Swim Co offers training courses to athletes and has prepared the following breakeven chart:Required:(a) State the breakeven sales revenue for Swim Co and estimate, to the nearest $10,000, the company’s profit if 500 athletes attend a training course. (2 m
题目
Swim Co offers training courses to athletes and has prepared the following breakeven chart:
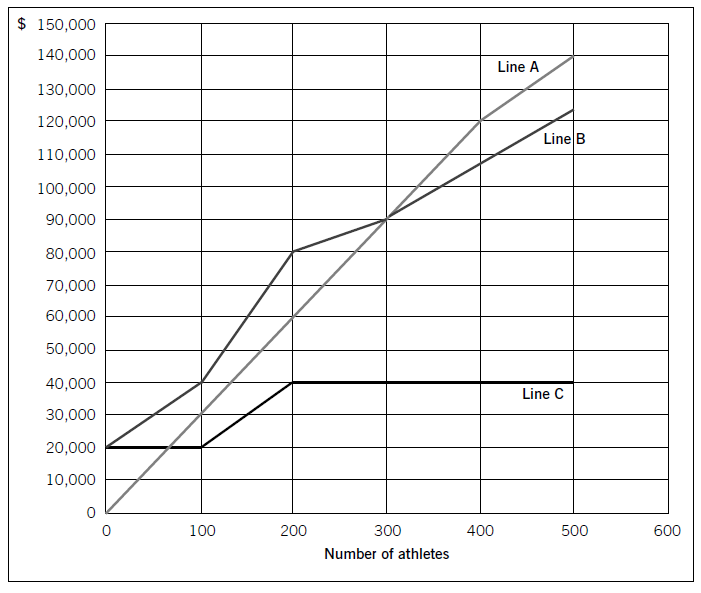
Required:
(a) State the breakeven sales revenue for Swim Co and estimate, to the nearest $10,000, the company’s profit if 500 athletes attend a training course. (2 marks)
(b) Using the chart above, explain the cost and revenue structure of the company. (8 marks)
相似考题
更多“Swim Co offers training courses to athletes and has prepared the following breakeven chart:Required:(a) State the breakeven sales revenue for Swim Co and estimate, to the nearest $10,000, the company’s profit if 500 athletes attend a training course. (2 m”相关问题
-
第1题:
2 The draft financial statements of Rampion, a limited liability company, for the year ended 31 December 2005
included the following figures:
$
Profit 684,000
Closing inventory 116,800
Trade receivables 248,000
Allowance for receivables 10,000
No adjustments have yet been made for the following matters:
(1) The company’s inventory count was carried out on 3 January 2006 leading to the figure shown above. Sales
between the close of business on 31 December 2005 and the inventory count totalled $36,000. There were no
deliveries from suppliers in that period. The company fixes selling prices to produce a 40% gross profit on sales.
The $36,000 sales were included in the sales records in January 2006.
(2) $10,000 of goods supplied on sale or return terms in December 2005 have been included as sales and
receivables. They had cost $6,000. On 10 January 2006 the customer returned the goods in good condition.
(3) Goods included in inventory at cost $18,000 were sold in January 2006 for $13,500. Selling expenses were
$500.
(4) $8,000 of trade receivables are to be written off.
(5) The allowance for receivables is to be adjusted to the equivalent of 5% of the trade receivables after allowing for
the above matters, based on past experience.
Required:
(a) Prepare a statement showing the effect of the adjustments on the company’s net profit for the year ended
31 December 2005. (5 marks)
正确答案:
-
第2题:
2 Plaza, a limited liability company, is a major food retailer. Further to the success of its national supermarkets in the
late 1990s it has extended its operations throughout Europe and most recently to Asia, where it is expanding rapidly.
You are a manager in Andando, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants. You have been approached by Duncan
Seymour, the chief finance officer of Plaza, to advise on a bid that Plaza is proposing to make for the purchase of
MCM. You have ascertained the following from a briefing note received from Duncan.
MCM provides training in management, communications and marketing to a wide range of corporate clients, including
multi-nationals. The ‘MCM’ name is well regarded in its areas of expertise. MCM is currently wholly-owned by
Frontiers, an international publisher of textbooks, whose shares are quoted on a recognised stock exchange. MCM
has a National and an International business.
The National business comprises 11 training centres. The audited financial statements show revenue of
$12·5 million and profit before taxation of $1·3 million for this geographic segment for the year to 31 December
2004. Most of the National business’s premises are owned or held on long leases. Trainers in the National business
are mainly full-time employees.
The International business has five training centres in Europe and Asia. For these segments, revenue amounted to
$6·3 million and profit before tax $2·4 million for the year to 31 December 2004. Most of the International business’s
premises are held on operating leases. International trade receivables at 31 December 2004 amounted to
$3·7 million. Although the International centres employ some full-time trainers, the majority of trainers provide their
services as freelance consultants.
Required:
(a) Define ‘due diligence’ and describe the nature and purpose of a due diligence review. (4 marks)
正确答案:
2 MCM
(a) Nature and purpose of a ‘due diligence’ review
■ ‘Due diligence’ may be defined as the process of systematically obtaining and assessing information in order to identify
and contain the risks associated with a transaction (e.g. buying a business) to an acceptable level.
■ The nature of such a review is therefore that it involves:
? an investigation (e.g. into a company whose equity may be sold); and
? disclosure (e.g. to a potential investor) of findings.
■ A due diligence assignment consists primarily of inquiry and analytical procedures.
Tutorial note: It will not, for example, routinely involve tests of control or substantive procedures.
* As the timescale for a due diligence review is often relatively short, but wider in scope than the financial statements
(e.g. business prospects, market valuation), there may be no expression of assurance.
■ Its purpose is to find all the facts that would be of material interest to an investor or acquirer of a business. It may not
uncover all such factors but should be designed with a reasonable expectation of so doing.
■ Professional accountants will not be held liable for non-disclosure of information that failed to be uncovered if their
review was conducted with ‘due diligence’. -
第3题:
(c) Maxwell Co is audited by Lead & Co, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants. Leo Sabat has enquired as to
whether your firm would be prepared to conduct a joint audit in cooperation with Lead & Co, on the future
financial statements of Maxwell Co if the acquisition goes ahead. Leo Sabat thinks that this would enable your
firm to improve group audit efficiency, without losing the cumulative experience that Lead & Co has built up while
acting as auditor to Maxwell Co.
Required:
Define ‘joint audit’, and assess the advantages and disadvantages of the audit of Maxwell Co being conducted
on a ‘joint basis’. (7 marks)
正确答案:
(c) A joint audit is when two or more audit firms are jointly responsible for giving the audit opinion. This is very common in a
group situation where the principal auditor is appointed jointly with the auditor of a subsidiary to provide a joint opinion on
the subsidiary’s financial statements. There are several advantages and disadvantages in a joint audit being performed.
Advantages
It can be beneficial in terms of audit efficiency for a joint audit to be conducted, especially in the case of a new subsidiary.
In this case, Lead & Co will have built up an understanding of Maxwell Co’s business, systems and controls, and financial
statement issues. It will be time efficient for the two firms of auditors to work together in order for Chien & Co to build up
knowledge of the new subsidiary. This is a key issue, as Chien & Co need to acquire a thorough understanding of the
subsidiary in order to assess any risks inherent in the company which could impact on the overall assessment of risk within
the group. Lead & Co will be able to provide a good insight into the company, and advise Chien & Co of the key risk areas
they have previously identified.
On the practical side, it seems that Maxwell Co is a significant addition to the group, as it is expected to increase operating
facilities by 40%. If Chien & Co were appointed as sole auditors to Maxwell Co it may be difficult for the audit firm to provide
adequate resources to conduct the audit at the same time as auditing the other group companies. A joint audit will allow
sufficient resources to be allocated to the audit of Maxwell Co, assuring the quality of the opinion provided.
If there is a tight deadline, as is common with the audit of subsidiaries, which should be completed before the group audit
commences, then having access to two firms’ resources should enable the audit to be completed in good time.
The audit should also benefit from an improvement in quality. The two audit firms may have different points of view, and
would be able to discuss contentious issues throughout the audit process. In particular, the newly appointed audit team will
have a ‘fresh pair of eyes’ and be able to offer new insight to matters identified. It should be easier to challenge management
and therefore ensure that the auditors’ position is taken seriously.
Tutorial note: Candidates may have referred to the recent debate over whether joint audits increase competition in the
profession. In particular, joint audits have been proposed as a way for ‘mid tier’ audit firms to break into the market of
auditing large companies and groups, which at the moment is monopolised by the ‘Big 4’. Although this does not answer
the specific question set, credit will be awarded for demonstration of awareness of this topical issue.
Disadvantages
For the client, it is likely to be more expensive to engage two audit firms than to have the audit opinion provided by one firm.
