4 The transition to International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRSs) involves major change for companies as IFRSsintroduce significant changes in accounting practices that were often not required by national generally acceptedaccounting practice. It is
题目
4 The transition to International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRSs) involves major change for companies as IFRSs
introduce significant changes in accounting practices that were often not required by national generally accepted
accounting practice. It is important that the interpretation and application of IFRSs is consistent from country to
country. IFRSs are partly based on rules, and partly on principles and management’s judgement. Judgement is more
likely to be better used when it is based on experience of IFRSs within a sound financial reporting infrastructure. It is
hoped that national differences in accounting will be eliminated and financial statements will be consistent and
comparable worldwide.
Required:
(a) Discuss how the changes in accounting practices on transition to IFRSs and choice in the application of
individual IFRSs could lead to inconsistency between the financial statements of companies. (17 marks)
相似考题
参考答案和解析
(a) The transition to International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) involves major change for companies as IFRS introduces
significant changes in accounting practices that often were not required by national GAAPs. For example financial instruments
and share-based payment plans in many instances have appeared on the statements of financial position of companies for
the first time. As a result IFRS financial statements are often significantly more complex than financial statements based on
national GAAP. This complexity is caused by the more extensive recognition and measurement rules in IFRS and a greater
number of disclosure requirements. Because of this complexity, it can be difficult for users of financial statements which have
been produced using IFRS to understand and interpret them, and thus can lead to inconsistency of interpretation of those
financial statements.
The form. and presentation of financial statements is dealt with by IAS1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’. This standard
sets out alternative forms or presentations of financial statements. Additionally local legislation often requires supplementary
information to be disclosed in financial statements, and best practice as to the form. or presentation of financial statements
has yet to emerge internationally. As a result companies moving to IFRS have tended to adopt IFRS in a way which minimises
the change in the form. of financial reporting that was applied under national GAAP. For example UK companies have tended
to present a statement of recognised income and expense, and a separate statement of changes in equity whilst French
companies tend to present a single statement of changes in equity.
It is possible to interpret standards in different ways and in some standards there is insufficient guidance. For example there
are different acceptable methods of classifying financial assets under IAS39 ‘Financial Instruments: Recognition and
Measurement’ in the statement of financial position as at fair value through profit or loss (subject to certain conditions) or
available for sale.
IFRSs are not based on a consistent set of principles, and there are conceptual inconsistencies within and between standards.
Certain standards allow alternative accounting treatments, and this is a further source of inconsistency amongst financial
statements. IAS31 ‘Interests in Joint Ventures’ allows interests in jointly controlled entities to be accounted for using the equity
method or proportionate consolidation. Companies may tend to use the method which was used under national GAAP.
Another example of choice in accounting methods under IFRS is IAS16 ‘Property, Plant and equipment’ where the cost or
revaluation model can be used for a class of property, plant and equipment. Also there is very little industry related accounting
guidance in IFRS. As a result judgement plays an important role in the selection of accounting policies. In certain specific
areas this can lead to a degree of inconsistency and lack of comparability.
IFRS1, ‘First time Adoption of International Financial Reporting Standards’, allows companies to use a number of exemptions
from the requirements of IFRS. These exemptions can affect financial statements for several years. For example, companies
can elect to recognise all cumulative actuarial gains and losses relating to post-employment benefits at the date of transition
to IFRS but use the ‘corridor’ approach thereafter. Thus the effect of being able to use a ‘one off write off’ of any actuarial
losses could benefit future financial statements significantly, and affect comparability. Additionally after utilising the above
exemption, companies can elect to recognise subsequent gains and losses outside profit or loss in ‘other comprehensive
income’ in the period in which they occur and not use the ‘corridor’ approach thus affecting comparability further.
Additionally IAS18 ‘Revenue’ allows variations in the way revenue is recognised. There is no specific guidance in IFRS on
revenue arrangements with multiple deliverables. Transactions have to be analysed in accordance with their economic
substance but there is often no more guidance than this in IFRS. The identification of the functional currency under IAS21,
‘The effects of changes in foreign exchange rates’, can be subjective. For example the functional currency can be determined
by the currency in which the commodities that a company produces are commonly traded, or the currency which influences
its operating costs, and both can be different.
Another source of inconsistency is the adoption of new standards and interpretations earlier than the due date of application
of the standard. With the IASB currently preparing to issue standards with an adoption date of 1 January 2009, early adoption
or lack of it could affect comparability although IAS8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors’
requires a company to disclose the possible impact of a new standard on its initial application. Many companies make very
little reference to the future impact of new standards.
更多“4 The transition to International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRSs) involves major change for companies as IFRSsintroduce significant changes in accounting practices that were often not required by national generally acceptedaccounting practice. It is”相关问题
-
第1题:
(b) Prepare the balance sheet of York at 31 October 2006, using International Financial Reporting Standards,
discussing the nature of the accounting treatments selected, the adjustments made and the values placed
on the items in the balance sheet. (20 marks)
正确答案: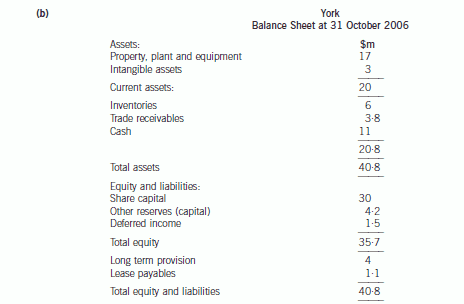
Gow’s net assets
IAS36 ‘Impairment of Assets’, sets out the events that might indicate that an asset is impaired. These circumstances include
external events such as the decline in the market value of an asset and internal events such as a reduction in the cash flows
to be generated from an asset or cash generating unit. The loss of the only customer of a cash generating unit (power station)
would be an indication of the possible impairment of the cash generating unit. Therefore, the power station will have to be
impairment tested.
The recoverable amount will have to be determined and compared to the value given to the asset on the setting up of the
joint venture. The recoverable amount is the higher of the cash generating unit’s fair value less costs to sell, and its value-inuse.
The fair value less costs to sell will be $15 million which is the offer for the purchase of the power station ($16 million)
less the costs to sell ($1 million). The value-in-use is the discounted value of the future cash flows expected to arise from the
cash generating unit. The future dismantling costs should be provided for as it has been agreed with the government that it
will be dismantled. The cost should be included in the future cash flows for the purpose of calculating value-in-use and
provided for in the financial statements and the cost added to the property, plant and equipment ($4 million ($5m/1·064)).
The value-in-use based on a discount rate of 6 per cent is $21 million (working). Therefore, the recoverable amount is
$21 million which is higher than the carrying value of the cash generating unit ($20 million) and, therefore, the value of the
cash generating unit is not impaired when compared to the present carrying value of $20 million (value before impairment
test).
Additionally IAS39, ‘Financial Instruments: recognition and measurement’, says that an entity must assess at each balance
sheet date whether a financial asset is impaired. In this case the receivable of $7 million is likely to be impaired as Race is
going into administration. The present value of the estimated future cash flows will be calculated. Normally cash receipts from
trade receivables will not be discounted but because the amounts are not likely to be received for a year then the anticipated
cash payment is 80% of ($5 million × 1/1·06), i.e. $3·8 million. Thus a provision for the impairment of the trade receivables
of $3·2 million should be made. The intangible asset of $3 million would be valueless as the contract has been terminated.
Glass’s Net Assets
The leased property continues to be accounted for as property, plant and equipment and the carrying amount will not be
adjusted. However, the remaining useful life of the property will be revised to reflect the shorter term. Thus the property will
be depreciated at $2 million per annum over the next two years. The change to the depreciation period is applied prospectively
not retrospectively. The lease liability must be assessed under IAS39 in order to determine whether it constitutes a
de-recognition of a financial liability. As the change is a modification of the lease and not an extinguishment, the lease liability
would not be derecognised. The lease liability will be adjusted for the one off payment of $1 million and re-measured to the
present value of the revised future cash flows. That is $0·6 million/1·07 + $0·6 million/(1·07 × 1·07) i.e. $1·1 million. The
adjustment to the lease liability would normally be recognised in profit or loss but in this case it will affect the net capital
contributed by Glass.
The termination cost of the contract cannot be treated as an intangible asset. It is similar to redundancy costs paid to terminate
a contract of employment. It represents compensation for the loss of future income for the agency. Therefore it must be
removed from the balance sheet of York. The recognition criteria for an intangible asset require that there should be probable
future economic benefits flowing to York and the cost can be measured reliably. The latter criterion is met but the first criterion
is not. The cost of gaining future customers is not linked to this compensation.
IAS18 ‘Revenue’ contains a concept of a ‘multiple element’ arrangement. This is a contract which contains two or more
elements which are in substance separate and are separately identifiable. In other words, the two elements can operate
independently from each other. In this case, the contract with the overseas company has two distinct elements. There is a
contract not to supply gas to any other customer in the country and there is a contract to sell gas at fair value to the overseas
company. The contract has not been fulfilled as yet and therefore the payment of $1·5 million should not be taken to profit
or loss in its entirety at the first opportunity. The non supply of gas to customers in that country occurs over the four year
period of the contract and therefore the payment should be recognised over that period. Therefore the amount should be
shown as deferred income and not as a deduction from intangible assets. The revenue on the sale of gas will be recognised
as normal according to IAS18.
There may be an issue over the value of the net assets being contributed. The net assets contributed by Glass amount to
$21·9 million whereas those contributed by Gow only total $13·8 million after taking into account any adjustments required
by IFRS. The joint venturers have equal shareholding in York but no formal written agreements, thus problems may arise ifGlass feels that the contributions to the joint venture are unequal.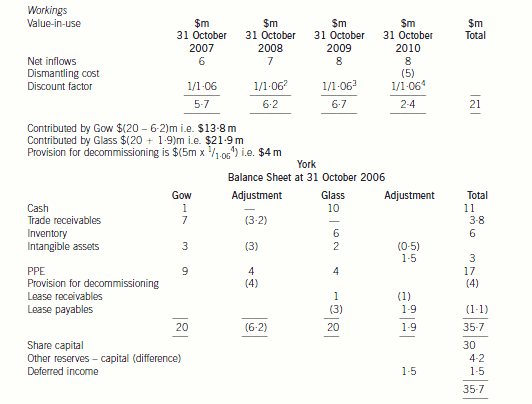
-
第2题:
5 Financial statements have seen an increasing move towards the use of fair values in accounting. Advocates of ‘fair
value accounting’ believe that fair value is the most relevant measure for financial reporting whilst others believe that
historical cost provides a more useful measure.
Issues have been raised over the reliability and measurement of fair values, and over the nature of the current level
of disclosure in financial statements in this area.
Required:
(a) Discuss the problems associated with the reliability and measurement of fair values and the nature of any
additional disclosures which may be required if fair value accounting is to be used exclusively in corporate
reporting. (13 marks)
正确答案:
(a) Reliability and Measurement
Fair value can be defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability. The fair value can
be thought of as an ‘exit price’. A fair value measurement assumes that the transaction to sell the asset or transfer the liability
occurs in the principal market for the asset or liability or, in the absence of a principal market, the most advantageous market
for the asset or liability which is the market in which the reporting entity would sell the asset or transfer the liability with the
price that maximises the amount that would be received or minimises the amount that would be paid. IAS39 ‘Financial
Instruments: Recognition and Measurement’ requires an entity to use the most advantageous active market in measuring the
fair value of a financial asset or liability when multiple markets exist whereas IAS41 ‘Agriculture’ requires an entity to use the
most relevant market. Thus there can be different approaches for estimating exit prices. Additionally valuation techniques and
current replacement cost could be used.
A hierarchy of fair value measurements would have to be developed in order to convey information about the nature of the
information used in creating the fair values. For example quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets would provide better
quality information than quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets which would provide better quality
information than prices which reflect the reporting entity’s own thinking about the assumptions that market participants would
use in pricing the asset or liability. Enron made extensive use of what it called ‘mark-to-market’ accounting which was based
on valuation techniques and estimates. IFRSs currently do not have a single hierarchy that applies to all fair value measures.
Instead individual standards indicate preferences for certain inputs and measures of fair value over others, but this guidance
is not consistent among all IFRSs.
Some companies, in order to effectively manage their businesses, have already developed models for determining fair values.
Businesses manage their operations by managing risks. A risk management process often requires measurement of fair values
of contracts, financial instruments, and risk positions.
If markets were liquid and transparent for all assets and liabilities, fair value accounting clearly would give reliable information
which is useful in the decision making process. However, because many assets and liabilities do not have an active market,
the inputs and methods for estimating their fair value are more subjective and, therefore, the valuations are less reliable. Fair
value estimates can vary greatly, depending on the valuation inputs and methodology used. Where management uses
significant judgment in selecting market inputs when market prices are not available, reliability will continue to be an issue.
Management can use significant judgment in the valuation process. Management bias, whether intentional or unintentional,
may result in inappropriate fair value measurements and consequently misstatements of earnings and equity capital. Without
reliable fair value estimates, the potential for misstatements in financial statements prepared using fair value measurements
will be even greater.
Consideration must be given to revenue recognition issues in a fair value system. It must be ensured that unearned revenue
is not recognised early as it recently was by certain high-tech companies.
As the variety and complexity of financial instruments increases, so does the need for independent verification of fair value
estimates. However, verification of valuations that are not based on observable market prices is very challenging. Users of
financial statements will need to place greater emphasis on understanding how assets and liabilities are measured and how
reliable these valuations are when making decisions based on them.
Disclosure
Fair values reflect point estimates and do not result in transparent financial statements. Additional disclosures are necessary
to bring meaning to these fair value estimates. These disclosures might include key drivers affecting valuations, fair-valuerange
estimates, and confidence levels. Another important disclosure consideration relates to changes in fair value amounts.
For example, changes in fair values on securities can arise from movements in interest rates, foreign-currency rates, and credit
quality, as well as purchases and sales from the portfolio. For users to understand fair value estimates, they must be given
adequate disclosures about what factors caused the changes in fair value. It could be argued that the costs involved in
determining fair values may exceed the benefits derived therefrom. When considering how fair value information should be
presented in the financial statements, it is important to consider what type of financial information investors want. There are
indications that some investors desire both fair value information and historical cost information. One of the issues affecting
the credibility of fair value disclosures currently is that a number of companies include ‘health warnings’ with their disclosures
indicating that the information is not used by management. This language may contribute to users believing that the fair value
disclosures lack credibility.
-
第3题:
(b) Prepare a consolidated statement of financial position of the Ribby Group at 31 May 2008 in accordance
with International Financial Reporting Standards. (35 marks)
正确答案:

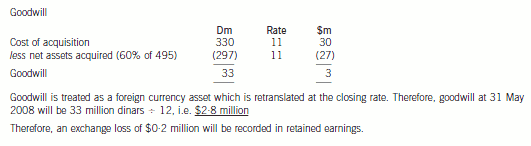
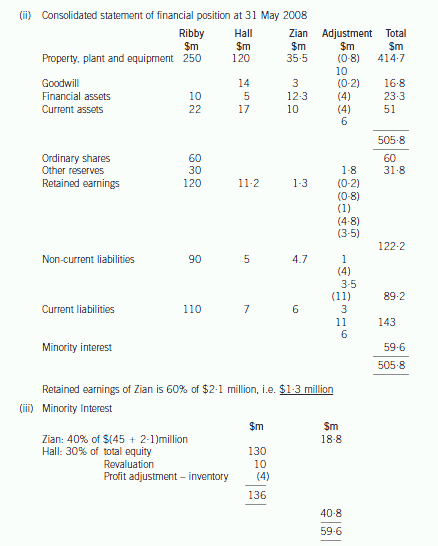

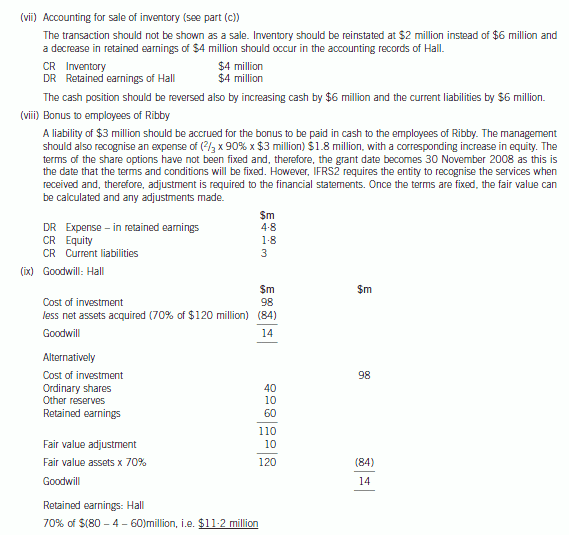


-
第4题:
(c) On 1 May 2007 Sirus acquired another company, Marne plc. The directors of Marne, who were the only
shareholders, were offered an increased profit share in the enlarged business for a period of two years after the
date of acquisition as an incentive to accept the purchase offer. After this period, normal remuneration levels will
be resumed. Sirus estimated that this would cost them $5 million at 30 April 2008, and a further $6 million at
30 April 2009. These amounts will be paid in cash shortly after the respective year ends. (5 marks)
Required:
Draft a report to the directors of Sirus which discusses the principles and nature of the accounting treatment of
the above elements under International Financial Reporting Standards in the financial statements for the year
ended 30 April 2008.
正确答案:
(c) Acquisition of Marne
All business combinations within the scope of IFRS 3 ‘Business Combinations’ must be accounted for using the purchase
method. (IFRS 3.14) The pooling of interests method is prohibited. Under IFRS 3, an acquirer must be identified for all
business combinations. (IFRS 3.17) Sirus will be identified as the acquirer of Marne and must measure the cost of a business
combination at the sum of the fair values, at the date of exchange, of assets given, liabilities incurred or assumed, in exchange
for control of Marne; plus any costs directly attributable to the combination. (IFRS 3.24) If the cost is subject to adjustment
contingent on future events, the acquirer includes the amount of that adjustment in the cost of the combination at the
acquisition date if the adjustment is probable and can be measured reliably. (IFRS 3.32) However, if the contingent payment
either is not probable or cannot be measured reliably, it is not measured as part of the initial cost of the business combination.
If that adjustment subsequently becomes probable and can be measured reliably, the additional consideration is treated as
an adjustment to the cost of the combination. (IAS 3.34) The issue with the increased profit share payable to the directors
of Marne is whether the payment constitutes remuneration or consideration for the business acquired. Because the directors
of Marne fall back to normal remuneration levels after the two year period, it appears that this additional payment will
constitute part of the purchase consideration with the resultant increase in goodwill. It seems as though these payments can
be measured reliably and therefore the cost of the acquisition should be increased by the net present value of $11 million at
1 May 2007 being $5 million discounted for 1 year and $6 million for 2 years. -
第5题:
Required:
Discuss the principles and practices which should be used in the financial year to 30 November 2008 to account
for:(b) the costs incurred in extending the network; (7 marks)
正确答案:
Costs incurred in extending network
The cost of an item of property, plant and equipment should be recognised when
(i) it is probable that future economic benefits associated with the item will flow to the entity, and
(ii) the cost of the item can be measured reliably (IAS16, ‘Property, plant and equipment’ (PPE))
It is necessary to assess the degree of certainty attaching to the flow of economic benefits and the basis of the evidence available
at the time of initial recognition. The cost incurred during the initial feasibility study ($250,000) should be expensed as incurred,
as the flow of economic benefits to Johan as a result of the study would have been uncertain.
IAS16 states that the cost of an item of PPE comprises amongst other costs, directly attributable costs of bringing the asset to the
location and condition necessary for it to be capable of operating in a manner intended by management (IAS16, para 16).
Examples of costs given in IAS16 are site preparation costs, and installation and assembly costs. The selection of the base station
site is critical for the optimal operation of the network and is part of the process of bringing the network assets to a working
condition. Thus the costs incurred by engaging a consultant ($50,000) to find an optimal site can be capitalised as it is part of
the cost of constructing the network and depreciated accordingly as planning permission has been obtained.
Under IAS17, ‘Leases’, a lease is defined as an agreement whereby the lessor conveys to the lessee, in return for a payment or
series of payments, the right to use an asset for an agreed period of time. A finance lease is a lease that transfers substantially all
the risks and rewards incidental to ownership of the leased asset to the lessee. An operating lease is a lease other than a finance
lease. In the case of the contract regarding the land, there is no ownership transfer and the term is not for the major part of the
asset’s life as it is land which has an indefinite economic life. Thus substantially all of the risks and rewards incidental to ownership
have not been transferred. The contract should be treated, therefore, as an operating lease. The payment of $300,000 should be
treated as a prepayment in the statement of financial position and charged to the income statement over the life of the contract on
the straight line basis. The monthly payments will be expensed and no value placed on the lease contract in the statement of
financial position -
第6题:
5 An enterprise has made a material change to an accounting policy in preparing its current financial statements.
Which of the following disclosures are required by IAS 8 Accounting policies, changes in accounting estimates
and errors in these financial statements?
1 The reasons for the change.
2 The amount of the consequent adjustment in the current period and in comparative information for prior periods.
3 An estimate of the effect of the change on future periods, where possible.
A 1 and 2 only
B 1 and 3 only
C 2 and 3 only
D All three items
正确答案:A
-
第7题:
(b) The Sarbanes-Oxley Act contains provisions for the attestation (verification) and reporting to shareholders of
internal controls over financial reporting.
Required:
Describe the typical contents of an external report on internal controls. (8 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Internal control statement
The United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) guidelines are to disclose in the annual report as follows:
A statement of management’s responsibility for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting
for the company. This will always include the nature and extent of involvement by the chairman and chief executive, but may
also specify the other members of the board involved in the internal controls over financial reporting. The purpose is for
shareholders to be clear about who is accountable for the controls.
A statement identifying the framework used by management to evaluate the effectiveness of this internal control. This will
usually involve a description of the key metrics, measurement methods (e.g. rates of compliance, fair value measures, etc)
and tolerances allowed within these. Within a rules-based environment, these are likely to be underpinned by law.
Management’s assessment of the effectiveness of this internal control as at the end of the company’s most recent fiscal year.
This may involve reporting on rates of compliance, failures, costs, resources committed and outputs (if measurable) achieved.
A statement that its auditor has issued an attestation report on management’s assessment. Any qualification to the attestation
should be reported in this statement.
Tutorial note: guidance from other corporate governance codes is also acceptable. -
第8题:
4 (a) The purpose of ISA 510 ‘Initial Engagements – Opening Balances’ is to establish standards and provide guidance
regarding opening balances when the financial statements are audited for the first time or when the financial
statements for the prior period were audited by another auditor.
Required:
Explain the auditor’s reporting responsibilities that are specific to initial engagements. (5 marks)
正确答案:
4 JOHNSTON CO
(a) Reporting responsibilities specific to initial engagements
For initial audit engagements, the auditor should obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence that:
■ the opening balances do not contain misstatements that materially affect the current period’s financial statements;
■ the prior period’s closing balances have been correctly brought forward to the current period (or, where appropriate, have
been restated); and
■ appropriate accounting policies are consistently applied or changes in accounting policies have been properly accounted
for (and adequately presented and disclosed).
If the auditor is unable to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence concerning opening balances there will be a limitation
on the scope of the audit. The auditor’s report should include:
■ a qualified (‘except for’) opinion;
■ a disclaimer of opinion; or
■ in those jurisdictions where it is permitted, an opinion which is:
– qualified (or disclaimed) regarding the results of operations (i.e. on the income statement); and
– unqualified regarding financial position (i.e. on the balance sheet).
If the effect of a misstatement in the opening balances is not properly accounted for and adequately presented and disclosed,
the auditor should express a qualified (‘except for’ disagreement) opinion or an adverse opinion, as appropriate.
If the current period’s accounting policies have not been consistently applied in relation to opening balances and if the change
has not been properly accounted for and adequately presented and disclosed, the auditor should similarly express
disagreement (‘except for’ or adverse opinion as appropriate).
However, if a modification regarding the prior period’s financial statements remains relevant and material to the current
period’s financial statements, the auditor should modify the current auditor’s report accordingly. -
第9题:
4 (a) The purpose of ISA 250 Consideration of Laws and Regulations in an Audit of Financial Statements is to
establish standards and provide guidance on the auditor’s responsibility to consider laws and regulations in an
audit of financial statements.
Explain the auditor’s responsibilities for reporting non-compliance that comes to the auditor’s attention
during the conduct of an audit. (5 marks)
正确答案:
4 CLEEVES CO
(a) Reporting non-compliance
Non-compliance refers to acts of omission or commission by the entity being audited, either intentional or unintentional, that
are contrary to the prevailing laws or regulations.
To management
Regarding non-compliance that comes to the auditor’s attention the auditor should, as soon as practicable, either:
■ communicate with those charged with governance; or
■ obtain audit evidence that they are appropriately informed.
However, the auditor need not do so for matters that are clearly inconsequential or trivial and may reach agreement1 in
advance on the nature of such matters to be communicated.
If in the auditor’s judgment the non-compliance is believed to be intentional and material, the auditor should communicate
the finding without delay.
If the auditor suspects that members of senior management are involved in non-compliance, the auditor should report the
matter to the next higher level of authority at the entity, if it exists (e.g. an audit committee or a supervisory board). Where
no higher authority exists, or if the auditor believes that the report may not be acted upon or is unsure as to the person to
whom to report, the auditor would consider seeking legal advice.
To the users of the auditor’s report on the financial statements
If the auditor concludes that the non-compliance has a material effect on the financial statements, and has not been properly
reflected in the financial statements, the auditor expresses a qualified (i.e. ‘except for disagreement’) or an adverse opinion.
If the auditor is precluded by the entity from obtaining sufficient appropriate audit evidence to evaluate whether or not noncompliance
that may be material to the financial statements has (or is likely to have) occurred, the auditor should express a
qualified opinion or a disclaimer of opinion on the financial statements on the basis of a limitation on the scope of the audit.
Tutorial note: For example, if management denies the auditor access to information from which he would be able to assess
whether or not illegal dumping had taken place (and, if so, the extent of it).
If the auditor is unable to determine whether non-compliance has occurred because of limitations imposed by circumstances
rather than by the entity, the auditor should consider the effect on the auditor’s report.
Tutorial note: For example, if new legal requirements have been announced as effective but the detailed regulations are not
yet published.
To regulatory and enforcement authorities
The auditor’s duty of confidentiality ordinarily precludes reporting non-compliance to a third party. However, in certain
circumstances, that duty of confidentiality is overridden by statute, law or by courts of law (e.g. in some countries the auditor
is required to report non-compliance by financial institutions to the supervisory authorities). The auditor may need to seek
legal advice in such circumstances, giving due consideration to the auditor’s responsibility to the public interest. -
第10题:
At the end of 2004, there were around 6,000 foreign printing companies in China, ______ up around 4 percent of national total.
A:made
B:to make
C:making
D:having made
正确答案:C -
第11题:
The two most common specialized fields of accounting in practice are().A.managerial accounting and financial accounting
B.managerial accounting and environmental accounting
C.forensic accounting and financial accounting
D.financial accounting and tax accounting systems
正确答案:A
-
第12题:
Software configuration management(SCM)is the task of tracking and controlling changes in the software. Configuration management practices include configuration identification,change control, ( ) and configuration audit.A.milestones marking
B.status reporting
C.stakeholder management
D.quality audit答案:B解析:软件配置管理(SCM)是一种跟踪和控制软件的变化的技术。配置管理包括配置标识、变更控制、状态报告和配置审计。 -
第13题:
5 International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRSs) are primarily designed for use by publicly listed companies and
in many countries the majority of companies using IFRSs are listed companies. In other countries IFRSs are used as
national Generally Accepted Accounting Practices (GAAP) for all companies including unlisted entities. It has been
argued that the same IFRSs should be used by all entities or alternatively a different body of standards should apply
to small and medium entities (SMEs).
Required:
(a) Discuss whether there is a need to develop a set of IFRSs specifically for SMEs. (7 marks)
正确答案:
5 (a) IFRSs were not designed specifically for listed companies. However, in many countries the main users of IFRS are listed
companies. Currently SMEs who adopt IFRS have to follow all the requirements and not all SMEs take exception to applying
IFRS because it gives their financial statements enhanced reliability, relevance and credibility, and results in fair presentation.
However, other SMEs will wish to comply with IFRS for consistency and comparability purposes within their own country and
internationally but wish to apply simplified or different standards relevant to SMEs on the grounds that some IFRS are
unnecessarily demanding and some of the information produced is not used by users of SME financial statements.
The objectives of general purpose financial statements are basically appropriate for SMEs and publicly listed companies alike.
Therefore there is an argument that there is a need for only one set of IFRS which could be used nationally and internationally.
However, some SMEs require different financial information than listed companies. For example expanded related party
disclosures may be useful as SMEs often raise capital from shareholders, directors and suppliers. Additionally directors often
offer personal assets as security for bank finance.
The cost burden of applying the full set of IFRS may not be justified on the basis of user needs. The purpose and usage of
the financial statements, and the nature of the accounting expertise available to the SME, will not be the same as for listed
companies. These circumstances themselves may provide justification for a separate set of IFRSs for SMEs. A problem which
might arise is that users become familiar with IFRS as opposed to local GAAP thus creating a two tier system which could
lead to local GAAP being seen as an inferior or even a superior set of accounting rules.
One course of action would be for GAAP for SMEs to be developed on a national basis with IFRS being focused on accounting
for listed company activities. The main issue here would be that the practices developed for SMEs may not be consistent and
may lack comparability across national boundaries. This may mean that where SMEs wish to list their shares on a capital
market, the transition to IFRSs may be difficult. It seems that national standards setters are strongly supportive of thedevelopment of IFRSs for SMEs. -
第14题:
4 The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) has begun a joint project to revisit its conceptual framework for
financial accounting and reporting. The goals of the project are to build on the existing frameworks and converge them
into a common framework.
Required:
(a) Discuss why there is a need to develop an agreed international conceptual framework and the extent to which
an agreed international conceptual framework can be used to resolve practical accounting issues.
(13 marks)
正确答案:
(a) The IASB wish their standards to be ‘principles-based’ and in order for this to be the case, the standards must be based on
fundamental concepts. These concepts need to constitute a framework which is sound, comprehensive and internally
consistent. Without agreement on a framework, standard setting is based upon the personal conceptual frameworks of the
individual standard setters which may change as the membership of the body changes and results in standards that are not
consistent with each other. Such a framework is designed not only to assist standard setters, but also preparers of financial
statements, auditors and users.
A common goal of the IASB is to converge their standards with national standard setters. The IASB will encounter difficulties
converging their standards if decisions are based on different frameworks. The IASB has been pursuing a number of projects
that are aimed at achieving short term convergence on certain issues with national standard setters as well as major projects
with them. Convergence will be difficult if there is no consistency in the underlying framework being used.
Frameworks differ in their authoritative status. The IASB’s Framework requires management to expressly consider the
Framework if no standard or interpretation specifically applies or deals with a similar and related issue. However, certain
frameworks have a lower standing. For example, entities are not required to consider the concepts embodied in certain
national frameworks in preparing financial statements. Thus the development of an agreed framework would eliminate
differences in the authoritative standing of conceptual frameworks and lead to greater consistency in financial statements
internationally.
The existing concepts within most frameworks are quite similar. However, these concepts need revising to reflect changes in
markets, business practices and the economic environment since the concepts were developed. The existing frameworks need
developing to reflect these changes and to fill gaps in the frameworks. For example, the IASB’s Framework does not contain
a definition of the reporting entity. An agreed international framework could deal with this problem, especially if priority was
given to the issues likely to give short-term standard setting benefits.
Many standard setting bodies attempted initially to resolve accounting and reporting problems by developing accounting
standards without an accepted theoretical frame. of reference. The result has been inconsistency in the development of
standards both nationally and internationally. The frameworks were developed when several of their current standards were
in existence. In the absence of an agreed conceptual framework the same theoretical issues are revisited on several occasions
by standard setters. The result is inconsistencies and incompatible concepts. Examples of this are substance over form. and
matching versus prudence. Some standard setters such as the IASB permit two methods of accounting for the same set of
circumstances. An example is the accounting for joint ventures where the equity method and proportionate consolidation are
allowed.
Additionally there have been differences in the way that standard setters have practically used the principles in the framework.
Some national standard setters have produced a large number of highly detailed accounting rules with less emphasis on
general principles. A robust framework might reduce the need for detailed rules although some companies operate in a
different legal and statutory context than other entities. It is important that a framework must result in standards that account
appropriately for actual business practice.
An agreed framework will not solve all accounting issues, nor will it obviate the need for judgement to be exercised in resolving
accounting issues. It can provide a framework within which those judgements can be made.
A framework provides standard setters with both a foundation for setting standards, and concepts to use as tools for resolving
accounting and reporting issues. A framework provides a basic reasoning on which to consider the merits of alternatives. It
does not provide all the answers, but narrows the range of alternatives to be considered by eliminating some that are
inconsistent with it. It, thereby, contributes to greater efficiency in the standard setting process by avoiding the necessity of
having to redebate fundamental issues and facilitates any debate about specific technical issues. A framework should also
reduce political pressures in making accounting judgements. The use of a framework reduces the influence of personal biases
in accounting decisions.
However, concepts statements are by their nature very general and theoretical in their wording, which leads to alternative
conclusions being drawn. Whilst individual standards should be consistent with the Framework, in the absence of a specific
standard, it does not follow that concepts will provide practical solutions. IAS8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting
Estimates and Errors’ sets out a hierarchy of authoritative guidance that should be considered in the absence of a standard.
In this case, management can use its judgement in developing and applying an accounting policy, albeit by considering the
IASB framework, but can also use accounting standards issued by other bodies. Thus an international framework may nottotally provide solutions to practical accounting problems. -
第15题:
(b) When a director retires, amounts become payable to the director as a form. of retirement benefit as an annuity.
These amounts are not based on salaries paid to the director under an employment contract. Sirus has
contractual or constructive obligations to make payments to former directors as at 30 April 2008 as follows:
(i) certain former directors are paid a fixed annual amount for a fixed term beginning on the first anniversary of
the director’s retirement. If the director dies, an amount representing the present value of the future payment
is paid to the director’s estate.
(ii) in the case of other former directors, they are paid a fixed annual amount which ceases on death.
The rights to the annuities are determined by the length of service of the former directors and are set out in the
former directors’ service contracts. (6 marks)
Required:
Draft a report to the directors of Sirus which discusses the principles and nature of the accounting treatment of
the above elements under International Financial Reporting Standards in the financial statements for the year
ended 30 April 2008.
正确答案:
(b) Directors’ retirement benefits
The directors’ retirement benefits are unfunded plans which may fall under IAS19 ‘Employee Benefits’.
Sirus should review its contractual or constructive obligation to make retirement benefit payments to its former directors at the
time when they leave the firm. The payments may create a financial liability under IAS32, or may give rise to a liability of
uncertain timing and amount which may fall within the scope of IAS37 ‘Provisions, contingent liabilities and contingent
assets’. Certain former directors are paid a fixed annuity for a fixed term which is payable annually, and on death, the present
value of future payments are paid to the director’s estate. An annuity meets the definition of a financial liability under IAS32,
if there is a contractual obligation to deliver cash or a financial asset. The latter form. of annuity falls within the scope of
IAS32/39. The present value of the annuity payments should be determined. The liability is recognised because the directors
have a contractual right to the annuity and the firm has no discretion in terms of withholding the payment. As the rights to
the annuities are earned over the period of the service of the directors, then the costs should have been recognised also over
the service period.
Where an annuity has a life contingent element and, therefore, embodies a mortality risk, it falls outside the scope of IAS39
because the annuity will meet the definition of an insurance contract which is scoped out of IAS39, along with employers’
rights and obligations under IAS19. Such annuities will, therefore, fall within the scope of IAS37 if a constructive obligation
exists. Sirus should assess the probability of the future cash outflow of the present obligation. Because there are a number of
similar obligations, IAS37 requires that the class of obligations as a whole should be considered (similar to a warranty
provision). A provision should be made for the best estimate of the costs of the annuity and this would include any liability
for post retirement payments to directors earned to date. The liability should be built up over the service period rather than
just when the director leaves. In practice the liability will be calculated on an actuarial basis consistent with the principles in
IAS19. The liability should be recalculated on an annual basis, as for any provision, to take account of changes in directors
and other factors. The liability will be discounted where the effect is material. -
第16题:
(d) Sirus raised a loan with a bank of $2 million on 1 May 2007. The market interest rate of 8% per annum is to
be paid annually in arrears and the principal is to be repaid in 10 years time. The terms of the loan allow Sirus
to redeem the loan after seven years by paying the full amount of the interest to be charged over the ten year
period, plus a penalty of $200,000 and the principal of $2 million. The effective interest rate of the repayment
option is 9·1%. The directors of Sirus are currently restructuring the funding of the company and are in initial
discussions with the bank about the possibility of repaying the loan within the next financial year. Sirus is
uncertain about the accounting treatment for the current loan agreement and whether the loan can be shown as
a current liability because of the discussions with the bank. (6 marks)
Appropriateness of the format and presentation of the report and quality of discussion (2 marks)
Required:
Draft a report to the directors of Sirus which discusses the principles and nature of the accounting treatment of
the above elements under International Financial Reporting Standards in the financial statements for the year
ended 30 April 2008.
正确答案:
(d) Repayment of the loan
If at the beginning of the loan agreement, it was expected that the repayment option would not be exercised, then the effective
interest rate would be 8% and at 30 April 2008, the loan would be stated at $2 million in the statement of financial position
with interest of $160,000 having been paid and accounted for. If, however, at 1 May 2007, the option was expected to be
exercised, then the effective interest rate would be 9·1% and at 30 April 2008, the cash interest paid would have been
$160,000 and the interest charged to the income statement would have been (9·1% x $2 million) $182,000, giving a
statement of financial position figure of $2,022,000 for the amount of the financial liability. However, IAS39 requires the
carrying amount of the financial instrument to be adjusted to reflect actual and revised estimated cash flows. Thus, even if
the option was not expected to be exercised at the outset but at a later date exercise became likely, then the carrying amount
would be revised so that it represented the expected future cash flows using the effective interest rate. As regards the
discussions with the bank over repayment in the next financial year, if the loan was shown as current, then the requirements
of IAS1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’ would not be met. Sirus has an unconditional right to defer settlement for longer
than twelve months and the liability is not due to be legally settled in 12 months. Sirus’s discussions should not be considered
when determining the loan’s classification.
It is hoped that the above report clarifies matters. -
第17题:
4 Whilst acknowledging the importance of high quality corporate reporting, the recommendations to improve it are
sometimes questioned on the basis that the marketplace for capital can determine the nature and quality of corporate
reporting. It could be argued that additional accounting and disclosure standards would only distort a market
mechanism that already works well and would add costs to the reporting mechanism, with no apparent benefit. It
could be said that accounting standards create costly, inefficient, and unnecessary regulation. It could be argued that
increased disclosure reduces risks and offers a degree of protection to users. However, increased disclosure has several
costs to the preparer of financial statements.
Required:
(a) Explain why accounting standards are needed to help the market mechanism work effectively for the benefit
of preparers and users of corporate reports. (9 marks)
正确答案:
(a) It could be argued that the marketplace already offers powerful incentives for high-quality reporting as it rewards such by
easing or restricting access to capital or raising or lowering the cost of borrowing capital depending on the quality of the entity’s
reports. However, accounting standards play an important role in helping the market mechanism work effectively. Accounting
standards are needed because they:
– Promote a common understanding of the nature of corporate performance and this facilitates any negotiations between
users and companies about the content of financial statements. For example, many loan agreements specify that a
company provide the lender with financial statements prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting
principles or International Financial Reporting Standards. Both the company and the lender understand the terms and
are comfortable that statements prepared according to those standards will meet certain information needs. Without
standards, the statements would be less useful to the lender, and the company and the lender would have to agree to
create some form. of acceptable standards which would be inefficient and less effective.
– Assist neutral and unbiased reporting. Companies may wish to portray their past performance and future prospects in
the most favourable light. Users are aware of this potential bias and are sceptical about the information they receive.
Standards build credibility and confidence in the capital marketplace to the benefit of both users and companies.
– Improve the comparability of information across companies and national boundaries. Without standards, there would be
little basis to compare one company with others across national boundaries which is a key feature of relevant
information.
– Create credibility in financial statements. Auditors verify that information is reported in accordance with standards and
this creates public confidence in financial statements
– Facilitate consistency of information by producing data in accordance with an agreed conceptual framework. A consistent
approach to the development and presentation of information assists users in accessing information in an efficient
manner and facilitates decision-making. -
第18题:
19 Which of the following statements about intangible assets in company financial statements are correct according
to international accounting standards?
1 Internally generated goodwill should not be capitalised.
2 Purchased goodwill should normally be amortised through the income statement.
3 Development expenditure must be capitalised if certain conditions are met.
A 1 and 3 only
B 1 and 2 only
C 2 and 3 only
D All three statements are correct
正确答案:A
-
第19题:
(c) Construct the arguments in favour of Professor Leroi’s remark that external reporting requirements on internal
controls were ‘too ambitious’ for small and medium companies. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(c) The external reporting requirements (from the Sarbanes-Oxley section 404) being ‘too ambitious’ for small and medium
companies
There are several arguments to support Professor Leroi’s remark.
Fewer spare resources to carry out internal control. SMEs tend to operate with lower levels of spare resource than larger
businesses and conducting internal reviews would be more of a challenge for them.
The extra attestation fee (over and above normal audit fee) for the attestation of the internal control report could be a constraint
for many SMEs.
Lack of expertise from within existing employees (to internally audit/police as well as carry out internal activities) would be a
likely constraint.
SMEs will have fewer activities and less complexity, hence less need for shareholders to require the information (less to go
wrong). -
第20题:
6 The explosive growth of investing and raising capital in the global markets has put new emphasis on the development
of international accounting, auditing and ethical standards. The International Federation of Accountants (IFAC) has
been at the forefront of the development of the worldwide accountancy profession through its activities in ethics,
auditing and education.
Required:
Explain the developments in each of the following areas and indicate how they affect Chartered Certified
Accountants:
(a) IFAC’s ‘Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants’; (5 marks)
正确答案:
6 DEVELOPMENTS AND CERTIFIED CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS
Tutorial note: The answer which follows is indicative of the range of points which might be made. Other relevant material will
be given suitable credit.
(a) IFAC’s ‘Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants’
Since its issue in 1996, IFAC’s ‘Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants’ (‘The Code’) has undergone several revisions
(1996, 1998, 2001, 2004 and 2005). IFAC holds the view that due to national differences (of culture, language, legal and
social systems) the task of preparing detailed ethical requirements is primarily that of the member bodies in each country
concerned (and that they also have the responsibility to implement and enforce such requirements).
In recognizing the responsibilities of the accountancy profession, IFAC considers its own role to be in providing guidance and
promoting harmonization. IFAC has established ‘The Code’ to provide a basis on which the ethical requirements for
professional accountants in each country should be founded.
IFAC’s conceptual approach is principles-based. It provides a route to convergence that emphasises the profession’s integrity.
This approach may be summarised as:
■ identifying and evaluating circumstances and relationships that create threats (e.g. to independence); and
■ taking appropriate action to:
– eliminate these threats; or
– reduce them to an acceptable level by the application of safeguards.
If no safeguards are available to reduce a threat to an acceptable level an assurance engagement must be refused or
discontinued.
This approach was first introduced to Section 8 of The Code, on independence, and is applicable to assurance engagements
when the assurance report is dated on or after 31 December 2004.
Further to the cases of Enron, Worldcom and Parmalat, IFAC issued a revised Code in July 2005 that applies to all professional
accountants, whether in public practice, business, industry or government2.
A member body of IFAC may not apply less stringent standards than those stated in the Code. The Code is effective from
30 June 2006.
Practicing accountants and members in business must maintain the high standards of professional ethics that are expected
by their professional bodies (such as ACCA). These developments codify current best practice in the wake of the
aforementioned recent corporate scandals.
The developments in The Code have wider application in that it:
■ applies to all assurance services (not just audit);
■ considers the standpoints of the firm and of the assurance team.
Since ACCA is a member-body of IFAC the elevation of The Code to a standard will affect all Chartered Certified Accountants.
. -
第21题:
6 Certain practices have developed that threaten to damage the integrity and objectivity of professional accountants and
the reputation of the accounting profession.
Required:
Explain the following practices and associated ethical risks and discuss whether current ethical guidance is
sufficient:
(a) ‘lowballing’; (5 marks)
正确答案:
6 CERTAIN PRACTICES
Tutorial note: The answer which follows is indicative of the range of points which might be made. Other relevant material will
be given suitable credit.
(a) ‘Lowballing’
Explanation of term
‘Lowballing’ is the ‘loss-leading’ practice in which auditors compete for clients by reducing their fees for statutory audits.
Lower audit fees are then compensated by the auditor carrying out more lucrative non-audit work (e.g. consultancy and tax
advice). Audits may even be offered for free.
Such ‘predatory pricing’ may undercut an incumbent auditor to secure an appointment into which higher price consultancy
services may be sold.
Ethical risks
There is a risk of incompetence if the non-audit work does not materialise and the lowballing firm comes under pressure to
cut corners or resort to irregular practices (e.g. the falsification of audit working papers) in order to ‘keep within budget’.
However, a lack of audit quality may only be discovered if the situation arises that the company collapses and the auditors
are charged with negligence.
If, rather than comprise the quality of the audit, an audit firm substantially increases audit fees, a fee dispute could arise. In
this case the client might refuse to pay the higher fee. It could be difficult then for the firm to take the matter to arbitration
if the client was misled. Thus an advocacy threat may arise.
Financial dependence is a direct incentive that threatens independence. A self-interest threat therefore arises when, having
secured the audit, the audit firm needs the client to retain its services in order to recoup any losses initially incurred.
The provision of many other services gives rise to a self-review threat (as well as a self-interest threat).
Sufficiency of current ethical guidance
In current ethical guidance, the fact that an accountancy firm quotes a lower fee than other tendering firms is not improper,
providing that the prospective client is not misled about:
– the precise range of services that the quoted fee is intended to cover; and
– the likely level of fees for any other work undertaken.
This is clearly insufficient to prevent the practice of lowballing.
Legal prohibitions on the provision of many non-audit services (e.g. bookkeeping, financial information systems design and
implementation, valuation services, actuarial services, internal audit (outsourced), human resource services for executive
positions, investment and legal services) should make lowballing a riskier pricing strategy. This may curb the tendency to
lowball.
Lowballing could be eliminated if, for example, auditors were required to act ‘exclusively as auditors’. Although regulatory
environments have moved towards this there is not a total prohibition on non-audit services. -
第22题:
听力原文:M: The primary objective of financial reporting is to provide information useful for making investment and lending decisions.
W: The information must be relevant, reliable, and comparable.
Q: What is the primary objective of financial reporting?
(15)
A.To make investment.
B.To record data.
C.To provide useful information.
D.To understand some basic accounting principles.
正确答案:C
解析:根据男士的说法,财务报告的作用在于为投资决策和筹资决策提供有用的信息。 -
第23题:
Change management would typically be composed of the raising and recording of changes, assessing the impact, cost, benefit and risk of proposed changes,developing business justification and obtaining approval, managing and coordinating change implementation, monitoring and reporting on implementation, reviewing and closing ().
A. change reason
B. change model
C. remediation plan
D. change requests
答案:D解析:
