈自己认为20世纪最应该记住的发明是什么。
文章本身并不难写,首先要确定自己的观点,就是20世纪最重要的发明是什么。所谓“最应该记住”,就是说它对整个世界的变化影响最大。写作时,可以有两种方法:一种是一一列举该发明的重要性,对社会的发展、人们的生活有什么重大的影响,论证时还可以用反证法说如果没有这种发明世界会怎么样;另外一种就是在列举该发明重要性的同时,将它和其他较为重要的发明进行对比,从而更加凸显其重要性。 -
第2题:
(c) Acting as an external consultant to Semer, discuss the validity of the proposed strategy to increase gearing, and explain whether or not the estimates produced in (b) above are likely to be accurate. (10 marks)
正确答案:(c) Report on the proposed adjustment of gearing through the repurchase of ordinary shares
The effect of capital structure on the value of a company is not fully understood.
Increasing the proportion of debt in the capital structure may reduce the overall cost of capital due to the interest on debt being a tax allowable expense. Even if a company is in a non-tax paying position, mixing additional low cost debt with relatively expensive equity might reduce the weighted average cost of capital. In such circumstances the proposed strategy to increase gearing would have some validity. However, increasing gearing can also bring problems. Risk to investors, and therefore the required returns on equity and debt, will increase as gearing increases. Very high levels of gearing might lead to
direct and indirect bankruptcy costs, with a detrimental effect on cash flow and corporate value. Any benefits from increasing the proportion of debt in the capital structure will be to some extent offset as a result of increased risk with high gearing.
The revised estimates of the effect on the cost of capital and value of Semer are not likely to be accurate. Reasons for this include:
(i) The company will not be able to repurchase the necessary shares at their current market value. Approximately £240 million value of equity would need to be repurchased, or more than one third of the existing market value of equity.
As repurchases take place it is likely that the share price will significantly increase.
(ii) The cost of debt is unlikely to remain constant. As more debt is issued lenders will demand a higher interest rate to compensate for the extra risk resulting from higher gearing levels. The cost of equity will also increase with higher gearing. These effects will increase the weighted average cost of capital to a higher level than that estimated.
(iii) The precise market values of debt and equity after the repurchase are unknown, and again will reflect the market attitude
to the new risk of the higher gearing.
The value of the company is likely to be much lower than that estimated, as the weighted average cost of capital is likely to be underestimated. -
第3题:
(d) Family owned and managed businesses often find delegation and succession difficult processes to get right.
What models would you recommend that Tony use in looking to change his leadership and management style
to create a culture in the Shirtmaster Group better able to deal with the challenges it faces? (10 marks)
正确答案:
(d) Much has been written on the links between leadership and culture and in particular the influence of the founder on the
culture of the organisation. Schein actually argues that leadership and culture are two sides of the same coin. Tony’s father
had a particular vision of the type of company he wanted and importance of product innovation to the success of the business.
Tony is clearly influenced by that cultural legacy and has maintained a dominant role in the business though there is little
evidence of continuing innovation. Using the McKinsey 7-S model the founder or leader is the main influence on the
development of the shared values in the firm that shapes the culture. However, it is clear from the scenario that Tony through
his ‘hands-on’ style. of leadership is affecting the other elements in the model – strategy, structure and systems – the ‘hard’
factors and the senior staff and their skills – the ‘soft’ factors – in making strategic decisions.
Delegation has been highlighted as one of the problems Tony has to face and it is a familiar one in family firms. Certainly
there could be need for him to give his senior management team the responsibility for the functional areas they nominally
control. Tony’s style. is very much a ‘hands-on’ style. but this may be inappropriate for handling the problems that the company
faces. Equally, he seems too responsible for the strategic decisions the company is taking and not effectively involving his
team in the strategy process. Style. is seen as a key factor in influencing the culture of an organisation and getting the right
balance between being seen as a paternalistic owner-manager and a chairman and chief executive looking to develop his
senior management team is difficult. Leadership is increasingly being seen as encouraging and enabling others to handle
change and challenge and questioning the assumptions that have influenced Shirtmaster’s strategic thinking and development
to date. The positive side of Tony’s style. of leadership is that he is both known and well regarded by the staff on the factory
floor. Unfortunately, if the decision is taken to source shirts from abroad this may mean that the manufacturing capability
disappears.
6D–ENGAA
Paper 3.5
Tony should be aware that changing the culture of an organisation is not an easy task and that as well as his leadership style
influencing, his leadership can also be constrained by the existing culture that exists in the Shirtmaster Group. Other models
that could be useful include Johnson, Scholes and Whittington’s cultural web and Lewin’s three-stage model of change and
forcefield analysis. Finally, Peters and Waterman in their classic study ‘In search of excellence’ provides insights into the closerelationship between leadership and creating a winning culture. -
第4题:
(b) ‘Strategic positioning’ is about the way that a company as a whole is placed in its environment and concerns its
‘fit’ with the factors in its environment.
With reference to the case as appropriate, explain how a code of ethics can be used as part of a company’s
overall strategic positioning. (7 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Code of ethics and strategic positioning
Strategic positioning is about the way that a whole company is placed in its environment as opposed to the operational level,
which considers the individual parts of the organisation.
Ethical reputation and practice can be a key part of environmental ‘fit’, along with other strategic issues such as generic
strategy, quality and product range.
The ‘fit’ enables the company to more fully meet the expectations, needs and demands of its relevant stakeholders – in this
case, European customers.
The ‘quality’ of the strategic ‘fit’ is one of the major determinants of business performance and so is vital to the success of
the business.
HPC has carefully manoeuvred itself to have the strategic position of being the highest ethical performer locally and has won
orders on that basis.
It sees its strategic position as being the ethical ‘benchmark’ in its industry locally and protects this position against its parent
company seeking to impose a new code of ethics.
The ethical principles are highly internalised in Mr Hogg and in the company generally, which is essential for effective strategic
implementation. -
第5题:
(b) Discuss FOUR factors that distinguish service from manufacturing organisations and explain how each of
these factors relates to the services provided by the Dental Health Partnership. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(b) The major characteristics of services which distinguish services from manufacturing are as follows:
– Intangibility.
When a dentist provides a service to a client there are many intangible factors involved such as for example the
appearance of the surgery, the personality of the dentist, the manner and efficiency of the dental assistant. The output
of the service is ‘performance’ by the dentist as opposed to tangible goods.
– Simultaneity.
The service provided by the dentist to the patient is created by the dentist at the same time as the patient consumed it
thus preventing any advance verification of quality.
– Heterogeneity.
Many service organisations face the problem of achieving consistency in the quality of its output. Whilst each of the
dentists within the Dental Health Partnership will have similar professional qualifications there will be differences in the
manner they provide services to clients.
– Perishability.
Many services are perishable. The services of a dentist are purchased only for the duration of an appointment. -
第6题:
(b) Using sensitivity analysis, estimate by what percentage each of the under-mentioned items, taken separately,
would need to change before the recommendation in (a) above is varied:
(i) Initial outlay;
(ii) Annual contribution. (4 marks)
正确答案: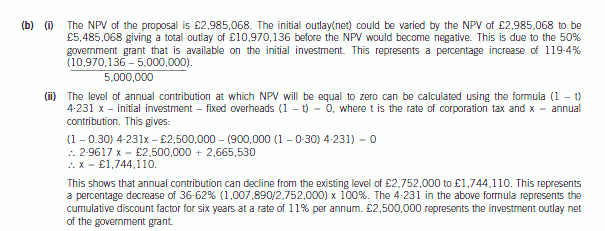
-
第7题:
(b) Explain FIVE critical success factors to the performance of HSC on which the directors must focus if HSC is
to achieve success in its marketplace. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Critical success factors are as follows:
Product quality
The fact that the production staff have no previous experience in a food production environment is likely to prove problematic.
It is vital that a comprehensive training programme is put in place at the earliest opportunity. HSC need to reach and maintain
the highest level of product quality as soon as possible.
Supply quality
The quality of delivery into SFG supermarkets assumes critical significance. Time literally will be of the essence since 90%
of all sandwiches are sold in SFG’s supermarkets before 2 pm each day. Hence supply chain management must be extremely
robust as there is very little scope for error.
Technical quality
Compliance with existing regulations regarding food production including all relevant factory health and safety requirements
is vital in order to establish and maintain the reputation of HSC as a supplier of quality products. The ability to store products
at the correct temperature is critical because sandwiches are produced for human consumption and in extreme circumstance
could cause fatalities.
External credibility
Accreditation by relevant trade associations/regulators will be essential if nationwide acceptance of HSC as a major producer
of sandwiches is to be established.
New product development
Whilst HSC have developed a range of healthy eating sandwiches it must be recognised that consumer tastes change and
that in the face of competition there will always be a need for a continuous focus on new product development.
Margin
Whilst HSC need to recognise all other critical success factors they should always be mindful that the need to obtain the
desired levels of gross and net margin remain of the utmost importance.
