(d) Sirus raised a loan with a bank of $2 million on 1 May 2007. The market interest rate of 8% per annum is tobe paid annually in arrears and the principal is to be repaid in 10 years time. The terms of the loan allow Sirusto redeem the loan after seven
题目
(d) Sirus raised a loan with a bank of $2 million on 1 May 2007. The market interest rate of 8% per annum is to
be paid annually in arrears and the principal is to be repaid in 10 years time. The terms of the loan allow Sirus
to redeem the loan after seven years by paying the full amount of the interest to be charged over the ten year
period, plus a penalty of $200,000 and the principal of $2 million. The effective interest rate of the repayment
option is 9·1%. The directors of Sirus are currently restructuring the funding of the company and are in initial
discussions with the bank about the possibility of repaying the loan within the next financial year. Sirus is
uncertain about the accounting treatment for the current loan agreement and whether the loan can be shown as
a current liability because of the discussions with the bank. (6 marks)
Appropriateness of the format and presentation of the report and quality of discussion (2 marks)
Required:
Draft a report to the directors of Sirus which discusses the principles and nature of the accounting treatment of
the above elements under International Financial Reporting Standards in the financial statements for the year
ended 30 April 2008.
相似考题
参考答案和解析
(d) Repayment of the loan
If at the beginning of the loan agreement, it was expected that the repayment option would not be exercised, then the effective
interest rate would be 8% and at 30 April 2008, the loan would be stated at $2 million in the statement of financial position
with interest of $160,000 having been paid and accounted for. If, however, at 1 May 2007, the option was expected to be
exercised, then the effective interest rate would be 9·1% and at 30 April 2008, the cash interest paid would have been
$160,000 and the interest charged to the income statement would have been (9·1% x $2 million) $182,000, giving a
statement of financial position figure of $2,022,000 for the amount of the financial liability. However, IAS39 requires the
carrying amount of the financial instrument to be adjusted to reflect actual and revised estimated cash flows. Thus, even if
the option was not expected to be exercised at the outset but at a later date exercise became likely, then the carrying amount
would be revised so that it represented the expected future cash flows using the effective interest rate. As regards the
discussions with the bank over repayment in the next financial year, if the loan was shown as current, then the requirements
of IAS1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’ would not be met. Sirus has an unconditional right to defer settlement for longer
than twelve months and the liability is not due to be legally settled in 12 months. Sirus’s discussions should not be considered
when determining the loan’s classification.
It is hoped that the above report clarifies matters.
更多“(d) Sirus raised a loan with a bank of $2 million on 1 May 2007. The market interest rate of 8% per annum is tobe paid annually in arrears and the principal is to be repaid in 10 years time. The terms of the loan allow Sirusto redeem the loan after seven ”相关问题
-
第1题:
3 Seejoy is a famous football club but has significant cash flow problems. The directors and shareholders wish to take
steps to improve the club’s financial position. The following proposals had been drafted in an attempt to improve the
cash flow of the club. However, the directors need advice upon their implications.
(a) Sale and leaseback of football stadium (excluding the land element)
The football stadium is currently accounted for using the cost model in IAS16, ‘Property, Plant, and Equipment’.
The carrying value of the stadium will be $12 million at 31 December 2006. The stadium will have a remaining
life of 20 years at 31 December 2006, and the club uses straight line depreciation. It is proposed to sell the
stadium to a third party institution on 1 January 2007 and lease it back under a 20 year finance lease. The sale
price and fair value are $15 million which is the present value of the minimum lease payments. The agreement
transfers the title of the stadium back to the football club at the end of the lease at nil cost. The rental is
$1·2 million per annum in advance commencing on 1 January 2007. The directors do not wish to treat this
transaction as the raising of a secured loan. The implicit interest rate on the finance in the lease is 5·6%.
(9 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above proposals would be dealt with in the financial statements of Seejoy for the year ending
31 December 2007, setting out their accounting treatment and appropriateness in helping the football club’s
cash flow problems.
(Candidates do not need knowledge of the football finance sector to answer this question.)
正确答案:

-
第2题:
(c) On 1 May 2007 Sirus acquired another company, Marne plc. The directors of Marne, who were the only
shareholders, were offered an increased profit share in the enlarged business for a period of two years after the
date of acquisition as an incentive to accept the purchase offer. After this period, normal remuneration levels will
be resumed. Sirus estimated that this would cost them $5 million at 30 April 2008, and a further $6 million at
30 April 2009. These amounts will be paid in cash shortly after the respective year ends. (5 marks)
Required:
Draft a report to the directors of Sirus which discusses the principles and nature of the accounting treatment of
the above elements under International Financial Reporting Standards in the financial statements for the year
ended 30 April 2008.
正确答案:
(c) Acquisition of Marne
All business combinations within the scope of IFRS 3 ‘Business Combinations’ must be accounted for using the purchase
method. (IFRS 3.14) The pooling of interests method is prohibited. Under IFRS 3, an acquirer must be identified for all
business combinations. (IFRS 3.17) Sirus will be identified as the acquirer of Marne and must measure the cost of a business
combination at the sum of the fair values, at the date of exchange, of assets given, liabilities incurred or assumed, in exchange
for control of Marne; plus any costs directly attributable to the combination. (IFRS 3.24) If the cost is subject to adjustment
contingent on future events, the acquirer includes the amount of that adjustment in the cost of the combination at the
acquisition date if the adjustment is probable and can be measured reliably. (IFRS 3.32) However, if the contingent payment
either is not probable or cannot be measured reliably, it is not measured as part of the initial cost of the business combination.
If that adjustment subsequently becomes probable and can be measured reliably, the additional consideration is treated as
an adjustment to the cost of the combination. (IAS 3.34) The issue with the increased profit share payable to the directors
of Marne is whether the payment constitutes remuneration or consideration for the business acquired. Because the directors
of Marne fall back to normal remuneration levels after the two year period, it appears that this additional payment will
constitute part of the purchase consideration with the resultant increase in goodwill. It seems as though these payments can
be measured reliably and therefore the cost of the acquisition should be increased by the net present value of $11 million at
1 May 2007 being $5 million discounted for 1 year and $6 million for 2 years. -
第3题:
单句理解
听力原文:For one full year when the full principal plus interest is paid together, compound interest and simple interest yield the same dollar amount.
(1)
A.If the time period of the loan is one year, the simple interest and compound interest are the same.
B.If the time period of the loan is the same, the simple interest and compound interest are the same.
C.When the full principal plus interest is paid together, compound interest and simple interest are of the same dollar amount.
D.When the full principal plus interest is paid together, compound interest and simple interest are not of the same dollar amount.
正确答案:A
解析:单句意思为“当本金和利息整整一年才一起支付时,复利计息和单利计息的数额一样”。 -
第4题:
听力原文: Some banks offer other types of loans repayable by monthly installments, such as business development loans, house improvement loans, and farm development loans. These may be either secured or unsecured. Secured loans attract a slightly lower rate of interest than unsecured loans. Some banks offer revolving credit schemes. These normally involve loans repayable by regular monthly installments, but they differ from other loans repayable by installments in two respects. First, the borrower need not take up the full amount of the loan at the outset. Secondly, as his repayments reduce his indebtedness, he can "top up" his loan by borrowing more, provided that the total debt outstanding does not exceed his agreed credit limit. In 1967 some banks introduced a new form. of account called a "budget account". The object is to allow personal customers to spread the incidence of normal personal and household expenditure.
24. Which of the following loans is not repaid by installments?
25.Which of the following loans would attract a lower rate of interest?
26.How does a borrower "top up" his loan?
27.What is the objective of introduction of the budget account?
(24)
A.Business development loans.
B.House improvement loans.
C.Farm development loans.
D.Overdrafts.
正确答案:D
解析:录音原文一开始提到Some banks offer...and farm development loans. 一些银行推出其他种类按月分期还款的贷款,例如商业发展贷款、住房改善贷款和农业发展贷款。 -
第5题:
______ is a large loan, generally more than USD10 million, negotiated between a borrower and a single bank, but actually funded by a number of banks.
A.A project loan
B.A syndicated loan
C.An export credit
D.Consumer credit
正确答案:B
解析:project loan项目贷款。export credit出口信贷。consumer credit消费信贷。 -
第6题:
The bank's request for loan security is ______.
A.to make the loan more profitable
B.to make the loan more diversified
C.to reduce the loss in case of default
D.to guard against deterioration of loan collateral
正确答案:C
解析:文章第一段提到The main reason for requesting that…to repay the loan at maturity.银行在发放贷款时向借款人要求一定的抵押品,主要是为了降低风险,在借款人不能按时还款时,可以处置抵押品来降低贷款损失。 -
第7题:
The rate of interest paid on a bank loan will depend () your firm’s standing with the bank and may be 2 per cent or 3 percent.
A、of
B、upon
C、for
D、in
参考答案:B
-
第8题:
听力原文:M: The rate on a personal loan is fixed according to the base rate at the time when the loan is made.
W: But it is always higher than the base rate, isn't it?
Q: What is determined when a personal loan is made?
(14)
A.Rate on the personal loan.
B.Base rate of the bank.
C.The amount of payment.
D.Personal loan's time period.
正确答案:A
解析:根据对话中"The rate on a personal loan is fixed"可知A项正确。 -
第9题:
The following trial balance relates to Sandown at 30 September 2009:
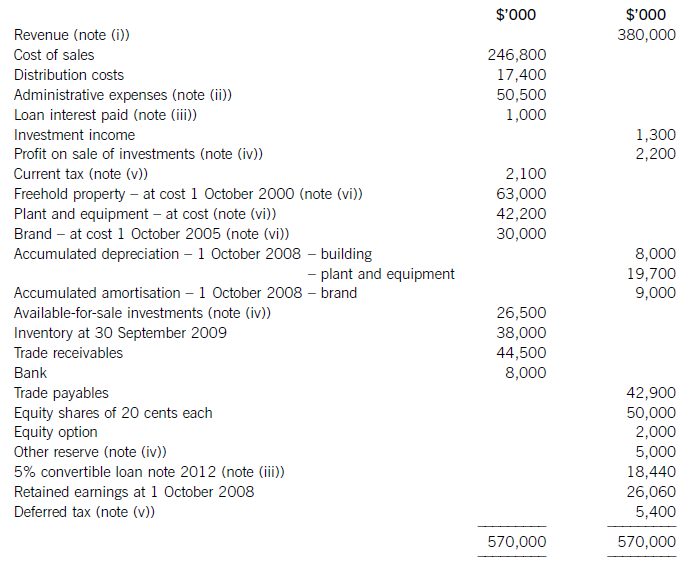
The following notes are relevant:
(i) Sandown’s revenue includes $16 million for goods sold to Pending on 1 October 2008. The terms of the sale are that Sandown will incur ongoing service and support costs of $1·2 million per annum for three years after the sale. Sandown normally makes a gross profit of 40% on such servicing and support work. Ignore the time value of money.
(ii) Administrative expenses include an equity dividend of 4·8 cents per share paid during the year.
(iii) The 5% convertible loan note was issued for proceeds of $20 million on 1 October 2007. It has an effective interest rate of 8% due to the value of its conversion option.
(iv) During the year Sandown sold an available-for-sale investment for $11 million. At the date of sale it had a
carrying amount of $8·8 million and had originally cost $7 million. Sandown has recorded the disposal of the
investment. The remaining available-for-sale investments (the $26·5 million in the trial balance) have a fair value of $29 million at 30 September 2009. The other reserve in the trial balance represents the net increase in the value of the available-for-sale investments as at 1 October 2008. Ignore deferred tax on these transactions.
(v) The balance on current tax represents the under/over provision of the tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2008. The directors have estimated the provision for income tax for the year ended 30 September 2009 at $16·2 million. At 30 September 2009 the carrying amounts of Sandown’s net assets were $13 million in excess of their tax base. The income tax rate of Sandown is 30%.
(vi) Non-current assets:
The freehold property has a land element of $13 million. The building element is being depreciated on a
straight-line basis.
Plant and equipment is depreciated at 40% per annum using the reducing balance method.
