(c) During the year Albreda paid $0·1 million (2004 – $0·3 million) in fines and penalties relating to breaches ofhealth and safety regulations. These amounts have not been separately disclosed but included in cost of sales.(5 marks)Required:For each of t
题目
(c) During the year Albreda paid $0·1 million (2004 – $0·3 million) in fines and penalties relating to breaches of
health and safety regulations. These amounts have not been separately disclosed but included in cost of sales.
(5 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Albreda Co for the year ended
30 September 2005.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
相似考题
参考答案和解析
(c) Fines and penalties
(i) Matters
■ $0·1 million represents 5·6% of profit before tax and is therefore material. However, profit has fallen, and
compared with prior year profit it is less than 5%. So ‘borderline’ material in quantitative terms.
■ Prior year amount was three times as much and represented 13·6% of profit before tax.
■ Even though the payments may be regarded as material ‘by nature’ separate disclosure may not be necessary if,
for example, there are no external shareholders.
■ Treatment (inclusion in cost of sales) should be consistent with prior year (‘The Framework’/IAS 1 ‘Presentation of
Financial Statements’).
■ The reason for the fall in expense. For example, whether due to an improvement in meeting health and safety
regulations and/or incomplete recording of liabilities (understatement).
■ The reason(s) for the breaches. For example, Albreda may have had difficulty implementing new guidelines in
response to stricter regulations.
■ Whether expenditure has been adjusted for in the income tax computation (as disallowed for tax purposes).
■ Management’s attitude to health and safety issues (e.g. if it regards breaches as an acceptable operational practice
or cheaper than compliance).
■ Any references to health and safety issues in other information in documents containing audited financial
statements that might conflict with Albreda incurring these costs.
■ Any cost savings resulting from breaches of health and safety regulations would result in Albreda possessing
proceeds of its own crime which may be a money laundering offence.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ A schedule of amounts paid totalling $0·1 million with larger amounts being agreed to the cash book/bank
statements.
■ Review/comparison of current year schedule against prior year for any apparent omissions.
■ Review of after-date cash book payments and correspondence with relevant health and safety regulators (e.g. local
authorities) for liabilities incurred before 30 September 2005.
■ Notes in the prior year financial statements confirming consistency, or otherwise, of the lack of separate disclosure.
■ A ‘signed off’ review of ‘other information’ (i.e. directors’ report, chairman’s statement, etc).
■ Written management representation that there are no fines/penalties other than those which have been reflected in
the financial statements.
更多“(c) During the year Albreda paid $0·1 million (2004 – $0·3 million) in fines and penalties relating to breaches ofhealth and safety regulations. These amounts have not been separately disclosed but included in cost of sales.(5 marks)Required:For each of t”相关问题
-
第1题:
(b) One of the hotels owned by Norman is a hotel complex which includes a theme park, a casino and a golf course,
as well as a hotel. The theme park, casino, and hotel were sold in the year ended 31 May 2008 to Conquest, a
public limited company, for $200 million but the sale agreement stated that Norman would continue to operate
and manage the three businesses for their remaining useful life of 15 years. The residual interest in the business
reverts back to Norman after the 15 year period. Norman would receive 75% of the net profit of the businesses
as operator fees and Conquest would receive the remaining 25%. Norman has guaranteed to Conquest that the
net minimum profit paid to Conquest would not be less than $15 million. (4 marks)
Norman has recently started issuing vouchers to customers when they stay in its hotels. The vouchers entitle the
customers to a $30 discount on a subsequent room booking within three months of their stay. Historical
experience has shown that only one in five vouchers are redeemed by the customer. At the company’s year end
of 31 May 2008, it is estimated that there are vouchers worth $20 million which are eligible for discount. The
income from room sales for the year is $300 million and Norman is unsure how to report the income from room
sales in the financial statements. (4 marks)
Norman has obtained a significant amount of grant income for the development of hotels in Europe. The grants
have been received from government bodies and relate to the size of the hotel which has been built by the grant
assistance. The intention of the grant income was to create jobs in areas where there was significant
unemployment. The grants received of $70 million will have to be repaid if the cost of building the hotels is less
than $500 million. (4 marks)
Appropriateness and quality of discussion (2 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above income would be treated in the financial statements of Norman for the year ended
31 May 2008.
正确答案:
(b) Property is sometimes sold with a degree of continuing involvement by the seller so that the risks and rewards of ownership
have not been transferred. The nature and extent of the buyer’s involvement will determine how the transaction is accounted
for. The substance of the transaction is determined by looking at the transaction as a whole and IAS18 ‘Revenue’ requires
this by stating that where two or more transactions are linked, they should be treated as a single transaction in order to
understand the commercial effect (IAS18 paragraph 13). In the case of the sale of the hotel, theme park and casino, Norman
should not recognise a sale as the company continues to enjoy substantially all of the risks and rewards of the businesses,
and still operates and manages them. Additionally the residual interest in the business reverts back to Norman. Also Norman
has guaranteed the income level for the purchaser as the minimum payment to Conquest will be $15 million a year. The
transaction is in substance a financing arrangement and the proceeds should be treated as a loan and the payment of profits
as interest.
The principles of IAS18 and IFRIC13 ‘Customer Loyalty Programmes’ require that revenue in respect of each separate
component of a transaction is measured at its fair value. Where vouchers are issued as part of a sales transaction and are
redeemable against future purchases, revenue should be reported at the amount of the consideration received/receivable less
the voucher’s fair value. In substance, the customer is purchasing both goods or services and a voucher. The fair value of the
voucher is determined by reference to the value to the holder and not the cost to the issuer. Factors to be taken into account
when estimating the fair value, would be the discount the customer obtains, the percentage of vouchers that would be
redeemed, and the time value of money. As only one in five vouchers are redeemed, then effectively the hotel has sold goods
worth ($300 + $4) million, i.e. $304 million for a consideration of $300 million. Thus allocating the discount between the
two elements would mean that (300 ÷ 304 x $300m) i.e. $296·1 million will be allocated to the room sales and the balance
of $3·9 million to the vouchers. The deferred portion of the proceeds is only recognised when the obligations are fulfilled.
The recognition of government grants is covered by IAS20 ‘Accounting for government grants and disclosure of government
assistance’. The accruals concept is used by the standard to match the grant received with the related costs. The relationship
between the grant and the related expenditure is the key to establishing the accounting treatment. Grants should not be
recognised until there is reasonable assurance that the company can comply with the conditions relating to their receipt and
the grant will be received. Provision should be made if it appears that the grant may have to be repaid.
There may be difficulties of matching costs and revenues when the terms of the grant do not specify precisely the expense
towards which the grant contributes. In this case the grant appears to relate to both the building of hotels and the creation of
employment. However, if the grant was related to revenue expenditure, then the terms would have been related to payroll or
a fixed amount per job created. Hence it would appear that the grant is capital based and should be matched against the
depreciation of the hotels by using a deferred income approach or deducting the grant from the carrying value of the asset
(IAS20). Additionally the grant is only to be repaid if the cost of the hotel is less than $500 million which itself would seem
to indicate that the grant is capital based. If the company feels that the cost will not reach $500 million, a provision should
be made for the estimated liability if the grant has been recognised. -
第2题:
(ii) The percentage change in revenue, total costs and net assets during the year ended 31 May 2008 that
would have been required in order to have achieved a target ROI of 20% by the Beetown centre. Your
answer should consider each of these three variables in isolation. State any assumptions that you make.
(6 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) The ROI of Beetown is currently 13·96%. In order to obtain an ROI of 20%, operating profit would need to increase to
(20% x $3,160,000) = $632,000, based on the current level of net assets. Three alternative ways in which a target
ROI of 20% could be achieved for the Beetown centre are as follows:
(1) Attempts could be made to increase revenue by attracting more clients while keeping invested capital and operating
profit per $ of revenue constant. Revenue would have to increase to $2,361,644, assuming that the current level
of profitability is maintained and fixed costs remain unchanged. The current rate of contribution to revenue is
$2,100,000 – $567,000 = $1,533,000/$2,100,000 = 73%. Operating profit needs to increase by $191,000
in order to achieve an ROI of 20%. Therefore, revenue needs to increase by $191,000/0·73 = $261,644 =
12·46%.
(2) Attempts could be made to decrease the level of operating costs by, for example, increasing the efficiency of
maintenance operations. This would have the effect of increasing operating profit per $ of revenue. This would
require that revenue and invested capital were kept constant. Total operating costs would need to fall by $191,000
in order to obtain an ROI of 20%. This represents a percentage decrease of 191,000/1,659,000 = 11·5%. If fixed
costs were truly fixed, then variable costs would need to fall to a level of $376,000, which represents a decrease
of 33·7%.
(3) Attempts could be made to decrease the net asset base of HFG by, for example, reducing debtor balances and/or
increasing creditor balances, while keeping turnover and operating profit per $ of revenue constant. Net assets
would need to fall to a level of ($441,000/0·2) = $2,205,000, which represents a percentage decrease
amounting to $3,160,000 – $2,205,000 = 955,000/3,160,000 = 30·2%. -
第3题:
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Albreda Co, a limited liability company, and its subsidiaries. The
group mainly operates a chain of national restaurants and provides vending and other catering services to corporate
clients. All restaurants offer ‘eat-in’, ‘take-away’ and ‘home delivery’ services. The draft consolidated financial
statements for the year ended 30 September 2005 show revenue of $42·2 million (2004 – $41·8 million), profit
before taxation of $1·8 million (2004 – $2·2 million) and total assets of $30·7 million (2004 – $23·4 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) In September 2005 the management board announced plans to cease offering ‘home delivery’ services from the
end of the month. These sales amounted to $0·6 million for the year to 30 September 2005 (2004 – $0·8
million). A provision of $0·2 million has been made as at 30 September 2005 for the compensation of redundant
employees (mainly drivers). Delivery vehicles have been classified as non-current assets held for sale as at 30
September 2005 and measured at fair value less costs to sell, $0·8 million (carrying amount,
$0·5 million). (8 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Albreda Co for the year ended
30 September 2005.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:3 ALBREDA CO
(a) Cessation of ‘home delivery’ service
(i) Matters
■ $0·6 million represents 1·4% of reported revenue (prior year 1·9%) and is therefore material.
Tutorial note: However, it is clearly not of such significance that it should raise any doubts whatsoever regarding
the going concern assumption. (On the contrary, as revenue from this service has declined since last year.)
■ The home delivery service is not a component of Albreda and its cessation does not classify as a discontinued
operation (IFRS 5 ‘Non-current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations’).
? It is not a cash-generating unit because home delivery revenues are not independent of other revenues
generated by the restaurant kitchens.
? 1·4% of revenue is not a ‘major line of business’.
? Home delivery does not cover a separate geographical area (but many areas around the numerous
restaurants).
■ The redundancy provision of $0·2 million represents 11·1% of profit before tax (10% before allowing for the
provision) and is therefore material. However, it represents only 0·6% of total assets and is therefore immaterial
to the balance sheet.
■ As the provision is a liability it should have been tested primarily for understatement (completeness).
■ The delivery vehicles should be classified as held for sale if their carrying amount will be recovered principally
through a sale transaction rather than through continuing use. For this to be the case the following IFRS 5 criteria
must be met:
? the vehicles must be available for immediate sale in their present condition; and
? their sale must be highly probable.
Tutorial note: Highly probable = management commitment to a plan + initiation of plan to locate buyer(s) +
active marketing + completion expected in a year.