Notes: (i) Only five critical success factors were required.
(ii) Alternative relevant discussion and examples would be acceptable. -
第8题:
(b) Using the information provided, state the financial statement risks arising and justify an appropriate audit
approach for Indigo Co for the year ending 31 December 2005. (14 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Financial statement risks
Assets
■ There is a very high risk that inventory could be materially overstated in the balance sheet (thereby overstating profit)
because:
? there is a high volume of metals (hence material);
? valuable metals are made more portable;
? subsidy gives an incentive to overstate purchases (and hence inventory);
? inventory may not exist due to lack of physical controls (e.g. aluminium can blow away);
? scrap metal in the stockyard may have zero net realisable value (e.g. iron is rusty and slow-moving);
? quantities per counts not attended by an auditor have increased by a third.
■ Inventory could be otherwise misstated (over or under) due to:
? the weighbridge being inaccurate;
? metal qualities being estimated;
? different metals being mixed up; and
? the lack of an independent expert to identify/measure/value metals.
■ Tangible non-current assets are understated as the parts of the furnaces that require replacement (the linings) are not
capitalised (and depreciated) as separate items but treated as repairs/maintenance/renewals and expensed.
■ Cash may be understated due to incomplete recording of sales.
■ Recorded cash will be overstated if it does not exist (e.g. if it has been stolen).
■ Trade receivables may be understated if cash receipts from credit customers have been misappropriated.
Liabilities
■ The provision for the replacement of the furnace linings is overstated by the amount provided in the current and previous
year (i.e. in its entirety).
Tutorial note: Last replacement was two years ago.
Income statement
■ Revenue will be understated in respect of unrecorded cash sales of salvaged metals and ‘clinker’.
■ Scrap metal purchases (for cash) are at risk of overstatement:
? to inflate the 15% subsidy;
? to conceal misappropriated cash.
■ The income subsidy will be overstated if quantities purchased are overstated and/or overvalued (on the quarterly returns)
to obtain the amount of the subsidy.
■ Cash receipts/payments that were recorded only in the cash book in November are at risk of being unrecorded (in the
absence of cash book postings for November), especially if they are of a ‘one-off’ nature.
Tutorial note: Cash purchases of scrap and sales of salvaged metal should be recorded elsewhere (i.e. in the manual
inventory records). However, a one-off expense (of a capital or revenue nature) could be omitted in the absence of
another record.
■ Expenditure is overstated in respect of the 25% provision for replacing the furnace linings. However, as depreciation
will be similarly understated (as the furnace linings have not been capitalised) there is no risk of material misstatement
to the income statement overall.
Disclosure risk
■ A going concern (‘failure’) risk may arise through the loss of:
? sales revenue (e.g. through misappropriation of salvaged metals and/or cash);
? the subsidy (e.g. if returns are prepared fraudulently);
? cash (e.g. if material amounts stolen).
Any significant doubts about going concern must be suitably disclosed in the notes to the financial statements.
Disclosure risk arises if the requirements of IAS 1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’ are not met.
■ Disclosure risk arises if contingent liabilities in connection with the dumping of ‘clinker’ (e.g. for fines and penalties) are
not adequately disclosed in accordance with IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets’.
Appropriate audit approach
Tutorial note: In explaining why AN audit approach is appropriate for Indigo it can be relevant to comment on the
unsuitability of other approaches.
■ A risk-based approach is suitable because:
? inherent risk is high at the entity and financial assertion levels;
? material errors are likely to arise in inventory where a high degree of subjectivity will be involved (regarding quality
of metals, quantities, net realisable value, etc);
? it directs the audit effort to inventory, purchases, income (sales and subsidy) and other risk areas (e.g. contingent
liabilities).
■ A systems-based/compliance approach is not suited to the risk areas identified because controls are lacking/ineffective
(e.g. over inventory and cash). Also, as the audit appointment was not more than three months ago and no interim
audit has been conducted (and the balance sheet date is only three weeks away) testing controls is likely to be less
efficient than a substantive approach.
■ A detailed substantive/balance sheet approach would be suitable to direct audit effort to the appropriate valuation of
assets (and liabilities) existing at balance sheet date. Principal audit work would include:
? attendance at a full physical inventory count at 31 December 2005;
? verifying cash at bank (through bank confirmation and reconciliation) and in hand (through physical count);
? confirming the accuracy of the quarterly returns to the local authority.