Sandown’s brand in the trial balance relates to a product line that received bad publicity during the year which led to falling sales revenues. An impairment review was conducted on 1 April 2009 which concluded that, based on estimated future sales, the brand had a value in use of $12 million and a remaining life of only three years.
However, on the same date as the impairment review, Sandown received an offer to purchase the brand for
$15 million. Prior to the impairment review, it was being depreciated using the straight-line method over a
10-year life.
No depreciation/amortisation has yet been charged on any non-current asset for the year ended 30 September
2009. Depreciation, amortisation and impairment charges are all charged to cost of sales.
Required:
(a) Prepare the statement of comprehensive income for Sandown for the year ended 30 September 2009.
(13 marks)
(b) Prepare the statement of financial position of Sandown as at 30 September 2009. (12 marks)
Notes to the financial statements are not required.
A statement of changes in equity is not required.
正确答案:
(i)IAS18Revenuerequiresthatwheresalesrevenueincludesanamountforaftersalesservicingandsupportcoststhenaproportionoftherevenueshouldbedeferred.Theamountdeferredshouldcoverthecostandareasonableprofit(inthiscaseagrossprofitof40%)ontheservices.Astheservicingandsupportisforthreeyearsandthedateofthesalewas1October2008,revenuerelatingtotwoyears’servicingandsupportprovisionmustbedeferred:($1·2millionx2/0·6)=$4million.Thisisshownas$2millioninbothcurrentandnon-currentliabilities. -
第10题:
(a) The following figures have been calculated from the financial statements (including comparatives) of Barstead for
the year ended 30 September 2009:
increase in profit after taxation 80%
increase in (basic) earnings per share 5%
increase in diluted earnings per share 2%
Required:
Explain why the three measures of earnings (profit) growth for the same company over the same period can
give apparently differing impressions. (4 marks)
(b) The profit after tax for Barstead for the year ended 30 September 2009 was $15 million. At 1 October 2008 the company had in issue 36 million equity shares and a $10 million 8% convertible loan note. The loan note will mature in 2010 and will be redeemed at par or converted to equity shares on the basis of 25 shares for each $100 of loan note at the loan-note holders’ option. On 1 January 2009 Barstead made a fully subscribed rights issue of one new share for every four shares held at a price of $2·80 each. The market price of the equity shares of Barstead immediately before the issue was $3·80. The earnings per share (EPS) reported for the year ended 30 September 2008 was 35 cents.
Barstead’s income tax rate is 25%.
Required:
Calculate the (basic) EPS figure for Barstead (including comparatives) and the diluted EPS (comparatives not required) that would be disclosed for the year ended 30 September 2009. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(a)Whilstprofitaftertax(anditsgrowth)isausefulmeasure,itmaynotgiveafairrepresentationofthetrueunderlyingearningsperformance.Inthisexample,userscouldinterpretthelargeannualincreaseinprofitaftertaxof80%asbeingindicativeofanunderlyingimprovementinprofitability(ratherthanwhatitreallyis:anincreaseinabsoluteprofit).Itispossible,evenprobable,that(someof)theprofitgrowthhasbeenachievedthroughtheacquisitionofothercompanies(acquisitivegrowth).Wherecompaniesareacquiredfromtheproceedsofanewissueofshares,orwheretheyhavebeenacquiredthroughshareexchanges,thiswillresultinagreaternumberofequitysharesoftheacquiringcompanybeinginissue.ThisiswhatappearstohavehappenedinthecaseofBarsteadastheimprovementindicatedbyitsearningspershare(EPS)isonly5%perannum.ThisexplainswhytheEPS(andthetrendofEPS)isconsideredamorereliableindicatorofperformancebecausetheadditionalprofitswhichcouldbeexpectedfromthegreaterresources(proceedsfromthesharesissued)ismatchedwiththeincreaseinthenumberofshares.Simplylookingatthegrowthinacompany’sprofitaftertaxdoesnottakeintoaccountanyincreasesintheresourcesusedtoearnthem.Anyincreaseingrowthfinancedbyborrowings(debt)wouldnothavethesameimpactonprofit(asbeingfinancedbyequityshares)becausethefinancecostsofthedebtwouldacttoreduceprofit.ThecalculationofadilutedEPStakesintoaccountanypotentialequitysharesinissue.Potentialordinarysharesarisefromfinancialinstruments(e.g.convertibleloannotesandoptions)thatmayentitletheirholderstoequitysharesinthefuture.ThedilutedEPSisusefulasitalertsexistingshareholderstothefactthatfutureEPSmaybereducedasaresultofsharecapitalchanges;inasenseitisawarningsign.InthiscasethelowerincreaseinthedilutedEPSisevidencethatthe(higher)increaseinthebasicEPShas,inpart,beenachievedthroughtheincreaseduseofdilutingfinancialinstruments.Thefinancecostoftheseinstrumentsislessthantheearningstheirproceedshavegeneratedleadingtoanincreaseincurrentprofits(andbasicEPS);however,inthefuturetheywillcausemoresharestobeissued.ThiscausesadilutionwherethefinancecostperpotentialnewshareislessthanthebasicEPS. -
第11题:
John, CPA, is auditing the financial statements of ABC Bank Co.for the year ended December 31,20×8. The following information is available:
(a)John assessed the risk of material misstatements in short-term loan account at 80% and plans to limit to 10% the risk of failing to detect misstatements in the account equal to the tolerable error assigned to the account.
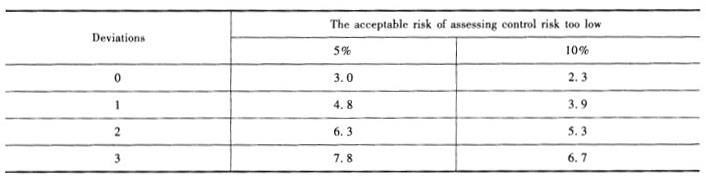
(b) John is testing the operating effectiveness of the loan approval procedure(a control activ- ity) related to granting loans. In 20×8,ABC Bank granted to 10 000 loans in total. John deter- mined that the acceptable risk of assessing control risk too low is 10%. He selected a sample made up of 60 sampling units and tested without any deviation found. Some Poisson Risk Factors(Relia- bility Factors) are reprinted as follows:
(c) John is using the Ratio Estimation Variable Sampling method to test the long-term loan balance at December 31, 20×8. The total recorded balance is RMB¥300 billion , made up of 4 000 items. John designed a sample made up of 200 items . The book value of the sample is RMB¥16. 5 billion. However, the audited value is RMB¥15. 6 billion.
