单选题若x和y是程序中的两个整型变量,则下列if语句中正确的是( )。A if(x==0)y=1;else y=2;B if(x==0)then y=l else y=2;C if(x==0)y=l else y=2;D if x==0 y=1;else y=2;
题目
if(x==0)y=1;else y=2;
if(x==0)then y=l else y=2;
if(x==0)y=l else y=2;
if x==0 y=1;else y=2;
相似考题
更多“单选题若x和y是程序中的两个整型变量,则下列if语句中正确的是( )。A if(x==0)y=1;else y=2;B if(x==0)then y=l else y=2;C if(x==0)y=l else y=2;D if x==0 y=1;else y=2;”相关问题
-
第1题:
若x和y是程序中的两个整型变量,则下列if语句中正确的是( )。
A.if(x==0)y=l;else y=2;
B.if(x==0)theny=1 elsey=2
C.if(x=0)y=l else y=2;
D.ifx==0y=1 else y=2;
正确答案:A
解析:if…else语句的格式:if(<条件>)<语句1>else<语句2>,注意语句结束要以分号结尾,对照题中选项可知A正确。 -
第2题:
有以下程序: #include<stdio.h> main( ) {int x=1,y=0; if(!x)y++; else if(x==0) if(x)y+=2; else y+=3; Drintf("%d\n"。v); } 程序运行后的输出结果是( )。
A.3
B.2
C.1
D.0
正确答案:D
因为x!=0,所以下列的循环不执行,只执行y++,最后结果为0。 -
第3题:
下列程序的运行结果是( )。 main() { int a=-5,b=1,c=1; int x=0,y=2,z=0; if(c>0)x=x+y; if(a<=0) { if(b>O) if(c<=0)y=x-y; } else if(c>0)y=x-y; else z=y; printf("%d,%d,%d\n",x,y,z); }
A.2,2,0
B.2,2,2
C.0,2,0
D.2,0,2
正确答案:A
解析: 本题考查if else语句的使用。先判断第1个if语句,因为c=1>0,所以x=x+y=0+2=2。第1个if语句,因为a=-50,所以进入下列的复合语句。经判断发现,复合语句中第2个if语句的条件均不满足,不执行任何语句退出,在这个过程中y和z的值没有发生变化。 -
第4题:
有如下程序main(){ float x=2.0,y;if(x<0.0)y=0.0;else if(x>10.0)y=1.O/x;else y=1.0;printf("%有如下程序 main() { float x=2.0,y; if(x<0.0)y=0.0; else if(x>10.0)y=1.O/x; else y=1.0; printf("%f\n",y);} 该程序的输出结果是
A.0
B.0.25
C.0.5
D.1
正确答案:D
解析:本题考查if语句中的一种表达方式,即:if…elseif…。该表达式的语句是:if(表达式1)语句1elseif(表达式2)语句2elseif(表达式3)语句3else语句4……本题执行elsey=1.0,并且以“%f”输出。注意:条件表达式在if语句中的使用。 -
第5题:
与“y=(x>0?1:x<0?-1:0)”;的功能相同的if 语句是( )。
A.if(x>0)y=1; else if(x<0)y=1; else="" y="0;
B." x="">0)y=1; else if(x<0)y=-l; else="" y="0;"
C.y="-l" x="">O)y=1; else if(x=-0)y=0; else y=-l;
D.y=0; if(x>=0) if(x>=0)y=1; else y=-l;
正确答案:B
y=(x=)071:x<0?-1:0)中有两个三目运算符,因此按从右到在的顺序运算,可写成y=(x>071:(x<0?-1:0)),故选择8选项。 -
第6题:
有如下程序includevoid main( ){float x=2.O,y;if(x 有如下程序 #include<iostream.h> void main( ) { float x=2.O,y; if(x<O.0)y=0.0; else if(x<10.O)y=1.0/x; else y=1.0; cout<<y; } 该程序的输出结果是
A.0
B.0.25
C.0.5
D.1
正确答案:C
解析:该表达式的语句是该表达式的语句是if(表达式1)语句1elseif(表达式2)语句2elseif(表达式3)语句3else语句4......由if表达式可知,题中直接执行if语句的第2条elseif(x10.0)y=1.O/x;。注意:else总是与最近的没有匹配的if匹配。第7题:
下列程序的输出结果是______。main(){ float x=2.0,y; if(x<0.0)y=0.0; else if(x<10.0)y=1.0/x; else y=1.0; printf("%f\n",y);}
A.0
B.0.25
C.0.5
D.1
正确答案:C
第8题:
与y=(x>0? 1:x<0? -1:0);的功能相同的if语句是A.if(x>0)y=1 else if(x<0)y=-1; else y=O;B.i与y=(x>0? 1:x<0? -1:0);的功能相同的if语句是
A.if(x>0)y=1 else if(x<0)y=-1; else y=O;
B.if(x) if(x>0)y=1; else if(x<0)y=-1;
C.y=-1; if(x) if(x>0)y=1; else if(x==0)y=0; else y=-1;
D.y=0; if(x>=0) if(x>0)y=1; else y=-1;
正确答案:A
解析:条件运算符要求有三个操作对象,它是c++语言中惟一的一个三目运算符。条件表达式的一般形式为:表达式1?表达式2:表达式3,先求解表达式1,若为非0(真)则求解表达式2,此时表达式2的值就作为整个条件表达式的值。若表达式1的值为0(假),则求解表达式3,表达式3的值就是整个条件表达式的值。本题中用了两次三目运算符。第9题:
有一函数:
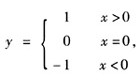 以下程序段中不能根据x值正确计算出y值的是
以下程序段中不能根据x值正确计算出y值的是A.if(x>0)y=1; else if(x= =0)y=0; else y=-1;
B.y=0; if(x>0)y=1; else if(x<0)y=-1;
C.y = 0; if (x> = 0) if (x>0) y = 1; else y = -1;
D.if ( x > = 0) if ( x>0)y = 1; else y = 0; else y = -1;
正确答案:C
第10题:
(27)有以下程序
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{ int x=1,y=0;
if(!x) y++;
else if(x==0)
if (x) y+=2;
else y+=3;
printf("%d\n",y);
}
程序运行后的输出结果是
A)3
B)2
C)1
D)0
正确答案:D
第11题:
以下不能实现符号函数y=sgn(x)的程序段是()。
- A、if x>0 then y=1 else if x=0 then y=0 else y= -1
- B、if x>0 then y=1 else if x<0 then y= -1 else y=0
- C、if x>=0 then if x=0 then y=0 else y= -1 else y=1
- D、if x<>0 then if x<0 then y= -1 else y= 1 else y=0
正确答案:C第12题:
单选题有以下程序:#include main(){ int x=1,y=0; if(!x)y++; else if(x==0) if(x)y+=2; else y+=3; printf(%d,y);}程序运行后的输出结果是( )。A3
B2
C1
D0
正确答案: D解析:
else子句总是与前面最近的不带else的if相结合,与书写格式无关。本题中的层次关系是:if(!x)与else if(x==0)是一组,位于条件判断的最外层。而if(x)与else是一组,位于else if(x==0)条件的内层。由此可知条件均不成立,所以y未进行任何操作,仍为0。答案选择D选项。第13题:
有关c++问题1.计算下列分段函数,X由键盘输入。
0 (x<=-10.0)
y= x (-10.0<x<=10.0)
2x-3(x>10.0)
#include"stdio.h"
main()
{
float x,y;
if(x<=-10.0)y=0;
else if ( 1 ) y=x;
else y=2*x-3;
printf(“%f\n”,x);
}
1. x>-10.0 && x<=10.0
x>-10.0 && x<=10.0
第14题:
给出以下程序: SET TALK OFF X=0 Y=0 DO WHILE X<100 X=X+1 IF INT(X/2)=X/2 LOOP ELSE Y=Y+X ENDIF ENDDO ?"Y=",Y RETURN 运行结果为 ______。
A.Y=500
B.Y=1500
C.Y=2000
D.Y=2500
正确答案:D
解析:程序所要完成的操作是求1到100之间的奇数和。程序首先将X,Y赋值为O,然后用DOWHILE循环来依次判断1-100中的数字,INT(X/2)=)X/2用于判断此数是否为偶数,如果为偶数,执行LOOP返回到DOWHILE判断循环条件,条件满足,使X加1重新判断是否为偶数,如果不是,表示此数为奇数,执行ELSE后面的语句,将其累加到Y中。第15题:
下列程序的运行结果是( )。
main()
{ int a=-5,b=1,c=1;
int x=0,y=2,z=0;
if(c>0) x=x+y;
if(a<=0)
{ if(b>0)
if(c<=0) y=x-y;
}
else if(c>0) y=x-y;
else z=y;
printf("%d,%d,%d\n",x,y,z);
}
A.2,2,0
B.2,2,2
C.0,2,0
D.2,0,2
正确答案:A
解析:本题考查if else语句的使用。 先判断第1个if语句,因为c=1>0,所以x=x+y=0+2=2。第1个 if语句,因为a=-50,所以进入下列的复合语句。经判断发现,复合语句中第2个汀语句的条件均不满足,不执行任何语句退出,在这个过程中y和x的值没有发生变化。第16题:
下列程序段的执行结果为 X=2 Y=5 If X * Y <1 Then Y=Y - 1 Else Y=-1 Print Y-X>0A.TrueB.下列程序段的执行结果为 X=2 Y=5 If X * Y <1 Then Y=Y - 1 Else Y=-1 Print Y-X>0
A.True
B.False
C.-1
D.1
正确答案:B
解析:Print方法具有计算和输出双重功能,对于表达式,它先计算后输出,此题中经过第一步的条件语句后,Y的数值为-1,则Y-X的值为-3,小于0,所以Y-X>0为逻辑假,故输出结果应该为False。第17题:
有以下程序
#inclUde<stdio.h>
main()
{int x=1。y=0;
if(!x)y++;
else if(x==0)
if(x)y+=2;
else y+=3; .
printf(“%d\n”,y);
}
程序运行后的输出结果是
A.3
B.2
C.1
D.0
正确答案:D
解析:本题主要考查的知识点为if语句的嵌套.变量x的值(为1。既不满址表达式!x为真.也不满足表达式x==0.故不执行if语句,而直接执行printf函数输出y的值0。第18题:
有以下程序
#include
main()
{ int x=1,y=0;
if(!x) y++;
else if(x==0)
if (x) y+=2;
else y+=3;
printf("%d\n",y);
}
程序运行后的输出结果是
A.3
B.2
C.1
D.0
正确答案:D
第19题:
与“y=(x>0?1:x<0?-1:0)”;的功能相同的if 语句是( )。
A.if(x>0)y=1; else if(x<0)y=1; else y=0;
B.if(x) if(x>0)y=1; else if(x<0)y=-l; else y=0;
C.y=-l if(x) if(x>O)y=1; else if(x=-0)y=0; else y=-l;
D.y=0; if(x>=0) if(x>=0)y=1; else y=-l;
正确答案:B
y=(x=)071:x<0?-1:0)中有两个三目运算符,因此按从右到在的顺序运算,可写成y=(x>071:(x<0?-1:0)),故选择8选项。第20题:
与y=(x>0?1:x<0?-1:0):的功能相同的if语句是()A.if(x>0)y=1; else if(x<0)y=-1; else y=0; else与y=(x>0?1:x<0?-1:0):的功能相同的if语句是( )
A.if(x>0)y=1; else if(x<0)y=-1; else y=0; else y=0;
B.if(x) if(x>0)y=1; else if(x<0)y=-1;
C.y=-1; if(x) if(x>0)y=1; else if(x==0)y=0; else y=-1;
D.y=0; if(x>=0) if(x>0)y=1; else y=-1:
正确答案:A
第21题:
下面的程序段所表示的数学函数关系是( ) y=-l; if( x!= 0)if(x>0)y=l; else y=0 ; 1(x<0) 1(x<0)
A.y= { 0(x= 0)
B.y={-l(X=0) 1(X>0) 0(X>0) o(X< 0) -l(X< 0)
C.y= {-1(x= 0)
D.y={ 1(X= 0) 1(X> 0) 0(X> 0)
正确答案:C
程序段首先置变量y的值为一l,接着按变量x值的不同情况重置变量y的值。重置的首要条件是x!=0,若变量x的值为0,则不再重置变量y的值,所以在X值为0情况下,y的值是-l。在变量X的值不等于0的条件下,若X的值大于0,重置变量y的值为1;若变量X的值小于0,重置变量y的值为0。所以程序段实现当变量x的值为0时,变量y的值为-1;当变量X的值大于0时,置变量y的值为1;当变量X的值小于0时,置变量y的值为0。正确解答为C。第22题:
以下不正确的if语句形式是()
- A、if(x>y&&x!=y);
- B、if(x==y)x+=y;
- C、if(x!=y){x=2;y=3;}else{x=0;y=0;}
- D、if(x<y){x++;y++;}
正确答案:A第23题:
单选题若x和y是程序中的两个整型变量,则下列if语句中正确的是( )。Aif(x==0)y=1;else y=2;
Bif(x==0)then y=l else y=2;
Cif(x==0)y=l else y=2;
Dif x==0 y=1;else y=2;
正确答案: C解析:
if-else语句的形式为:if(<条件>)<语句1>else<语句2>,所以只有A项符合以上形式的if-else语句。第24题:
单选题以下不能实现符号函数y=sgn(x)的程序段是()。Aif x>0 then y=1 else if x=0 then y=0 else y= -1
Bif x>0 then y=1 else if x<0 then y= -1 else y=0
Cif x>=0 then if x=0 then y=0 else y= -1 else y=1
Dif x<>0 then if x<0 then y= -1 else y= 1 else y=0
正确答案: D解析: 暂无解析