■ A cyclical approach/directional testing is unlikely to be suitable as cycles are incomplete. For example the purchases
cycle for metals is ‘purchase/cash’ rather than ‘purchase/payable/cash’ and there is no independent third party evidence
to compensate for that which would be available if there were trade payables (i.e. suppliers’ statements). Also the cycles
are inextricably inter-related to cash and inventory – amounts of which are subject to high inherent risk.
■ Analytical procedures may be of limited use for substantive purposes. Factors restricting the use of substantive analytical
procedures include:
? fluctuating margins (e.g. as many factors will influence the price at which scrap is purchased and subsequently
sold, when salvaged, sometime later);
? a lack of reliable/historic information on which to make comparisons. -
第9题:
Examine the structure of the STUDENTS table: STUDENT_ID NUMBER NOT NULL, Primary Key STUDENT_NAME VARCHAR2(30) COURSE_ID VARCHAR2(10) NOT NULL MARKS NUMBER START_DATE DATE FINISH_DATE DATE You need to create a report of the 10 students who achieved the highest ranking in the course INT SQL and who completed the course in the year 1999. Which SQL statement accomplishes this task?()
- A、SELECT student_ id, marks, ROWNUM "Rank" FROM students WHERE ROWNUM <= 10 AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-99' AND course_id = 'INT_SQL' ORDER BY marks DESC;
- B、SELECT student_id, marks, ROWID "Rank" FROM students WHERE ROWID <= 10 AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-99' AND course_id = 'INT_SQL' ORDER BY marks;
- C、SELECT student_id, marks, ROWNUM "Rank" FROM (SELECT student_id, marks FROM students WHERE ROWNUM <= 10 AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-99' AND course_id = 'INT_SQL' ORDER BY marks DESC);
- D、SELECT student_id, marks, ROWNUM "Rank" FROM (SELECT student_id, marks FROM students ORDER BY marks DESC) WHERE ROWNUM <= 10 AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-99' AND course _ id ='INT _ SQL';
正确答案:D -
第10题:
单选题What is the best title for this passage?AGlobalization of the World
BRapid Development of High-tech Communication Equipment and Overseas Market
CSecret of Success for Modern Business
DKey Factors for Business and Business People in Modern World
正确答案: D解析:
文章主旨题。通读全文之后可以发现该篇文章的主要内容包括:现代通讯设备的发展使人们的交流更加便利;海外生意的不断发展;海外工作经验对升迁的作用;外语的掌握在商业方面的重要性。因此选项D符合包含了文章的主要内容,可作为文章标题。 -
第11题:
单选题Examine the structure of the STUDENTS table: STUDENT_ID NUMBER NOT NULL, Primary Key STUDENT_NAME VARCHAR2(30) COURSE_ID VARCHAR2(10) NOT NULL MARKS NUMBER START_DATE DATE FINISH_DATE DATE You need to create a report of the 10 students who achieved the highest ranking in the course INT SQL and who completed the course in the year 1999. Which SQL statement accomplishes this task? ()ASELECT student_ id, marks, ROWNUM Rank FROM students WHERE ROWNUM <= 10 AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-99 AND course_id = 'INT_SQL' ORDER BY mark DESC;
BSELECT student_id, marks, ROWID Rank FROM students WHERE ROWID <= 10 AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-99' AND course_id = 'INT_SQL' ORDER BY mark;
CSELECT student_id, marks, ROWNUM Rank FROM (SELECT student_id, marks FROM students WHERE ROWNUM <= 10 AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC- 99' AND course_id = 'INT_SQL' ORDER BY mark DESC;
DSELECT student_id, marks, ROWNUM Rank FROM (SELECT student_id, marks FROM students WHERE (finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99 AND '31-DEC-99' AND course_id = 'INT_SQL' ORDER BY marks DESC) WHERE ROWNUM <= 10;
ESELECT student id, marks, ROWNUM Rank FROM (SELECT student_id, marks FROM students ORDER BY marks) WHERE ROWNUM <= 10 AND finish date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-99' AND course _ id 'INT_SQL';
正确答案: B解析: 暂无解析 -
第12题:
单选题Examine the structure of the STUDENTS table: STUDENT_ID NUMBER NOT NULL, Primary Key STUDENT_NAME VARCHAR2(30) COURSE_ID VARCHAR2(10) NOT NULL MARKS NUMBER START_DATE DATE FINISH_DATE DATE You need to create a report of the 10 students who achieved the highest ranking in the course INT SQL and who completed the course in the year 1999. Which SQL statement accomplishes this task?()ASELECT student_ id, marks, ROWNUM Rank FROM students WHERE ROWNUM <= 10 AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-99 AND course_id = 'INT_SQL' ORDER BY mark DESC;
BSELECT student_id, marks, ROWID Rank FROM students WHERE ROWID <= 10 AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-99' AND course_id = 'INT_SQL' ORDER BY mark;
CSELECT student_id, marks, ROWNUM Rank FROM (SELECT student_id, marks FROM students WHERE ROWNUM <= 10 AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC- 99' AND course_id = 'INT_SQL' ORDER BY mark DESC;
DSELECT student_id, marks, ROWNUM Rank FROM (SELECT student_id, marks FROM students WHERE (finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99 AND '31-DEC-99' AND course_id = 'INT_SQL' ORDER BY marks DESC) WHERE ROWNUM <= 10;
ESELECT student id, marks, ROWNUM Rank FROM (SELECT student_id, marks FROM students ORDER BY marks) WHERE ROWNUM <= 10 AND finish date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-99' AND course _ id 'INT_SQL';
正确答案: D解析: 暂无解析 -
第13题:
5 An organisation’s goals can only be achieved through the efforts of motivated individuals.
Required:
Explain what is meant by the following terms:
(a) Hygiene factors. (8 marks)
正确答案:
5 Overview
Understanding what motivates people is necessary at all levels of management. It is important that professional accountants
understand the relevance of individual motivation. Unless individuals are well managed and motivated they are unlikely to cooperate
to achieve the organisation’s objectives.
Part (a):
(a) Hygiene (or maintenance) factors lead to job dissatisfaction because of the need to avoid unpleasantness. They are so called
because they can in turn be avoided by the use of ‘hygienic’ methods, that is, they can be prevented. Attention to these
hygiene factors prevents dissatisfaction but does not on its own provide motivation.
Hygiene factors (or ‘dissatisfiers’) are concerned with those factors associated with, but not directly a part of, the job itself.
Herzberg suggested that these are mainly salary and the perceived differences with others’ salaries, job security, working
conditions, the level and quality of supervision, organisational policy and administration and the nature of interpersonal
relationships. Resolution of hygiene factors, however, is short term, longer term resolution requires motivator factors. -
第14题:
The senior management team is aware of your success in implementing necessary change following a change in
ownership and control.
(c) Identify and explain the key areas of change likely to be needed in Bonar Paint in order to implement a
successful buyout. (15 marks)
正确答案:
(c) A management buyout represents a change in ownership rather than a change in strategy. However it should, as suggested
above, lead to a comprehensive review of the customers and product groups the firm chooses to supply and the basis on
which it seeks to achieve competitive advantage. In terms of the strategy pursued prior to the buyout, Bonar Paint seems to
be trying to achieve a differentiation focus strategy but without being able to achieve the higher profit margins associated with
the successful implementation of such a strategy.
If as seems likely Bonar Paint chooses to become a more focused company through product range reduction and serving fewer
customers, implementation of such a strategy will have clear implications for the whole of the organisation. Using the
McKinsey 7S model strategy change will lead to changes in the structure of the organisation. The departure of Bill and Jim
Bonar will have major repercussions for the roles taken by the three senior managers. Decisions will be needed on who is to
lead the company and the responsibilities of the other two managers. Bonar Paint has a very traditional functional structure
with the managers being responsible for discrete areas of activity. The change in ownership gives a major opportunity to see
whether this structure continues to be an appropriate one for handling the challenges of an increasingly competitive
environment. Any significant change to the product and/or customer portfolio as proposed by Tony Edmunds will need to be
implemented through a change to the structure. Product divisions may need to be set up if there is a decision to enter the
market for D-I-Y paints.
Systems will also need to change to accommodate any reduction in the product range and numbers of customers. Reference
has already been made to the impact on the production side of the business of such a strategic decision and the associated
consequences for areas such as sales and finance. Clearly, the lack of marketing information on product sales, customers and
profitability needs to be quickly addressed before any divestment decisions are taken. Making strategic decisions using poor
or inadequate information is a recipe for disaster. Decisions on new product development also will require a system that better
integrates the interests and information of the key functional areas.
Staff are the critical resource without which the buyout will not succeed. The change in ownership will cause uncertainty and
the buyout managers will need to spell out the changes that are both necessary and needed. Changes to the product and
customer portfolio will have a significant impact on some members of staff. Issues of redundancy/redeployment are best
addressed early, along with opportunities the change in strategy will create. Closely linked to staff are the skills those staff
will need to implement chosen strategy. The need to have a greater awareness of customer and competitor activity will require
new skills in the marketing area. Any investment in new production technology will affect the type of skills needed to use it.