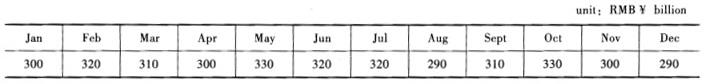
(d) John is performing substantive procedures on interest income from short-term loan. The average annual market interest rate for short-term loan is 5 percent. The audited short-term loan balances of ABC Bank Co. at the end of each month in 20×8 are as follows:
Required :
(1) Based on (a) , calculate the acceptable detection risk.
(2) Based on (b) , calculate the upper limit of population deviation rate.
(3) Based on (c), make a point estimate of the misstatement in the population. Sampling error need not to be considered.
(4) Based on (d) , develop the expected result of interest income from short-term loan.
(5) Assume that after the tests mentioned in (d) , John found that the interest income from short-term loan was understated by RMB¥0. 05billion. Prepare the adjusting entry.
答案:解析:(1) acceptable detection risk = audit risk/the risk of material misstatement s = 10%/80% = 12. 5%
(2) The upper limit of population deviation rate = Poisson risk factor/sample size = 2. 3/60 = 3. 83 %
(3) ratio = 156/165 = 94. 54%
estimate the actual value of the population = 3 000*94. 54% = 283. 62 billion a point estimate of the misstatement in of the population =3 000 -283. 62 *10 = 16. 38 billion
(4) the expected result of interest income from short-term loan = (300 +320 +310 +300 + 330 +320 +320 +290 +310 +330 +300 +290)*5% =18. 6 billion
(5) the adjusting accounting entry:
Dr: Interest suspense 156
Cr: Interest income 156
-
第12题:
问答题◆Topic 2: Does blacklisting student loan defaulters help repayments to banks? News report: Between 2005 and 2007, the China Development Bank offered 1.66 billion yuan worth of loans to 243,000 students from poor families in central China’s Henan Province. Last May, the Bank and the Henan Provincial Education Department jointly issued an ultimatum requiring 223 college graduates to pay off the interest on their student loan within 30 days. Nevertheless, the students failed to repay the debts as required. Now the colleges and banks cannot contact these students after their graduation as they have not notified banks of their changes of address. It is in this situation that the China Development Bank and the Education Department decided to publish the personal information of these students in accordance with relevant regulations concerning student loans. Questions for reference: 1. Should the personal information of these students be published or not? Give your reasons. 2. How should the student loan system be improved and perfected? 3. What are the possible consequences that might follow if the personal information of such students are published?正确答案: 【参考答案】
My name is...My registration number is...Today I will talk about the question…Does blacklisting student loan defaulters help repayments to banks?
Here is the thing: The students have failed to repay the debts as required by banks and they are now out of contact after their graduation as they have not notified banks of their changes of addresses. Therefore some banks have decided to publish the personal information of these students in accordance with relevant regulations concerning student loans. As a consequence, those who fail to contact their schools and banks in time will have their bad credit record included in the central bank’s personal credit information database, which will clearly place a black mark on these students’ future lives and careers.
This question claims for more comprehensive consideration. Here I want to point out that many people have shown their sympathy for these students. As for students who depend on loans for completing college education, they sometimes have a sense of inferiority and often face some kind of psychological pressure. Faced with the tight employment situation, they are already becoming worried whether they can repay education loans. Now, banks’ exposure of students defaulting on education loans will undoubtedly cast a bigger shadow on them. The exposure of their “bad credit record” would make it difficult for them to find a job after graduation. Worse still, the exposure may even deprive an already employed student of a job, further harming his ability to pay off the loan. In other words, to expose their personal information will often damage students’ reputations and may well deprive many students of valuable future jobs and promotion opportunities, putting them in an even more difficult financial position. One of the ways to deal with loan defaulters is to go to court, file litigation against them, and settle the issue through legal means. On the other hand, banks and education authorities could take further measures and improve the loan system so as to avoid the occurrence of defaulting on payment of education loans.解析: 暂无解析 -
第13题:
3 (a) Leigh, a public limited company, purchased the whole of the share capital of Hash, a limited company, on 1 June
2006. The whole of the share capital of Hash was formerly owned by the five directors of Hash and under the
terms of the purchase agreement, the five directors were to receive a total of three million ordinary shares of $1
of Leigh on 1 June 2006 (market value $6 million) and a further 5,000 shares per director on 31 May 2007,
if they were still employed by Leigh on that date. All of the directors were still employed by Leigh at 31 May
2007.
Leigh granted and issued fully paid shares to its own employees on 31 May 2007. Normally share options issued
to employees would vest over a three year period, but these shares were given as a bonus because of the
company’s exceptional performance over the period. The shares in Leigh had a market value of $3 million
(one million ordinary shares of $1 at $3 per share) on 31 May 2007 and an average fair value of
$2·5 million (one million ordinary shares of $1 at $2·50 per share) for the year ended 31 May 2007. It is
expected that Leigh’s share price will rise to $6 per share over the next three years. (10 marks)
Required:
Discuss with suitable computations how the above share based transactions should be accounted for in the
financial statements of Leigh for the year ended 31 May 2007.
正确答案:
(a) The shares issued to the management of Hash by Leigh (three million ordinary shares of $1) for the purchase of the company
would not be accounted for under IFRS2 ‘Share-based payment’ but would be dealt with under IFRS3 ‘Business
Combinations’.
The cost of the business combination will be the total of the fair values of the consideration given by the acquirer plus any
attributable cost. In this case the shares of Leigh will be fair valued at $6 million with $3 million being shown as share capital
and $3million as share premium. However, the shares issued as contingent consideration may be accounted for under IFRS2.
The terms of the issuance of shares will need to be examined. Where part of the consideration may be reliant on uncertain
future events, and it is probable that the additional consideration is payable and can be measured reliably, then it is included
in the cost of the business consideration at the acquisition date. However, the question to be answered in the case of the
additional 5,000 shares per director is whether the shares are compensation or part of the purchase price. There is a need
to understand why the acquisition agreement includes a provision for a contingent payment. It is possible that the price paid
initially by Leigh was quite low and, therefore, this then represents a further purchase consideration. However, in this instance
the additional payment is linked to continuing employment and, therefore, it would be argued that because of the link between
the contingent consideration and continuing employment that it represents a compensation arrangement which should be
included within the scope of IFRS2.
Thus as there is a performance condition, (the performance condition will apply as it is not a market condition) the substance
of the agreement is that the shares are compensation, then they will be fair valued at the grant date and not when the shares
vest. Therefore, the share price of $2 per share will be used to give compensation of $50,000 (5 x 5,000 x $2). (Under
IFRS3, fair value is measured at the date the consideration is provided and discounted to presented value. No guidance is
provided on what the appropriate discount rate might be. Thus the fair value used would have been $3 per share at 31 May
2007.) The compensation will be charged to the income statement and included in equity.
The shares issued to the employees of Leigh will be accounted for under IFRS2. The issuance of fully paid shares will be
presumed to relate to past service. The normal vesting period for share options is irrelevant, as is the average fair value of the
shares during the period. The shares would be expensed at a value of $3 million with a corresponding increase in equity.
Goods or services acquired in a share based payment transaction should be recognised when they are received. In the case
of goods then this will be when this occurs. However, it is somewhat more difficult sometimes to determine when services
are received. In a case of goods the vesting date is not really relevant, however, it is highly relevant for employee services. If
shares are issued that vest immediately then there is a presumption that these are a consideration for past employee services. -
第14题:
3 You are an audit manager in Webb & Co, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants. Your audit client, Mulligan Co,
designs and manufactures wooden tables and chairs. The business has expanded rapidly in the last two years, since
the arrival of Patrick Tiler, an experienced sales and marketing manager.
The directors want to secure a loan of $3 million in order to expand operations, following the design of a completely
new range of wooden garden furniture. The directors have approached LCT Bank for the loan. The bank’s lending
criteria stipulate the following:
‘Loan applications must be accompanied by a detailed business plan, including an analysis of how the finance will
be used. LCT Bank need to see that the finance requested is adequate for the proposed business purpose. The
business plan must be supported by an assurance opinion on the adequacy of the requested finance.’
The $3 million finance raised will be used as follows:
$000
Construction of new factory 1,250
Purchase of new machinery 1,000
Initial supply of timber raw material 250
Advertising and marketing of new product 500
Your firm has agreed to review the business plan and to provide an assurance opinion on the completeness of the
finance request. A meeting will be held tomorrow to discuss this assignment.
Required:
(a) Identify and explain the matters relating to the assurance assignment that should be discussed at the meeting
with Mulligan Co. (8 marks)
正确答案:
3 MULLIGAN CO
(a) Matters to be discussed would include the following:
The exact content of the business plan which could include:
– Description of past business performance and key products
– Discussion of the new product
– Evidence of the marketability of the new product
– Cash flow projections
– Capital expenditure forecasts
– Key business assumptions.
The form. of the assurance report that is required – in an assurance engagement the nature and wording of the expected
opinion should be discussed. Webb & Co should clarify that an opinion of ‘negative assurance’ will be required, and whether
this will meet the bank’s lending criteria.
The intended recipient of the report – Webb & Co need to clarify the name and address of the recipient at LCT Bank. For the
limitation of professional liability, it should be clarified that LCT Bank will be the only recipient, and that the assurance opinion
is being used only as part of the bank’s overall lending decision.
Limiting liability – Webb & Co may want to receive in writing a statement that the report is for information purposes only, and
does not give rise to any responsibility, liability, duty or obligation from the firm to the lender.
Deadlines – it should be discussed when the bank need the report. This in turn will be influenced by when Mulligan Co needs
the requested $3 million finance. The bank may need a considerable period of time to assess the request, review the report,
and ensure that their lending criteria have been fully met prior to advancing the finance.
Availability of evidence – Mulligan Co should be made aware that in order to express an opinion on the finance request, they
must be prepared to provide all the necessary paperwork to assist the assurance provider. Evidence is likely to include
discussions with key management, and written representations of discussions may be required.
Professional regulation – Webb & Co should discuss the kind of procedures that will be undertaken, and confirm that they
will be complying with relevant professional guidance, for example:
– ISAE 3000 Assurance Engagements other than Audits or Reviews of Historical Financial Information
– ISAE 3400 The Examination of Prospective Financial Information
Engagement administration – any points not yet discussed in detail when deciding to take the assurance engagement should
be finalised at the meeting. These points could include the following:
– Fees – the total fee and billing arrangements must be agreed before any work is carried out
– Personnel – Webb & Co should identify the key personnel who will be involved in the assignment
– Complaints procedures – should be briefly outlined (the complaints procedures in an assurance engagement may differ
from an audit assignment)
– Engagement letter – if not already signed by both Webb & Co and Mulligan Co, the engagement letter should be
discussed and signed at the meeting before any assignment work is conducted.
Tutorial note: the scenario states that Webb & Co have already decided to take the assurance assignment for their existing
client, therefore the answer to this requirement should not focus on client or engagement acceptance procedures. -
第15题:
Usually the borrowing firm of term loans promises to repay ______.
A.the principal and interest until the end of the loan period
B.the principal and interest at the end of the loan period
C.the loan in a series of installments
D.at any time when cash is more abundant ______.
正确答案:C
解析:第一段第二句后半句...and then pledges to meet the scheduled repayment in a series of installments(often payments are made every quarter or even monthly),意指借款企业向银行保证分期还款,通常是按月或者按季度分期还款。Installment分期还款。 -
第16题:
听力原文:M: Most banks tend to decline loan proposals which are highly speculative.
W: I think because the banks expect the loan to generate sufficient profit and positive cash-flow for themselves and for the clients.