From a cost/benefit point of view there is clearly no point in paying twice for one opinion to be provided. Despite the audit
workload being shared, both firms will have a high cost for being involved in the audit in terms of senior manager and partner
time. These costs will be passed on to the client within the audit fee.
The two audit firms may use very different audit approaches and terminology. This could make it difficult for the audit firms
to work closely together, negating some of the efficiency and cost benefits discussed above. Problems could arise in deciding
which firm’s method to use, for example, to calculate materiality, design and pick samples for audit procedures, or evaluate
controls within the accounting system. It may be impossible to reconcile two different methods and one firm’s methods may
end up dominating the audit process, which then eliminates the benefit of a joint audit being conducted. It could be time
consuming to develop a ‘joint’ audit approach, based on elements of each of the two firms’ methodologies, time which
obviously would not have been spent if a single firm was providing the audit.
There may be problems for the two audit firms to work together harmoniously. Lead & Co may feel that ultimately they will
be replaced by Chien & Co as audit provider, and therefore could be unwilling to offer assistance and help.
Potentially, problems could arise in terms of liability. In the event of litigation, because both firms have provided the audit
opinion, it follows that the firms would be jointly liable. The firms could blame each other for any negligence which was
discovered, making the litigation process more complex than if a single audit firm had provided the opinion. However, it could
be argued that joint liability is not necessarily a drawback, as the firms should both be covered by professional indemnity
insurance. -
第4题:
What is Mr. Jones’s position in his company ()A. He is the president of Bestway Co.
B.He is the general manager of Nile Co. C.He is the sales manager of Lee Brothers’.
参考答案:B
-
第5题:
Shoe Co, a shoe manufacturer, has developed a new product called the ‘Smart Shoe’ for children, which has a built-in tracking device. The shoes are expected to have a life cycle of two years, at which point Shoe Co hopes to introduce a new type of Smart Shoe with even more advanced technology. Shoe Co plans to use life cycle costing to work out the total production cost of the Smart Shoe and the total estimated profit for the two-year period.
Shoe Co has spent $5·6m developing the Smart Shoe. The time spent on this development meant that the company missed out on the opportunity of earning an estimated $800,000 contribution from the sale of another product.
The company has applied for and been granted a ten-year patent for the technology, although it must be renewed each year at a cost of $200,000. The costs of the patent application were $500,000, which included $20,000 for the salary costs of Shoe Co’s lawyer, who is a permanent employee of the company and was responsible for preparing the application.
The following information is also available for the next two years:
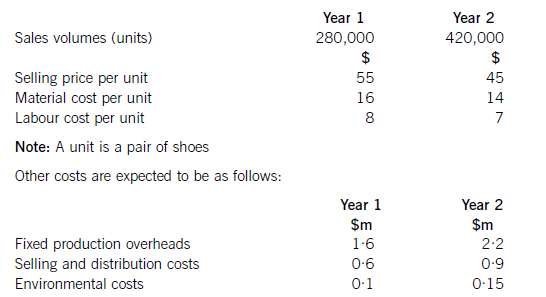
Shoe Co is still negotiating with marketing companies with regard to its advertising campaign, so is uncertain as to what the total marketing costs will be each year. However, the following information is available as regards the probabilities of the range of costs which are likely to be incurred:

Required:
Applying the principles of life cycle costing, calculate the total expected profit for Shoe Co for the two-year period.
(10 marks)
正确答案:
Totalsalesrevenue=(280,000x$55)+(420,000x$45)=$15·4m+18·9m=$34·3m.NoteTheexpectedprofithasbeencalculatedusinglifecyclecostingnotrelevantcosting.Hence,the$20,000salarycostincludedinpatentcostsshouldbeincludedinthelifecyclecost.Similarly,theopportunitycostof$800,000isnotincludedusinglifecyclecostingwhereasifrelevantcostingwasbeingusedtodecideonaparticularcourseofaction,theopportunitycostwouldbeincluded.Working1Expectedmarketingcostinyear1:(0·2x$2·2m)+(0·5x$2·6m)+(0·3x$2·9m)=$2·61mExpectedmarketingcostyear2:(0·3x$1·8m)+(0·4x$2·1m)+(0·3x$2·3m)=$2·07mTotalexpectedmarketingcost=$4·68m -
第6题:
(a) Contrast the role of internal and external auditors. (8 marks)
(b) Conoy Co designs and manufactures luxury motor vehicles. The company employs 2,500 staff and consistently makes a net profit of between 10% and 15% of sales. Conoy Co is not listed; its shares are held by 15 individuals, most of them from the same family. The maximum shareholding is 15% of the share capital.
The executive directors are drawn mainly from the shareholders. There are no non-executive directors because the company legislation in Conoy Co’s jurisdiction does not require any. The executive directors are very successful in running Conoy Co, partly from their training in production and management techniques, and partly from their ‘hands-on’ approach providing motivation to employees.
The board are considering a significant expansion of the company. However, the company’s bankers are
concerned with the standard of financial reporting as the financial director (FD) has recently left Conoy Co. The board are delaying provision of additional financial information until a new FD is appointed.
Conoy Co does have an internal audit department, although the chief internal auditor frequently comments that the board of Conoy Co do not understand his reports or provide sufficient support for his department or the internal control systems within Conoy Co. The board of Conoy Co concur with this view. Anders & Co, the external auditors have also expressed concern in this area and the fact that the internal audit department focuses work on control systems, not financial reporting. Anders & Co are appointed by and report to the board of Conoy Co.
The board of Conoy Co are considering a proposal from the chief internal auditor to establish an audit committee.
The committee would consist of one executive director, the chief internal auditor as well as three new appointees.
One appointee would have a non-executive seat on the board of directors.
Required:
Discuss the benefits to Conoy Co of forming an audit committee. (12 marks)
正确答案:
(a)Roleofinternalandexternalauditors–differencesObjectivesThemainobjectiveofinternalauditistoimproveacompany’soperations,primarilyintermsofvalidatingtheefficiencyandeffectivenessoftheinternalcontrolsystemsofacompany.Themainobjectiveoftheexternalauditoristoexpressanopiniononthetruthandfairnessofthefinancialstatements,andotherjurisdictionspecificrequirementssuchasconfirmingthatthefinancialstatementscomplywiththereportingrequirementsincludedinlegislation.ReportingInternalauditreportsarenormallyaddressedtotheboardofdirectors,orotherpeoplechargedwithgovernancesuchastheauditcommittee.Thosereportsarenotpubliclyavailable,beingconfidentialbetweentheinternalauditorandtherecipient.Externalauditreportsareprovidedtotheshareholdersofacompany.Thereportisattachedtotheannualfinancialstatementsofthecompanyandisthereforepubliclyavailabletotheshareholdersandanyreaderofthefinancialstatements.ScopeofworkTheworkoftheinternalauditornormallyrelatestotheoperationsoftheorganisation,includingthetransactionprocessingsystemsandthesystemstoproducetheannualfinancialstatements.Theinternalauditormayalsoprovideotherreportstomanagement,suchasvalueformoneyauditswhichexternalauditorsrarelybecomeinvolvedwith.Theworkoftheexternalauditorrelatesonlytothefinancialstatementsoftheorganisation.However,theinternalcontrolsystemsoftheorganisationwillbetestedastheseprovideevidenceonthecompletenessandaccuracyofthefinancialstatements.RelationshipwithcompanyInmostorganisations,theinternalauditorisanemployeeoftheorganisation,whichmayhaveanimpactontheauditor’sindependence.However,insomeorganisationstheinternalauditfunctionisoutsourced.Theexternalauditorisappointedbytheshareholdersofanorganisation,providingsomedegreeofindependencefromthecompanyandmanagement.