The links between strategic decisions and human resource strategy need to be appreciated.
Style. concerns the way the three buyout managers carry out their new roles and communicate with staff. There is a significant
difference between leading and managing the business and each of the buyout managers will need to communicate a clear
sense of where the firm is going and inspiring staff to follow their vision and mission. This links closely with the concept of
shared values and the overall culture of the firm. The exit of the founders of the business could potentially create a cultural
void, which could lead to staff uncertainty. Unless quickly addressed good staff may leave the firm and adversely affect the
strategic change the new owners and managers are trying to introduce.
In implementing a chosen strategy there is a danger that the ‘hard’ Ss of strategy, structure and systems are attended to while
the soft Ss of staff, skills, style. and shared values are largely ignored. There is compelling evidence to suggest that it is thesoft Ss which will determine the success or otherwise of the management buyout. -
第15题:
(b) What are the advantages and disadvantages of using franchising to develop La Familia Amable budget hotel
chain? (8 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Franchising is typically seen as a quick and cost effective way of growing the business but Ramon should be aware of both
the advantages and disadvantages of using it as the preferred method of growth. Franchised chains are argued to benefit from
the sort of brand recognition and economies of scale not enjoyed by independent owner/managers. When combined with the
high levels of motivation normally associated with owner/managed businesses, franchises can be argued to get the best of
both worlds.
Franchising is defined as ‘a contractual agreement between two legally independent companies whereby the franchisor grants
the right to the franchisee to sell the franchisor’s product or do business under its trademarks in a given location for a specified
period of time. In return, the franchisee agrees to pay the franchisor a combination of fees, usually including an up-front
franchise fee, royalties calculated as a percentage of unit revenues, and an advertising conbribution that is also usually a
percentage of unit sales.’
Ramon is considering a type of franchising called ‘business-format franchising’, where the franchisor sells a way of doing
business to its franchisees. Business-format franchising is a model frequently found in the fast food and restaurant industry,
hotels and motels, construction and maintenance, and non-food retailing. Often these franchises are labour intensive and
relatively small-scale operations.
Franchising is seen as a safer alternative to growing the business organically, so while this may be true of well established
global franchises, failure rates among franchised small businesses were greater than those of independent businesses (in one
US study a 34·7% failure rate for franchises as opposed to 28·0% for independents over a six or seven year period). Often
it is the failure of the franchisor that brings down its franchisees. Failure stems from the franchisee not only having to rely on
their own skills and enthusiasm but also the capacity of the franchisor and other franchisees to make the overall operation
work.
The advantages to the franchisee are through gaining access to a well-regarded brand name that will generate a higher level
of demand and use of a tried and tested business model that should reduce the franchisee’s operating costs. Both of these
benefits stem from being a member of a well-established franchised system. Yet La Familia Amable along with many other
franchises will be new and small. These smaller franchises tend to be regional in scope, and fairly unknown outside their
regional market. This has a significant effect on what the franchisees can expect to gain from their franchisors and their
prospects of success. Both parties need to carefully assess the strengths and weaknesses of the system. Companies growing
via franchises need to take the time to understand their business model thoroughly and determine how franchising fits with
their long-term strategy. Care must be taken with the franchise agreement that creates a genuine partnership with the rightbalance between freedom and control over the franchisees. -
第16题:
(b) Discuss ways in which the traditional budgeting process may be seen as a barrier to the achievement of the
aims of EACH of the following models for the implementation of strategic change:
(i) benchmarking;
(ii) balanced scorecard; and
(iii) activity-based models. (12 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Benchmarking
Benchmarks enable goals to be set that may be based on either external measures of ‘best practice’ organisations or internal
cross-functional comparisons which exhibit ‘best practice’. A primary aim of the traditional budgeting process is the setting of
realistic targets that can be achieved within the budget period. The setting of realistic targets means that the extent of
underperformance against ‘best practice’ standards loses visibility, and thus short-term financial targets remain the
predominant focus of the traditional budgeting process. It is arguable that because the budgetary reporting system purports
to give managers ‘control’, there is very little real incentive to seek out benchmarks which may be used to raise budgeted
performance targets. Much depends upon the prevailing organisational culture since benchmarking may be viewed as an
attempt by top management to impose impossible targets upon operational managers. The situation is further exacerbated
where organisations do not measure their success relative to their competition.