Q: What will the banks usually do to the highly speculative loan proposals?
(15)
A.The banks will disapprove them.
B.The banks will approve them.
C.The Bank will benefit from the loans.
D.The bank will make profit from lending.
正确答案:A
解析:根据男士的话可知银行对投机性高的贷款申请的态度是“decline”,即“拒绝”,A项正确。 -
第17题:
Usually, a loan to government is safer than a loan to a private-sector borrower.
A.Right
B.Wrong
C.Doesn't say
正确答案:A
解析:从文中第三句话In any case, a loan to the foreign nation's government or its agencies is generally safer than a loan to a private-sector borrower.可以看出。 -
第18题:
The value of the collateral must be ______.
A.greater than the loan amount
B.the same as or be greater than the loan amount
C.smaller than the loan amount
D.the same as the loan amount
正确答案:B
解析:文章第二段提到it is imperative that…or greater than, the amount of the loan.抵押品的价值一般应高于或等于贷款的金额,这样才能控制贷款风险的作用。 -
第19题:
单句理解
听力原文:Collateral can never make a bad loan good, but it can turn a good loan into a better one.
(1)
A.Collateral sometimes turns a bad loan into a good one.
B.Good loans can be turned into better loans with collaterals.
C.Collateral can turn a good loan into a bad one.
D.Collateral can turn a bad loan into a worse one.
正确答案:B
解析:单句给出的信息是“贷款抵押物从不会使账目由坏变好,但可以由好变更好”,B项意思正确。 -
第20题:
The bank (56) borrowers enough interest to pay the expense of the bank and have something left over for (57) . The interest cannot be higher than the legal rate, which is established by state law and in most states is 6% per year. (58) big loans, the interest rate is much less, even as low as 2%. The rate depends on the money market, when there is plenty of money (59) to be borrowed, banks charge low rates of interest. A savings bank may pay its depositors 2% and lend the money at 3.5% or 4%. But when money is tight, interest rates go up, and a savings bank may try to (60) depositors by offering 4% or 4.5% or even more and lending the money at 5% or 6%.
(41)
A.receives
B.gets
C.charges
D.pays
正确答案:C
解析:句意:银行向贷款人索取足够的利息以支付银行日常开销,并保证部分盈余。这里表示索取费用的词是charge。receive收到。pay支付,交纳。 -
第21题:
(a) The following information relates to Crosswire a publicly listed company.
Summarised statements of financial position as at:
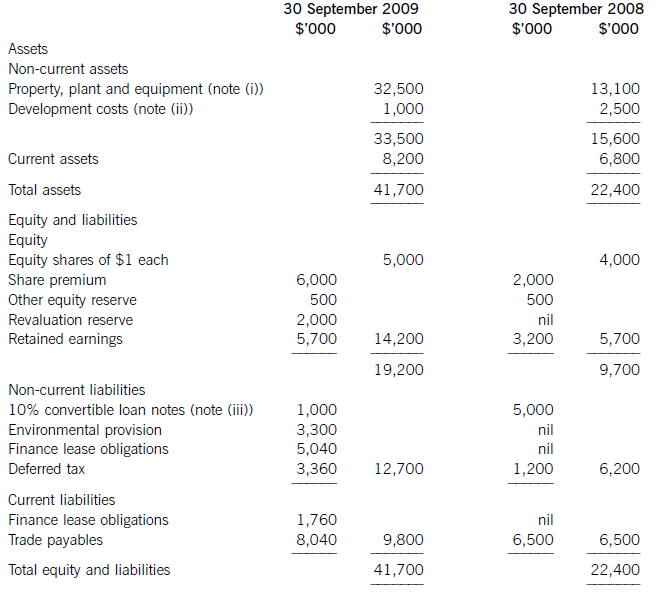
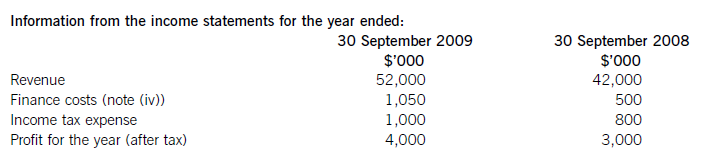
The following information is available:
(i) During the year to 30 September 2009, Crosswire embarked on a replacement and expansion programme for its non-current assets. The details of this programme are:
On 1 October 2008 Crosswire acquired a platinum mine at a cost of $5 million. A condition of mining the
platinum is a requirement to landscape the mining site at the end of its estimated life of ten years. The
present value of this cost at the date of the purchase was calculated at $3 million (in addition to the
purchase price of the mine of $5 million).
Also on 1 October 2008 Crosswire revalued its freehold land for the first time. The credit in the revaluation
reserve is the net amount of the revaluation after a transfer to deferred tax on the gain. The tax rate applicable to Crosswire for deferred tax is 20% per annum.
On 1 April 2009 Crosswire took out a finance lease for some new plant. The fair value of the plant was
$10 million. The lease agreement provided for an initial payment on 1 April 2009 of $2·4 million followed
by eight six-monthly payments of $1·2 million commencing 30 September 2009.
Plant disposed of during the year had a carrying amount of $500,000 and was sold for $1·2 million. The
remaining movement on the property, plant and equipment, after charging depreciation of $3 million, was
the cost of replacing plant.
(ii) From 1 October 2008 to 31 March 2009 a further $500,000 was spent completing the development
project at which date marketing and production started. The sales of the new product proved disappointing
and on 30 September 2009 the development costs were written down to $1 million via an impairment
charge.
(iii) During the year ended 30 September 2009, $4 million of the 10% convertible loan notes matured. The
loan note holders had the option of redemption at par in cash or to exchange them for equity shares on the
basis of 20 new shares for each $100 of loan notes. 75% of the loan-note holders chose the equity option.
Ignore any effect of this on the other equity reserve.
All the above items have been treated correctly according to International Financial Reporting Standards.