■ However, even if the classification as held for sale is appropriate the measurement basis is incorrect.
■ Non-current assets classified as held for sale should be carried at the lower of carrying amount and fair value less
costs to sell.
■ It is incorrect that the vehicles are being measured at fair value less costs to sell which is $0·3 million in excess
of the carrying amount. This amounts to a revaluation. Wherever the credit entry is (equity or income statement)
it should be reversed. $0·3 million represents just less than 1% of assets (16·7% of profit if the credit is to the
income statement).
■ Comparison of fair value less costs to sell against carrying amount should have been made on an item by item
basis (and not on their totals).
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Copy of board minute documenting management’s decision to cease home deliveries (and any press
releases/internal memoranda to staff).
■ An analysis of revenue (e.g. extracted from management accounts) showing the amount attributed to home delivery
sales.
■ Redundancy terms for drivers as set out in their contracts of employment.
■ A ‘proof in total’ for the reasonableness/completeness of the redundancy provision (e.g. number of drivers × sum
of years employed × payment per year of service).
■ A schedule of depreciated cost of delivery vehicles extracted from the non-current asset register.
■ Checking of fair values on a sample basis to second hand market prices (as published/advertised in used vehicle
guides).
■ After-date net sale proceeds from sale of vehicles and comparison of proceeds against estimated fair values.
■ Physical inspection of condition of unsold vehicles.
■ Separate disclosure of the held for sale assets on the face of the balance sheet or in the notes.
■ Assets classified as held for sale (and other disposals) shown in the reconciliation of carrying amount at the
beginning and end of the period.
■ Additional descriptions in the notes of:
? the non-current assets; and
? the facts and circumstances leading to the sale/disposal (i.e. cessation of home delivery service). -
第4题:
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Volcan, a long-established limited liability company. Volcan operates
a national supermarket chain of 23 stores, five of which are in the capital city, Urvina. All the stores are managed in
the same way with purchases being made through Volcan’s central buying department and product pricing, marketing,
advertising and human resources policies being decided centrally. The draft financial statements for the year ended
31 March 2005 show revenue of $303 million (2004 – $282 million), profit before taxation of $9·5 million (2004
– $7·3 million) and total assets of $178 million (2004 – $173 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) On 1 May 2005, Volcan announced its intention to downsize one of the stores in Urvina from a supermarket to
a ‘City Metro’ in response to a significant decline in the demand for supermarket-style. shopping in the capital.
The store will be closed throughout June, re-opening on 1 July 2005. Goodwill of $5·5 million was recognised
three years ago when this store, together with two others, was bought from a national competitor. It is Volcan’s
policy to write off goodwill over five years. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Volcan for the year ended
31 March 2005.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
3 VOLCAN
(a) Store impairment
(i) Matters
■ Materiality
? The cost of goodwill represents 3·1% of total assets and is therefore material.
? However, after three years the carrying amount of goodwill ($2·2m) represents only 1·2% of total assets –
and is therefore immaterial in the context of the balance sheet.
? The annual amortisation charge ($1·1m) represents 11·6% profit before tax (PBT) and is therefore also
material (to the income statement).
? The impact of writing off the whole of the carrying amount would be material to PBT (23%).
Tutorial note: The temporary closure of the supermarket does not constitute a discontinued operation under IFRS 5
‘Non-Current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations’.
■ Under IFRS 3 ‘Business Combinations’ Volcan should no longer be writing goodwill off over five years but
subjecting it to an annual impairment test.
■ The announcement is after the balance sheet date and is therefore a non-adjusting event (IAS 10 ‘Events After the
Balance Sheet Date’) insofar as no provision for restructuring (for example) can be made.
■ However, the event provides evidence of a possible impairment of the cash-generating unit which is this store and,
in particular, the value of goodwill assigned to it.
■ If the carrying amount of goodwill ($2·2m) can be allocated on a reasonable and consistent basis to this and the
other two stores (purchased at the same time) Volcan’s management should have applied an impairment test to
the goodwill of the downsized store (this is likely to show impairment).
■ If more than 22% of goodwill is attributable to the City Metro store – then its write-off would be material to PBT
(22% × $2·2m ÷ $9·5m = 5%).
■ If the carrying amount of goodwill cannot be so allocated; the impairment test should be applied to the
cash-generating unit that is the three stores (this may not necessarily show impairment).
■ Management should have considered whether the other four stores in Urvina (and elsewhere) are similarly
impaired.
■ Going concern is unlikely to be an issue unless all the supermarkets are located in cities facing a downward trend
in demand.
Tutorial note: Marks will be awarded for stating the rules for recognition of an impairment loss for a cash-generating
unit. However, as it is expected that the majority of candidates will not deal with this matter, the rules of IAS 36 are
not reproduced here.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Board minutes approving the store’s ‘facelift’ and documenting the need to address the fall in demand for it as a
supermarket.
■ Recomputation of the carrying amount of goodwill (2/5 × $5·5m = $2·2m).
■ A schedule identifying all the assets that relate to the store under review and the carrying amounts thereof agreed
to the underlying accounting records (e.g. non-current asset register).
■ Recalculation of value in use and/or fair value less costs to sell of the cash-generating unit (i.e. the store that is to
become the City Metro, or the three stores bought together) as at 31 March 2005.
Tutorial note: If just one of these amounts exceeds carrying amount there will be no impairment loss. Also, as
there is a plan NOT to sell the store it is most likely that value in use should be used.
■ Agreement of cash flow projections (e.g. to approved budgets/forecast revenues and costs for a maximum of five
years, unless a longer period can be justified).
■ Written management representation relating to the assumptions used in the preparation of financial budgets.
■ Agreement that the pre-tax discount rate used reflects current market assessments of the time value of money (and
the risks specific to the store) and is reasonable. For example, by comparison with Volcan’s weighted average cost
of capital.
■ Inspection of the store (if this month it should be closed for refurbishment).
■ Revenue budgets and cash flow projections for:
– the two stores purchased at the same time;
– the other stores in Urvina; and
– the stores elsewhere.
Also actual after-date sales by store compared with budget. -
第5题:
(b) A sale of industrial equipment to Deakin Co in May 2005 resulted in a loss on disposal of $0·3 million that has
been separately disclosed on the face of the income statement. The equipment cost $1·2 million when it was
purchased in April 1996 and was being depreciated on a straight-line basis over 20 years. (6 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Keffler Co for the year ended
31 March 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
(b) Sale of industrial equipment
(i) Matters
■ The industrial equipment was in use for nine years (from April 1996) and would have had a carrying value of
$660,000 at 31 March 2005 (11/20 × $1·2m – assuming nil residual value and a full year’s depreciation charge
in the year of acquisition and none in the year of disposal). Disposal proceeds were therefore only $360,000.
■ The $0·3m loss represents 15% of PBT (for the year to 31 March 2006) and is therefore material. The equipment
was material to the balance sheet at 31 March 2005 representing 2·6% of total assets ($0·66/$25·7 × 100).
■ Separate disclosure, of a material loss on disposal, on the face of the income statement is in accordance with
IAS 16 ‘Property, Plant and Equipment’. However, in accordance with IAS 1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’,
it should not be captioned in any way that might suggest that it is not part of normal operating activities (i.e. not
‘extraordinary’, ‘exceptional’, etc).
Tutorial note: However, note that if there is a prior period error to be accounted for (see later), there would be
no impact on the current period income statement requiring consideration of any disclosure.
■ The reason for the sale. For example, whether the equipment was:
– surplus to operating requirements (i.e. not being replaced); or
– being replaced with newer equipment (thereby contributing to the $8·1m increase (33·8 – 25·7) in total
assets).
■ The reason for the loss on sale. For example, whether:
– the sale was at an under-value (e.g. to a related party);
– the equipment had a bad maintenance history (or was otherwise impaired);
– the useful life of the equipment is less than 20 years;
– there is any deferred consideration not yet recorded;
– any non-cash disposal proceeds have been overlooked (e.g. if another asset was acquired in a part-exchange).
■ If the useful life was less than 20 years, tangible non-current assets may be materially overstated in respect of other
items of equipment that are still in use and being depreciated on the same basis.
■ If the sale was to a related party then additional disclosure should be required in a note to the financial statements
for the year to 31 March 2006 (IAS 24 ‘Related Party Disclosures’).
Tutorial note: Since there are no specific pointers to a related party transaction (RPT), this point is not expanded
on.
■ Whether the sale was identified in the prior year audit’s post balance sheet event review. If so:
– the disclosure made in the prior year’s financial statements (IAS 10 ‘Events After the Balance Sheet Date’);
– whether an impairment loss was recognised at 31 March 2005.
■ If not, and the equipment was impaired at 31 March 2005, a prior period error should be accounted for (IAS 8
‘Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors’). An impairment loss of $0·3m would have
been material to prior year profit (12·5%).
Tutorial note: Unless this was a RPT or the impairment arose after 31 March 2005 a prior period adjustment
should be made.
■ Failure to account for a prior period error (if any) would result in modification of the audit opinion ‘except for’ noncompliance
with IAS 8 (in the current year) and IAS 36 (in the prior period).
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Carrying amount ($0·66m as above) agreed to the non-current asset register balances at 31 March 2005 and
recalculation of the loss on disposal.
■ Cost and accumulated depreciation removed from the asset register in the year to 31 March 2006.
■ Receipt of proceeds per cash book agreed to bank statement.
■ Sales invoice transferring title to Deakin.
■ A review of maintenance expenses and records (e.g. to confirm reason for loss on sale).
■ Post balance sheet event review on prior year audit working papers file.
■ Management representation confirming that Deakin is not a related party (provided that there is no evidence to
suggest otherwise). -
第6题:
(b) You are the audit manager of Johnston Co, a private company. The draft consolidated financial statements for
the year ended 31 March 2006 show profit before taxation of $10·5 million (2005 – $9·4 million) and total
assets of $55·2 million (2005 – $50·7 million).
Your firm was appointed auditor of Tiltman Co when Johnston Co acquired all the shares of Tiltman Co in March
2006. Tiltman’s draft financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2006 show profit before taxation of
$0·7 million (2005 – $1·7 million) and total assets of $16·1 million (2005 – $16·6 million). The auditor’s
report on the financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2005 was unmodified.
You are currently reviewing two matters that have been left for your attention on the audit working paper files for
the year ended 31 March 2006:
(i) In December 2004 Tiltman installed a new computer system that properly quantified an overvaluation of
inventory amounting to $2·7 million. This is being written off over three years.
(ii) In May 2006, Tiltman’s head office was relocated to Johnston’s premises as part of a restructuring.
Provisions for the resulting redundancies and non-cancellable lease payments amounting to $2·3 million
have been made in the financial statements of Tiltman for the year ended 31 March 2006.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of these two matters for your auditor’s reports on the financial
statements of Johnston Co and Tiltman Co for the year ended 31 March 2006. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Tiltman Co
Tiltman’s total assets at 31 March 2006 represent 29% (16·1/55·2 × 100) of Johnston’s total assets. The subsidiary is
therefore material to Johnston’s consolidated financial statements.
Tutorial note: Tiltman’s profit for the year is not relevant as the acquisition took place just before the year end and will
therefore have no impact on the consolidated income statement. Calculations of the effect on consolidated profit before
taxation are therefore inappropriate and will not be awarded marks.
(i) Inventory overvaluation
This should have been written off to the income statement in the year to 31 March 2005 and not spread over three
years (contrary to IAS 2 ‘Inventories’).
At 31 March 2006 inventory is overvalued by $0·9m. This represents all Tiltmans’s profit for the year and 5·6% of
total assets and is material. At 31 March 2005 inventory was materially overvalued by $1·8m ($1·7m reported profit
should have been a $0·1m loss).
Tutorial note: 1/3 of the overvaluation was written off in the prior period (i.e. year to 31 March 2005) instead of $2·7m.
That the prior period’s auditor’s report was unmodified means that the previous auditor concurred with an incorrect
accounting treatment (or otherwise gave an inappropriate audit opinion).
As the matter is material a prior period adjustment is required (IAS 8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting
Estimates and Errors’). $1·8m should be written off against opening reserves (i.e. restated as at 1 April 2005).
(ii) Restructuring provision
$2·3m expense has been charged to Tiltman’s profit and loss in arriving at a draft profit of $0·7m. This is very material.
(The provision represents 14·3% of Tiltman’s total assets and is material to the balance sheet date also.)
The provision for redundancies and onerous contracts should not have been made for the year ended 31 March 2006
unless there was a constructive obligation at the balance sheet date (IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and
Contingent Assets’). So, unless the main features of the restructuring plan had been announced to those affected (i.e.
redundancy notifications issued to employees), the provision should be reversed. However, it should then be disclosed
as a non-adjusting post balance sheet event (IAS 10 ‘Events After the Balance Sheet Date’).
Given the short time (less than one month) between acquisition and the balance sheet it is very possible that a
constructive obligation does not arise at the balance sheet date. The relocation in May was only part of a restructuring
(and could be the first evidence that Johnston’s management has started to implement a restructuring plan).
There is a risk that goodwill on consolidation of Tiltman may be overstated in Johnston’s consolidated financial
statements. To avoid the $2·3 expense having a significant effect on post-acquisition profit (which may be negligible
due to the short time between acquisition and year end), Johnston may have recognised it as a liability in the
determination of goodwill on acquisition.
However, the execution of Tiltman’s restructuring plan, though made for the year ended 31 March 2006, was conditional
upon its acquisition by Johnston. It does not therefore represent, immediately before the business combination, a
present obligation of Johnston. Nor is it a contingent liability of Johnston immediately before the combination. Therefore
Johnston cannot recognise a liability for Tiltman’s restructuring plans as part of allocating the cost of the combination
(IFRS 3 ‘Business Combinations’).
Tiltman’s auditor’s report
The following adjustments are required to the financial statements:
■ restructuring provision, $2·3m, eliminated;
■ adequate disclosure of relocation as a non-adjusting post balance sheet event;
■ current period inventory written down by $0·9m;
■ prior period inventory (and reserves) written down by $1·8m.
Profit for the year to 31 March 2006 should be $3·9m ($0·7 + $0·9 + $2·3).
If all these adjustments are made the auditor’s report should be unmodified. Otherwise, the auditor’s report should be
qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of disagreement. If none of the adjustments are made, the qualification should still be
‘except for’ as the matters are not pervasive.
Johnston’s auditor’s report
If Tiltman’s auditor’s report is unmodified (because the required adjustments are made) the auditor’s report of Johnston
should be similarly unmodified. As Tiltman is wholly-owned by Johnston there should be no problem getting the
adjustments made.
If no adjustments were made in Tiltman’s financial statements, adjustments could be made on consolidation, if
necessary, to avoid modification of the auditor’s report on Johnston’s financial statements.
The effect of these adjustments on Tiltman’s net assets is an increase of $1·4m. Goodwill arising on consolidation (if
any) would be reduced by $1·4m. The reduction in consolidated total assets required ($0·9m + $1·4m) is therefore
the same as the reduction in consolidated total liabilities (i.e. $2·3m). $2·3m is material (4·2% consolidated total
assets). If Tiltman’s financial statements are not adjusted and no adjustments are made on consolidation, the
consolidated financial position (balance sheet) should be qualified ‘except for’. The results of operations (i.e. profit for
the period) should be unqualified (if permitted in the jurisdiction in which Johnston reports).
Adjustment in respect of the inventory valuation may not be required as Johnston should have consolidated inventory
at fair value on acquisition. In this case, consolidated total liabilities should be reduced by $2·3m and goodwill arising
on consolidation (if any) reduced by $2·3m.
Tutorial note: The effect of any possible goodwill impairment has been ignored as the subsidiary has only just been
acquired and the balance sheet date is very close to the date of acquisition. -
第7题:
(b) Seymour offers health-related information services through a wholly-owned subsidiary, Aragon Co. Goodwill of
$1·8 million recognised on the purchase of Aragon in October 2004 is not amortised but included at cost in the
consolidated balance sheet. At 30 September 2006 Seymour’s investment in Aragon is shown at cost,
$4·5 million, in its separate financial statements.
Aragon’s draft financial statements for the year ended 30 September 2006 show a loss before taxation of
$0·6 million (2005 – $0·5 million loss) and total assets of $4·9 million (2005 – $5·7 million). The notes to
Aragon’s financial statements disclose that they have been prepared on a going concern basis that assumes that
Seymour will continue to provide financial support. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Seymour Co for the year ended
30 September 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
(b) Goodwill
(i) Matters
■ Cost of goodwill, $1·8 million, represents 3·4% consolidated total assets and is therefore material.
Tutorial note: Any assessments of materiality of goodwill against amounts in Aragon’s financial statements are
meaningless since goodwill only exists in the consolidated financial statements of Seymour.
■ It is correct that the goodwill is not being amortised (IFRS 3 Business Combinations). However, it should be tested
at least annually for impairment, by management.
■ Aragon has incurred losses amounting to $1·1 million since it was acquired (two years ago). The write-off of this
amount against goodwill in the consolidated financial statements would be material (being 61% cost of goodwill,
8·3% PBT and 2·1% total assets).
■ The cost of the investment ($4·5 million) in Seymour’s separate financial statements will also be material and
should be tested for impairment.
■ The fair value of net assets acquired was only $2·7 million ($4·5 million less $1·8 million). Therefore the fair
value less costs to sell of Aragon on other than a going concern basis will be less than the carrying amount of the
investment (i.e. the investment is impaired by at least the amount of goodwill recognised on acquisition).
■ In assessing recoverable amount, value in use (rather than fair value less costs to sell) is only relevant if the going
concern assumption is appropriate for Aragon.
■ Supporting Aragon financially may result in Seymour being exposed to actual and/or contingent liabilities that
should be provided for/disclosed in Seymour’s financial statements in accordance with IAS 37 Provisions,
Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Carrying values of cost of investment and goodwill arising on acquisition to prior year audit working papers and
financial statements.
■ A copy of Aragon’s draft financial statements for the year ended 30 September 2006 showing loss for year.
■ Management’s impairment test of Seymour’s investment in Aragon and of the goodwill arising on consolidation at
30 September 2006. That is a comparison of the present value of the future cash flows expected to be generated
by Aragon (a cash-generating unit) compared with the cost of the investment (in Seymour’s separate financial
statements).
■ Results of any impairment tests on Aragon’s assets extracted from Aragon’s working paper files.
■ Analytical procedures on future cash flows to confirm their reasonableness (e.g. by comparison with cash flows for
the last two years).
■ Bank report for audit purposes for any guarantees supporting Aragon’s loan facilities.
■ A copy of Seymour’s ‘comfort letter’ confirming continuing financial support of Aragon for the foreseeable future. -
第8题:
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Lamont Co. The company’s principal activity is wholesaling frozen
fish. The draft consolidated financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2007 show revenue of $67·0 million
(2006 – $62·3 million), profit before taxation of $11·9 million (2006 – $14·2 million) and total assets of
$48·0 million (2006 – $36·4 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) In early 2007 a chemical leakage from refrigeration units owned by Lamont caused contamination of some of its
property. Lamont has incurred $0·3 million in clean up costs, $0·6 million in modernisation of the units to
prevent future leakage and a $30,000 fine to a regulatory agency. Apart from the fine, which has been expensed,
these costs have been capitalised as improvements. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Lamont Co for the year ended
31 March 2007.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
3 LAMONT CO
(a) Chemical leakage
(i) Matters
■ $30,000 fine is very immaterial (just 1/4% profit before tax). This is revenue expenditure and it is correct that it
has been expensed to the income statement.
■ $0·3 million represents 0·6% total assets and 2·5% profit before tax and is not material on its own. $0·6 million
represents 1·2% total assets and 5% profit before tax and is therefore material to the financial statements.
■ The $0·3 million clean-up costs should not have been capitalised as the condition of the property is not improved
as compared with its condition before the leakage occurred. Although not material in isolation this amount should
be adjusted for and expensed, thereby reducing the aggregate of uncorrected misstatements.
■ It may be correct that $0·6 million incurred in modernising the refrigeration units should be capitalised as a major
overhaul (IAS 16 Property, Plant and Equipment). However, any parts scrapped as a result of the modernisation
should be treated as disposals (i.e. written off to the income statement).
■ The carrying amount of the refrigeration units at 31 March 2007, including the $0·6 million for modernisation,
should not exceed recoverable amount (i.e. the higher of value in use and fair value less costs to sell). If it does,
an allowance for the impairment loss arising must be recognised in accordance with IAS 36 Impairment of Assets.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ A breakdown/analysis of costs incurred on the clean-up and modernisation amounting to $0·3 million and
$0·6 million respectively.
■ Agreement of largest amounts to invoices from suppliers/consultants/sub-contractors, etc and settlement thereof
traced from the cash book to the bank statement.
■ Physical inspection of the refrigeration units to confirm their modernisation and that they are in working order. (Do
they contain frozen fish?)
■ Sample of components selected from the non-current asset register traced to the refrigeration units and inspected
to ensure continuing existence.
■ $30,000 penalty notice from the regulatory agency and corresponding cash book payment/payment per the bank
statement.
■ Written management representation that there are no further penalties that should be provided for or disclosed other
than the $30,000 that has been accounted for. -
第9题:
(b) You are the manager responsible for the audit of Poppy Co, a manufacturing company with a year ended
31 October 2008. In the last year, several investment properties have been purchased to utilise surplus funds
and to provide rental income. The properties have been revalued at the year end in accordance with IAS 40
Investment Property, they are recognised on the statement of financial position at a fair value of $8 million, and
the total assets of Poppy Co are $160 million at 31 October 2008. An external valuer has been used to provide
the fair value for each property.
Required:
(i) Recommend the enquiries to be made in respect of the external valuer, before placing any reliance on their
work, and explain the reason for the enquiries; (7 marks)
正确答案:
(b) (i) Enquiries in respect of the external valuer
Enquiries would need to be made for two main reasons, firstly to determine the competence, and secondly the objectivity
of the valuer. ISA 620 Using the Work of an Expert contains guidance in this area.
Competence
Enquiries could include:
– Is the valuer a member of a recognised professional body, for example a nationally or internationally recognised
institute of registered surveyors?
– Does the valuer possess any necessary licence to carry out valuations for companies?
– How long has the valuer been a member of the recognised body, or how long has the valuer been licensed under
that body?
– How much experience does the valuer have in providing valuations of the particular type of investment properties
held by Poppy Co?
– Does the valuer have specific experience of evaluating properties for the purpose of including their fair value within
the financial statements?