Balanced scorecard
The Balanced scorecard is often misunderstood as a consequence of the failure by top management to ensure that it is
implemented effectively within the organisation. Thus it may be viewed as the addition of a few non-financial measures to
the conventional budget. In an attempt to overcome this misperception many management teams now establish a
performance-rewards linkage based upon the achievement of Scorecard targets for the forthcoming budget period.
Unfortunately this can precipitate dysfunctional behaviour at every level within the organisation.
Even in situations where the Scorecard has been well-designed and well-implemented it is difficult for it to gain widespread
acceptance. This is because all too often there exists a culture which places a very high value upon the achievement of the
fixed annual targets in order to avoid the loss of status, recognition and rewards.
A well-constructed Scorecard contains a mix of long-term and short-term measures and therefore drives the company in the
direction of medium-term strategic goals which are supported by cross-functional initiatives. On the other hand, the budgeting
process focuses the organisation on the achievement of short-term financial goals supported by the initiatives of individual
departments. Budgets can also act as an impediment to the acceptance of responsibility by local managers for the
achievement of the Scorecard targets. This is often the case in situations where a continued emphasis exists on meeting shortterm
e.g. quarterly targets.
Activity-based models
Traditional budgets show the costs of functions and departments (e.g. staff costs and establishment costs) instead of the costs
of those activities that are performed by people (e.g. receipt of goods inwards, processing and dispatch of orders etc). Thus
managers have no visibility of the real ‘cost drivers’ of their business. In addition, it is probable that a traditional budget
contains a significant amount of non-value-added costs that are not visible to the managers. The annual budget also tends
to fix capacity for the forthcoming budget period thereby undermining the potential of Activity-based management (ABM)
analysis to determine required capacity from a customer demand perspective. Those experienced in the use of ABM
techniques are used to dealing with such problems, however their tasks would be much easier to perform. and their results
made more reliable if these problems were removed. -
第17题:
(ii) the factors that should be considered in the design of a reward scheme for BGL; (7 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) The factors that should be considered in the design of a reward scheme for BGL.
– Whether performance targets should be set with regard to results or effort. It is more difficult to set targets for
administrative and support staff since in many instances the results of their efforts are not easily quantifiable. For
example, sales administrators will improve levels of customer satisfaction but quantifying this is extremely difficult.
– Whether rewards should be monetary or non-monetary. Money means different things to different people. In many
instances people will prefer increased job security which results from improved organisational performance and
adopt a longer term-perspective. Thus the attractiveness of employee share option schemes will appeal to such
individuals. Well designed schemes will correlate the prosperity of the organisation with that of the individuals it
employs.
– Whether the reward promise should be implicit or explicit. Explicit reward promises are easy to understand but in
many respects management will have their hands tied. Implicit reward promises such as the ‘promise’ of promotion
for good performance is also problematic since not all organisations are large enough to offer a structured career
progression. Thus in situations where not everyone can be promoted there needs to be a range of alternative reward
systems in place to acknowledge good performance and encourage commitment from the workforce.
– The size and time span of the reward. This can be difficult to determine especially in businesses such as BGL
which are subject to seasonal variations. i.e. summerhouses will invariably be purchased prior to the summer
season! Hence activity levels may vary and there remains the potential problem of assessing performance when
an organisation operates with surplus capacity.
– Whether the reward should be individual or group based. This is potentially problematic for BGL since the assembly
operatives comprise some individuals who are responsible for their own output and others who work in groups.
Similarly with regard to the sales force then the setting of individual performance targets is problematic since sales
territories will vary in terms of geographical spread and customer concentration.
– Whether the reward scheme should involve equity participation? Such schemes invariably appeal to directors and
senior managers but should arguably be open to all individuals if ‘perceptions of inequity’ are to be avoided.
– Tax considerations need to be taken into account when designing a reward scheme. -
第18题:
(c) Using sensitivity analysis, estimate by what percentage the life cycle of the Snowballer would need to change
before the recommendation in (a) above is varied. (4 marks)
正确答案: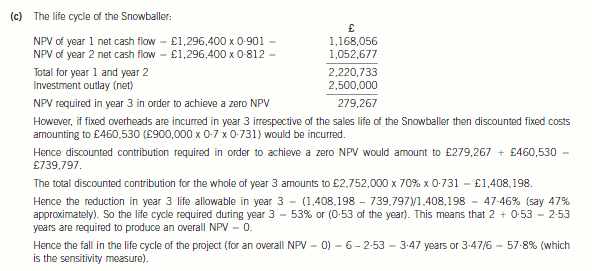
-
第19题:
(b) Identify the most appropriate approved share option scheme for Happy Home Ltd. Outline the scheme
requirements and the tax benefits of using it compared to the current unapproved scheme. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Share option scheme
The scheme that is best suited to Happy Home Limited is the enterprise management incentive (EMI) scheme. This share
option scheme is aimed at small fast growing companies, and because the potential risks are considered to be higher, the
available rewards are greater.