(iv) The finance costs are made up of:
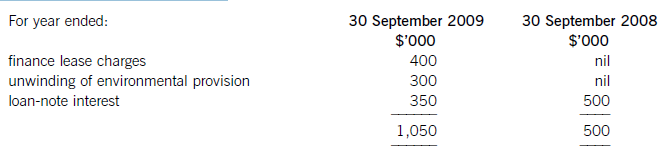
Required:
(i) Prepare a statement of the movements in the carrying amount of Crosswire’s non-current assets for the
year ended 30 September 2009; (9 marks)
(ii) Calculate the amounts that would appear under the headings of ‘cash flows from investing activities’
and ‘cash flows from financing activities’ in the statement of cash flows for Crosswire for the year ended
30 September 2009.
Note: Crosswire includes finance costs paid as a financing activity. (8 marks)
(b) A substantial shareholder has written to the directors of Crosswire expressing particular concern over the
deterioration of the company’s return on capital employed (ROCE)
Required:
Calculate Crosswire’s ROCE for the two years ended 30 September 2008 and 2009 and comment on the
apparent cause of its deterioration.
Note: ROCE should be taken as profit before interest on long-term borrowings and tax as a percentage of equity plus loan notes and finance lease obligations (at the year end). (8 marks)
正确答案:
(i)Thecashelementsoftheincreaseinproperty,plantandequipmentare$5millionforthemine(thecapitalisedenvironmentalprovisionisnotacashflow)and$2·4millionforthereplacementplantmakingatotalof$7·4million.(ii)Ofthe$4millionconvertibleloannotes(5,000–1,000)thatwereredeemedduringtheyear,75%($3million)ofthesewereexchangedforequitysharesonthebasisof20newsharesforeach$100inloannotes.Thiswouldcreate600,000(3,000/100x20)newsharesof$1eachandsharepremiumof$2·4million(3,000–600).As1million(5,000–4,000)newshareswereissuedintotal,400,000musthavebeenforcash.Theremainingincrease(aftertheeffectoftheconversion)inthesharepremiumof$1·6million(6,000–2,000b/f–2,400conversion)mustrelatetothecashissueofshares,thuscashproceedsfromtheissueofsharesis$2million(400nominalvalue+1,600premium).(iii)Theinitialleaseobligationis$10million(thefairvalueoftheplant).At30September2009totalleaseobligationsare$6·8million(5,040+1,760),thusrepaymentsintheyearwere$3·2million(10,000–6,800).(b)TakingthedefinitionofROCEfromthequestion:Fromtheaboveitcanbeclearlyseenthatthe2009operatingmarginhasimprovedbynearly1%point,despitethe$2millionimpairmentchargeonthewritedownofthedevelopmentproject.ThismeansthedeteriorationintheROCEisduetopoorerassetturnover.Thisimpliestherehasbeenadecreaseintheefficiencyintheuseofthecompany’sassetsthisyearcomparedtolastyear.Lookingatthemovementinthenon-currentassetsduringtheyearrevealssomemitigatingpoints:Thelandrevaluationhasincreasedthecarryingamountofproperty,plantandequipmentwithoutanyphysicalincreaseincapacity.Thisunfavourablydistortsthecurrentyear’sassetturnoverandROCEfigures.TheacquisitionoftheplatinummineappearstobeanewareaofoperationforCrosswirewhichmayhaveadifferent(perhapslower)ROCEtootherpreviousactivitiesoritmaybethatitwilltakesometimefortheminetocometofullproductioncapacity.Thesubstantialacquisitionoftheleasedplantwashalf-waythroughtheyearandcanonlyhavecontributedtotheyear’sresultsforsixmonthsatbest.Infutureperiodsafullyear’scontributioncanbeexpectedfromthisnewinvestmentinplantandthisshouldimprovebothassetturnoverandROCE.Insummary,thefallintheROCEmaybeduelargelytotheabovefactors(effectivelythereplacementandexpansionprogramme),ratherthantopooroperatingperformance,andinfutureperiodsthismaybereversed.ItshouldalsobenotedthathadtheROCEbeencalculatedontheaveragecapitalemployedduringtheyear(ratherthantheyearendcapitalemployed),whichisarguablymorecorrect,thenthedeteriorationintheROCEwouldnothavebeenaspronounced. -
第22题:
Moonstar Co is a property development company which is planning to undertake a $200 million commercial property development. Moonstar Co has had some difficulties over the last few years, with some developments not generating the expected returns and the company has at times struggled to pay its finance costs. As a result Moonstar Co’s credit rating has been lowered, affecting the terms it can obtain for bank finance. Although Moonstar Co is listed on its local stock exchange, 75% of the share capital is held by members of the family who founded the company. The family members who are shareholders do not wish to subscribe for a rights issue and are unwilling to dilute their control over the company by authorising a new issue of equity shares. Moonstar Co’s board is therefore considering other methods of financing the development, which the directors believe will generate higher returns than other recent investments, as the country where Moonstar Co is based appears to be emerging from recession.
Securitisation proposals
One of the non-executive directors of Moonstar Co has proposed that it should raise funds by means of a securitisation process, transferring the rights to the rental income from the commercial property development to a special purpose vehicle. Her proposals assume that the leases will generate an income of 11% per annum to Moonstar Co over a ten-year period. She proposes that Moonstar Co should use 90% of the value of the investment for a collateralised loan obligation which should be structured as follows:
– 60% of the collateral value to support a tranche of A-rated floating rate loan notes offering investors LIBOR plus 150 basis points
– 15% of the collateral value to support a tranche of B-rated fixed rate loan notes offering investors 12%
– 15% of the collateral value to support a tranche of C-rated fixed rate loan notes offering investors 13%
– 10% of the collateral value to support a tranche as subordinated certificates, with the return being the excess of receipts over payments from the securitisation process
The non-executive director believes that there will be sufficient demand for all tranches of the loan notes from investors. Investors will expect that the income stream from the development to be low risk, as they will expect the property market to improve with the recession coming to an end and enough potential lessees to be attracted by the new development.
The non-executive director predicts that there would be annual costs of $200,000 in administering the loan. She acknowledges that there would be interest rate risks associated with the proposal, and proposes a fixed for variable interest rate swap on the A-rated floating rate notes, exchanging LIBOR for 9·5%.
However the finance director believes that the prediction of the income from the development that the non-executive director has made is over-optimistic. He believes that it is most likely that the total value of the rental income will be 5% lower than the non-executive director has forecast. He believes that there is some risk that the returns could be so low as to jeopardise the income for the C-rated fixed rate loan note holders.
Islamic finance
Moonstar Co’s chief executive has wondered whether Sukuk finance would be a better way of funding the development than the securitisation.
Moonstar Co’s chairman has pointed out that a major bank in the country where Moonstar Co is located has begun to offer a range of Islamic financial products. The chairman has suggested that a Mudaraba contract would be the most appropriate method of providing the funds required for the investment.
Required:
(a) Calculate the amounts in $ which each of the tranches can expect to receive from the securitisation arrangement proposed by the non-executive director and discuss how the variability in rental income affects the returns from the securitisation. (11 marks)
(b) Discuss the benefits and risks for Moonstar Co associated with the securitisation arrangement that the non-executive director has proposed. (6 marks)
(c) (i) Discuss the suitability of Sukuk finance to fund the investment, including an assessment of its appeal to potential investors. (4 marks)
(ii) Discuss whether a Mudaraba contract would be an appropriate method of financing the investment and discuss why the bank may have concerns about providing finance by this method. (4 marks)
正确答案:(a) An annual cash flow account compares the estimated cash flows receivable from the property against the liabilities within the securitisation process. The swap introduces leverage into the arrangement.
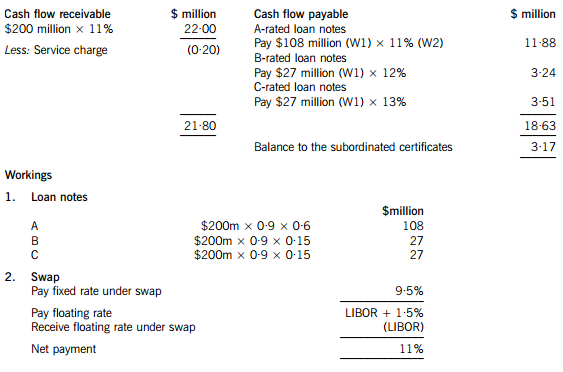
The holders of the certificates are expected to receive $3·17million on $18 million, giving them a return of 17·6%. If the cash flows are 5% lower than the non-executive director has predicted, annual revenue received will fall to $20·90 million, reducing the balance available for the subordinated certificates to $2·07 million, giving a return of 11·5% on the subordinated certificates, which is below the returns offered on the B and C-rated loan notes. The point at which the holders of the certificates will receive nothing and below which the holders of the C-rated loan notes will not receive their full income will be an annual income of $18·83 million (a return of 9·4%), which is 14·4% less than the income that the non-executive director has forecast.
(b) Benefits
The finance costs of the securitisation may be lower than the finance costs of ordinary loan capital. The cash flows from the commercial property development may be regarded as lower risk than Moonstar Co’s other revenue streams. This will impact upon the rates that Moonstar Co is able to offer borrowers.
The securitisation matches the assets of the future cash flows to the liabilities to loan note holders. The non-executive director is assuming a steady stream of lease income over the next 10 years, with the development probably being close to being fully occupied over that period.
The securitisation means that Moonstar Co is no longer concerned with the risk that the level of earnings from the properties will be insufficient to pay the finance costs. Risks have effectively been transferred to the loan note holders.
Risks
Not all of the tranches may appeal to investors. The risk-return relationship on the subordinated certificates does not look very appealing, with the return quite likely to be below what is received on the C-rated loan notes. Even the C-rated loan note holders may question the relationship between the risk and return if there is continued uncertainty in the property sector.
If Moonstar Co seeks funding from other sources for other developments, transferring out a lower risk income stream means that the residual risks associated with the rest of Moonstar Co’s portfolio will be higher. This may affect the availability and terms of other borrowing.
It appears that the size of the securitisation should be large enough for the costs to be bearable. However Moonstar Co may face unforeseen costs, possibly unexpected management or legal expenses.
(c) (i) Sukuk finance could be appropriate for the securitisation of the leasing portfolio. An asset-backed Sukuk would be the same kind of arrangement as the securitisation, where assets are transferred to a special purpose vehicle and the returns and repayments are directly financed by the income from the assets. The Sukuk holders would bear the risks and returns of the relationship.
The other type of Sukuk would be more like a sale and leaseback of the development. Here the Sukuk holders would be guaranteed a rental, so it would seem less appropriate for Moonstar Co if there is significant uncertainty about the returns from the development.
The main issue with the asset-backed Sukuk finance is whether it would be as appealing as certainly the A-tranche of the securitisation arrangement which the non-executive director has proposed. The safer income that the securitisation offers A-tranche investors may be more appealing to investors than a marginally better return from the Sukuk. There will also be costs involved in establishing and gaining approval for the Sukuk, although these costs may be less than for the securitisation arrangement described above.
(ii) A Mudaraba contract would involve the bank providing capital for Moonstar Co to invest in the development. Moonstar Co would manage the investment which the capital funded. Profits from the investment would be shared with the bank, but losses would be solely borne by the bank. A Mudaraba contract is essentially an equity partnership, so Moonstar Co might not face the threat to its credit rating which it would if it obtained ordinary loan finance for the development. A Mudaraba contract would also represent a diversification of sources of finance. It would not require the commitment to pay interest that loan finance would involve.
Moonstar Co would maintain control over the running of the project. A Mudaraba contract would offer a method of obtaining equity funding without the dilution of control which an issue of shares to external shareholders would bring. This is likely to make it appealing to Moonstar Co’s directors, given their desire to maintain a dominant influence over the business.
The bank would be concerned about the uncertainties regarding the rental income from the development. Although the lack of involvement by the bank might appeal to Moonstar Co's directors, the bank might not find it so attractive. The bank might be concerned about information asymmetry – that Moonstar Co’s management might be reluctant to supply the bank with the information it needs to judge how well its investment is performing.
-
第23题:
单选题The banker will explain the terms of the loan to you_______detail.Aon
Bin
Cwith
Dout of
正确答案: D解析:
