9 Which of the following items must be disclosed in a company’s published financial statements (including notes)if material, according to IAS1 Presentation of financial statements?1 Finance costs.2 Staff costs.3 Depreciation and amortisation expense.4 Mov
题目
9 Which of the following items must be disclosed in a company’s published financial statements (including notes)
if material, according to IAS1 Presentation of financial statements?
1 Finance costs.
2 Staff costs.
3 Depreciation and amortisation expense.
4 Movements on share capital.
A 1 and 3 only
B 1, 2 and 4 only
C 2, 3 and 4 only
D All four items
相似考题
更多“9 Which of the following items must be disclosed in a company’s published financial statements (including notes)if material, according to IAS1 Presentation of financial statements?1 Finance costs.2 Staff costs.3 Depreciation and amortisation expense.4 Mov”相关问题
-
第1题:
(iv) Tyre recently undertook a sales campaign whereby customers can obtain free car accessories, by presenting a
coupon, which has been included in an advertisement in a national newspaper, on the purchase of a vehicle.
The offer is valid for a limited time period from 1 January 2006 until 31 July 2006. The management are unsure
as to how to treat this offer in the financial statements for the year ended 31 May 2006.
(5 marks)
Required:
Advise the directors of Tyre on how to treat the above items in the financial statements for the year ended
31 May 2006.
(The mark allocation is shown against each of the above items)
正确答案:
(iv) Car accessories
An obligation should not be recognised for the coupons and no provision created under IAS37 ‘Provisions, Contingent
Liabilities and Contingent Assets’. A provision should only be recognised where there is an obligating event. There has to be
a present obligation (legal or constructive), the probability of an outflow of resources and the ability to make a reliable estimate
of the amount of the obligation. These conditions do not seem to have been met. Until the vehicle is purchased the
accessories cannot be obtained. That is the point at which the present obligation arises, the outflow of resources occurs and
an estimate of the amount of the obligation can be made. When the car is purchased, the accessories become part of the
cost of the sale. The revenue recognised will be the amount received from the customer (the sales price). The revenue will
not be grossed up to include the value of the accessories. -
第2题:
4 (a) Router, a public limited company operates in the entertainment industry. It recently agreed with a television
company to make a film which will be broadcast on the television company’s network. The fee agreed for the
film was $5 million with a further $100,000 to be paid every time the film is shown on the television company’s
channels. It is hoped that it will be shown on four occasions. The film was completed at a cost of $4 million and
delivered to the television company on 1 April 2007. The television company paid the fee of $5 million on
30 April 2007 but indicated that the film needed substantial editing before they were prepared to broadcast it,
the costs of which would be deducted from any future payments to Router. The directors of Router wish to
recognise the anticipated future income of $400,000 in the financial statements for the year ended 31 May
2007. (5 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above items should be dealt with in the group financial statements of Router for the year ended
31 May 2007.
正确答案:
(a) Under IAS18 ‘Revenue’, revenue on a service contract is recognised when the outcome of the transaction can be measured
reliably. For revenue arising from the rendering of services, provided that all of the following criteria are met, revenue should
be recognised by reference to the stage of completion of the transaction at the balance sheet date (the percentage-ofcompletion
method) (IAS18 para 20):
(a) the amount of revenue can be measured reliably;
(b) it is probable that the economic benefits will flow to the seller;
(c) the stage of completion at the balance sheet date can be measured reliably; and
(d) the costs incurred, or to be incurred, in respect of the transaction can be measured reliably.
When the above criteria are not met, revenue arising from the rendering of services should be recognised only to the extent
of the expenses recognised that are recoverable. Because the only revenue which can be measured reliably is the fee for
making the film ($5 million), this should therefore be recognised as revenue in the year to 31 May 2007 and matched against
the cost of the film of $4 million. Only when the television company shows the film should any further amounts of $100,000
be recognised as there is an outstanding ‘performance’ condition in the form. of the editing that needs to take place before the
television company will broadcast the film. The costs of the film should not be carried forward and matched against
anticipated future income unless they can be deemed to be an intangible asset under IAS 38 ‘Intangible Assets’. Additionally,
when assessing revenue to be recognised in future years, the costs of the editing and Router’s liability for these costs should
be assessed.
-
第3题:
19 Which of the following statements about intangible assets in company financial statements are correct according
to international accounting standards?
1 Internally generated goodwill should not be capitalised.
2 Purchased goodwill should normally be amortised through the income statement.
3 Development expenditure must be capitalised if certain conditions are met.
A 1 and 3 only
B 1 and 2 only
C 2 and 3 only
D All three statements are correct
正确答案:A
-
第4题:
5 The directors of Quapaw, a limited liability company, are reviewing the company’s draft financial statements for the
year ended 31 December 2004.
The following material matters are under discussion:
(a) During the year the company has begun selling a product with a one-year warranty under which manufacturing
defects are remedied without charge. Some claims have already arisen under the warranty. (2 marks)
Required:
Advise the directors on the correct treatment of these matters, stating the relevant accounting standard which
justifies your answer in each case.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three matters
正确答案:
(a) The correct treatment is to provide for the best estimate of the costs likely to be incurred under the warranty, as required by
IAS37 Provisions, contingent liabilities and contingent assets. -
第5题:
The following information is relevant for questions 9 and 10
A company’s draft financial statements for 2005 showed a profit of $630,000. However, the trial balance did not agree,
and a suspense account appeared in the company’s draft balance sheet.
Subsequent checking revealed the following errors:
(1) The cost of an item of plant $48,000 had been entered in the cash book and in the plant account as $4,800.
Depreciation at the rate of 10% per year ($480) had been charged.
(2) Bank charges of $440 appeared in the bank statement in December 2005 but had not been entered in the
company’s records.
(3) One of the directors of the company paid $800 due to a supplier in the company’s payables ledger by a personal
cheque. The bookkeeper recorded a debit in the supplier’s ledger account but did not complete the double entry
for the transaction. (The company does not maintain a payables ledger control account).
(4) The payments side of the cash book had been understated by $10,000.
9 Which of the above items would require an entry to the suspense account in correcting them?
A All four items
B 3 and 4 only
C 2 and 3 only
D 1, 2 and 4 only
正确答案:B
-
第6题:
21 Which of the following items must be disclosed in a company’s published financial statements?
1 Authorised share capital
2 Movements in reserves
3 Finance costs
4 Movements in non-current assets
A 1, 2 and 3 only
B 1, 2 and 4 only
C 2, 3 and 4 only
D All four items
正确答案:D
-
第7题:
(b) Seymour offers health-related information services through a wholly-owned subsidiary, Aragon Co. Goodwill of
$1·8 million recognised on the purchase of Aragon in October 2004 is not amortised but included at cost in the
consolidated balance sheet. At 30 September 2006 Seymour’s investment in Aragon is shown at cost,
$4·5 million, in its separate financial statements.
Aragon’s draft financial statements for the year ended 30 September 2006 show a loss before taxation of
$0·6 million (2005 – $0·5 million loss) and total assets of $4·9 million (2005 – $5·7 million). The notes to
Aragon’s financial statements disclose that they have been prepared on a going concern basis that assumes that
Seymour will continue to provide financial support. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Seymour Co for the year ended
30 September 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
(b) Goodwill
(i) Matters
■ Cost of goodwill, $1·8 million, represents 3·4% consolidated total assets and is therefore material.
Tutorial note: Any assessments of materiality of goodwill against amounts in Aragon’s financial statements are
meaningless since goodwill only exists in the consolidated financial statements of Seymour.
■ It is correct that the goodwill is not being amortised (IFRS 3 Business Combinations). However, it should be tested
at least annually for impairment, by management.
■ Aragon has incurred losses amounting to $1·1 million since it was acquired (two years ago). The write-off of this
amount against goodwill in the consolidated financial statements would be material (being 61% cost of goodwill,
8·3% PBT and 2·1% total assets).
■ The cost of the investment ($4·5 million) in Seymour’s separate financial statements will also be material and
should be tested for impairment.
■ The fair value of net assets acquired was only $2·7 million ($4·5 million less $1·8 million). Therefore the fair
value less costs to sell of Aragon on other than a going concern basis will be less than the carrying amount of the
investment (i.e. the investment is impaired by at least the amount of goodwill recognised on acquisition).
■ In assessing recoverable amount, value in use (rather than fair value less costs to sell) is only relevant if the going
concern assumption is appropriate for Aragon.
■ Supporting Aragon financially may result in Seymour being exposed to actual and/or contingent liabilities that
should be provided for/disclosed in Seymour’s financial statements in accordance with IAS 37 Provisions,
Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Carrying values of cost of investment and goodwill arising on acquisition to prior year audit working papers and
financial statements.
■ A copy of Aragon’s draft financial statements for the year ended 30 September 2006 showing loss for year.
■ Management’s impairment test of Seymour’s investment in Aragon and of the goodwill arising on consolidation at
30 September 2006. That is a comparison of the present value of the future cash flows expected to be generated
by Aragon (a cash-generating unit) compared with the cost of the investment (in Seymour’s separate financial
statements).
■ Results of any impairment tests on Aragon’s assets extracted from Aragon’s working paper files.
■ Analytical procedures on future cash flows to confirm their reasonableness (e.g. by comparison with cash flows for
the last two years).
■ Bank report for audit purposes for any guarantees supporting Aragon’s loan facilities.
■ A copy of Seymour’s ‘comfort letter’ confirming continuing financial support of Aragon for the foreseeable future. -
第8题:
5 You are the audit manager for three clients of Bertie & Co, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants. The financial
year end for each client is 30 September 2007.
You are reviewing the audit senior’s proposed audit reports for two clients, Alpha Co and Deema Co.
Alpha Co, a listed company, permanently closed several factories in May 2007, with all costs of closure finalised and
paid in August 2007. The factories all produced the same item, which contributed 10% of Alpha Co’s total revenue
for the year ended 30 September 2007 (2006 – 23%). The closure has been discussed accurately and fully in the
chairman’s statement and Directors’ Report. However, the closure is not mentioned in the notes to the financial
statements, nor separately disclosed on the financial statements.
The audit senior has proposed an unmodified audit opinion for Alpha Co as the matter has been fully addressed in
the chairman’s statement and Directors’ Report.
In October 2007 a legal claim was filed against Deema Co, a retailer of toys. The claim is from a customer who slipped
on a greasy step outside one of the retail outlets. The matter has been fully disclosed as a material contingent liability
in the notes to the financial statements, and audit working papers provide sufficient evidence that no provision is
necessary as Deema Co’s lawyers have stated in writing that the likelihood of the claim succeeding is only possible.
The amount of the claim is fixed and is adequately covered by cash resources.
The audit senior proposes that the audit opinion for Deema Co should not be qualified, but that an emphasis of matter
paragraph should be included after the audit opinion to highlight the situation.
Hugh Co was incorporated in October 2006, using a bank loan for finance. Revenue for the first year of trading is
$750,000, and there are hopes of rapid growth in the next few years. The business retails luxury hand made wooden
toys, currently in a single retail outlet. The two directors (who also own all of the shares in Hugh Co) are aware that
due to the small size of the company, the financial statements do not have to be subject to annual external audit, but
they are unsure whether there would be any benefit in a voluntary audit of the first year financial statements. The
directors are also aware that a review of the financial statements could be performed as an alternative to a full audit.
Hugh Co currently employs a part-time, part-qualified accountant, Monty Parkes, who has prepared a year end
balance sheet and income statement, and who produces summary management accounts every three months.
Required:
(a) Evaluate whether the audit senior’s proposed audit report is appropriate, and where you disagree with the
proposed report, recommend the amendment necessary to the audit report of:
(i) Alpha Co; (6 marks)
正确答案:
5 BERTIE & CO
(a) (i) Alpha Co
The factory closures constitute a discontinued operation per IFRS 5 Non-Current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued
Operations, due to the discontinuance of a separate major component of the business. It is a major component due to
the 10% contribution to revenue in the year to 30 September 2007 and 23% contribution in 2006. It is a separate
business component of the company due to the factories having made only one item, indicating a separate income
generating unit.
Under IFRS 5 there must be separate disclosure on the face of the income statement of the post tax results of the
discontinued operation, and of any profit or loss resulting from the closures. The revenue and costs of the discontinued
operation should be separately disclosed either on the face of the income statement or in the notes to the financial
statements. Cash flows relating to the discontinued operation should also be separately disclosed per IAS 7 Cash Flow
Statements.
In addition, as Alpha Co is a listed company, IFRS 8 Operating Segments requires separate segmental disclosure of
discontinued operations.
Failure to disclose the above information in the financial statements is a material breach of International Accounting
Standards. The audit opinion should therefore be qualified on the grounds of disagreement on disclosure (IFRS 5,
IAS 7 and IFRS 8). The matter is material, but not pervasive, and therefore an ‘except for’ opinion should be issued.
The opinion paragraph should clearly state the reason for the disagreement, and an indication of the financial
significance of the matter.
The audit opinion relates only to the financial statements which have been audited, and the contents of the other
information (chairman’s statement and Directors’ Report) are irrelevant when deciding if the financial statements show
a true and fair view, or are fairly presented.
Tutorial note: there is no indication in the question scenario that Alpha Co is in financial or operational difficulty
therefore no marks are awarded for irrelevant discussion of going concern issues and the resultant impact on the audit
opinion. -
第9题:
The finance director of Blod Co, Uma Thorton, has requested that your firm type the financial statements in the form
to be presented to shareholders at the forthcoming company general meeting. Uma has also commented that the
previous auditors did not use a liability disclaimer in their audit report, and would like more information about the use
of liability disclaimer paragraphs.
Required:
(b) Discuss the ethical issues raised by the request for your firm to type the financial statements of Blod Co.
(3 marks)
正确答案:
(b) It is not uncommon for audit firms to word process and typeset the financial statements of their clients, especially where the
client is a relatively small entity, which may lack the resources and skills to perform. this task. It is not prohibited by ethical
standards.
However, there could be a perceived threat to independence, with risk magnified in the case of Blod Co, which is a listed
company. The auditors could be perceived to be involved with the preparation of the financial statements of a listed client
company, which is prohibited by ethical standards. IFAC’s Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants states that for a listed
client, the audit firm should not be involved with the preparation of financial statements, which would create a self-review
threat so severe that safeguards could not reduce the threat to an acceptable level. Although the typing of financial statements
itself is not prohibited by ethical guidance, the risk is that providing such a service could be perceived to be an element of
the preparation of the financial statements.
It is possible that during the process of typing the financial statements, decisions and judgments would be made. This could
be perceived as making management decisions in relation to the financial statements, a clear breach of independence.
Therefore to eliminate any risk exposure, the prudent decision would be not to type the financial statements, ensuring that
Blod Co appreciates the ethical problems that this would cause.
Tutorial note: This is an area not specifically covered by ethical guides, where different audit firms may have different views
on whether it is acceptable to provide a typing service for the financial statements of their clients. Credit will be awarded for
sensible discussion of the issues raised bearing in mind other options for the audit firm, for example, it could be argued that
it is acceptable to offer the typing service provided that it is performed by people independent of the audit team, and that
the matter has been discussed with the audit committee/those charged with governance -
第10题:
One of your audit clients is Tye Co a company providing petrol, aviation fuel and similar oil based products to the government of the country it is based in. Although the company is not listed on any stock exchange, it does follow best practice regarding corporate governance regulations. The audit work for this year is complete, apart from the matter referred to below.
As part of Tye Co’s service contract with the government, it is required to hold an emergency inventory reserve of 6,000 barrels of aviation fuel. The inventory is to be used if the supply of aviation fuel is interrupted due to unforeseen events such as natural disaster or terrorist activity.
This fuel has in the past been valued at its cost price of $15 a barrel. The current value of aviation fuel is $120 a barrel. Although the audit work is complete, as noted above, the directors of Tye Co have now decided to show the ‘real’ value of this closing inventory in the financial statements by valuing closing inventory of fuel at market value, which does not comply with relevant accounting standards. The draft financial statements of Tye Co currently show a profit of approximately $500,000 with net assets of $170 million.
Required:
(a) List the audit procedures and actions that you should now take in respect of the above matter. (6 marks)
(b) For the purposes of this section assume from part (a) that the directors have agreed to value inventory at
$15/barrel.
Having investigated the matter in part (a) above, the directors present you with an amended set of financial
statements showing the emergency reserve stated not at 6,000 barrels, but reported as 60,000 barrels. The final financial statements now show a profit following the inclusion of another 54,000 barrels of oil in inventory. When queried about the change from 6,000 to 60,000 barrels of inventory, the finance director stated that this change was made to meet expected amendments to emergency reserve requirements to be published in about six months time. The inventory will be purchased this year, and no liability will be shown in the financial statements for this future purchase. The finance director also pointed out that part of Tye Co’s contract with the government requires Tye Co to disclose an annual profit and that a review of bank loans is due in three months. Finally the finance director stated that if your audit firm qualifies the financial statements in respect of the increase in inventory, they will not be recommended for re-appointment at the annual general meeting. The finance director refuses to amend the financial statements to remove this ‘fictitious’ inventory.
Required:
(i) State the external auditor’s responsibilities regarding the detection of fraud; (4 marks)
(ii) Discuss to which groups the auditors of Tye Co could report the ‘fictitious’ aviation fuel inventory;
(6 marks)
(iii) Discuss the safeguards that the auditors of Tye Co can use in an attempt to overcome the intimidation
threat from the directors of Tye Co. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(a)Valuationofaviationinventory–ReviewGAAPtoensurethattherearenoexceptionsforaviationfuelorinventoryheldforemergencypurposeswhichwouldsuggestamarketvaluationshouldbeused.–Calculatethedifferenceinvaluation.Theerrorininventoryvaluationis$105*6,000barrelsor$630k,whichisamaterialamountcomparedtoprofit.–Reviewprioryearworkingpaperstodeterminewhetherasimilarsituationoccurredlastyearandascertaintheoutcomeatthatstage.–Discussthematterwiththedirectorstoobtainreasonswhytheybelievethatmarketvalueshouldbeusedfortheinventorythisyear.–Warnthedirectorsthatinyouropinion,aviationfuelshouldbevaluedatthelowerofcostornetrealisablevalue(thatis$15/barrel)andthatusingmarketvaluewillresultinamodificationtotheauditreport.–Ifthedirectorsnowamendthefinancialstatementstoshowinventoryvaluedatcost,thenconsidermentioningtheissueintheweaknessletteranddonotmodifytheauditreportinrespectofthismatter.–Ifthedirectorswillnotamendthefinancialstatements,quantifytheeffectofthedisagreementinthevaluationmethod–thesumof$630,000ismaterialtothefinancialstatementsasTyeCo’sincomestatementfigureisdecreasedfromasmalllosstoalossof$130,000althoughnetassetsdecreasebyonlyabout0·3%.–ObtainamanagementrepresentationletterfromthedirectorsofTyeCoconfirmingthatmarketvalueistobeusedfortheemergencyinventoryofaviationfuel.–Ifthedirectorswillnotamendthefinancialstatements,drafttherelevantsectionsoftheauditreport,showingaqualificationonthegroundsofdisagreementwiththeaccountingpolicyforvaluationofinventory.(b)(i)ExternalauditorresponsibilitiesregardingdetectionoffraudOverallresponsibilityofauditorTheexternalauditorisprimarilyresponsiblefortheauditopiniononthefinancialstatementsfollowingtheinternationalauditingstandards(ISAs).ISA240(Redrafted)TheAuditor’sResponsibilitiesRelatingtoFraudinanAuditofFinancialStatementsisrelevanttoauditworkregardingfraud.Themainfocusofauditworkisthereforetoensurethatthefinancialstatementsshowatrueandfairview.Thedetectionoffraudisthereforenotthemainfocusoftheexternalauditor’swork.Anauditorisresponsibleforobtainingreasonableassurancethatthefinancialstatementsasawholearefreefrommaterialmisstatement,whethercausedbyfraudorerror.Theauditorisresponsibleformaintaininganattitudeofprofessionalscepticismthroughouttheaudit,consideringthepotentialformanagementoverrideofcontrolsandrecognisingthefactthatauditproceduresthatareeffectivefordetectingerrormaynotbeeffectivefordetectingfraud.MaterialityISA240statesthattheauditorshouldreduceauditrisktoanacceptablylowlevel.Therefore,inreachingtheauditopinionandperformingauditwork,theexternalauditortakesintoaccounttheconceptofmateriality.Inotherwords,theexternalauditorisnotresponsibleforcheckingallthetransactions.Auditproceduresareplannedtohaveareasonablelikelihoodofidentifyingmaterialfraud.DiscussionamongtheauditteamAdiscussionisrequiredamongtheengagementteamplacingparticularemphasisonhowandwheretheentity’sfinancialstatementsmaybesusceptibletomaterialmisstatementduetofaud,includinghowfraudmightoccur.IdentificationoffraudInsituationswheretheexternalauditordoesdetectfraud,thentheauditorwillneedtoconsidertheimplicationsfortheentireaudit.Inotherwords,theexternalauditorhasaresponsibilitytoextendtestingintootherareasbecausetheriskofprovidinganincorrectauditopinionwillhaveincreased.(ii)GroupstoreportfraudtoReporttoauditcommitteeDisclosethesituationtotheauditcommitteeastheyarechargedwithmaintainingahighstandardofgovernanceinthecompany.Thecommitteeshouldbeabletodiscussthesituationwiththedirectorsandrecommendthattheytakeappropriateactione.g.amendthefinancialstatements.ReporttogovernmentAsTyeCoisactingunderagovernmentcontract,andtheover-statementofinventorywillmeanTyeCobreachesthatcontract(thereportedprofitbecomingaloss),thentheauditormayhavetoreportthesituationdirectlytothegovernment.TheauditorofTyeConeedstoreviewthecontracttoconfirmthereportingrequiredunderthatcontract.ReporttomembersIfthefinancialstatementsdonotshowatrueandfairviewthentheauditorneedstoreportthisfacttothemembersofTyeCo.Theauditreportwillbequalifiedwithanexceptfororadverseopinion(dependingonmateriality)andinformationconcerningthereasonforthedisagreementgiven.Inthiscasetheauditorislikelytostatefactuallytheproblemofinventoryquantitiesbeingincorrect,ratherthanstatingorimplyingthatthedirectorsareinvolvedinfraud.ReporttoprofessionalbodyIftheauditorisuncertainastothecorrectcourseofaction,advicemaybeobtainedfromtheauditor’sprofessionalbody.Dependingontheadvicereceived,theauditormaysimplyreporttothemembersintheauditreport,althoughresignationandtheconveningofageneralmeetingisanotherreportingoption.(iii)Intimidationthreat–safeguardsInresponsetotheimpliedthreatofdismissaliftheauditreportismodifiedregardingthepotentialfraud/error,thefollowingsafeguardsareavailabletotheauditor.DiscusswithauditcommitteeThesituationcanbediscussedwiththeauditcommittee.Astheauditcommitteeshouldcomprisenon-executivedirectors,theywillbeabletodiscussthesituationwiththefinancedirectorandpointoutclearlytheauditor’sopinion.Theycanalsoremindthedirectorsasawholethattheappointmentoftheauditorrestswiththemembersontherecommendationoftheauditcommittee.Iftherecommendationoftheauditcommitteeisrejectedbytheboard,goodcorporategovernancerequiresdisclosureofthereasonforrejection.ObtainsecondpartnerreviewTheengagementpartnercanaskasecondpartnertoreviewtheworkingpapersandotherevidencerelatingtotheissueofpossiblefraud.Whilethisactiondoesnotresolvetheissue,itdoesprovideadditionalassurancethatthefindingsandactionsoftheengagementpartnerarevalid.ResignationIfthematterisserious,thentheauditorcanconsiderresignationratherthannotbeingre-appointed.Resignationhastheadditionalsafeguardthattheauditorcannormallyrequirethedirectorstoconveneageneralmeetingtoconsiderthecircumstancesoftheresignation. -
第11题:
单选题Which of the following statements is NOT true according to the passage?ANatural disasters can account for disappearance of languages.
BThe acceleration of language death didn’t start until 200 years ago.
CThe study is conducted with the financial support of UNESCO.
DThe language of Ainu was long neglected before the late l980s.
正确答案: C解析:
事实细节的找寻和判断。录音中提到“However, the past 300 years or so have seen a dramatic increase in the death or disappearance of languages…”,由此可知,大约300年前,某些语言就出现了加速消亡的现象。因此选项B(直到200年前,语言才出现加速消亡的现象)与录音原文不符。
【录音原文】
Half of the 6,000 or so languages spoken in the world are under threat and a wealth of human knowledge could be lost with them, according to a new study. The study says pressures from dominant languages such as English, French, Spanish and Russian are drowning out minority tongues at an accelerating pace. “The dying and disappearance of languages has been going on for thousands of years as a natural event in human society, but at a slow rate,” says the study funded by UNESCO. “However, the past 300 years or so have seen a dramatic increase in the death or disappearance of languages leading to a situation today in which 3,000 or so languages that are still spoken are endangered, seriously endangered or dying.” The study cites several reasons for the disappearance of languages, ranging from repressive government policies and assimilation to economic pressures, migratory trends, disease and natural disasters. While sounding the alarm, it notes that a determined multilingual approach can rescue even the most threatened tongues. In Japan, only eight elderly people spoke Ainu on Hokkaido Island by the late l980s after decades of official neglect, but promotional policies have since revived the language. -
第12题:
单选题Which of the following statements is NOT true according to the passage?ANew England winters are cold.
BSome taxi drivers are impolite.
CThe U. S. A is a popular place for tourists.
DHotel staff are often sympathetic.
正确答案: D解析:
结论推断题。答案出处为全文。A和B两项可以分别在原文的第三、四段找到。C项在原文中虽不能直接找到,但原文开头提到more than a million and a half foreign tourists就可以证明美国深受游客欢迎。D项与第四段中的unsympathetic相反,故选D项。 -
第13题:
(b) Describe with suitable calculations how the goodwill arising on the acquisition of Briars will be dealt with in
the group financial statements and how the loan to Briars should be treated in the financial statements of
Briars for the year ended 31 May 2006. (9 marks)
正确答案:(b) IAS21 ‘The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates’ requires goodwill arising on the acquisition of a foreign operation
and fair value adjustments to acquired assets and liabilities to be treated as belonging to the foreign operation. They should
be expressed in the functional currency of the foreign operation and translated at the closing rate at each balance sheet date.
Effectively goodwill is treated as a foreign currency asset which is retranslated at the closing rate. In this case the goodwillarising on the acquisition of Briars would be treated as follows:
At 31 May 2006, the goodwill will be retranslated at 2·5 euros to the dollar to give a figure of $4·4 million. Therefore this
will be the figure for goodwill in the balance sheet and an exchange loss of $1·4 million recorded in equity (translation
reserve). The impairment of goodwill will be expensed in profit or loss to the value of $1·2 million. (The closing rate has been
used to translate the impairment; however, there may be an argument for using the average rate.)
The loan to Briars will effectively be classed as a financial liability measured at amortised cost. It is the default category for
financial liabilities that do not meet the definition of financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss. For most entities,
most financial liabilities will fall into this category. When a financial liability is recognised initially in the balance sheet, the
liability is measured at fair value. Fair value is the amount for which a liability can be settled, between knowledgeable, willing
parties in an arm’s length transaction. In other words, fair value is an actual or estimated transaction price on the reporting
date for a transaction taking place between unrelated parties that have adequate information about the asset or liability being
measured.
Since fair value is a market transaction price, on initial recognition fair value generally is assumed to equal the amount of
consideration paid or received for the financial asset or financial liability. Accordingly, IAS39 specifies that the best evidence
of the fair value of a financial instrument at initial recognition generally is the transaction price. However for longer-term
receivables or payables that do not pay interest or pay a below-market interest, IAS39 does require measurement initially at
the present value of the cash flows to be received or paid.
Thus in Briars financial statements the following entries will be made: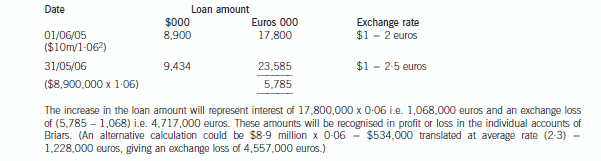
-
第14题:
5 An enterprise has made a material change to an accounting policy in preparing its current financial statements.
Which of the following disclosures are required by IAS 8 Accounting policies, changes in accounting estimates
and errors in these financial statements?
1 The reasons for the change.
2 The amount of the consequent adjustment in the current period and in comparative information for prior periods.
3 An estimate of the effect of the change on future periods, where possible.
A 1 and 2 only
B 1 and 3 only
C 2 and 3 only
D All three items
正确答案:A
-
第15题:
22 Which of the following statements about limited liability companies’ accounting is/are correct?
1 A revaluation reserve arises when a non-current asset is sold at a profit.
2 The authorised share capital of a company is the maximum nominal value of shares and loan notes the company
may issue.
3 The notes to the financial statements must contain details of all adjusting events as defined in IAS10 Events after
the balance sheet date.
A All three statements
B 1 and 2 only
C 2 and 3 only
D None of the statements
正确答案:D
-
第16题:
8 Which of the following statements about accounting concepts and conventions are correct?
(1) The money measurement concept requires all assets and liabilities to be accounted for at historical cost.
(2) The substance over form. convention means that the economic substance of a transaction should be reflected in
the financial statements, not necessarily its legal form.
(3) The realisation concept means that profits or gains cannot normally be recognised in the income statement until
realised.
(4) The application of the prudence concept means that assets must be understated and liabilities must be overstated
in preparing financial statements.
A 1 and 3
B 2 and 3
C 2 and 4
D 1 and 4.
正确答案:B
-
第17题:
12 Which of the following statements are correct?
(1) Contingent assets are included as assets in financial statements if it is probable that they will arise.
(2) Contingent liabilities must be provided for in financial statements if it is probable that they will arise.
(3) Details of all adjusting events after the balance sheet date must be given in notes to the financial statements.
(4) Material non-adjusting events are disclosed by note in the financial statements.
A 1 and 2
B 2 and 4
C 3 and 4
D 1 and 3
正确答案:B
-
第18题:
(b) You are an audit manager with specific responsibility for reviewing other information in documents containing
audited financial statements before your firm’s auditor’s report is signed. The financial statements of Hegas, a
privately-owned civil engineering company, show total assets of $120 million, revenue of $261 million, and profit
before tax of $9·2 million for the year ended 31 March 2005. Your review of the Annual Report has revealed
the following:
(i) The statement of changes in equity includes $4·5 million under a separate heading of ‘miscellaneous item’
which is described as ‘other difference not recognized in income’. There is no further reference to this
amount or ‘other difference’ elsewhere in the financial statements. However, the Management Report, which
is required by statute, is not audited. It discloses that ‘changes in shareholders’ equity not recognized in
income includes $4·5 million arising on the revaluation of investment properties’.
The notes to the financial statements state that the company has implemented IAS 40 ‘Investment Property’
for the first time in the year to 31 March 2005 and also that ‘the adoption of this standard did not have a
significant impact on Hegas’s financial position or its results of operations during 2005’.
(ii) The chairman’s statement asserts ‘Hegas has now achieved a position as one of the world’s largest
generators of hydro-electricity, with a dedicated commitment to accountable ethical professionalism’. Audit
working papers show that 14% of revenue was derived from hydro-electricity (2004: 12%). Publicly
available information shows that there are seven international suppliers of hydro-electricity in Africa alone,
which are all at least three times the size of Hegas in terms of both annual turnover and population supplied.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of the above matters for the auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Hegas for the year ended 31 March 2005. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Implications for the auditor’s report
(i) Management Report
■ $4·5 million represents 3·75% of total assets, 1·7% of revenue and 48·9% profit before tax. As this is material
by any criteria (exceeding all of 2% of total assets, 1/2% revenue and 5% PBT), the specific disclosure requirements
of IASs need to be met (IAS 1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’).
■ The Management Report discloses the amount and the reason for a material change in equity whereas the financial
statements do not show the reason for the change and suggest that it is immaterial. As the increase in equity
attributable to this adjustment is nearly half as much as that attributable to PBT there is a material inconsistency
between the Management Report and the audited financial statements.
■ Amendment to the Management Report is not required.
Tutorial note: Marks will be awarded for arguing, alternatively, that the Management Report disclosure needs to
be amended to clarify that the revaluation arises from the first time implementation.
■ Amendment to the financial statements is required because the disclosure is:
– incorrect – as, on first adoption of IAS 40, the fair value adjustment should be against the opening balance
of retained earnings; and
– inadequate – because it is being ‘supplemented’ by additional disclosure in a document which is not within
the scope of the audit of financial statements.
■ Whilst it is true that the adoption of IAS 40 did not have a significant impact on results of operations, Hegas’s
financial position has increased by nearly 4% in respect of the revaluation (to fair value) of just one asset category
(investment properties). As this is significant, the statement in the notes should be redrafted.
■ If the financial statements are not amended, the auditor’s report should be qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of
disagreement (non-compliance with IAS 40) as the matter is material but not pervasive. Additional disclosure
should also be given (e.g. that the ‘other difference’ is a fair value adjustment).
■ However, it is likely that when faced with the prospect of a qualified auditor’s report Hegas’s management will
rectify the financial statements so that an unmodified auditor’s report can be issued.
Tutorial note: Marks will be awarded for other relevant points e.g. citing IAS 8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in
Accounting Estimates and Errors’.
(ii) Chairman’s statement
Tutorial note: Hegas is privately-owned therefore IAS 14 ‘Segment Reporting’ does not apply and the proportion of
revenue attributable to hydro-electricity will not be required to be disclosed in the financial statements. However, credit
will be awarded for discussing the implications for the auditor’s report if it is regarded as a material inconsistency on
the assumption that segment revenue (or similar) is reported in the financial statements.
■ The assertion in the chairman’s statement, which does not fall within the scope of the audit of the financial
statements, claims two things, namely that the company:
(1) is ‘one of the world’s largest generators of hydro-electricity’; and
(2) has ‘a dedicated commitment to accountable ethical professionalism’.
■ To the extent that this information does not relate to matters disclosed in the financial statements it may give rise
to a material misstatement of fact. In particular, the first statement presents a misleading impression of the
company’s size. In misleading a user of the financial statements with this statement, the second statement is not
true (as it is not ethical or professional to mislead the reader and potentially undermine the credibility of the
financial statements).
■ The first statement is a material misstatement of fact because, for example:
– the company is privately-owned, and publicly-owned international/multi-nationals are larger;
– the company’s main activity is civil engineering not electricity generation (only 14% of revenue is derived from
HEP);
– as the company ranks at best eighth against African companies alone it ranks much lower globally.
■ Hegas should be asked to reconsider the wording of the chairman’s statement (i.e. removing these assertions) and
consult, as necessary, the company’s legal advisor.
■ If the statement is not changed there will be no grounds for qualification of the opinion on the audited financial
statements. The audit firm should therefore take legal advice on how the matter should be reported.
■ However, an emphasis of matter paragraph may be used to report on matters other than those affecting the audited
financial statements. For example, to explain the misstatement of fact if management refuses to make the
amendment.
Tutorial note: Marks will also be awarded for relevant comments about the chairman’s statement being perceived by
many readers to be subject to audit and therefore that the unfounded statement might undermine the credibility of the
financial statements. Shareholders tend to rely on the chairman’s statement, even though it is not regulated or audited,
because modern financial statements are so complex. -
第19题:
4 (a) The purpose of ISA 250 Consideration of Laws and Regulations in an Audit of Financial Statements is to
establish standards and provide guidance on the auditor’s responsibility to consider laws and regulations in an
audit of financial statements.
Explain the auditor’s responsibilities for reporting non-compliance that comes to the auditor’s attention
during the conduct of an audit. (5 marks)
正确答案:
4 CLEEVES CO
(a) Reporting non-compliance
Non-compliance refers to acts of omission or commission by the entity being audited, either intentional or unintentional, that
are contrary to the prevailing laws or regulations.
To management
Regarding non-compliance that comes to the auditor’s attention the auditor should, as soon as practicable, either:
■ communicate with those charged with governance; or
■ obtain audit evidence that they are appropriately informed.
However, the auditor need not do so for matters that are clearly inconsequential or trivial and may reach agreement1 in
advance on the nature of such matters to be communicated.
If in the auditor’s judgment the non-compliance is believed to be intentional and material, the auditor should communicate
the finding without delay.
If the auditor suspects that members of senior management are involved in non-compliance, the auditor should report the
matter to the next higher level of authority at the entity, if it exists (e.g. an audit committee or a supervisory board). Where
no higher authority exists, or if the auditor believes that the report may not be acted upon or is unsure as to the person to
whom to report, the auditor would consider seeking legal advice.
To the users of the auditor’s report on the financial statements
If the auditor concludes that the non-compliance has a material effect on the financial statements, and has not been properly
reflected in the financial statements, the auditor expresses a qualified (i.e. ‘except for disagreement’) or an adverse opinion.
If the auditor is precluded by the entity from obtaining sufficient appropriate audit evidence to evaluate whether or not noncompliance
that may be material to the financial statements has (or is likely to have) occurred, the auditor should express a
qualified opinion or a disclaimer of opinion on the financial statements on the basis of a limitation on the scope of the audit.
Tutorial note: For example, if management denies the auditor access to information from which he would be able to assess
whether or not illegal dumping had taken place (and, if so, the extent of it).
If the auditor is unable to determine whether non-compliance has occurred because of limitations imposed by circumstances
rather than by the entity, the auditor should consider the effect on the auditor’s report.
Tutorial note: For example, if new legal requirements have been announced as effective but the detailed regulations are not
yet published.
To regulatory and enforcement authorities
The auditor’s duty of confidentiality ordinarily precludes reporting non-compliance to a third party. However, in certain
circumstances, that duty of confidentiality is overridden by statute, law or by courts of law (e.g. in some countries the auditor
is required to report non-compliance by financial institutions to the supervisory authorities). The auditor may need to seek
legal advice in such circumstances, giving due consideration to the auditor’s responsibility to the public interest. -
第20题:
You are the manager responsible for performing hot reviews on audit files where there is a potential disagreement
between your firm and the client regarding a material issue. You are reviewing the going concern section of the audit
file of Dexter Co, a client with considerable cash flow difficulties, and other, less significant operational indicators of
going concern problems. The working papers indicate that Dexter Co is currently trying to raise finance to fund
operating cash flows, and state that if the finance is not received, there is significant doubt over the going concern
status of the company. The working papers conclude that the going concern assumption is appropriate, but it is
recommended that the financial statements should contain a note explaining the cash flow problems faced by the
company, along with a description of the finance being sought, and an evaluation of the going concern status of the
company. The directors do not wish to include the note in the financial statements.
Required:
(b) Consider and comment on the possible reasons why the directors of Dexter Co are reluctant to provide the
note to the financial statements. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Directors reluctance to disclose
The directors are likely to have several reasons behind their reluctance to disclose the note as recommended by the audit
manager. The first is that the disclosure of Dexter Co’s poor cash flow position and perilous going concern status may reflect
badly on the directors themselves. The company’s shareholders and other stakeholders will be displeased to see the company
in such a poor position, and the directors will be held accountable for the problems. Of course it may not be the case that
the directors have exercised poor management of the company – the problems could be caused by external influences outside
the control of the directors. However, it is natural that the directors will not want to highlight the situation in order to protect
their own position.
Secondly, the note could itself trigger further financial distress for the company. Dexter Co is trying to raise finance, and it is
probable that the availability of further finance will be detrimentally affected by the disclosure of the company’s financial
problems. In particular, if the cash flow difficulties are highlighted, providers of finance will consider the company too risky
an investment, and are not likely to make funds available for fear of non-repayment. Existing lenders may seek repayment of
their funds in fear that the company may be unable in the future to meet repayments.
In addition, the disclosures could cause operational problems, for example, suppliers may curtail trading relationships as they
become concerned that they will not be paid, or customers may be deterred from purchasing from the company if they feel
that there is no long-term future for the business. Unfortunately the mere disclosure of financial problems can be self-fulfilling,
and cause such further problems for the company that it is pushed into non-going concern status.
The directors may also be concerned that if staff were to hear of this they may worry about the future of the company and
seek alternative employment, which could lead in turn to the loss of key members of staff. This would be detrimental to the
business and trigger further operational problems.
Finally, the reluctance to disclose may be caused by an entirely different reason. The directors could genuinely feel that the
cash flow and operational problems faced by the company do not constitute factors affecting the going concern status. They
may be confident that although a final decision has not been made regarding financing, the finance is likely to be forthcoming,
and therefore there is no long-term material uncertainty over the future of the company. However audit working papers
conclude that there is a significant level of doubt over the going concern status of Dexter Co, and therefore it seems that the
directors may be over optimistic if they feel that there is no significant doubt to be disclosed in the financial statements. -
第21题:
听力原文:M: There are several reasons why careful analysis of financial statements is necessary. What are they?
W: First, financial statements are general-purpose statements. Secondly, the relationships between amounts on successive financial statements are not obvious without analysis. And thirdly, users of financial statements may be interested in seeing how well a company is performing.
Q: What are they talking about?
(17)
A.The methods of financial statements.
B.The necessity of careful analysis of financial statements
C.The relationship among financial statements.
D.The purpose of financial statements.
正确答案:B
解析:男士问的是仔细分析财务报表的必要性的理由,故B选项符合。D项说的是财务报表的目的,并非分析财务报表的目的。 -
第22题:
You are an audit manager at Rockwell & Co, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants. You are responsible for the audit of the Hopper Group, a listed audit client which supplies ingredients to the food and beverage industry worldwide.
The audit work for the year ended 30 June 2015 is nearly complete, and you are reviewing the draft audit report which has been prepared by the audit senior. During the year the Hopper Group purchased a new subsidiary company, Seurat Sweeteners Co, which has expertise in the research and design of sugar alternatives. The draft financial statements of the Hopper Group for the year ended 30 June 2015 recognise profit before tax of $495 million (2014 – $462 million) and total assets of $4,617 million (2014: $4,751 million). An extract from the draft audit report is shown below:
Basis of modified opinion (extract)
In their calculation of goodwill on the acquisition of the new subsidiary, the directors have failed to recognise consideration which is contingent upon meeting certain development targets. The directors believe that it is unlikely that these targets will be met by the subsidiary company and, therefore, have not recorded the contingent consideration in the cost of the acquisition. They have disclosed this contingent liability fully in the notes to the financial statements. We do not feel that the directors’ treatment of the contingent consideration is correct and, therefore, do not believe that the criteria of the relevant standard have been met. If this is the case, it would be appropriate to adjust the goodwill balance in the statement of financial position.
We believe that any required adjustment may materially affect the goodwill balance in the statement of financial position. Therefore, in our opinion, the financial statements do not give a true and fair view of the financial position of the Hopper Group and of the Hopper Group’s financial performance and cash flows for the year then ended in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards.
Emphasis of Matter Paragraph
We draw attention to the note to the financial statements which describes the uncertainty relating to the contingent consideration described above. The note provides further information necessary to understand the potential implications of the contingency.
Required:
(a) Critically appraise the draft audit report of the Hopper Group for the year ended 30 June 2015, prepared by the audit senior.
Note: You are NOT required to re-draft the extracts from the audit report. (10 marks)
(b) The audit of the new subsidiary, Seurat Sweeteners Co, was performed by a different firm of auditors, Fish Associates. During your review of the communication from Fish Associates, you note that they were unable to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence with regard to the breakdown of research expenses. The total of research costs expensed by Seurat Sweeteners Co during the year was $1·2 million. Fish Associates has issued a qualified audit opinion on the financial statements of Seurat Sweeteners Co due to this inability to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence.
Required:
Comment on the actions which Rockwell & Co should take as the auditor of the Hopper Group, and the implications for the auditor’s report on the Hopper Group financial statements. (6 marks)
(c) Discuss the quality control procedures which should be carried out by Rockwell & Co prior to the audit report on the Hopper Group being issued. (4 marks)
正确答案:(a) Critical appraisal of the draft audit report
Type of opinion
When an auditor issues an opinion expressing that the financial statements ‘do not give a true and fair view’, this represents an adverse opinion. The paragraph explaining the modification should, therefore, be titled ‘Basis of Adverse Opinion’ rather than simply ‘Basis of Modified Opinion’.
An adverse opinion means that the auditor considers the misstatement to be material and pervasive to the financial statements of the Hopper Group. According to ISA 705 Modifications to Opinions in the Independent Auditor’s Report, pervasive matters are those which affect a substantial proportion of the financial statements or fundamentally affect the users’ understanding of the financial statements. It is unlikely that the failure to recognise contingent consideration is pervasive; the main effect would be to understate goodwill and liabilities. This would not be considered a substantial proportion of the financial statements, neither would it be fundamental to understanding the Hopper Group’s performance and position.
However, there is also some uncertainty as to whether the matter is even material. If the matter is determined to be material but not pervasive, then a qualified opinion would be appropriate on the basis of a material misstatement. If the matter is not material, then no modification would be necessary to the audit opinion.
Wording of opinion/report
The auditor’s reference to ‘the acquisition of the new subsidiary’ is too vague; the Hopper Group may have purchased a number of subsidiaries which this phrase could relate to. It is important that the auditor provides adequate description of the event and in these circumstances it would be appropriate to name the subsidiary referred to.
The auditor has not quantified the amount of the contingent element of the consideration. For the users to understand the potential implications of any necessary adjustments, they need to know how much the contingent consideration will be if it becomes payable. It is a requirement of ISA 705 that the auditor quantifies the financial effects of any misstatements, unless it is impracticable to do so.
In addition to the above point, the auditor should provide more description of the financial effects of the misstatement, including full quantification of the effect of the required adjustment to the assets, liabilities, incomes, revenues and equity of the Hopper Group.
The auditor should identify the note to the financial statements relevant to the contingent liability disclosure rather than just stating ‘in the note’. This will improve the understandability and usefulness of the contents of the audit report.
The use of the term ‘we do not feel that the treatment is correct’ is too vague and not professional. While there may be some interpretation necessary when trying to apply financial reporting standards to unique circumstances, the expression used is ambiguous and may be interpreted as some form. of disclaimer by the auditor with regard to the correct accounting treatment. The auditor should clearly explain how the treatment applied in the financial statements has departed from the requirements of the relevant standard.
Tutorial note: As an illustration to the above point, an appropriate wording would be: ‘Management has not recognised the acquisition-date fair value of contingent consideration as part of the consideration transferred in exchange for the acquiree, which constitutes a departure from International Financial Reporting Standards.’
The ambiguity is compounded by the use of the phrase ‘if this is the case, it would be appropriate to adjust the goodwill’. This once again suggests that the correct treatment is uncertain and perhaps open to interpretation.
If the auditor wishes to refer to a specific accounting standard they should refer to its full title. Therefore instead of referring to ‘the relevant standard’ they should refer to International Financial Reporting Standard 3 Business Combinations.
The opinion paragraph requires an appropriate heading. In this case the auditors have issued an adverse opinion and the paragraph should be headed ‘Adverse Opinion’.
As with the basis paragraph, the opinion paragraph lacks authority; suggesting that the required adjustments ‘may’ materially affect the financial statements implies that there is a degree of uncertainty. This is not the case; the amount of the contingent consideration will be disclosed in the relevant purchase agreement, so the auditor should be able to determine whether the required adjustments are material or not. Regardless, the sentence discussing whether the balance is material or not is not required in the audit report as to warrant inclusion in the report the matter must be considered material. The disclosure of the nature and financial effect of the misstatement in the basis paragraph is sufficient.
Finally, the emphasis of matter paragraph should not be included in the audit report. An emphasis of matter paragraph is only used to draw attention to an uncertainty/matter of fundamental importance which is correctly accounted for and disclosed in the financial statements. An emphasis of matter is not required in this case for the following reasons:
– Emphasis of matter is only required to highlight matters which the auditor believes are fundamental to the users’ understanding of the business. An example may be where a contingent liability exists which is so significant it could lead to the closure of the reporting entity. That is not the case with the Hopper Group; the contingent liability does not appear to be fundamental.
– Emphasis of matter is only used for matters where the auditor has obtained sufficient appropriate evidence that the matter is not materially misstated in the financial statements. If the financial statements are materially misstated, in this regard the matter would be fully disclosed by the auditor in the basis of qualified/adverse opinion paragraph and no emphasis of matter is necessary.
(b) Communication from the component auditor
The qualified opinion due to insufficient evidence may be a significant matter for the Hopper Group audit. While the possible adjustments relating to the current year may not be material to the Hopper Group, the inability to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence with regard to a material matter in Seurat Sweeteners Co’s financial statements may indicate a control deficiency which the auditor was not aware of at the planning stage and it could indicate potential problems with regard to the integrity of management, which could also indicate a potential fraud. It could also indicate an unwillingness of management to provide information, which could create problems for future audits, particularly if research and development costs increase in future years. If the group auditor suspects that any of these possibilities are true, they may need to reconsider their risk assessment and whether the audit procedures performed are still appropriate.
If the detail provided in the communication from the component auditor is insufficient, the group auditor should first discuss the matter with the component auditor to see whether any further information can be provided. The group auditor can request further working papers from the component auditor if this is necessary. However, if Seurat Sweeteners has not been able to provide sufficient appropriate evidence, it is unlikely that this will be effective.
If the discussions with the component auditor do not provide satisfactory responses to evaluate the potential impact on the Hopper Group, the group auditor may need to communicate with either the management of Seurat Sweeteners or the Hopper Group to obtain necessary clarification with regard to the matter.
Following these procedures, the group auditor needs to determine whether they have sufficient appropriate evidence to draw reasonable conclusions on the Hopper Group’s financial statements. If they believe the lack of information presents a risk of material misstatement in the group financial statements, they can request that further audit procedures be performed, either by the component auditor or by themselves.
Ultimately the group engagement partner has to evaluate the effect of the inability to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence on the audit opinion of the Hopper Group. The matter relates to research expenses totalling $1·2 million, which represents 0·2% of the profit for the year and 0·03% of the total assets of the Hopper Group. It is therefore not material to the Hopper Group’s financial statements. For this reason no modification to the audit report of the Hopper Group would be required as this does not represent a lack of sufficient appropriate evidence with regard to a matter which is material to the Group financial statements.
Although this may not have an impact on the Hopper Group audit opinion, this may be something the group auditor wishes to bring to the attention of those charged with governance. This would be particularly likely if the group auditor believed that this could indicate some form. of fraud in Seurat Sweeteners Co, a serious deficiency in financial reporting controls or if this could create problems for accepting future audits due to management’s unwillingness to provide access to accounting records.
(c) Quality control procedures prior to issuing the audit report
ISA 220 Quality Control for an Audit of Financial Statements and ISQC 1 Quality Control for Firms that Perform. Audits and Reviews of Historical Financial Information, and Other Assurance and Related Services Agreements require that an engagement quality control reviewer shall be appointed for audits of financial statements of listed entities. The audit engagement partner then discusses significant matters arising during the audit engagement with the engagement quality control reviewer.
The engagement quality control reviewer and the engagement partner should discuss the failure to recognise the contingent consideration and its impact on the auditor’s report. The engagement quality control reviewer must review the financial statements and the proposed auditor’s report, in particular focusing on the conclusions reached in formulating the auditor’s report and consideration of whether the proposed auditor’s opinion is appropriate. The audit documentation relating to the acquisition of Seurat Sweeteners Co will be carefully reviewed, and the reviewer is likely to consider whether procedures performed in relation to these balances were appropriate.
Given the listed status of the Hopper Group, any modification to the auditor’s report will be scrutinised, and the firm must be sure of any decision to modify the report, and the type of modification made. Once the engagement quality control reviewer has considered the necessity of a modification, they should consider whether a qualified or an adverse opinion is appropriate in the circumstances. This is an important issue, given that it requires judgement as to whether the matters would be material or pervasive to the financial statements.
The engagement quality control reviewer should ensure that there is adequate documentation regarding the judgements used in forming the final audit opinion, and that all necessary matters have been brought to the attention of those charged with governance.
The auditor’s report must not be signed and dated until the completion of the engagement quality control review.
Tutorial note: In the case of the Hopper Group’s audit, the lack of evidence in respect of research costs is unlikely to be discussed unless the audit engagement partner believes that the matter could be significant, for example, if they suspected the lack of evidence is being used to cover up a financial statements fraud.
-
第23题:
单选题If verhofen’s arguments and statements are all correct, which of the following statements can accurately be inferred?ABiotechnology executives who aggressively raise investment capital for bioengineered products with no conceivable market should be held responsible if biotechnology stocks crash.
BInvestors should make financial decisions only with the advice of qualified financial advisors, such as investment bankers or fund managers.
CIf people lose money on investments that they inadequately researched, they have only themselves to blame.
DIf insurance companies provide home insurance for homes built in a hurricane zone and those homes are subsequently all destroyed by a major hurricane, the insurance company should be blamed for any investment losses suffered by its shareholders.
EThe collapse of Internet stocks would not have occurred if companies had not attempted to sell bulky items, like dog food, over the Internet.
正确答案: C解析:
推断题。根据第二段内容可知,Verhofen认为互联网企业家盲目的推销想法,但是缺乏有效的商业模型支持,导致了互联网泡沫,由此可知推断A项是正确的。
