有以下程序 include struct NODE {int num;stmct NODE*next;}; main() { struct NODE有以下程序#include<stdlib.h>struct NODE{ int num;stmct NODE*next;};main(){ struct NODE*p,*q,*r;p=(struct NODE*)malloc(sizeof(struct NODE));q=(struct NODE*)malloc(sizeof(struct NODE));r=(
题目
有以下程序
#include<stdlib.h>
struct NODE
{ int num;stmct NODE*next;};
main()
{ struct NODE*p,*q,*r;
p=(struct NODE*)malloc(sizeof(struct NODE));
q=(struct NODE*)malloc(sizeof(struct NODE));
r=(struct NODE*)malloc(sizeof(struct NODE));
p->num=10;q->num=20;r->num=30;
p->next=q;q->next=r;
printf(“%d\n”,p->num+q->next->num);
}
程序运行后的输出结果是
A.10
B.20
C.30
D.40
相似考题
更多“有以下程序 #include<stdlib.h> struct NODE {int num;stmct NODE*next;}; main() { struct NODE ”相关问题
-
第1题:
已知形成链表的存储结构如下图所示,则下述类型描述中的空白处应填______。 struct 1ink { char data; }node;
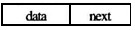
A.struct link next
B.link*next
C.sluct next link
D.struct link*next
正确答案:D
解析:在单向链表中,由于每个结点需要存储下—个结点的地址,且下—个结点的数据类型与前—个结点的数据类型完全相同,故应为strect link*next。 -
第2题:
下而程序实现十进制向其他进制的转换。
[C++程序]
include"ioStream.h"
include"math.h"
include <conio.h>
typedef struct node{
int data;
node *next;
}Node;
class Transform
{
public:
void Trans(int d,int i); //d为数字;i为进制
void print();
private:
Node *top;
};
void Transform.:Trans(int d,int i)
{
int m,n=0;
Node *P;
while(d>0)
{
(1) ;
d=d/i;
p=new Node;
if(!n){
P->data=m;
(2) j
(3) ;
n++;
}
else{
p->data=m;
(4) ;
(5) ;
}
}
}
void Transform.:print()
{
Node *P;
while(top!=NULL)
{
p=top;
if(P->data>9)
cout<<data+55:
else
cout<<data;
top=p->next;
delete P;
}
}
正确答案:(1)m=d%i (2) top=p (3) top->next=NULL (4) p->next=top (5) top=p
(1)m=d%i (2) top=p (3) top->next=NULL (4) p->next=top (5) top=p 解析:本题考查C++编程,主要考查了链表的使用。
所有的问题只出在函数Trans中,它的功能是完成将十进制数d转换为任意进制i的数,并存在数组中。函数中首先定义了一个指向链表节点的指针,然后开始进行转换,进制转换应该是一个很常见的问题,就是不断地求模运算,所以(1)处应填入“m=d%i”。然后,我们要把求模的结果保存到链表节点中,并使链表首指针指向该节点,节点中指向下一个节点的指针设为空,所以(2)处应填入top=p,(3)处应填入top->next=NULL。由于求模运算是从低位到高位逐位求出的,所以在进行完第二次求模运算后,应该将第二次运算的结果放到链表首位,所以(4)处应填入p->next=top,(5)处应填入top=p。 -
第3题:
以下程序中函数fun的功能是:构成—个如图所示的带头结点的单向链表,在结点的数据域中放入了具有两个字符的字符串。函数disp的功能是显示输出该单向链表中所有结点中的字符串。请填空完成函数disp。

include<stdio.h>
typedef struct node /*链表结点结构*/
{ char sub[3];
struct node *next;
}Node;
Node fun(char s) /* 建立链表*/
{ ...... }
void disp(Node *h)
{ Node *p;
p=h->next;
while([ ])
{printf("%s\n",p->sub);p=[ ];}
}
main()
{ Node *hd;
hd=fun(); disp(hd);printf("\n");
}
正确答案:p!=NULL 或 p 或 p!=0 或 p!='0' p->next 或 (*P).next
p!=NULL 或 p 或 p!=0 或 p!='0' p->next 或 (*P).next 解析:此题主要考核的是用指针处理链表。自定义结构体类型名为Node,并定义一个指向结点类型的指针next。用Node来定义头结点指针变量h,并定义另—个指针变量p指向了第—个结点,在满足p未指向最后—个结点的空指针时,输出p所指向结点的字符串,所以第—个空填p!=NULL或p或p!=0或p!='\0',然后将p指向下一个非空结点,所以第二个空填p->next或与其等效的形式,反复执行直到所有的结点都输出,即遇到p的值为NULL。 -