(b)BenefitsofauditcommitteeinConoyCoAssistancewithfinancialreporting(nofinanceexpertise)TheexecutivedirectorsofConoyCodonotappeartohaveanyspecificfinancialskills–asthefinancialdirectorhasrecentlyleftthecompanyandhasnotyetbeenreplaced.ThismaymeanthatfinancialreportinginConoyCoislimitedorthattheothernon-financialdirectorsspendasignificantamountoftimekeepinguptodateonfinancialreportingissues.AnauditcommitteewillassistConoyCobyprovidingspecialistknowledgeoffinancialreportingonatemporarybasis–atleastoneofthenewappointeesshouldhaverelevantandrecentfinancialreportingexperienceundercodesofcorporategovernance.ThiswillallowtheexecutivedirectorstofocusonrunningConoyCo.EnhanceinternalcontrolsystemsTheboardofConoyCodonotnecessarilyunderstandtheworkoftheinternalauditor,ortheneedforcontrolsystems.ThismeansthatinternalcontrolwithinConoyComaybeinadequateorthatemployeesmaynotrecognisetheimportanceofinternalcontrolsystemswithinanorganisation.TheauditcommitteecanraiseawarenessoftheneedforgoodinternalcontrolsystemssimplybybeingpresentinConoyCoandbyeducatingtheboardontheneedforsoundcontrols.Improvingtheinternalcontrol‘climate’willensuretheneedforinternalcontrolsisunderstoodandreducecontrolerrors.RelianceonexternalauditorsConoyCo’sinternalauditorscurrentlyreporttotheboardofConoyCo.Aspreviouslynoted,thelackoffinancialandcontrolexpertiseontheboardwillmeanthatexternalauditorreportsandadvicewillnotnecessarilybeunderstood–andtheboardmayrelytoomuchonexternalauditorsIfConoyCoreporttoanauditcommitteethiswilldecreasethedependenceoftheboardontheexternalauditors.Theauditcommitteecantaketimetounderstandtheexternalauditor’scomments,andthenviathenon-executivedirector,ensurethattheboardtakeactiononthosecomments.AppointmentofexternalauditorsAtpresent,theboardofConoyCoappointtheexternalauditors.Thisraisesissuesofindependenceastheboardmaybecometoofamiliarwiththeexternalauditorsandsoappointonthisfriendshipratherthanmerit.Ifanauditcommitteeisestablished,thenthiscommitteecanrecommendtheappointmentoftheexternalauditors.Thecommitteewillhavethetimeandexpertisetoreviewthequalityofserviceprovidedbytheexternalauditors,removingtheindependenceissue.Corporategovernancerequirements–bestpracticeConoyCodonotneedtofollowcorporategovernancerequirements(thecompanyisnotlisted).However,notfollowingthoserequirementsmaystarttohaveadverseeffectsonConoy.Forexample,ConoyCo’sbankisalreadyconcernedaboutthelackoftransparencyinreporting.EstablishinganauditcommitteewillshowthattheboardofConoyCoarecommittedtomaintainingappropriateinternalsystemsinthecompanyandprovidingthestandardofreportingexpectedbylargecompanies.Obtainingthenewbankloanshouldalsobeeasierasthebankwillbesatisfiedwithfinancialreportingstandards.Givennonon-executives–independentadvicetoboardCurrentlyConoyCodoesnothaveanynon-executivedirectors.Thismeansthatthedecisionsoftheexecutivedirectorsarenotbeingchallengedbyotherdirectorsindependentofthecompanyandwithlittleornofinancialinterestinthecompany.Theappointmentofanauditcommitteewithonenon-executivedirectorontheboardofConoyCowillstarttoprovidesomenon-executiveinputtoboardmeetings.Whilenotsufficientintermsofcorporategovernancerequirements(aboutequalnumbersofexecutiveandnon-executivedirectorsareexpected)itdoesshowtheboardofConoyCoareattemptingtoestablishappropriategovernancesystems.AdviceonriskmanagementFinally,thereareothergeneralareaswhereConoyCowouldbenefitfromanauditcommittee.Forexample,lackofcorporategovernancestructuresprobablymeansConoyCodoesnothaveariskmanagementcommittee.Theauditcommitteecanalsoprovideadviceonriskmanagement,helpingtodecreasetheriskexposureofthecompany. -
第7题:
(a) An assistant of yours has been criticised over a piece of assessed work that he produced for his study course for giving the definition of a non-current asset as ‘a physical asset of substantial cost, owned by the company, which will last longer than one year’.
Required:
Provide an explanation to your assistant of the weaknesses in his definition of non-current assets when
compared to the International Accounting Standards Board’s (IASB) view of assets. (4 marks)
(b) The same assistant has encountered the following matters during the preparation of the draft financial statements of Darby for the year ending 30 September 2009. He has given an explanation of his treatment of them.
(i) Darby spent $200,000 sending its staff on training courses during the year. This has already led to an
improvement in the company’s efficiency and resulted in cost savings. The organiser of the course has stated that the benefits from the training should last for a minimum of four years. The assistant has therefore treated the cost of the training as an intangible asset and charged six months’ amortisation based on the average date during the year on which the training courses were completed. (3 marks)
(ii) During the year the company started research work with a view to the eventual development of a new
processor chip. By 30 September 2009 it had spent $1·6 million on this project. Darby has a past history
of being particularly successful in bringing similar projects to a profitable conclusion. As a consequence the
assistant has treated the expenditure to date on this project as an asset in the statement of financial position.
Darby was also commissioned by a customer to research and, if feasible, produce a computer system to
install in motor vehicles that can automatically stop the vehicle if it is about to be involved in a collision. At
30 September 2009, Darby had spent $2·4 million on this project, but at this date it was uncertain as to
whether the project would be successful. As a consequence the assistant has treated the $2·4 million as an
expense in the income statement. (4 marks)
(iii) Darby signed a contract (for an initial three years) in August 2009 with a company called Media Today to
install a satellite dish and cabling system to a newly built group of residential apartments. Media Today will
provide telephone and television services to the residents of the apartments via the satellite system and pay
Darby $50,000 per annum commencing in December 2009. Work on the installation commenced on
1 September 2009 and the expenditure to 30 September 2009 was $58,000. The installation is expected
to be completed by 31 October 2009. Previous experience with similar contracts indicates that Darby will
make a total profit of $40,000 over the three years on this initial contract. The assistant correctly recorded
the costs to 30 September 2009 of $58,000 as a non-current asset, but then wrote this amount down to
$40,000 (the expected total profit) because he believed the asset to be impaired.
The contract is not a finance lease. Ignore discounting. (4 marks)
Required:
For each of the above items (i) to (iii) comment on the assistant’s treatment of them in the financial
statements for the year ended 30 September 2009 and advise him how they should be treated under
International Financial Reporting Standards.
Note: the mark allocation is shown against each of the three items above.
正确答案:
(a)Therearefourelementstotheassistant’sdefinitionofanon-currentassetandheissubstantiallyincorrectinrespectofallofthem.Thetermnon-currentassetswillnormallyincludeintangibleassetsandcertaininvestments;theuseoftheterm‘physicalasset’wouldbespecifictotangibleassetsonly.Whilstitisusuallythecasethatnon-currentassetsareofrelativelyhighvaluethisisnotadefiningaspect.Awastepaperbinmayexhibitthecharacteristicsofanon-currentasset,butonthegroundsofmaterialityitisunlikelytobetreatedassuch.Furthermorethepastcostofanassetmaybeirrelevant;nomatterhowmuchanassethascost,itistheexpectationoffutureeconomicbenefitsflowingfromaresource(normallyintheform.offuturecashinflows)thatdefinesanassetaccordingtotheIASB’sFrameworkforthepreparationandpresentationoffinancialstatements.Theconceptofownershipisnolongeracriticalaspectofthedefinitionofanasset.Itisprobablythecasethatmostnoncurrentassetsinanentity’sstatementoffinancialpositionareownedbytheentity;however,itistheabilityto‘control’assets(includingpreventingothersfromhavingaccesstothem)thatisnowadefiningfeature.Forexample:thisisanimportantcharacteristicintreatingafinanceleaseasanassetofthelesseeratherthanthelessor.Itisalsotruethatmostnon-currentassetswillbeusedbyanentityformorethanoneyearandapartofthedefinitionofproperty,plantandequipmentinIAS16Property,plantandequipmentreferstoanexpectationofuseinmorethanoneperiod,butthisisnotnecessarilyalwaysthecase.Itmaybethatanon-currentassetisacquiredwhichprovesunsuitablefortheentity’sintendeduseorisdamagedinanaccident.Inthesecircumstancesassetsmaynothavebeenusedforlongerthanayear,butneverthelesstheywerereportedasnon-currentsduringthetimetheywereinuse.Anon-currentassetmaybewithinayearoftheendofitsusefullifebut(unlessasaleagreementhasbeenreachedunderIFRS5Non-currentassetsheldforsaleanddiscontinuedoperations)wouldstillbereportedasanon-currentassetifitwasstillgivingeconomicbenefits.Anotherdefiningaspectofnon-currentassetsistheirintendedusei.e.heldforcontinuinguseintheproduction,supplyofgoodsorservices,forrentaltoothersorforadministrativepurposes.(b)(i)TheexpenditureonthetrainingcoursesmayexhibitthecharacteristicsofanassetinthattheyhaveandwillcontinuetobringfutureeconomicbenefitsbywayofincreasedefficiencyandcostsavingstoDarby.However,theexpenditurecannotberecognisedasanassetonthestatementoffinancialpositionandmustbechargedasanexpenseasthecostisincurred.Themainreasonforthislieswiththeissueof’control’;itisDarby’semployeesthathavethe‘skills’providedbythecourses,buttheemployeescanleavethecompanyandtaketheirskillswiththemor,throughaccidentorinjury,maybedeprivedofthoseskills.AlsothecapitalisationofstafftrainingcostsisspecificallyprohibitedunderInternationalFinancialReportingStandards(specificallyIAS38Intangibleassets).(ii)Thequestionspecificallystatesthatthecostsincurredtodateonthedevelopmentofthenewprocessorchipareresearchcosts.IAS38statesthatresearchcostsmustbeexpensed.Thisismainlybecauseresearchistherelativelyearlystageofanewprojectandanyfuturebenefitsaresofarinthefuturethattheycannotbeconsideredtomeetthedefinitionofanasset(probablefutureeconomicbenefits),despitethegoodrecordofsuccessinthepastwithsimilarprojects.Althoughtheworkontheautomaticvehiclebrakingsystemisstillattheresearchstage,thisisdifferentinnaturefromthepreviousexampleastheworkhasbeencommissionedbyacustomer,Assuch,fromtheperspectiveofDarby,itisworkinprogress(acurrentasset)andshouldnotbewrittenoffasanexpense.Anoteofcautionshouldbeaddedhereinthatthequestionsaysthatthesuccessoftheprojectisuncertainwhichpresumablymeansitmaynotbecompleted.ThisdoesnotmeanthatDarbywillnotreceivepaymentfortheworkithascarriedout,butitshouldbecheckedtothecontracttoensurethattheamountithasspenttodate($2·4million)willberecoverable.Intheeventthatsay,forexample,thecontractstatedthatonly$2millionwouldbeallowedforresearchcosts,thiswouldplacealimitonhowmuchDarbycouldtreatasworkinprogress.Ifthiswerethecasethen,forthisexample,Darbywouldhavetoexpense$400,000andtreatonly$2millionasworkinprogress.(iii)Thequestionsuggeststhecorrecttreatmentforthiskindofcontractistotreatthecostsoftheinstallationasanon-currentassetand(presumably)depreciateitoveritsexpectedlifeof(atleast)threeyearsfromwhenitbecomesavailableforuse.Inthiscasetheassetwillnotcomeintouseuntilthenextfinancialyear/reportingperiodandnodepreciationneedstobeprovidedat30September2009.Thecapitalisedcoststodateof$58,000shouldonlybewrittendownifthereisevidencethattheassethasbecomeimpaired.Impairmentoccurswheretherecoverableamountofanassetislessthanitscarryingamount.Theassistantappearstobelievethattherecoverableamountisthefutureprofit,whereas(inthiscase)itisthefuture(net)cashinflows.Thusanyimpairmenttestat30September2009shouldcomparethecarryingamountof$58,000withtheexpectednetcashflowfromthesystemof$98,000($50,000perannumforthreeyearslessfuturecashoutflowstocompletiontheinstallationof$52,000(seenotebelow)).Asthefuturenetcashflowsareinexcessofthecarryingamount,theassetisnotimpairedanditshouldnotbewrittendownbutshownasanon-currentasset(underconstruction)atcostof$58,000.Note:asthecontractisexpectedtomakeaprofitof$40,000onincomeof$150,000,thetotalcostsmustbe$110,000,withcoststodateat$58,000thisleavescompletioncostsof$52,000. -
第8题:
The following information is available for a manufacturing company which produces multiple products:
(i) The product mix ratio
(ii) Contribution to sales ratio for each product
(iii) General fixed costs
(iv) Method of apportioning general fixed costs
Which of the above are required in order to calculate the break-even sales revenue for the company?
A.All of the above
B.(i), (ii) and (iii) only
C.(i), (iii) and (iv) only
D.(ii) and (iii) only
正确答案:BThe method of apportioning general fixed costs is not required to calculate the break-even sales revenue.
-
第9题:
资料:From: Peter Manx pmanx@bettertraining.co.au
To: John Morgan jmorgan@ISB.co.au
Date: March 23
Subject: Better Training Ltd.
Dear Mr. Morgan,
As a leading human resource specialist, Better Training Ltd. is uniquely able to respond to your current training needs. Please take the time to review the attached brochure. I am confident that you will find courses of immediate relevance to ISB International Ltd.
Our standard curriculum covers topics such as managerial development, technical training, sales, marketing, and more. Our instructors-professionals and leaders in their fields-conduct engaging seminars while maintaining the quality for which we are known. In addition to our regular courses, we can deliver individually tailored programs at the location of your choice.
I am certain that your organization will benefit from our services Contact us today to see how we can help your employees increase their technical and professional expertise.
Sincerely,
Peter Manx
President
What does Peter Manx hope to arrange?A.business relationship with ISB International.
B.Assistance with an advertising campaign.
C.Revisions of a company brochure.
D.Technical support for Better Training staff.答案:A解析:本题考查的是细节理解。
【关键词】 Peter Manx hope to arrange
【主题句】第3自然段I am certain that your organization will benefit from our services.我确信您的公司将从我们的服务中获益。Contact us today to see how we can help your employees increase their technical and professional expertise.请今天就与我们联系,看看我们能如何帮助您的雇员增进技术和专业技能。
【解析】本题的问题是“Peter Manx希望如何安排”。A选项“与ISB国际建立商业联系”,B选项“为广告活动提供援助”,C选项“校订公司宣传册”,D选项“为Better Training的员工提供技术支持”。根据主题句可知,Peter Manx是Better Training的董事长,希望为ISB国际提供商业服务。 -
第10题:
A customer has purchased three IBM System Storage DS8300 systems and would like to have their SAN and storage administrator trained. The customer is worried about having much of their staff out of the office at the same time attending courses. Which training alternative provides the necessary training with the least impact()
- A、purchase the training CD for the disk subsystem and have the staff do self-paced training
- B、have the IBM Service Support Representative perform the training
- C、contact IBM Education Services for an onsite training class
- D、send one person at a time to an IBM training session
正确答案:C -
第11题:
单选题Passage2The way people work has changed. The increasing use of technology presents new and continual challenges to small and large businesses,employees and managers,teachers and students.Everyone,it seems,is being affected by the technological revolution. Store clerks,for example,now use increasingly complex computerized cash registers,while university professors must learn to adapt their teaching skills in order to lead distance learning course.In today's world,training and learning do not stop when we finish school;they must now continue throughout our working lives. The Hong Kong government conducted a survey on the employment concerns,and training needs of its workforce. For many managers and other professionals the biggest challenge,as well as change,in the workplace,was the increased use of computers and computerized machinery or equipment. The need for experienced employees who could use this kind of equipment rose drastically. Many of those in the workplace at this time experienced changes in job requirements and had to attend job-related training or re-training courses.The changing work environment is also affecting education and how we learn. In Finland, a report on strategies for education and training in the information age discussed the changing roles of both teacher and student. With the increased use of technology and the growth of distance learning, the teacher has become more of a tutor who guides a student, rather than a lecturer. In turn, the student has to take more responsibility for his or her learning in the absence of direct teacher contact. The report also stressed that high school and university students should learn computer skills in order to cope with the demands of the future workplace.The Finnish report also highlighted the need for teacher training, and re-training, and suggested that the salaries and job descriptions of teachers be reviewed because of future demands expected in their jobs. Previously university professors may have held lectures between the weekday hours of 9:00A.M. and 5:00 P.M. in large halls filled with students. Now, they may spend part of their day lecturing larger groups of students on campus, and then conduct afternoon or evening classes online, with students in five different countries.As technologies grow and develop, ongoing training will continue to be necessary. To be successful in the workplace, people will not stop learning when they leave school-lifelong learning will become a way of life.From the first paragraph of the passage we know that_______.Aeveryone has to learn how to use complex computers
Btechnological revolution has brought changes to people's work
Cthe use of new technology has got small business into large ones
Deven university professors have to learn the new technology in distance courses
正确答案: C解析: -
第12题:
单选题Which definition best describes the staff training service component within the implement phase? Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:()。Aimproving the network management system and the performance and functionality of infrastructure operations
Bproviding a step-by-step plan that details the installation and service-commission tasks required in order to create a controlled-implementation environment that emulates a customer network
Cdeveloping and implementing a training plan using classes, workshops, or c-learning courses
Dcompiling a training manual for use in ongoing operations
Ereducing the risk of downtime due to facilities-related problems
正确答案: C解析: 暂无解析 -
第13题:
(ii) The sales director has suggested to Damian, that to encourage the salesmen to accept the new arrangement,
the company should increase the value of the accessories of their own choice that can be fitted to the low
emission cars.
State, giving reasons, whether or not Damian should implement the sales director’s suggestion.
(2 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Damian should not agree to the sales director’s suggestion. The salesmen will each make a significant annual income
tax saving under the proposal, whereas the company will also be offset (at least partly) by the reduction in the dealer’s
bulk discount. Further, 100% first year allowance tax incentive for low emission cars is not guaranteed beyond 31 March
2008, and it is unlikely that any change in policy with regards to the provision of additional accessories will, once
implemented, be easily reversible. -
第14题:
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Lamont Co. The company’s principal activity is wholesaling frozen
fish. The draft consolidated financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2007 show revenue of $67·0 million
(2006 – $62·3 million), profit before taxation of $11·9 million (2006 – $14·2 million) and total assets of
$48·0 million (2006 – $36·4 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) In early 2007 a chemical leakage from refrigeration units owned by Lamont caused contamination of some of its
property. Lamont has incurred $0·3 million in clean up costs, $0·6 million in modernisation of the units to
prevent future leakage and a $30,000 fine to a regulatory agency. Apart from the fine, which has been expensed,
these costs have been capitalised as improvements. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Lamont Co for the year ended
31 March 2007.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
3 LAMONT CO
(a) Chemical leakage
(i) Matters
■ $30,000 fine is very immaterial (just 1/4% profit before tax). This is revenue expenditure and it is correct that it
has been expensed to the income statement.
■ $0·3 million represents 0·6% total assets and 2·5% profit before tax and is not material on its own. $0·6 million
represents 1·2% total assets and 5% profit before tax and is therefore material to the financial statements.
■ The $0·3 million clean-up costs should not have been capitalised as the condition of the property is not improved
as compared with its condition before the leakage occurred. Although not material in isolation this amount should
be adjusted for and expensed, thereby reducing the aggregate of uncorrected misstatements.
■ It may be correct that $0·6 million incurred in modernising the refrigeration units should be capitalised as a major
overhaul (IAS 16 Property, Plant and Equipment). However, any parts scrapped as a result of the modernisation
should be treated as disposals (i.e. written off to the income statement).
■ The carrying amount of the refrigeration units at 31 March 2007, including the $0·6 million for modernisation,
should not exceed recoverable amount (i.e. the higher of value in use and fair value less costs to sell). If it does,
an allowance for the impairment loss arising must be recognised in accordance with IAS 36 Impairment of Assets.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ A breakdown/analysis of costs incurred on the clean-up and modernisation amounting to $0·3 million and
$0·6 million respectively.
■ Agreement of largest amounts to invoices from suppliers/consultants/sub-contractors, etc and settlement thereof
traced from the cash book to the bank statement.
■ Physical inspection of the refrigeration units to confirm their modernisation and that they are in working order. (Do
they contain frozen fish?)
■ Sample of components selected from the non-current asset register traced to the refrigeration units and inspected
to ensure continuing existence.
■ $30,000 penalty notice from the regulatory agency and corresponding cash book payment/payment per the bank
statement.
■ Written management representation that there are no further penalties that should be provided for or disclosed other
than the $30,000 that has been accounted for. -
第15题:
MONTHLY MEETING MINUTES OF BOARD OF DIRECTORS Time: 2:30 p.m., March 5, 2015 Place: Conference room, second floor of 3T Co. Ltd. Participants: All the directors Chairman: Chairman of the board, Mr. William Forest Minutes keeper: Linda The main activities at the meeting are as follows: Firstly, Mr. William Forest, chairman of the board, made a report on the work and total sales of the company this season. Then the report was followed by a heated discussion. Secondly, all the directors agreed to hold a press conference for the company next month. Thirdly, the meeting suggested inviting experts from Canada to give a five-day training course to staff in the Sales Department. The meeting finished at 3:30 p.m.
1. Who are the meeting participants().
A. The executive assistants.
B. The directors.
C. The interviewees.
2. How many activities does the meeting have().
A. The executive assistants.
B. The directors.
C. The interviewees.
3. Mr. William Forest made a report ()this season.
A. on training course to staff in the Sales Department
B. on the advertisement policies of the company
C. on the work and total sales of the company
4. What did all the directors agree to do ()
A. To carry out a training project in the company next year.
B. To have another board meeting of all directors next season.
C. Tohave a press conference for the company next month.
5. How long did the meeting last ()
A.1.5 hours.
B.1 hour.
C.2 hour.
参考答案:子问题 1:B; 子问题 2:C; 子问题 3:C; 子问题 4:C; 子问题 5:B
-
第16题:
Which term means “the profit that a company has obtained from selling its products or services in a particular period of time, in relation to its sales for the period”?A、Annual income
B、operation profit
C、return on sales
D、net profit
参考答案:C
-
第17题:
Following a competitive tender, your audit firm Cal & Co has just gained a new audit client Tirrol Co. You are the manager in charge of planning the audit work. Tirrol Co’s year end is 30 June 2009 with a scheduled date to complete the audit of 15 August 2009. The date now is 3 June 2009.
Tirrol Co provides repair services to motor vehicles from 25 different locations. All inventory, sales and purchasing systems are computerised, with each location maintaining its own computer system. The software in each location is
the same because the programs were written specifically for Tirrol Co by a reputable software house. Data from each location is amalgamated on a monthly basis at Tirrol Co’s head office to produce management and financial accounts.
You are currently planning your audit approach for Tirrol Co. One option being considered is to re-write Cal & Co’s audit software to interrogate the computerised inventory systems in each location of Tirrol Co (except for head office)
as part of inventory valuation testing. However, you have also been informed that any computer testing will have to be on a live basis and you are aware that July is a major holiday period for your audit firm.
Required:
(a) (i) Explain the benefits of using audit software in the audit of Tirrol Co; (4 marks)
(ii) Explain the problems that may be encountered in the audit of Tirrol Co and for each problem, explain
how that problem could be overcome. (10 marks)
(b) Following a discussion with the management at Tirrol Co you now understand that the internal audit department are prepared to assist with the statutory audit. Specifically, the chief internal auditor is prepared to provide you with documentation on the computerised inventory systems at Tirrol Co. The documentation provides details of the software and shows diagrammatically how transactions are processed through the inventory system. This documentation can be used to significantly decrease the time needed to understand the computer systems and enable audit software to be written for this year’s audit.
Required:
Explain how you will evaluate the computer systems documentation produced by the internal audit
department in order to place reliance on it during your audit. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(a)(i)BenefitsofusingauditsoftwareStandardsystemsatclientThesamecomputerisedsystemsandprogramsasusedinall25branchesofTirrolCo.Thismeansthatthesameauditsoftwarecanbeusedineachlocationprovidingsignificanttimesavingscomparedtothesituationwhereclientsystemsaredifferentineachlocation.UseactualcomputerfilesnotcopiesorprintoutsUseofauditsoftwaremeansthattheTirrolCo’sactualinventoryfilescanbetestedratherthanhavingtorelyonprintoutsorscreenimages.Thelattercouldbeincorrect,byaccidentorbydeliberatemistake.Theauditfirmwillhavemoreconfidencethatthe‘real’fileshavebeentested.TestmoreitemsUseofsoftwarewillmeanthatmoreinventoryrecordscanbetested–itispossiblethatallproductlinescouldbetestedforobsolescenceratherthanasampleusingmanualtechniques.Theauditorwillthereforegainmoreevidenceandhavegreaterconfidencethatinventoryisvaluedcorrectly.CostTherelativecostofusingauditsoftwaredecreasesthemoreyearsthatsoftwareisused.Anycostoverrunsthisyearcouldbeoffsetagainsttheauditfeesinfutureyearswhentheactualexpensewillbeless.(ii)ProblemsontheauditofTirrolTimescale–sixweekreportingdeadline–auditplanningTheauditreportisduetobesignedsixweeksaftertheyearend.Thismeansthattherewillbeconsiderablepressureontheauditortocompleteauditworkwithoutcompromisingstandardsbyrushingprocedures.Thisproblemcanbeovercomebycarefulplanningoftheaudit,useofexperiencedstaffandensuringotherstaffsuchassecondpartnerreviewsarebookedwellinadvance.Timescale–sixweekreportingdeadline–softwareissuesTheauditreportisduetobesignedaboutsixweeksaftertheyearend.Thismeansthatthereislittletimetowriteandtestauditsoftware,letaloneusethesoftwareandevaluatetheresultsoftesting.Thisproblemcanbealleviatedbycarefulplanning.AccesstoTirrolCo’ssoftwareanddatafilesmustbeobtainedassoonaspossibleandworkcommencedontailoringCal&Co’ssoftwarefollowingthis.Specialistcomputerauditstaffshouldbebookedassoonaspossibletoperform.thiswork.FirstyearauditcostsTherelativecostsofanauditinthefirstyearataclienttendtobegreaterduetotheadditionalworkofascertainingclientsystems.ThismeansthatCal&Comayhavealimitedbudgettodocumentsystemsincludingcomputersystems.Thisproblemcanbealleviatedtosomeextentagainbygoodauditplanning.Themanagermustalsomonitortheauditprocesscarefully,ensuringthatanyadditionalworkcausedbytheclientnotprovidingaccesstosystemsinformationincludingcomputersystemsisidentifiedandaddedtothetotalbillingcostoftheaudit.StaffholidaysMostoftheauditworkwillbecarriedoutinJuly,whichisalsothemonthwhenmanyofCal&Costafftaketheirannualholiday.Thismeansthattherewillbeashortageofauditstaff,particularlyasauditworkforTirrolCoisbeingbookedwithlittlenotice.Theproblemcanbealleviatedbybookingstaffassoonaspossibleandthenidentifyinganyshortages.Wherenecessary,staffmaybeborrowedfromotherofficesorevendifferentcountriesonasecondmentbasiswhereshortagesareacute.Non-standardsystemsTirrolCo’scomputersoftwareisnon-standard,havingbeenwrittenspecificallyfortheorganisation.Thismeansthatmoretimewillbenecessarytounderstandthesystemthanifstandardsystemswereused.Thisproblemcanbealleviatedeitherbyobtainingdocumentationfromtheclientorbyapproachingthesoftwarehouse(withTirrolCo’spermission)toseeiftheycanassistwithprovisionofinformationondatastructuresfortheinventorysystems.ProvisionofthisinformationwilldecreasethetimetakentotailorauditsoftwareforuseinTirrolCo.IssuesoflivetestingCal&Cohasbeeninformedthatinventorysystemsmustbetestedonalivebasis.Thisincreasestheriskofaccidentalamendmentordeletionofclientdatasystemscomparedtotestingcopyfiles.Tolimitthepossibilityofdamagetoclientsystems,Cal&CocanconsiderperforminginventorytestingondayswhenTirrolCoisnotoperatinge.g.weekends.Attheworst,backupsofdatafilestakenfromthepreviousdaycanbere-installedwhenCal&Co’stestingiscomplete.ComputersystemsTheclienthas25locations,witheachlocationmaintainingitsowncomputersystem.Itispossiblethatcomputersystemsarenotcommonacrosstheclientduetoamendmentsmadeatthebranchlevel.Thisproblemcanbeovercometosomeextentbyaskingstaffateachbranchwhethersystemshavebeenamendedandfocusingauditworkonmaterialbranches.UsefulnessofauditsoftwareTheuseofauditsoftwareatTirrolCodoesappeartohavesignificantproblemsthisyear.Thismeansthateveniftheauditsoftwareisready,theremaystillbesomeriskofincorrectconclusionsbeingderivedduetolackoftesting,etc.Thisproblemcanbealleviatedbyseriouslyconsideringthepossibilityofusingamanualauditthisyear.Themanagermayneedtoinvestigatewhetheramanualauditisfeasibleandifsowhetheritcouldbecompletedwithinthenecessarytimescalewithminimalauditrisk.(b)RelianceoninternalauditdocumentationTherearetwoissuestoconsider;theabilityofinternalaudittoproducethedocumentationandtheactualaccuracyofthedocumentationitself.Theabilityoftheinternalauditdepartmenttoproducethedocumentationcanbedeterminedby:–Ensuringthatthedepartmenthasstaffwhohaveappropriatequalifications.Provisionofarelevantqualificatione.g.membershipofacomputerrelatedinstitutewouldbeappropriate.–Ensuringthatthisandsimilardocumentationisproducedusingarecognisedplanandthatthedocumentationistestedpriortouse.Theuseofdifferentstaffintheinternalauditdepartmenttoproduceandtestdocumentationwillincreaseconfidenceinitsaccuracy.–Ensuringthatthedocumentationisactuallyusedduringinternalauditworkandthatproblemswithdocumentationarenotedandinvestigatedaspartofthatwork.Beinggivenaccesstointernalauditreportsontheinventorysoftwarewillprovideappropriateevidence.Regardingtheactualdocumentation:–Reviewingthedocumentationtoensurethatitappearslogicalandthattermsandsymbolsareusedconsistentlythroughout.Thiswillprovideevidencethattheflowcharts,etcshouldbeaccurate.–Comparingthedocumentationagainstthe‘live’inventorysystemtoensureitcorrectlyreflectstheinventorysystem.Thiscomparisonwillincludetracingindividualtransactionsthroughtheinventorysystems.–UsingpartofthedocumentationtoamendCal&Co’sauditsoftware,andthenensuringthatthesoftwareprocessesinventorysystemdataaccurately.However,thisstagemaybelimitedduetotheneedtouselivefilesatTirrolCo. -
第18题:
The following financial information relates to HGR Co:
Statement of financial position at the current date (extracts)
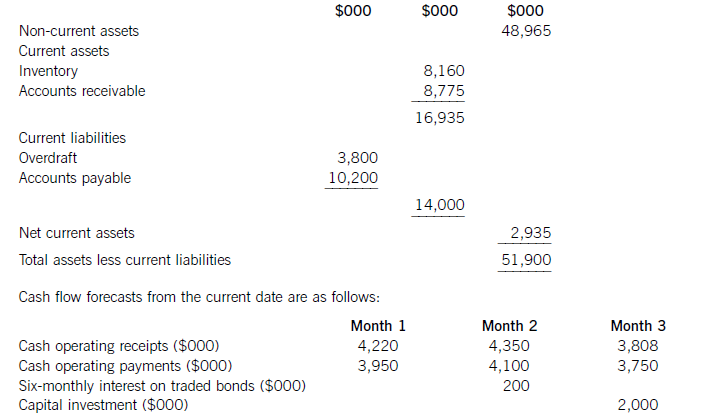
The finance director has completed a review of accounts receivable management and has proposed staff training and operating procedure improvements, which he believes will reduce accounts receivable days to the average sector value of 53 days. This reduction would take six months to achieve from the current date, with an equal reduction in each month. He has also proposed changes to inventory management methods, which he hopes will reduce inventory days by two days per month each month over a three-month period from the current date. He does not expect any change in the current level of accounts payable.
HGR Co has an overdraft limit of $4,000,000. Overdraft interest is payable at an annual rate of 6·17% per year, with payments being made each month based on the opening balance at the start of that month. Credit sales for the year to the current date were $49,275,000 and cost of sales was $37,230,000. These levels of credit sales and cost of sales are expected to be maintained in the coming year. Assume that there are 365 working days in each year.
Required:
(a) Discuss the working capital financing strategy of HGR Co. (7 marks)
(b) For HGR Co, calculate:
(i) the bank balance in three months’ time if no action is taken; and
(ii) the bank balance in three months’ time if the finance director’s proposals are implemented.
Comment on the forecast cash flow position of HGR Co and recommend a suitable course of action.
(10 marks)
(c) Discuss how risks arising from granting credit to foreign customers can be managed and reduced.
(8 marks)
正确答案:
(a)Whenconsideringthefinancingofworkingcapital,itisusefultodividecurrentassetsintofluctuatingcurrentassetsandpermanentcurrentassets.Fluctuatingcurrentassetsrepresentchangesinthelevelofcurrentassetsduetotheunpredictabilityofbusinessactivity.Permanentcurrentassetsrepresentthecorelevelofinvestmentincurrentassetsneededtosupportagivenlevelofturnoverorbusinessactivity.Asturnoverorlevelofbusinessactivityincreases,thelevelofpermanentcurrentassetswillalsoincrease.Thisrelationshipcanbemeasuredbytheratioofturnovertonetcurrentassets.Thefinancingchoiceasfarasworkingcapitalisconcernedisbetweenshort-termandlong-termfinance.Short-termfinanceismoreflexiblethanlong-termfinance:anoverdraft,forexample,isusedbyabusinessorganisationastheneedarisesandvariableinterestischargedontheoutstandingbalance.Short-termfinanceisalsomoreriskythanlong-termfinance:anoverdraftfacilitymaybewithdrawn,orashort-termloanmayberenewedonlessfavourableterms.Intermsofcost,thetermstructureofinterestratessuggeststhatshort-termdebtfinancehasalowercostthanlong-termdebtfinance.Thematchingprinciplesuggeststhatlong-termfinanceshouldbeusedforlong-terminvestment.Applyingthisprincipletoworkingcapitalfinancing,long-termfinanceshouldbematchedwithpermanentcurrentassetsandnon-currentassets.Afinancingpolicywiththisobjectiveiscalleda‘matchingpolicy’.HGRCoisnotusingthisfinancingpolicy,sinceofthe$16,935,000ofcurrentassets,$14,000,000or83%isfinancedfromshort-termsources(overdraftandtradepayables)andonly$2,935,000or17%isfinancedfromalong-termsource,inthiscaseequityfinance(shareholders’funds)ortradedbonds.ThefinancingpolicyorapproachtakenbyHGRCotowardsthefinancingofworkingcapital,whereshort-termfinanceispreferred,iscalledanaggressivepolicy.Relianceonshort-termfinancemakesthisriskierthanamatchingapproach,butalsomoreprofitableduetothelowercostofshort-termfinance.Followinganaggressiveapproachtofinancingcanleadtoovertrading(undercapitalisation)andthepossibilityofliquidityproblems.(b)Bankbalanceinthreemonths’timeifnoactionistaken:Workings:ReductioninaccountsreceivabledaysCurrentaccountsreceivabledays=(8,775/49,275)x365=65daysReductionindaysoversixmonths=65–53=12daysMonthlyreduction=12/6=2daysEachreceivablesdayisequivalentto8,775,000/65=$135,000(Alternatively,eachreceivablesdayisequivalentto49,275,000/365=$135,000)Monthlyreductioninaccountsreceivable=2x135,000=$270,000ReductionininventorydaysCurrentinventorydays=(8,160/37,230)x365=80daysEachinventorydayisequivalentto8,160,000/80=$102,000(Alternatively,eachinventoryday=37,230,000/365=$102,000)Monthlyreductionininventory=102,000x2=$204,000OverdraftinterestcalculationsMonthlyoverdraftinterestrate=1·06171/12=1·005or0·5%Ifnoactionistaken:Period1interest=3,800,000x0·005=$19,000Period2interest=3,549,000x0·005=$17,745or$18,000Period3interest=3,517,000x0·005=$17,585or$18,000Ifactionistaken:Period1interest=3,800,000x0.005=$19,000Period2interest=3,075,000x0.005=$15,375or$15,000Period3interest=2,566,000x0.005=$12,830or$13,000DiscussionIfnoactionistaken,thecashflowforecastshowsthatHGRCowillexceeditsoverdraftlimitof$4millionby$1·48millioninthreemonths’time.Ifthefinancedirector’sproposalsareimplemented,thereisapositiveeffectonthebankbalance,buttheoverdraftlimitisstillexceededinthreemonths’time,althoughonlyby$47,000ratherthanby$1·47million.Ineachofthethreemonthsfollowingthat,thecontinuingreductioninaccountsreceivabledayswillimprovethebankbalanceby$270,000permonth.Withoutfurtherinformationonoperatingreceiptsandpayments,itcannotbeforecastwhetherthebankbalancewillreturntolessthanthelimit,orevencontinuetoimprove.Themainreasonfortheproblemwiththebankbalanceisthe$2millioncapitalexpenditure.Purchaseofnon-currentassetsshouldnotbefinancedbyanoverdraft,butalong-termsourceoffinancesuchasequityorbonds.Ifthecapitalexpenditurewereremovedfromtheareaofworkingcapitalmanagement,theoverdraftbalanceattheendofthreemonthswouldbe$3·48millionifnoactionweretakenand$2·05millionifthefinancedirector’sproposalswereimplemented.GiventhatHGRCohasalmost$50millionofnon-currentassetsthatcouldpossiblybeusedassecurity,raisinglong-termdebtthrougheitherabankloanorabondissueappearstobesensible.Assumingabondinterestrateof10%peryear,currentlong-termdebtintheform.oftradedbondsisapproximately($200mx2)/0·1=$4m,whichismuchlessthantheamountofnoncurrentassets.AsuitablecourseofactionforHGRCotofollowwouldthereforebe,firstly,toimplementthefinancedirector’sproposalsand,secondly,tofinancethecapitalexpenditurefromalong-termsource.Considerationcouldalsobegiventousingsomelong-termdebtfinancetoreducetheoverdraftandtoreducethelevelofaccountspayable,currentlystandingat100days.(c)Whencreditisgrantedtoforeigncustomers,twoproblemsmaybecomeespeciallysignificant.First,thelongerdistancesoverwhichtradetakesplaceandthemorecomplexnatureoftradetransactionsandtheirelementsmeansforeignaccountsreceivableneedmoreinvestmentthantheirdomesticcounterparts.Longertransactiontimesincreaseaccountsreceivablebalancesandhencetheleveloffinancingandfinancingcosts.Second,theriskofbaddebtsishigherwithforeignaccountsreceivablethanwiththeirdomesticcounterparts.Inordertomanageandreducecreditrisks,therefore,exportersseektoreducetheriskofbaddebtandtoreducethelevelofinvestmentinforeignaccountsreceivable.Manyforeigntransactionsareon‘openaccount’,whichisanagreementtosettletheamountoutstandingonapredetermineddate.Openaccountreflectsagoodbusinessrelationshipbetweenimporterandexporter.Italsocarriesthehighestriskofnon-payment.Onewaytoreduceinvestmentinforeignaccountsreceivableistoagreeearlypaymentwithanimporter,forexamplebypaymentinadvance,paymentonshipment,orcashondelivery.Thesetermsoftradeareunlikelytobecompetitive,however,anditismorelikelythatanexporterwillseektoreceivecashinadvanceofpaymentbeingmadebythecustomer.Onewaytoacceleratecashreceiptsistousebillfinance.Billsofexchangewithasignedagreementtopaytheexporteronanagreedfuturedate,supportedbyadocumentaryletterofcredit,canbediscountedbyabanktogiveimmediatefunds.Thisdiscountingiswithoutrecourseifbillsofexchangehavebeencountersignedbytheimporter’sbank.Documentarylettersofcreditareapaymentguaranteebackedbyoneormorebanks.Theycarryalmostnorisk,providedtheexportercomplieswiththetermsandconditionscontainedintheletterofcredit.Theexportermustpresentthedocumentsstatedintheletter,suchasbillsoflading,shippingdocuments,billsofexchange,andsoon,whenseekingpayment.Aseachsupportingdocumentrelatestoakeyaspectoftheoveralltransaction,lettersofcreditgivesecuritytotheimporteraswellastheexporter.Companiescanalsomanageandreduceriskbygatheringappropriateinformationwithwhichtoassessthecreditworthinessofnewcustomers,suchasbankreferencesandcreditreports.Insurancecanalsobeusedtocoversomeoftherisksassociatedwithgivingcredittoforeigncustomers.Thiswouldavoidthecostofseekingtorecovercashduefromforeignaccountsreceivablethroughaforeignlegalsystem,wheretheexportercouldbeatadisadvantageduetoalackoflocalorspecialistknowledge.Exportfactoringcanalsobeconsidered,wheretheexporterpaysforthespecialistexpertiseofthefactorasawayofreducinginvestmentinforeignaccountsreceivableandreducingtheincidenceofbaddebts. -
第19题:
You are the audit supervisor of Maple & Co and are currently planning the audit of an existing client, Sycamore Science Co (Sycamore), whose year end was 30 April 2015. Sycamore is a pharmaceutical company, which manufactures and supplies a wide range of medical supplies. The draft financial statements show revenue of $35·6 million and profit before tax of $5·9 million.
Sycamore’s previous finance director left the company in December 2014 after it was discovered that he had been claiming fraudulent expenses from the company for a significant period of time. A new finance director was appointed in January 2015 who was previously a financial controller of a bank, and she has expressed surprise that Maple & Co had not uncovered the fraud during last year’s audit.
During the year Sycamore has spent $1·8 million on developing several new products. These projects are at different stages of development and the draft financial statements show the full amount of $1·8 million within intangible assets. In order to fund this development, $2·0 million was borrowed from the bank and is due for repayment over a ten-year period. The bank has attached minimum profit targets as part of the loan covenants.
The new finance director has informed the audit partner that since the year end there has been an increased number of sales returns and that in the month of May over $0·5 million of goods sold in April were returned.
Maple & Co attended the year-end inventory count at Sycamore’s warehouse. The auditor present raised concerns that during the count there were movements of goods in and out the warehouse and this process did not seem well controlled.
During the year, a review of plant and equipment in the factory was undertaken and surplus plant was sold, resulting in a profit on disposal of $210,000.
Required:
(a) State Maples & Co’s responsibilities in relation to the prevention and detection of fraud and error. (4 marks)
(b) Describe SIX audit risks, and explain the auditor’s response to each risk, in planning the audit of Sycamore Science Co. (12 marks)
(c) Sycamore’s new finance director has read about review engagements and is interested in the possibility of Maple & Co undertaking these in the future. However, she is unsure how these engagements differ from an external audit and how much assurance would be gained from this type of engagement.
Required:
(i) Explain the purpose of review engagements and how these differ from external audits; and (2 marks)
(ii) Describe the level of assurance provided by external audits and review engagements. (2 marks)
正确答案:(a) Fraud responsibility
Maple & Co must conduct an audit in accordance with ISA 240 The Auditor’s Responsibilities Relating to Fraud in an Audit of Financial Statements and are responsible for obtaining reasonable assurance that the financial statements taken as a whole are free from material misstatement, whether caused by fraud or error.
In order to fulfil this responsibility, Maple & Co is required to identify and assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements due to fraud.
They need to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence regarding the assessed risks of material misstatement due to fraud, through designing and implementing appropriate responses. In addition, Maple & Co must respond appropriately to fraud or suspected fraud identified during the audit.
When obtaining reasonable assurance, Maple & Co is responsible for maintaining professional scepticism throughout the audit, considering the potential for management override of controls and recognising the fact that audit procedures which are effective in detecting error may not be effective in detecting fraud.
To ensure that the whole engagement team is aware of the risks and responsibilities for fraud and error, ISAs require that a discussion is held within the team. For members not present at the meeting, Sycamore’s audit engagement partner should determine which matters are to be communicated to them.
(b) Audit risks and auditors’ responses



(c) (i) Review engagements
Review engagements are often undertaken as an alternative to an audit, and involve a practitioner reviewing financial data, such as six-monthly figures. This would involve the practitioner undertaking procedures to state whether anything has come to their attention which causes the practitioner to believe that the financial data is not in accordance with the financial reporting framework.
A review engagement differs to an external audit in that the procedures undertaken are not nearly as comprehensive as those in an audit, with procedures such as analytical review and enquiry used extensively. In addition, the practitioner does not need to comply with ISAs as these only relate to external audits.
(ii) Levels of assurance
The level of assurance provided by audit and review engagements is as follows:
External audit – A high but not absolute level of assurance is provided, this is known as reasonable assurance. This provides comfort that the financial statements present fairly in all material respects (or are true and fair) and are free of material misstatements.
Review engagements – where an opinion is being provided, the practitioner gathers sufficient evidence to be satisfied that the subject matter is plausible; in this case negative assurance is given whereby the practitioner confirms that nothing has come to their attention which indicates that the subject matter contains material misstatements.
-
第20题:
You are the audit manager of Chestnut & Co and are reviewing the key issues identified in the files of two audit clients.
Palm Industries Co (Palm)
Palm’s year end was 31 March 2015 and the draft financial statements show revenue of $28·2 million, receivables of $5·6 million and profit before tax of $4·8 million. The fieldwork stage for this audit has been completed.
A customer of Palm owed an amount of $350,000 at the year end. Testing of receivables in April highlighted that no amounts had been paid to Palm from this customer as they were disputing the quality of certain goods received from Palm. The finance director is confident the issue will be resolved and no allowance for receivables was made with regards to this balance.
Ash Trading Co (Ash)
Ash is a new client of Chestnut & Co, its year end was 31 January 2015 and the firm was only appointed auditors in February 2015, as the previous auditors were suddenly unable to undertake the audit. The fieldwork stage for this audit is currently ongoing.
The inventory count at Ash’s warehouse was undertaken on 31 January 2015 and was overseen by the company’s internal audit department. Neither Chestnut & Co nor the previous auditors attended the count. Detailed inventory records were maintained but it was not possible to undertake another full inventory count subsequent to the year end.
The draft financial statements show a profit before tax of $2·4 million, revenue of $10·1 million and inventory of $510,000.
Required:
For each of the two issues:
(i) Discuss the issue, including an assessment of whether it is material;
(ii) Recommend ONE procedure the audit team should undertake to try to resolve the issue; and
(iii) Describe the impact on the audit report if the issue remains UNRESOLVED.
Notes:
1 The total marks will be split equally between each of the two issues.
2 Audit report extracts are NOT required.
正确答案:Audit reports
Palm Industries Co (Palm)
(i) A customer of Palm’s owing $350,000 at the year end has not made any post year-end payments as they are disputing the quality of goods received. No allowance for receivables has been made against this balance. As the balance is being disputed, there is a risk of incorrect valuation as some or all of the receivable balance is overstated, as it may not be paid.
This $350,000 receivables balance represents 1·2% (0·35/28·2m) of revenue, 6·3% (0·35/5·6m) of receivables and 7·3% (0·35/4·8m) of profit before tax; hence this is a material issue.
(ii) A procedure to adopt includes:
– Review whether any payments have subsequently been made by this customer since the audit fieldwork was completed.
– Discuss with management whether the issue of quality of goods sold to the customer has been resolved, or whether it is still in dispute.
– Review the latest customer correspondence with regards to an assessment of the likelihood of the customer making payment.
(iii) If management refuses to provide against this receivable, the audit report will need to be modified. As receivables are overstated and the error is material but not pervasive a qualified opinion would be necessary.
A basis for qualified opinion paragraph would be needed and would include an explanation of the material misstatement in relation to the valuation of receivables and the effect on the financial statements. The opinion paragraph would be qualified ‘except for’.
Ash Trading Co (Ash)
(i) Chestnut & Co was only appointed as auditors subsequent to Ash’s year end and hence did not attend the year-end inventory count. Therefore, they have not been able to gather sufficient and appropriate audit evidence with regards to the completeness and existence of inventory.
Inventory is a material amount as it represents 21·3% (0·51/2·4m) of profit before tax and 5% (0·51/10·1m) of revenue; hence this is a material issue.
(ii) A procedure to adopt includes:
– Review the internal audit reports of the inventory count to identify the level of adjustments to the records to assess the reasonableness of relying on the inventory records.
– Undertake a sample check of inventory in the warehouse and compare to the inventory records and then from inventory records to the warehouse, to assess the reasonableness of the inventory records maintained by Ash.
(iii) The auditors will need to modify the audit report as they are unable to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence in relation to inventory which is a material but not pervasive balance. Therefore a qualified opinion will be required.
A basis for qualified opinion paragraph will be required to explain the limitation in relation to the lack of evidence over inventory. The opinion paragraph will be qualified ‘except for’.
-
第21题:
资料:From: Peter Manx pmanx@bettertraining.co.au
To: John Morgan jmorgan@ISB.co.au
Date: March 23
Subject: Better Training Ltd.
Dear Mr. Morgan,
As a leading human resource specialist, Better Training Ltd. is uniquely able to respond to your current training needs. Please take the time to review the attached brochure. I am confident that you will find courses of immediate relevance to ISB International Ltd.
Our standard curriculum covers topics such as managerial development, technical training, sales, marketing, and more. Our instructors-professionals and leaders in their fields-conduct engaging seminars while maintaining the quality for which we are known. In addition to our regular courses, we can deliver individually tailored programs at the location of your choice.
I am certain that your organization will benefit from our services Contact us today to see how we can help your employees increase their technical and professional expertise.
Sincerely,
Peter Manx
President
What is NOT mentioned in the e-mail?A.Reasonable prices.
B.Useful course content.
C.Flexible arrangements.
D.Well qualified teachers.答案:A解析:本题考查的是细节理解。
【关键词】NOT mentioned
【主题句】第2自然段Our standard curriculum covers topics such as managerial development, technical training, sales, marketing, and more. Our instructors-professionals and leaders in their fields-conduct engaging seminars while maintaining the quality for which we are known. In addition to our regular courses, we can deliver individually tailored programs at the location of your choice.我们的标准课程涵盖了包括管理发展、技术培训、销售、市场营销等各项内容。我们的教师是行业精英和各个领域的领导者,经常参加各类研讨会维持较高水准。除了常规课程外,我们可以根据您的选择提供个性化定制项目。
【解析】本题的问题是“下列哪项在邮件中没有提到?”。A选项“合理的价格”,B选项“有用的课程内容”,C选项“灵活的安排”,D选项“资质优秀的教师”。根据主题句,选项B、C、D都有提到。 -
第22题:
问答题Practice 1 ● You are the training manager of a company which has won a large export order. You have been asked to organise foreign language training for some of your staff. ● Write a memo to staff: ● explaining why the courses are necessary, ● saying which members of staff should attend, ● announcing when the courses will start. ● Write 40-50 words on a separate sheet.正确答案: 【参考范文】
Memo
To:
From:
Date:
Subject:
Memo
To: All staff
From: The Training Manager
Date: 1 March, 2012
Subject: A Foreign Language Training Course
I was told a foreign language training course needs to be organized for some employees because of the large export order we received recently. It will start next Monday. Those who are involved in the orders should attend the course.解析: 暂无解析 -
第23题:
单选题Which of the following measures has iMOVE taken to guarantee its high standards?AOffering different language courses.
BProviding modern training facilities.
CStarting training courses overseas.
DDeveloping quality standards.
正确答案: D解析:
细节题。根据题干信号词guarantee its high standards定位至文章第四段首句。文中提到提高保证数据库高质量的措施:为培训人员和他们的服务制定质量标准(quality standards),D项是原文的直接引用。选项A无中生有,iMOVE的目的不是提供语言课程。B项以偏概全,提供现代培训设施只是符合了质量标准。C项断章取义,文中提到该项目要扩展国际市场,开展海外培训课程,但与本题题意无关。