To qualify, the company must be a trading company, carrying out a qualifying trade in the United Kingdom, with gross assets
no more than £30m. The company must not be under the control of another company.
A qualifying company can grant each employee unexercised options over shares worth up to £100,000 per employee subject
to a total overall limit of unexercised options of £3 million. The options must be granted for commercial reasons to recruit and
retain the employee(s).
A qualifying employee is one who works on average 25 hours per week or 75% of their working time and who does not
(together with his/her associates) have a material interest in the company.
No income tax or national insurance is charged on either the grant or the exercise of the option provided that the option is
exercised not more than 10 years from the date of the grant and the amount paid is not less than the market value of the
shares at the time the option was granted.
On the sale of the shares, capital gains tax will apply, but business asset taper relief is available. Also in this case, the taper
relief starts from the date the option is granted and not from the date of exercise, as is the case with other option schemes. -
第20题:
What are three factors a network administrator must consider before implementing Netflow in the network?()
- A、CPU utilization
- B、where Netflow data will be sent
- C、number of devices exporting Netflow data
- D、port availability
- E、SNMP version
- F、WAN encapsulation
正确答案:A,B,C -
第21题:
Examine the structure of the STUDENTS table: STUDENT_ID NUMBER NOT NULL, Primary Key STUDENT_NAME VARCHAR2(30) COURSE_ID VARCHAR2(10) NOT NULL MARKS NUMBER START_DATE DATE FINISH_DATE DATE You need to create a report of the 10 students who achieved the highest ranking in the course INT SQL and who completed the course in the year 1999. Which SQL statement accomplishes this task? ()
- A、SELECT student_ id, marks, ROWNUM "Rank" FROM students WHERE ROWNUM <= 10 AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-99 AND course_id = 'INT_SQL' ORDER BY mark DESC;
- B、SELECT student_id, marks, ROWID "Rank" FROM students WHERE ROWID <= 10 AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-99' AND course_id = 'INT_SQL' ORDER BY mark;
- C、SELECT student_id, marks, ROWNUM "Rank" FROM (SELECT student_id, marks FROM students WHERE ROWNUM <= 10 AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC- 99' AND course_id = 'INT_SQL' ORDER BY mark DESC;
- D、SELECT student_id, marks, ROWNUM "Rank" FROM (SELECT student_id, marks FROM students WHERE (finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99 AND '31-DEC-99' AND course_id = 'INT_SQL' ORDER BY marks DESC) WHERE ROWNUM <= 10;
- E、SELECT student id, marks, ROWNUM "Rank" FROM (SELECT student_id, marks FROM students ORDER BY marks) WHERE ROWNUM <= 10 AND finish date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-99' AND course _ id 'INT_SQL';
正确答案:D -
第22题:
单选题What are hamburgers most likely to be named after?AThe recipe for making them.
BThe person who invented them.
CThe place where they were first sold.
DThe restaurant where they are initially served.
正确答案: C解析: -
第23题:
单选题Examine the structure of the STUDENTS table: STUDENT_ID NUMBER NOT NULL, Primary Key STUDENT_NAME VARCHAR2(30) COURSE_ID VARCHAR2(10) NOT NULL MARKS NUMBER START_DATE DATE FINISH_DATE DATE You need to create a report of the 10 students who achieved the highest ranking in the course INT SQL and who completed the course in the year 1999. Which SQL statement accomplishes this task?()ASELECT student_ id, marks, ROWNUM Rank FROM students WHERE ROWNUM <= 10 AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-99' AND course_id = 'INT_SQL' ORDER BY marks DESC;
BSELECT student_id, marks, ROWID Rank FROM students WHERE ROWID <= 10 AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-99' AND course_id = 'INT_SQL' ORDER BY marks;
CSELECT student_id, marks, ROWNUM Rank FROM (SELECT student_id, marks FROM students WHERE ROWNUM <= 10 AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-99' AND course_id = 'INT_SQL' ORDER BY marks DESC);
DSELECT student_id, marks, ROWNUM Rank FROM (SELECT student_id, marks FROM students ORDER BY marks DESC) WHERE ROWNUM <= 10 AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-99' AND course _ id ='INT _ SQL';
正确答案: D解析: 暂无解析
