针对以下C语言程序,请按要求回答问题。已知link. c源程序如下:/*link. c程序对单向链表进行操作,首先建立一个单向链表,然后根据用户的选择可以对其进行插入结点、删除结点和链表反转操作*/include<stdio. h>include<stdlib. h>typedef struct list_node * list_pointer; //定义链表指针typedef struct list_node{ //定义链表结构int data;list_pointer link;}list_node;
题目
针对以下C语言程序,请按要求回答问题。
已知link. c源程序如下:
/*link. c程序对单向链表进行操作,首先建立一个单向链表,然后根据用户的选择可以对其进行插入结点、删除结点和链表反转操作*/
include<stdio. h>
include<stdlib. h>
typedef struct list_node * list_pointer; //定义链表指针
typedef struct list_node{ //定义链表结构
int data;
list_pointer link;
}list_node;
//用到的操作函数
list_pointer create(); //建立一个单向链表
void insert(list_pointer * p_ptr,list_pointer node); //在node后加入一个新的结点
void delete_node(list_pointer * p_ptr,list_pointer trail,list_pointer node);
//删除前一个结点是trail的当前结点node
void print(list_pointer * p_ptr); //打印链表结点中的值
list_pointer invert(list_pointer lead); //反转链表
int main()
{
list_pointer ptr=NULL;
list_pointer node,trail;
list_pointer * P=&ptr;
int choose,location,i;
printf("you should create a link first:\n");
//建立一个单向链表
prt=create(); //ptr指向链表的第一个结点
print(ptr);
//根据用户的不同选择进行相应的操作:
printf("input number 0,you can quit the program\n");
printf("input number 1,you can insert a new node to link\n"):
printf("input number 2,you can delete a node from the link\n");
printf("input number 3,you can invert the link\n"):
printf("please input you choice\n");
scanf("%d",&choose);
while(choose!=0){
switch(choose){
case 1:
i=1:
while(i<location){
node=node->link;
i++:
}
insert(p,node); //p为指向ptr的指针
print(ptr);
break;
case 2:
printf("you will delete a node from the link\n");
printf("please input the location of the node:\n");
scanf("%d",&location):
node=ptr;
if(location==1)
trail=NULL;
trail=ptr;
i=1:
while(i<location){
trail=trail->link:
i++:
}
node=trail->link;
delete_node(p,trail,node);
print(ptr);
break;
case 3:
printf("you will invert the link\n");
ptr=invert(ptr);
print(ptr);
break;
default;
break;
return -1;
}
printf("please input you choice\n");
scanf("%d". &choose):
}
return 0;
//根据用户的输入值建立一个新的单向链表:
list_pointer create()
{
int i,current,length;
list_pointer p1,p2,head;
printf("please input the node number of the link:\n");
scanf("%d". &length):
printf("the number of the link is:%d",length);
printf("please input the data for the link node:\n");
i=0;
p1=p2=(list_pointer)malloc(sizeof(list_node));
head=p1;
for(i=1;i<length;i++){
scanf("%d",&current);
p1->data=current;
p2->link=p1;
p2=p1;
p1=(list_pointer)malloc(sizeof(list_node));
}
p2->link=NULL;
return head;
}
画出主函数main的控制流程图。
相似考题
参考答案和解析
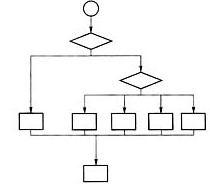
主函数的控制流程如下图所示。

更多“针对以下C语言程序,请按要求回答问题。 已知link. c源程序如下: /*link. c程序对单向链表进行操作 ”相关问题
-
第1题:
已知某高级语言源程序A经编译后得到机器C上的目标程序B,则(24)。
A.对B进行反编译,不能还原出源程序A
B.对B进行反汇编,不能得到与源程序A等价的汇编程序代码
C.对B进行反编译,得到的是源程序A的变量声明和算法流程
D.对A和B进行交叉编译,可以产生在机器C上运行的动态链接库
正确答案:A
解析:本题考查程序语言方面的基础知识。编译是将高级语言源程序翻译成机器语言程序(汇编形式或机器代码形式),反编译是编译的逆过程。反编译通常不能把可执行文件还原成高级语言源代码,只能转换成功能上等价的汇编程序。 -
第2题:
● 已知某高级语言源程序A经编译后得到机器C上的目标程序B,则 (21) 。
(21)
A. 对B进行反编译,一般不能还原出源程序A
B. 对B进行反汇编,不能得到与源程序A等价的汇编程序代码
C. 对B进行反编译,得到的是源程序A的变量声明和算法流程
D. 对A和B进行交叉编译,可以产生在机器C上运行的动态链接库
正确答案:A
-
第3题:
1.以下对C语言的描述中正确的是 。
A.C语言源程序中可以有重名的函数
B.C语言源程序中要求每行只能书写一条语句
C.注释可以出现在C语言源程序中的任何位置
D.最小的C语言源程序中没有任何内容
C -
第4题:
以下对C语言的描述中,正确的是______。
A.C语言源程序中可以有重名的函数
B.C语言源程序中要求每行只能书写一条语句
C.注释可以出现在C语言源程序中的任何位置
D.最小的C语言源程序中没有任何内容
正确答案:C
-
第5题:
已知某高级语言源程序A经编译后得到机器C上的目标程序B,则( )。A.B进行反编译,不能还原出源程序A
B.对B进行反汇编,不能得到与源程序A等价的汇编程序代码
C.对B进行反编译,得到的是源程序A的变量声明和算法流程
D.对A和B进行交叉编译,可以产生在机器C上运行的动态链接库答案:A解析:本题考查程序语言方面的基础知识。编译是将高级语言源程序翻译成机器语言程序(汇编形式或机器代码形式),反编译是编译的逆过程。反编译通常不能把可执行文件还原成高级语言源代码,只能转换成功能上等价的汇编程序。 -
第6题:
8、处理器芯片能够直接理解并执行的是()。
A.C语言源程序
B.汇编语言源程序
C.Python语言源程序
D.机器语言源程序
E.操作系统命令
机器语言源程序