第4题:
下列给定程序中,是建立一个带头结点的单向链表,并用随机函数为各结点数据域赋值。函数fun的作用是求出单向链表结点(不包括头结点)数据域中的最大值,并且作为函数值返回。
请改正程序指定部位的错误,使它能得到正确结果。
[注意] 不要改动main函数,不得增行或删行,也不得更改程序的结构。
[试题源程序]
include<stdio.h>
include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct aa
{
int data;
struct aa *next;
}NODE;
fun(NODE *h)
{
int max=-1;
NODE *p;
/***********found************/
p=h;
while(p)
{
if(p->data>max)
max=p->data;
/************found************/
p=h->next;
}
return max;
}
outresult(int s, FILE *Pf)
{
fprintf(pf, "\nThe max in link: %d\n", s);
}
NODE *creatlink(int n, int m)
{
NODE *h, *p, *s, *q;
int i, x;
h=p=(NODE *)malloc(sizeof(NODE));
h->data=9999;
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
s=(NODE *)malloc(sizeof(NODE));
s->data=rand()%m; s->next=p->next;
p->next=s; p=p->next;
}
p->next=NULL;
return h;
}
outlink(NODE *h, FILE *pf)
{
NODE *p;
p=h->next;
fprintf(Pf, "\nTHE LIST:\n\n HEAD");
while(P)
{
fprintf(pf, "->%d", P->datA); p=p->next;
}
fprintf(pf, "\n");
}
main()
{
NODE *head; int m;
head=cteatlink(12,100);
outlink(head, stdout);
m=fun(head);
printf("\nTHE RESULT"\n");
outresult(m, stdout);
}
正确答案:(1)错误:p=h; 正确:p:h->next; (2)错误:p=h->next; 正确:p=p->next;
(1)错误:p=h; 正确:p:h->next; (2)错误:p=h->next; 正确:p=p->next; 解析:程序中使用while循环语句并结合结构指针p来找到数据域中的最大值。
错误1:P指向形参结构指针h的next指针,所以应改为:p=h->next;
错误2:p指向自己的下一个结点,所以应改为:p=p->next -
第5题:
有以下程序: includestruct NODE { int num; struct NODE*next; }; main() { struct 有以下程序:
#include <stdlib.h>
struct NODE
{ int num; struct NODE *next; };
main()
{ struct NODE *p,*q,*r;
p=(struct NODE*)malloc(sizeof(struct NODE));
q=(struct NODE*)mallloc(sizeof(struct NODE));
r=(struct NODE*)malloc(sizeof(struct NODE));
p->num=10;q->num=20; r->num=30;
p->next=q;q->next=r;
printf("%d\n",p->num+q->next->num);
}
程序运行后的输出结果是( )。
A.10
B.20
C.30
D.40
正确答案:D
解析:本题在主函数中首先定义了3个结构体指针变量p,q,r。然后调用内存分配函数分别为其分配地址空间,程序中变量p->num的值为10,指针变量q->next指向指针变量r,r->num的值为30,所以变量q->next->num的值为30,因此,表达式p->num+q->next->num的值为10+30=40。所以4个选项中D正确。 -
第6题:
有以下程序: includestruct NODE{int nurn;struct NODE *next; }; main() { struct 有以下程序:
#include <stdlib.h>
struct NODE{
int nurn;
struct NODE *next;
};
main()
{ struct NODE *p,*q,*r;
int sum=0;
P=(struct NODE*)malloc(sizeof(struct NODE));
q=(struct NODE*)malloc(sizeof(struct NODE));
r=(struct NODE*)malloc(sizeof(struct NODE));
p->num=1;q->num=2;r->num=3;
p->next=q;q->next=r;r->next=NULL;
sum+=q->next->num;sum+=p->num;
Printf("%d\n",sum);
}
执行后的输出结果是( )。
A.3
B.4
C.5
D.6
正确答案:B
解析:本题中定义了一个结点structNODE,在主函数中定义了三个结点变量指针p、q和r,接着通过malloc函数分配了三个结点并让p、q和r分别指向他们,再接着给p、q和r所指向的结点的num域赋值为1、2、3,然后让结点p指向小让q指向r,r指向NULL。显然q->next->num的值为指针r所指向结点的num域的值为3,p->num的值为指针p所指向结点的num域的值为1,故最后输出s的值为3+1=4。所以,4个选项中选项B符合题意。