– Is there any evidence of the reputation of the valuer, e.g. professional references, recommendations from other
companies for which a valuation service has been provided?
– How much experience, if any, does the valuer have with Poppy Co?
Using the above enquiries, the auditor is trying to form. an opinion as to the relevance and reliability of the valuation
provided. ISA 500 Audit Evidence requires that the auditor gathers evidence that is both sufficient and appropriate. The
auditor needs to ensure that the fair values provided by the valuer for inclusion in the financial statements have been
arrived at using appropriate knowledge and skill which should be evidenced by the valuer being a member of a
professional body, and, if necessary, holding a licence under that body.
It is important that the fair values have been arrived at using methods allowed under IAS 40 Investment Property. If any
other valuation method has been used then the value recognised in the statement of financial position may not be in
accordance with financial reporting standards. Thus it is important to understand whether the valuer has experience
specifically in providing valuations that comply with IAS 40, and how many times the valuer has appraised properties
similar to those owned by Poppy Co.
In gauging the reliability of the fair value, the auditor may wish to consider how Poppy Co decided to appoint this
particular valuer, e.g. on the basis of a recommendation or after receiving references from companies for which
valuations had previously been provided.
It will also be important to consider how familiar the valuer is with Poppy Co’s business and environment, as a way to
assess the reliability and appropriateness of any assumptions used in the valuation technique.
Objectivity
Enquiries could include:
– Does the valuer have any financial interest in Poppy Co, e.g. shares held directly or indirectly in the company?
– Does the valuer have any personal relationship with any director or employee of Poppy Co?
– Is the fee paid for the valuation service reasonable and a fair, market based price?
With these enquiries, the auditor is gaining assurance that the valuer will perform. the valuation from an independent
point of view. If the valuer had a financial interest in Poppy Co, there would be incentive to manipulate the valuation in
a way best suited to the financial statements of the company. Equally if the valuer had a personal relationship with a
senior member of staff at Poppy Co, the valuer may feel pressured to give a favourable opinion on the valuation of the
properties.
The level of fee paid is important. It should be commensurate with the market rate paid for this type of valuation. If the
valuer was paid in excess of what might be considered a normal fee, it could indicate that the valuer was encouraged,
or even bribed, to provide a favourable valuation. -
第10题:
(a) The following information relates to Crosswire a publicly listed company.
Summarised statements of financial position as at:
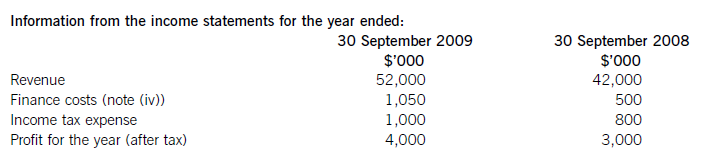
The following information is available:
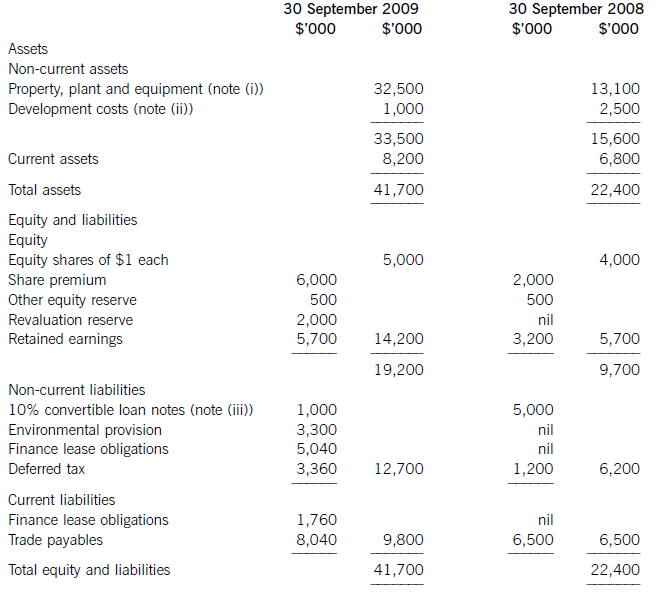
(i) During the year to 30 September 2009, Crosswire embarked on a replacement and expansion programme for its non-current assets. The details of this programme are:
On 1 October 2008 Crosswire acquired a platinum mine at a cost of $5 million. A condition of mining the
platinum is a requirement to landscape the mining site at the end of its estimated life of ten years. The
present value of this cost at the date of the purchase was calculated at $3 million (in addition to the
purchase price of the mine of $5 million).
Also on 1 October 2008 Crosswire revalued its freehold land for the first time. The credit in the revaluation
reserve is the net amount of the revaluation after a transfer to deferred tax on the gain. The tax rate applicable to Crosswire for deferred tax is 20% per annum.
On 1 April 2009 Crosswire took out a finance lease for some new plant. The fair value of the plant was
$10 million. The lease agreement provided for an initial payment on 1 April 2009 of $2·4 million followed
by eight six-monthly payments of $1·2 million commencing 30 September 2009.
Plant disposed of during the year had a carrying amount of $500,000 and was sold for $1·2 million. The
remaining movement on the property, plant and equipment, after charging depreciation of $3 million, was
the cost of replacing plant.
(ii) From 1 October 2008 to 31 March 2009 a further $500,000 was spent completing the development
project at which date marketing and production started. The sales of the new product proved disappointing
and on 30 September 2009 the development costs were written down to $1 million via an impairment
charge.
(iii) During the year ended 30 September 2009, $4 million of the 10% convertible loan notes matured. The
loan note holders had the option of redemption at par in cash or to exchange them for equity shares on the
basis of 20 new shares for each $100 of loan notes. 75% of the loan-note holders chose the equity option.
Ignore any effect of this on the other equity reserve.
All the above items have been treated correctly according to International Financial Reporting Standards.
(iv) The finance costs are made up of:
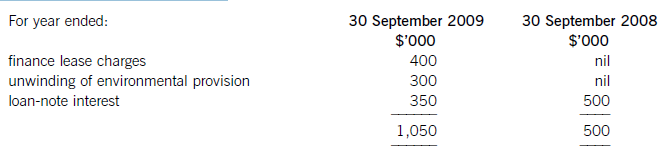
Required:
(i) Prepare a statement of the movements in the carrying amount of Crosswire’s non-current assets for the
year ended 30 September 2009; (9 marks)
(ii) Calculate the amounts that would appear under the headings of ‘cash flows from investing activities’
and ‘cash flows from financing activities’ in the statement of cash flows for Crosswire for the year ended
30 September 2009.
Note: Crosswire includes finance costs paid as a financing activity. (8 marks)
(b) A substantial shareholder has written to the directors of Crosswire expressing particular concern over the
deterioration of the company’s return on capital employed (ROCE)
Required:
Calculate Crosswire’s ROCE for the two years ended 30 September 2008 and 2009 and comment on the
apparent cause of its deterioration.
Note: ROCE should be taken as profit before interest on long-term borrowings and tax as a percentage of equity plus loan notes and finance lease obligations (at the year end). (8 marks)
正确答案:
(i)Thecashelementsoftheincreaseinproperty,plantandequipmentare$5millionforthemine(thecapitalisedenvironmentalprovisionisnotacashflow)and$2·4millionforthereplacementplantmakingatotalof$7·4million.(ii)Ofthe$4millionconvertibleloannotes(5,000–1,000)thatwereredeemedduringtheyear,75%($3million)ofthesewereexchangedforequitysharesonthebasisof20newsharesforeach$100inloannotes.Thiswouldcreate600,000(3,000/100x20)newsharesof$1eachandsharepremiumof$2·4million(3,000–600).As1million(5,000–4,000)newshareswereissuedintotal,400,000musthavebeenforcash.Theremainingincrease(aftertheeffectoftheconversion)inthesharepremiumof$1·6million(6,000–2,000b/f–2,400conversion)mustrelatetothecashissueofshares,thuscashproceedsfromtheissueofsharesis$2million(400nominalvalue+1,600premium).(iii)Theinitialleaseobligationis$10million(thefairvalueoftheplant).At30September2009totalleaseobligationsare$6·8million(5,040+1,760),thusrepaymentsintheyearwere$3·2million(10,000–6,800).(b)TakingthedefinitionofROCEfromthequestion:Fromtheaboveitcanbeclearlyseenthatthe2009operatingmarginhasimprovedbynearly1%point,despitethe$2millionimpairmentchargeonthewritedownofthedevelopmentproject.ThismeansthedeteriorationintheROCEisduetopoorerassetturnover.Thisimpliestherehasbeenadecreaseintheefficiencyintheuseofthecompany’sassetsthisyearcomparedtolastyear.Lookingatthemovementinthenon-currentassetsduringtheyearrevealssomemitigatingpoints:Thelandrevaluationhasincreasedthecarryingamountofproperty,plantandequipmentwithoutanyphysicalincreaseincapacity.Thisunfavourablydistortsthecurrentyear’sassetturnoverandROCEfigures.TheacquisitionoftheplatinummineappearstobeanewareaofoperationforCrosswirewhichmayhaveadifferent(perhapslower)ROCEtootherpreviousactivitiesoritmaybethatitwilltakesometimefortheminetocometofullproductioncapacity.Thesubstantialacquisitionoftheleasedplantwashalf-waythroughtheyearandcanonlyhavecontributedtotheyear’sresultsforsixmonthsatbest.Infutureperiodsafullyear’scontributioncanbeexpectedfromthisnewinvestmentinplantandthisshouldimprovebothassetturnoverandROCE.Insummary,thefallintheROCEmaybeduelargelytotheabovefactors(effectivelythereplacementandexpansionprogramme),ratherthantopooroperatingperformance,andinfutureperiodsthismaybereversed.ItshouldalsobenotedthathadtheROCEbeencalculatedontheaveragecapitalemployedduringtheyear(ratherthantheyearendcapitalemployed),whichisarguablymorecorrect,thenthedeteriorationintheROCEwouldnothavebeenaspronounced. -
第11题:
You are the audit supervisor of Maple & Co and are currently planning the audit of an existing client, Sycamore Science Co (Sycamore), whose year end was 30 April 2015. Sycamore is a pharmaceutical company, which manufactures and supplies a wide range of medical supplies. The draft financial statements show revenue of $35·6 million and profit before tax of $5·9 million.
Sycamore’s previous finance director left the company in December 2014 after it was discovered that he had been claiming fraudulent expenses from the company for a significant period of time. A new finance director was appointed in January 2015 who was previously a financial controller of a bank, and she has expressed surprise that Maple & Co had not uncovered the fraud during last year’s audit.
During the year Sycamore has spent $1·8 million on developing several new products. These projects are at different stages of development and the draft financial statements show the full amount of $1·8 million within intangible assets. In order to fund this development, $2·0 million was borrowed from the bank and is due for repayment over a ten-year period. The bank has attached minimum profit targets as part of the loan covenants.
The new finance director has informed the audit partner that since the year end there has been an increased number of sales returns and that in the month of May over $0·5 million of goods sold in April were returned.
Maple & Co attended the year-end inventory count at Sycamore’s warehouse. The auditor present raised concerns that during the count there were movements of goods in and out the warehouse and this process did not seem well controlled.
During the year, a review of plant and equipment in the factory was undertaken and surplus plant was sold, resulting in a profit on disposal of $210,000.
Required:
(a) State Maples & Co’s responsibilities in relation to the prevention and detection of fraud and error. (4 marks)
(b) Describe SIX audit risks, and explain the auditor’s response to each risk, in planning the audit of Sycamore Science Co. (12 marks)
(c) Sycamore’s new finance director has read about review engagements and is interested in the possibility of Maple & Co undertaking these in the future. However, she is unsure how these engagements differ from an external audit and how much assurance would be gained from this type of engagement.
Required:
(i) Explain the purpose of review engagements and how these differ from external audits; and (2 marks)
(ii) Describe the level of assurance provided by external audits and review engagements. (2 marks)
正确答案:(a) Fraud responsibility
Maple & Co must conduct an audit in accordance with ISA 240 The Auditor’s Responsibilities Relating to Fraud in an Audit of Financial Statements and are responsible for obtaining reasonable assurance that the financial statements taken as a whole are free from material misstatement, whether caused by fraud or error.
In order to fulfil this responsibility, Maple & Co is required to identify and assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements due to fraud.
They need to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence regarding the assessed risks of material misstatement due to fraud, through designing and implementing appropriate responses. In addition, Maple & Co must respond appropriately to fraud or suspected fraud identified during the audit.
When obtaining reasonable assurance, Maple & Co is responsible for maintaining professional scepticism throughout the audit, considering the potential for management override of controls and recognising the fact that audit procedures which are effective in detecting error may not be effective in detecting fraud.
To ensure that the whole engagement team is aware of the risks and responsibilities for fraud and error, ISAs require that a discussion is held within the team. For members not present at the meeting, Sycamore’s audit engagement partner should determine which matters are to be communicated to them.
(b) Audit risks and auditors’ responses



(c) (i) Review engagements
Review engagements are often undertaken as an alternative to an audit, and involve a practitioner reviewing financial data, such as six-monthly figures. This would involve the practitioner undertaking procedures to state whether anything has come to their attention which causes the practitioner to believe that the financial data is not in accordance with the financial reporting framework.
A review engagement differs to an external audit in that the procedures undertaken are not nearly as comprehensive as those in an audit, with procedures such as analytical review and enquiry used extensively. In addition, the practitioner does not need to comply with ISAs as these only relate to external audits.
(ii) Levels of assurance
The level of assurance provided by audit and review engagements is as follows:
External audit – A high but not absolute level of assurance is provided, this is known as reasonable assurance. This provides comfort that the financial statements present fairly in all material respects (or are true and fair) and are free of material misstatements.
Review engagements – where an opinion is being provided, the practitioner gathers sufficient evidence to be satisfied that the subject matter is plausible; in this case negative assurance is given whereby the practitioner confirms that nothing has come to their attention which indicates that the subject matter contains material misstatements.
-
第12题:
You are the audit manager of Chestnut & Co and are reviewing the key issues identified in the files of two audit clients.
Palm Industries Co (Palm)
Palm’s year end was 31 March 2015 and the draft financial statements show revenue of $28·2 million, receivables of $5·6 million and profit before tax of $4·8 million. The fieldwork stage for this audit has been completed.
A customer of Palm owed an amount of $350,000 at the year end. Testing of receivables in April highlighted that no amounts had been paid to Palm from this customer as they were disputing the quality of certain goods received from Palm. The finance director is confident the issue will be resolved and no allowance for receivables was made with regards to this balance.
Ash Trading Co (Ash)
Ash is a new client of Chestnut & Co, its year end was 31 January 2015 and the firm was only appointed auditors in February 2015, as the previous auditors were suddenly unable to undertake the audit. The fieldwork stage for this audit is currently ongoing.
The inventory count at Ash’s warehouse was undertaken on 31 January 2015 and was overseen by the company’s internal audit department. Neither Chestnut & Co nor the previous auditors attended the count. Detailed inventory records were maintained but it was not possible to undertake another full inventory count subsequent to the year end.
The draft financial statements show a profit before tax of $2·4 million, revenue of $10·1 million and inventory of $510,000.
Required:
For each of the two issues:
(i) Discuss the issue, including an assessment of whether it is material;
(ii) Recommend ONE procedure the audit team should undertake to try to resolve the issue; and
(iii) Describe the impact on the audit report if the issue remains UNRESOLVED.
Notes:
1 The total marks will be split equally between each of the two issues.
2 Audit report extracts are NOT required.
正确答案:Audit reports
Palm Industries Co (Palm)
(i) A customer of Palm’s owing $350,000 at the year end has not made any post year-end payments as they are disputing the quality of goods received. No allowance for receivables has been made against this balance. As the balance is being disputed, there is a risk of incorrect valuation as some or all of the receivable balance is overstated, as it may not be paid.
This $350,000 receivables balance represents 1·2% (0·35/28·2m) of revenue, 6·3% (0·35/5·6m) of receivables and 7·3% (0·35/4·8m) of profit before tax; hence this is a material issue.
(ii) A procedure to adopt includes:
– Review whether any payments have subsequently been made by this customer since the audit fieldwork was completed.
– Discuss with management whether the issue of quality of goods sold to the customer has been resolved, or whether it is still in dispute.
– Review the latest customer correspondence with regards to an assessment of the likelihood of the customer making payment.
(iii) If management refuses to provide against this receivable, the audit report will need to be modified. As receivables are overstated and the error is material but not pervasive a qualified opinion would be necessary.
A basis for qualified opinion paragraph would be needed and would include an explanation of the material misstatement in relation to the valuation of receivables and the effect on the financial statements. The opinion paragraph would be qualified ‘except for’.
Ash Trading Co (Ash)
(i) Chestnut & Co was only appointed as auditors subsequent to Ash’s year end and hence did not attend the year-end inventory count. Therefore, they have not been able to gather sufficient and appropriate audit evidence with regards to the completeness and existence of inventory.
Inventory is a material amount as it represents 21·3% (0·51/2·4m) of profit before tax and 5% (0·51/10·1m) of revenue; hence this is a material issue.
(ii) A procedure to adopt includes:
– Review the internal audit reports of the inventory count to identify the level of adjustments to the records to assess the reasonableness of relying on the inventory records.
– Undertake a sample check of inventory in the warehouse and compare to the inventory records and then from inventory records to the warehouse, to assess the reasonableness of the inventory records maintained by Ash.
(iii) The auditors will need to modify the audit report as they are unable to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence in relation to inventory which is a material but not pervasive balance. Therefore a qualified opinion will be required.
A basis for qualified opinion paragraph will be required to explain the limitation in relation to the lack of evidence over inventory. The opinion paragraph will be qualified ‘except for’.
-
第13题:
(c) On 1 May 2007 Sirus acquired another company, Marne plc. The directors of Marne, who were the only
shareholders, were offered an increased profit share in the enlarged business for a period of two years after the
date of acquisition as an incentive to accept the purchase offer. After this period, normal remuneration levels will
be resumed. Sirus estimated that this would cost them $5 million at 30 April 2008, and a further $6 million at
30 April 2009. These amounts will be paid in cash shortly after the respective year ends. (5 marks)
Required:
Draft a report to the directors of Sirus which discusses the principles and nature of the accounting treatment of
the above elements under International Financial Reporting Standards in the financial statements for the year
ended 30 April 2008.
正确答案:
(c) Acquisition of Marne
All business combinations within the scope of IFRS 3 ‘Business Combinations’ must be accounted for using the purchase
method. (IFRS 3.14) The pooling of interests method is prohibited. Under IFRS 3, an acquirer must be identified for all
business combinations. (IFRS 3.17) Sirus will be identified as the acquirer of Marne and must measure the cost of a business
combination at the sum of the fair values, at the date of exchange, of assets given, liabilities incurred or assumed, in exchange
for control of Marne; plus any costs directly attributable to the combination. (IFRS 3.24) If the cost is subject to adjustment
contingent on future events, the acquirer includes the amount of that adjustment in the cost of the combination at the
acquisition date if the adjustment is probable and can be measured reliably. (IFRS 3.32) However, if the contingent payment
either is not probable or cannot be measured reliably, it is not measured as part of the initial cost of the business combination.
If that adjustment subsequently becomes probable and can be measured reliably, the additional consideration is treated as
an adjustment to the cost of the combination. (IAS 3.34) The issue with the increased profit share payable to the directors
of Marne is whether the payment constitutes remuneration or consideration for the business acquired. Because the directors
of Marne fall back to normal remuneration levels after the two year period, it appears that this additional payment will
constitute part of the purchase consideration with the resultant increase in goodwill. It seems as though these payments can
be measured reliably and therefore the cost of the acquisition should be increased by the net present value of $11 million at
1 May 2007 being $5 million discounted for 1 year and $6 million for 2 years. -
第14题:
(b) The marketing director of CTC has suggested the introduction of a new toy ‘Nellie the Elephant’ for which the
following estimated information is available:
1. Sales volumes and selling prices per unit
Year ending, 31 May 2009 2010 2011
Sales units (000) 80 180 100
Selling price per unit ($) 50 50 50
2. Nellie will generate a contribution to sales ratio of 50% throughout the three year period.
3. Product specific fixed overheads during the year ending 31 May 2009 are estimated to be $1·6 million. It
is anticipated that these fixed overheads would decrease by 10% per annum during each of the years ending
31 May 2010 and 31 May 2011.
4. Capital investment amounting to $3·9 million would be required in June 2008. The investment would have
no residual value at 31 May 2011.
5. Additional working capital of $500,000 would be required in June 2008. A further $200,000 would be
required on 31 May 2009. These amounts would be recovered in full at the end of the three year period.
6. The cost of capital is expected to be 12% per annum.
Assume all cash flows (other than where stated) arise at the end of the year.
Required:
(i) Determine whether the new product is viable purely on financial grounds. (4 marks)
正确答案:
-
第15题:
(b) Historically, all owned premises have been measured at cost depreciated over 10 to 50 years. The management
board has decided to revalue these premises for the year ended 30 September 2005. At the balance sheet date
two properties had been revalued by a total of $1·7 million. Another 15 properties have since been revalued by
$5·4 million and there remain a further three properties which are expected to be revalued during 2006. A
revaluation surplus of $7·1 million has been credited to equity. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Albreda Co for the year ended
30 September 2005.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
(b) Revaluation of owned premises
(i) Matters
■ The revaluations are clearly material as $1·7 million, $5·4 million and $7·1 million represent 5·5% , 17·6% and
23·1% of total assets, respectively.
■ The change in accounting policy, from a cost model to a revaluation model, should be accounted for in accordance
with IAS 16 ‘Property, Plant and Equipment’ (i.e. as a revaluation).
Tutorial note: IAS 8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors’ does not apply to the initial
application of a policy to revalue assets in accordance with IAS 16.
■ The basis on which the valuations have been carried out, for example, market-based fair value (IAS 16).
■ Independence, qualifications and expertise of valuer(s).
■ IAS 16 does not permit the selective revaluation of assets thus the whole class of premises should have been
revalued.
■ The valuations of properties after the year end are adjusting events (i.e. providing additional evidence of conditions
existing at the year end) per IAS 10 ‘Events After the Balance Sheet Date’.
Tutorial note: It is ‘now’ still less than three months after the year end so these valuations can reasonably be
expected to reflect year-end values.
■ If $5·4 million is a net amount of surpluses and deficits it should be grossed up so that the credit to equity reflects
the sum of the surpluses with any deficits being expensed through profit and loss (IAS 36 ‘Impairment of Assets’).
■ The revaluation exercise is incomplete. If the revaluations on the remaining three properties are expected to be
material and cannot be reasonably estimated for inclusion in the financial statements for the year ended
30 September 2005 perhaps the change in policy should be deferred for a year.
■ Depreciation for the year should have been calculated on cost as usual to establish carrying amount before
revaluation.
■ Any premises held under finance leases should be similarly revalued.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ A schedule of depreciated cost of owned premises extracted from the non-current asset register.
■ Calculation of difference between valuation and depreciated cost by property. Separate summation of surpluses
and deficits.
■ Copy of valuation certificate for each property.
■ Physical inspection of properties with largest surpluses (including the two valued before the year end) to confirm
condition.
■ Extracts from local property guides/magazines indicating a range of values of similarly styled/sized properties.
■ Separate presentation of the revaluation surpluses (gross) in:
– the statement of changes in equity; and
– reconciliation of carrying amount at the beginning and end of the period.
■ IAS 16 disclosures in the notes to the financial statements including:
– the effective date of revaluation;
– whether an independent valuer was involved;
– the methods and significant assumptions applied in estimating fair values; and
– the carrying amount that would have been recognised under the cost model. -
第16题:
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Keffler Co, a private limited company engaged in the manufacture of
plastic products. The draft financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2006 show revenue of $47·4 million
(2005 – $43·9 million), profit before taxation of $2 million (2005 – $2·4 million) and total assets of $33·8 million
(2005 – $25·7 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) In April 2005, Keffler bought the right to use a landfill site for a period of 15 years for $1·1 million. Keffler
expects that the amount of waste that it will need to dump will increase annually and that the site will be
completely filled after just ten years. Keffler has charged the following amounts to the income statement for the
year to 31 March 2006:
– $20,000 licence amortisation calculated on a sum-of-digits basis to increase the charge over the useful life
of the site; and
– $100,000 annual provision for restoring the land in 15 years’ time. (9 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Keffler Co for the year ended
31 March 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
3 KEFFLER CO
Tutorial note: None of the issues have any bearing on revenue. Therefore any materiality calculations assessed on revenue are
inappropriate and will not be awarded marks.
(a) Landfill site
(i) Matters
■ $1·1m cost of the right represents 3·3% of total assets and is therefore material.
■ The right should be amortised over its useful life, that is just 10 years, rather than the 15-year period for which
the right has been granted.
Tutorial note: Recalculation on the stated basis (see audit evidence) shows that a 10-year amortisation has been
correctly used.
■ The amortisation charge represents 1% of profit before tax (PBT) and is not material.
■ The amortisation method used should reflect the pattern in which the future economic benefits of the right are
expected to be consumed by Keffler. If that pattern cannot be determined reliably, the straight-line method must
be used (IAS 38 ‘Intangible Assets’).
■ Using an increasing sum-of-digits will ‘end-load’ the amortisation charge (i.e. least charge in the first year, highest
charge in the last year). However, according to IAS 38 there is rarely, if ever, persuasive evidence to support an
amortisation method that results in accumulated amortisation lower than that under the straight-line method.
Tutorial note: Over the first half of the asset’s life, depreciation will be lower than under the straight-line basis
(and higher over the second half of the asset’s life).
■ On a straight line basis the annual amortisation charge would be $0·11m, an increase of $90,000. Although this
difference is just below materiality (4·5% PBT) the cumulative effect (of undercharging amortisation) will become
material.
■ Also, when account is taken of the understatement of cost (see below), the undercharging of amortisation will be
material.
■ The sum-of-digits method might be suitable as an approximation to the unit-of-production method if Keffler has
evidence to show that use of the landfill site will increase annually.
■ However, in the absence of such evidence, the audit opinion should be qualified ‘except for’ disagreement with the
amortisation method (resulting in intangible asset overstatement/amortisation expense understatement).
■ The annual restoration provision represents 5% of PBT and 0·3% of total assets. Although this is only borderline
material (in terms of profit), there will be a cumulative impact.
■ Annual provisioning is contrary to IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets’.
■ The estimate of the future restoration cost is (presumably) $1·5m (i.e. $0·1 × 15). The present value of this
amount should have been provided in full in the current year and included in the cost of the right.
■ Thus the amortisation being charged on the cost of the right (including the restoration cost) is currently understated
(on any basis).
Tutorial note: A 15-year discount factor at 10% (say) is 0·239. $1·5m × 0·239 is approximately $0·36m. The
resulting present value (of the future cost) would be added to the cost of the right. Amortisation over 10 years
on a straight-line basis would then be increased by $36,000, increasing the difference between amortisation
charged and that which should be charged. The lower the discount rate, the greater the understatement of
amortisation expense.
Total amount expensed ($120k) is less than what should have been expensed (say $146k amortisation + $36k
unwinding of discount). However, this is not material.
■ Whether Keffler will wait until the right is about to expire before restoring the land or might restore earlier (if the
site is completely filled in 10 years).
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Written agreement for purchase of right and contractual terms therein (e.g. to make restoration in 15 years’ time).
■ Cash book/bank statement entries in April 2005 for $1·1m payment.
■ Physical inspection of the landfill site to confirm Keffler’s use of it.
■ Annual dump budget/projection over next 10 years and comparison with sum-of-digits proportions.
■ Amount actually dumped in the year (per dump records) compared with budget and as a percentage/proportion of
the total available.
■ Recalculation of current year’s amortisation based on sum-of-digits. That is, $1·1m ÷ 55 = $20,000.
Tutorial note: The sum-of-digits from 1 to 10 may be calculated long-hand or using the formula n(n+1)/2 i.e.
(10 × 11)/2 = 55.
■ The basis of the calculation of the estimated restoration costs and principal assumptions made.
■ If estimated by a quantity surveyor/other expert then a copy of the expert’s report.
■ Written management representation confirming the planned timing of the restoration in 15 years (or sooner). -
第17题:
(c) In April 2006, Keffler was banned by the local government from emptying waste water into a river because the
water did not meet minimum standards of cleanliness. Keffler has made a provision of $0·9 million for the
technological upgrading of its water purifying process and included $45,000 for the penalties imposed in ‘other
provisions’. (5 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Keffler Co for the year ended
31 March 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
(c) Ban on emptying waste water
(i) Matter
■ $0·9m provision for upgrading the process represents 45% PBT and is very material. This provision is also
material to the balance sheet (2·7% of total assets).
■ The provision for penalties is immaterial (2·2% PBT and 0·1% total assets).
■ The ban is an adjusting post balance sheet event in respect of the penalties (IAS 10). It provides evidence that at
the balance sheet date Keffler was in contravention of local government standards. Therefore it is correct (in
accordance with IAS 37) that a provision has been made for the penalties. As the matter is not material inclusion
in ‘other provisions’ is appropriate.
■ However, even if Keffler has a legal obligation to meet minimum standards, there is no obligation for upgrading the
purifying process at 31 March 2006 and the $0·9m provision should be written back.
■ If the provision for upgrading is not written back the audit opinion should be qualified ‘except for’ (disagreement).
■ Keffler does not even have a contingent liability for upgrading the process because there is no present obligation to
do so. The obligation is to stop emptying unclean water into the river. Nor is there a possible obligation whose
existence will be confirmed by an uncertain future event not wholly within Keffler’s control.
Tutorial note: Consider that Keffler has alternatives wholly within its control. For example, it could ignore the ban
and incur fines, or relocate/close this particular plant/operation or perhaps dispose of the water by alternative
means.
■ The need for a technological upgrade may be an indicator of impairment. Management should have carried out
an impairment test on the carrying value of the water purifying process and recognised any impairment loss in the
profit for the year to 31 March 2006.
■ Management’s intention to upgrade the process is more appropriate to an environmental responsibility report (if
any).
■ Whether there is any other information in documents containing financial statements.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Penalty notices of fines received to confirm amounts and period/dates covered.
■ After-date payment of fines agreed to the cash book.
■ A copy of the ban and any supporting report on the local government’s findings.
■ Minutes of board meetings at which the ban was discussed confirming management’s intentions (e.g. to upgrade
the process).
Tutorial note: This may be disclosed in the directors’ report and/or as a non-adjusting post balance sheet event.
■ Any tenders received/costings for upgrading.
Tutorial note: This will be relevant if, for example, capital commitment authorised (by the board) but not
contracted for at the year end are disclosed in the notes to the financial statements.
■ Physical inspection of the emptying point at the river to confirm that Keffler is not still emptying waste water into
it (unless the upgrading has taken place).
Tutorial note: Thereby incurring further penalties. -
第18题:
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Seymour Co. The company offers information, proprietary foods and
medical innovations designed to improve the quality of life. (Proprietary foods are marketed under and protected by
registered names.) The draft consolidated financial statements for the year ended 30 September 2006 show revenue
of $74·4 million (2005 – $69·2 million), profit before taxation of $13·2 million (2005 – $15·8 million) and total
assets of $53·3 million (2005 – $40·5 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) In 2001, Seymour had been awarded a 20-year patent on a new drug, Tournose, that was also approved for
food use. The drug had been developed at a cost of $4 million which is being amortised over the life of the
patent. The patent cost $11,600. In September 2006 a competitor announced the successful completion of
preliminary trials on an alternative drug with the same beneficial properties as Tournose. The alternative drug is
expected to be readily available in two years time. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Seymour Co for the year ended
30 September 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
■ A change in the estimated useful life should be accounted for as a change in accounting estimate in accordance
with IAS 8 Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors. For example, if the development
costs have little, if any, useful life after the introduction of the alternative drug (‘worst case’ scenario), the carrying
value ($3 million) should be written off over the current and remaining years, i.e. $1 million p.a. The increase in
amortisation/decrease in carrying value ($800,000) is material to PBT (6%) and total assets (1·5%).
■ Similarly a change in the expected pattern of consumption of the future economic benefits should be accounted for
as a change in accounting estimate (IAS 8). For example, it may be that the useful life is still to 2020 but that
the economic benefits may reduce significantly in two years time.
■ After adjusting the carrying amount to take account of the change in accounting estimate(s) management should
have tested it for impairment and any impairment loss recognised in profit or loss.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ $3 million carrying amount of development costs brought forward agreed to prior year working papers and financial
statements.
■ A copy of the press release announcing the competitor’s alternative drug.
■ Management’s projections of future cashflows from Tournose-related sales as evidence of the useful life of the
development costs and pattern of consumption.
■ Reperformance of management’s impairment test on the development costs: Recalculation of management’s
calculation of the carrying amount after revising estimates of useful life and/or consumption of benefits compared
with management’s calculation of value in use.
■ Sensitivity analysis on management’s key assumptions (e.g. estimates of useful life, discount rate).
■ Written management representation on the key assumptions concerning the future that have a significant risk of
causing material adjustment to the carrying amount of the development costs. (These assumptions should be
disclosed in accordance with IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements.) -
第19题:
(c) In November 2006 Seymour announced the recall and discontinuation of a range of petcare products. The
product recall was prompted by the high level of customer returns due to claims of poor quality. For the year to
30 September 2006, the product range represented $8·9 million of consolidated revenue (2005 – $9·6 million)
and $1·3 million loss before tax (2005 – $0·4 million profit before tax). The results of the ‘petcare’ operations
are disclosed separately on the face of the income statement. (6 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Seymour Co for the year ended
30 September 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
■ The discontinuation of the product line after the balance sheet date provides additional evidence that, as at the
balance sheet date, it was of poor quality. Therefore, as at the balance sheet date:
– an allowance (‘provision’) may be required for credit notes for returns of products after the year end that were
sold before the year end;
– goods returned to inventory should be written down to net realisable value (may be nil);
– any plant and equipment used exclusively in the production of the petcare range of products should be tested
for impairment;
– any material contingent liabilities arising from legal claims should be disclosed.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ A copy of Seymour’s announcement (external ‘press release’ and any internal memorandum).
■ Credit notes raised/refunds paid after the year end for faulty products returned.
■ Condition of products returned as inspected during physical attendance of inventory count.
■ Correspondence from customers claiming reimbursement/compensation for poor quality.
■ Direct confirmation from legal adviser (solicitor) regarding any claims for customers including estimates of possible
payouts. -
第20题:
(b) You are the audit manager of Petrie Co, a private company, that retails kitchen utensils. The draft financial
statements for the year ended 31 March 2007 show revenue $42·2 million (2006 – $41·8 million), profit before
taxation of $1·8 million (2006 – $2·2 million) and total assets of $30·7 million (2006 – $23·4 million).
You are currently reviewing two matters that have been left for your attention on Petrie’s audit working paper file
for the year ended 31 March 2007:
(i) Petrie’s management board decided to revalue properties for the year ended 31 March 2007 that had
previously all been measured at depreciated cost. At the balance sheet date three properties had been
revalued by a total of $1·7 million. Another nine properties have since been revalued by $5·4 million. The
remaining three properties are expected to be revalued later in 2007. (5 marks)
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of these two matters for your auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Petrie Co for the year ended 31 March 2007.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the matters above.
正确答案:
(b) Implications for auditor’s report
(i) Selective revaluation of premises
The revaluations are clearly material to the balance sheet as $1·7 million and $5·4 million represent 5·5% and 17·6%
of total assets, respectively (and 23·1% in total). As the effects of the revaluation on line items in the financial statements
are clearly identified (e.g. revalued amount, depreciation, surplus in statement of changes in equity) the matter is not
pervasive.
The valuations of the nine properties after the year end provide additional evidence of conditions existing at the year end
and are therefore adjusting events per IAS 10 Events After the Balance Sheet Date.
Tutorial note: It is ‘now’ still less than three months after the year end so these valuations can reasonably be expected
to reflect year end values.
However, IAS 16 Property, Plant and Equipment does not permit the selective revaluation of assets thus the whole class
of premises would need to have been revalued for the year to 31 March 2007 to change the measurement basis for this
reporting period.
The revaluation exercise is incomplete. Unless the remaining three properties are revalued before the auditor’s report on
the financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2007 is signed off:
(1) the $7·1 revaluation made so far must be reversed to show all premises at depreciated cost as in previous years;
OR
(2) the auditor’s report would be qualified ‘except for’ disagreement regarding non-compliance with IAS 16.
When it is appropriate to adopt the revaluation model (e.g. next year) the change in accounting policy (from a cost model
to a revaluation model) should be accounted for in accordance with IAS 16 (i.e. as a revaluation).
Tutorial note: IAS 8 Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors does not apply to the initial
application of a policy to revalue assets in accordance with IAS 16.
Assuming the revaluation is written back, before giving an unmodified opinion, the auditor should consider why the three
properties were not revalued. In particular if there are any indicators of impairment (e.g. physical dilapidation) there
should be sufficient evidence on the working paper file to show that the carrying amount of these properties is not
materially greater than their recoverable amount (i.e. the higher of value in use and fair value less costs to sell).
If there is insufficient evidence to confirm that the three properties are not impaired (e.g. if the auditor was prevented
from inspecting the properties) the auditor’s report would be qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of limitation on scope.
If there is evidence of material impairment but management fail to write down the carrying amount to recoverable
amount the auditor’s report would be qualified ‘except for’ disagreement regarding non-compliance with IAS 36
Impairment of Assets.
-
第21题:
The following trial balance relates to Sandown at 30 September 2009:
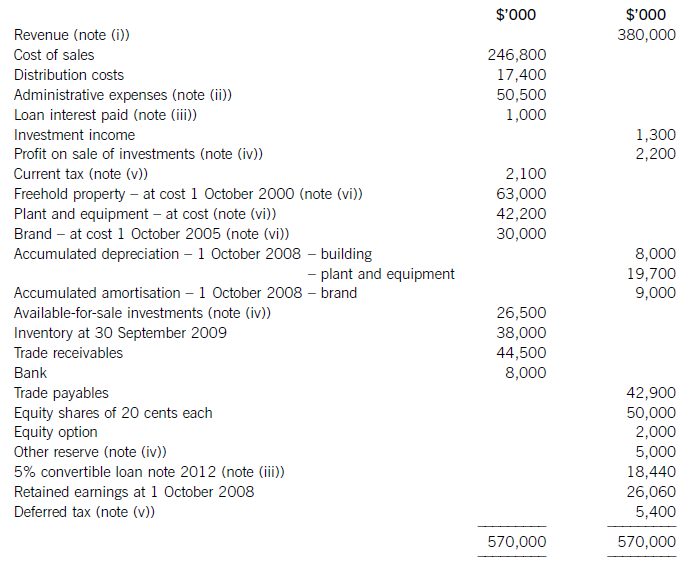
The following notes are relevant:
(i) Sandown’s revenue includes $16 million for goods sold to Pending on 1 October 2008. The terms of the sale are that Sandown will incur ongoing service and support costs of $1·2 million per annum for three years after the sale. Sandown normally makes a gross profit of 40% on such servicing and support work. Ignore the time value of money.
(ii) Administrative expenses include an equity dividend of 4·8 cents per share paid during the year.
(iii) The 5% convertible loan note was issued for proceeds of $20 million on 1 October 2007. It has an effective interest rate of 8% due to the value of its conversion option.
(iv) During the year Sandown sold an available-for-sale investment for $11 million. At the date of sale it had a
carrying amount of $8·8 million and had originally cost $7 million. Sandown has recorded the disposal of the
investment. The remaining available-for-sale investments (the $26·5 million in the trial balance) have a fair value of $29 million at 30 September 2009. The other reserve in the trial balance represents the net increase in the value of the available-for-sale investments as at 1 October 2008. Ignore deferred tax on these transactions.
(v) The balance on current tax represents the under/over provision of the tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2008. The directors have estimated the provision for income tax for the year ended 30 September 2009 at $16·2 million. At 30 September 2009 the carrying amounts of Sandown’s net assets were $13 million in excess of their tax base. The income tax rate of Sandown is 30%.
(vi) Non-current assets:
The freehold property has a land element of $13 million. The building element is being depreciated on a
straight-line basis.
Plant and equipment is depreciated at 40% per annum using the reducing balance method.
Sandown’s brand in the trial balance relates to a product line that received bad publicity during the year which led to falling sales revenues. An impairment review was conducted on 1 April 2009 which concluded that, based on estimated future sales, the brand had a value in use of $12 million and a remaining life of only three years.
However, on the same date as the impairment review, Sandown received an offer to purchase the brand for
$15 million. Prior to the impairment review, it was being depreciated using the straight-line method over a
10-year life.
No depreciation/amortisation has yet been charged on any non-current asset for the year ended 30 September
2009. Depreciation, amortisation and impairment charges are all charged to cost of sales.
Required:
(a) Prepare the statement of comprehensive income for Sandown for the year ended 30 September 2009.
(13 marks)
(b) Prepare the statement of financial position of Sandown as at 30 September 2009. (12 marks)
Notes to the financial statements are not required.
A statement of changes in equity is not required.
正确答案:
(i)IAS18Revenuerequiresthatwheresalesrevenueincludesanamountforaftersalesservicingandsupportcoststhenaproportionoftherevenueshouldbedeferred.Theamountdeferredshouldcoverthecostandareasonableprofit(inthiscaseagrossprofitof40%)ontheservices.Astheservicingandsupportisforthreeyearsandthedateofthesalewas1October2008,revenuerelatingtotwoyears’servicingandsupportprovisionmustbedeferred:($1·2millionx2/0·6)=$4million.Thisisshownas$2millioninbothcurrentandnon-currentliabilities. -
第22题:
(a) The following figures have been calculated from the financial statements (including comparatives) of Barstead for
the year ended 30 September 2009:
increase in profit after taxation 80%
increase in (basic) earnings per share 5%
increase in diluted earnings per share 2%
Required:
Explain why the three measures of earnings (profit) growth for the same company over the same period can
give apparently differing impressions. (4 marks)
(b) The profit after tax for Barstead for the year ended 30 September 2009 was $15 million. At 1 October 2008 the company had in issue 36 million equity shares and a $10 million 8% convertible loan note. The loan note will mature in 2010 and will be redeemed at par or converted to equity shares on the basis of 25 shares for each $100 of loan note at the loan-note holders’ option. On 1 January 2009 Barstead made a fully subscribed rights issue of one new share for every four shares held at a price of $2·80 each. The market price of the equity shares of Barstead immediately before the issue was $3·80. The earnings per share (EPS) reported for the year ended 30 September 2008 was 35 cents.
Barstead’s income tax rate is 25%.
Required:
Calculate the (basic) EPS figure for Barstead (including comparatives) and the diluted EPS (comparatives not required) that would be disclosed for the year ended 30 September 2009. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(a)Whilstprofitaftertax(anditsgrowth)isausefulmeasure,itmaynotgiveafairrepresentationofthetrueunderlyingearningsperformance.Inthisexample,userscouldinterpretthelargeannualincreaseinprofitaftertaxof80%asbeingindicativeofanunderlyingimprovementinprofitability(ratherthanwhatitreallyis:anincreaseinabsoluteprofit).Itispossible,evenprobable,that(someof)theprofitgrowthhasbeenachievedthroughtheacquisitionofothercompanies(acquisitivegrowth).Wherecompaniesareacquiredfromtheproceedsofanewissueofshares,orwheretheyhavebeenacquiredthroughshareexchanges,thiswillresultinagreaternumberofequitysharesoftheacquiringcompanybeinginissue.ThisiswhatappearstohavehappenedinthecaseofBarsteadastheimprovementindicatedbyitsearningspershare(EPS)isonly5%perannum.ThisexplainswhytheEPS(andthetrendofEPS)isconsideredamorereliableindicatorofperformancebecausetheadditionalprofitswhichcouldbeexpectedfromthegreaterresources(proceedsfromthesharesissued)ismatchedwiththeincreaseinthenumberofshares.Simplylookingatthegrowthinacompany’sprofitaftertaxdoesnottakeintoaccountanyincreasesintheresourcesusedtoearnthem.Anyincreaseingrowthfinancedbyborrowings(debt)wouldnothavethesameimpactonprofit(asbeingfinancedbyequityshares)becausethefinancecostsofthedebtwouldacttoreduceprofit.ThecalculationofadilutedEPStakesintoaccountanypotentialequitysharesinissue.Potentialordinarysharesarisefromfinancialinstruments(e.g.convertibleloannotesandoptions)thatmayentitletheirholderstoequitysharesinthefuture.ThedilutedEPSisusefulasitalertsexistingshareholderstothefactthatfutureEPSmaybereducedasaresultofsharecapitalchanges;inasenseitisawarningsign.InthiscasethelowerincreaseinthedilutedEPSisevidencethatthe(higher)increaseinthebasicEPShas,inpart,beenachievedthroughtheincreaseduseofdilutingfinancialinstruments.Thefinancecostoftheseinstrumentsislessthantheearningstheirproceedshavegeneratedleadingtoanincreaseincurrentprofits(andbasicEPS);however,inthefuturetheywillcausemoresharestobeissued.ThiscausesadilutionwherethefinancecostperpotentialnewshareislessthanthebasicEPS. -
第23题:
You are an audit manager at Rockwell & Co, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants. You are responsible for the audit of the Hopper Group, a listed audit client which supplies ingredients to the food and beverage industry worldwide.
The audit work for the year ended 30 June 2015 is nearly complete, and you are reviewing the draft audit report which has been prepared by the audit senior. During the year the Hopper Group purchased a new subsidiary company, Seurat Sweeteners Co, which has expertise in the research and design of sugar alternatives. The draft financial statements of the Hopper Group for the year ended 30 June 2015 recognise profit before tax of $495 million (2014 – $462 million) and total assets of $4,617 million (2014: $4,751 million). An extract from the draft audit report is shown below:
Basis of modified opinion (extract)
In their calculation of goodwill on the acquisition of the new subsidiary, the directors have failed to recognise consideration which is contingent upon meeting certain development targets. The directors believe that it is unlikely that these targets will be met by the subsidiary company and, therefore, have not recorded the contingent consideration in the cost of the acquisition. They have disclosed this contingent liability fully in the notes to the financial statements. We do not feel that the directors’ treatment of the contingent consideration is correct and, therefore, do not believe that the criteria of the relevant standard have been met. If this is the case, it would be appropriate to adjust the goodwill balance in the statement of financial position.
We believe that any required adjustment may materially affect the goodwill balance in the statement of financial position. Therefore, in our opinion, the financial statements do not give a true and fair view of the financial position of the Hopper Group and of the Hopper Group’s financial performance and cash flows for the year then ended in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards.
Emphasis of Matter Paragraph
We draw attention to the note to the financial statements which describes the uncertainty relating to the contingent consideration described above. The note provides further information necessary to understand the potential implications of the contingency.
Required:
(a) Critically appraise the draft audit report of the Hopper Group for the year ended 30 June 2015, prepared by the audit senior.
Note: You are NOT required to re-draft the extracts from the audit report. (10 marks)
(b) The audit of the new subsidiary, Seurat Sweeteners Co, was performed by a different firm of auditors, Fish Associates. During your review of the communication from Fish Associates, you note that they were unable to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence with regard to the breakdown of research expenses. The total of research costs expensed by Seurat Sweeteners Co during the year was $1·2 million. Fish Associates has issued a qualified audit opinion on the financial statements of Seurat Sweeteners Co due to this inability to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence.
Required:
Comment on the actions which Rockwell & Co should take as the auditor of the Hopper Group, and the implications for the auditor’s report on the Hopper Group financial statements. (6 marks)
(c) Discuss the quality control procedures which should be carried out by Rockwell & Co prior to the audit report on the Hopper Group being issued. (4 marks)
正确答案:(a) Critical appraisal of the draft audit report
Type of opinion
When an auditor issues an opinion expressing that the financial statements ‘do not give a true and fair view’, this represents an adverse opinion. The paragraph explaining the modification should, therefore, be titled ‘Basis of Adverse Opinion’ rather than simply ‘Basis of Modified Opinion’.
An adverse opinion means that the auditor considers the misstatement to be material and pervasive to the financial statements of the Hopper Group. According to ISA 705 Modifications to Opinions in the Independent Auditor’s Report, pervasive matters are those which affect a substantial proportion of the financial statements or fundamentally affect the users’ understanding of the financial statements. It is unlikely that the failure to recognise contingent consideration is pervasive; the main effect would be to understate goodwill and liabilities. This would not be considered a substantial proportion of the financial statements, neither would it be fundamental to understanding the Hopper Group’s performance and position.
However, there is also some uncertainty as to whether the matter is even material. If the matter is determined to be material but not pervasive, then a qualified opinion would be appropriate on the basis of a material misstatement. If the matter is not material, then no modification would be necessary to the audit opinion.
Wording of opinion/report
The auditor’s reference to ‘the acquisition of the new subsidiary’ is too vague; the Hopper Group may have purchased a number of subsidiaries which this phrase could relate to. It is important that the auditor provides adequate description of the event and in these circumstances it would be appropriate to name the subsidiary referred to.
The auditor has not quantified the amount of the contingent element of the consideration. For the users to understand the potential implications of any necessary adjustments, they need to know how much the contingent consideration will be if it becomes payable. It is a requirement of ISA 705 that the auditor quantifies the financial effects of any misstatements, unless it is impracticable to do so.
In addition to the above point, the auditor should provide more description of the financial effects of the misstatement, including full quantification of the effect of the required adjustment to the assets, liabilities, incomes, revenues and equity of the Hopper Group.
The auditor should identify the note to the financial statements relevant to the contingent liability disclosure rather than just stating ‘in the note’. This will improve the understandability and usefulness of the contents of the audit report.
The use of the term ‘we do not feel that the treatment is correct’ is too vague and not professional. While there may be some interpretation necessary when trying to apply financial reporting standards to unique circumstances, the expression used is ambiguous and may be interpreted as some form. of disclaimer by the auditor with regard to the correct accounting treatment. The auditor should clearly explain how the treatment applied in the financial statements has departed from the requirements of the relevant standard.
Tutorial note: As an illustration to the above point, an appropriate wording would be: ‘Management has not recognised the acquisition-date fair value of contingent consideration as part of the consideration transferred in exchange for the acquiree, which constitutes a departure from International Financial Reporting Standards.’
The ambiguity is compounded by the use of the phrase ‘if this is the case, it would be appropriate to adjust the goodwill’. This once again suggests that the correct treatment is uncertain and perhaps open to interpretation.
If the auditor wishes to refer to a specific accounting standard they should refer to its full title. Therefore instead of referring to ‘the relevant standard’ they should refer to International Financial Reporting Standard 3 Business Combinations.
The opinion paragraph requires an appropriate heading. In this case the auditors have issued an adverse opinion and the paragraph should be headed ‘Adverse Opinion’.
As with the basis paragraph, the opinion paragraph lacks authority; suggesting that the required adjustments ‘may’ materially affect the financial statements implies that there is a degree of uncertainty. This is not the case; the amount of the contingent consideration will be disclosed in the relevant purchase agreement, so the auditor should be able to determine whether the required adjustments are material or not. Regardless, the sentence discussing whether the balance is material or not is not required in the audit report as to warrant inclusion in the report the matter must be considered material. The disclosure of the nature and financial effect of the misstatement in the basis paragraph is sufficient.
Finally, the emphasis of matter paragraph should not be included in the audit report. An emphasis of matter paragraph is only used to draw attention to an uncertainty/matter of fundamental importance which is correctly accounted for and disclosed in the financial statements. An emphasis of matter is not required in this case for the following reasons:
– Emphasis of matter is only required to highlight matters which the auditor believes are fundamental to the users’ understanding of the business. An example may be where a contingent liability exists which is so significant it could lead to the closure of the reporting entity. That is not the case with the Hopper Group; the contingent liability does not appear to be fundamental.
– Emphasis of matter is only used for matters where the auditor has obtained sufficient appropriate evidence that the matter is not materially misstated in the financial statements. If the financial statements are materially misstated, in this regard the matter would be fully disclosed by the auditor in the basis of qualified/adverse opinion paragraph and no emphasis of matter is necessary.
(b) Communication from the component auditor
The qualified opinion due to insufficient evidence may be a significant matter for the Hopper Group audit. While the possible adjustments relating to the current year may not be material to the Hopper Group, the inability to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence with regard to a material matter in Seurat Sweeteners Co’s financial statements may indicate a control deficiency which the auditor was not aware of at the planning stage and it could indicate potential problems with regard to the integrity of management, which could also indicate a potential fraud. It could also indicate an unwillingness of management to provide information, which could create problems for future audits, particularly if research and development costs increase in future years. If the group auditor suspects that any of these possibilities are true, they may need to reconsider their risk assessment and whether the audit procedures performed are still appropriate.
If the detail provided in the communication from the component auditor is insufficient, the group auditor should first discuss the matter with the component auditor to see whether any further information can be provided. The group auditor can request further working papers from the component auditor if this is necessary. However, if Seurat Sweeteners has not been able to provide sufficient appropriate evidence, it is unlikely that this will be effective.
If the discussions with the component auditor do not provide satisfactory responses to evaluate the potential impact on the Hopper Group, the group auditor may need to communicate with either the management of Seurat Sweeteners or the Hopper Group to obtain necessary clarification with regard to the matter.
Following these procedures, the group auditor needs to determine whether they have sufficient appropriate evidence to draw reasonable conclusions on the Hopper Group’s financial statements. If they believe the lack of information presents a risk of material misstatement in the group financial statements, they can request that further audit procedures be performed, either by the component auditor or by themselves.
Ultimately the group engagement partner has to evaluate the effect of the inability to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence on the audit opinion of the Hopper Group. The matter relates to research expenses totalling $1·2 million, which represents 0·2% of the profit for the year and 0·03% of the total assets of the Hopper Group. It is therefore not material to the Hopper Group’s financial statements. For this reason no modification to the audit report of the Hopper Group would be required as this does not represent a lack of sufficient appropriate evidence with regard to a matter which is material to the Group financial statements.
Although this may not have an impact on the Hopper Group audit opinion, this may be something the group auditor wishes to bring to the attention of those charged with governance. This would be particularly likely if the group auditor believed that this could indicate some form. of fraud in Seurat Sweeteners Co, a serious deficiency in financial reporting controls or if this could create problems for accepting future audits due to management’s unwillingness to provide access to accounting records.
(c) Quality control procedures prior to issuing the audit report
ISA 220 Quality Control for an Audit of Financial Statements and ISQC 1 Quality Control for Firms that Perform. Audits and Reviews of Historical Financial Information, and Other Assurance and Related Services Agreements require that an engagement quality control reviewer shall be appointed for audits of financial statements of listed entities. The audit engagement partner then discusses significant matters arising during the audit engagement with the engagement quality control reviewer.
The engagement quality control reviewer and the engagement partner should discuss the failure to recognise the contingent consideration and its impact on the auditor’s report. The engagement quality control reviewer must review the financial statements and the proposed auditor’s report, in particular focusing on the conclusions reached in formulating the auditor’s report and consideration of whether the proposed auditor’s opinion is appropriate. The audit documentation relating to the acquisition of Seurat Sweeteners Co will be carefully reviewed, and the reviewer is likely to consider whether procedures performed in relation to these balances were appropriate.
Given the listed status of the Hopper Group, any modification to the auditor’s report will be scrutinised, and the firm must be sure of any decision to modify the report, and the type of modification made. Once the engagement quality control reviewer has considered the necessity of a modification, they should consider whether a qualified or an adverse opinion is appropriate in the circumstances. This is an important issue, given that it requires judgement as to whether the matters would be material or pervasive to the financial statements.
The engagement quality control reviewer should ensure that there is adequate documentation regarding the judgements used in forming the final audit opinion, and that all necessary matters have been brought to the attention of those charged with governance.
The auditor’s report must not be signed and dated until the completion of the engagement quality control review.
Tutorial note: In the case of the Hopper Group’s audit, the lack of evidence in respect of research costs is unlikely to be discussed unless the audit engagement partner believes that the matter could be significant, for example, if they suspected the lack of evidence is being used to cover up a financial statements fraud.
