(ii) State the taxation implications of both equity and loan finance from the point of view of a company.(3 marks)
题目
(ii) State the taxation implications of both equity and loan finance from the point of view of a company.
(3 marks)
相似考题
更多“(ii) State the taxation implications of both equity and loan finance from the point of view of a company.(3 marks)”相关问题
-
第1题:
(ii) An evaluation of the environmental and sustainability implications of the Giant Dam Project; (8 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Environmental and sustainability implications of the Giant Dam Project
In our preparation for the bid to act as principal contractor for the Giant Dam Project, we established that there were
two prominent negative implications of the project but these are, in our view, more than offset by two major
environmental positives.
The environmental arguments against the Giant Dam Project both concern the flooding of the valley behind the dam.
Regrettably, it seems that there will be some loss of important habitats. This, in turn, may mean the removal of balanced
environmental conditions for certain animal and plant species. In addition, the flooding of the valley will result in the
loss of productive farmland. This will mean reduced capacity for the host country to grow food and thus support citizens
such as the members of First Nation. From our point of view, as the board of R&M, however, we would remind
shareholders and other observers that the decisions involving the size and positioning of the Giant Dam were taken by
the client, the government. It is R&M’s job, having won the contract as principal contractor, to now carry out the plans,
regardless of our own views.
Happily, however, there are two very powerful environmental arguments in favour of the Giant Dam Project. It will create
a large source of clean energy for economic development that will be sustainable, as it will create no carbon emissions
nor will it consume any non-renewable resources as it does so (compared to, for example, fossil fuels).
At a time when people are becoming very concerned about greenhouse gases produced from conventional power
generation, the Giant Dam Project will contribute to the East Asian country’s internationally agreed carbon reduction
targets. This, in turn, will contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gases in the environment.
It is clear that the construction of the Giant Dam Project is an environmental conundrum with strong arguments on both
sides. The deciding factor may be the opinion that we each have of the desirability of economic growth in the East Asian
country (which the energy from the dam is intended to support). It seems that Stop-the-dam values the preservation of
the original environment more than the economic growth that the energy from the dam would support. The client does
not agree with this assessment and we are happy to be involved with a project that will create such a useful source of
renewable and non-polluting energy. -
第2题:
(c) State the tax consequences for both Glaikit Limited and Alasdair if he borrows money from the company, as
proposed, on 1 January 2006. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(c) Alasdair is not employed, nor is he a director, of Glaikit Limited. As he holds 25% of the shares in Glaikit Limited, he is a
participator in a close company and therefore the special close company provisions will apply. Thus Alsadair will be taxed
under the ‘loans to participator’ rules.
When the loan is written off, the amount waived will be treated as a gross distribution of £16,667 (£15,000 x 10/9). This
will be assessed in the tax year in which the loan is written off (expected to be 2006/07 or 2007/08). To the extent that this
additional income makes Alasdair a higher rate taxpayer in that year, he will have to pay additional income tax of 32·5% of
the gross amount, less the available 10% tax credit.
From the company’s perspective, Glaikit Limited will have to pay 25% of the net value of any loan made to Alasdair which
has not been repaid to the company (or written off) within nine months of the year end. As the loan will remain outstanding
as at 31 March 2006, Glaikit Limited will have to pay £3,750 (25% x £15,000) to the Revenue by 1 January 2007. This
amount will not be repaid until the loan is repaid or written off. This usually takes place nine months after the year end in
which the loan is written off, so Glaikit Limited should ensure that any write-off occurs prior to 31 March 2007, or else the
repayment may be delayed for up to one year.
As the loan is tax free, the Revenue may also seek to tax Alasdair under the beneficial loan rules. If the Revenue were to seek
an assessment in this manner, the value of the benefit would be calculated and taxed as a deemed distribution. However, as
Alasdair has no connection with the company other than as an investor, it is unlikely that the beneficial loan benefit will lead
to such a deemed distribution. -
第3题:
(b) (i) Advise Benny of the income tax implications of the grant and exercise of the share options in Summer
Glow plc on the assumption that the share price on 1 September 2007 and on the day he exercises the
options is £3·35 per share. Explain why the share option scheme is not free from risk by reference to
the rules of the scheme and the circumstances surrounding the company. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(b) (i) The share options
There are no income tax implications on the grant of the share options.
In the tax year in which Benny exercises the options and acquires the shares, the excess of the market value of the
shares over the price paid, i.e. £11,500 ((£3·35 – £2·20) x 10,000) will be subject to income tax.
Benny’s financial exposure is caused by the rule within the share option scheme obliging him to hold the shares for a
year before he can sell them. If the company’s expansion into Eastern Europe fails, such that its share price
subsequently falls to less than £2·20 before Benny has the chance to sell the shares, Benny’s financial position may be
summarised as follows:
– Benny will have paid £22,000 (£2·20 x 10,000) for shares which are now worth less than that.
– He will also have paid income tax of £4,600 (£11,500 x 40%). -
第4题:
(b) Explain the advantages from a tax point of view of operating the new business as a partnership rather than
as a company whilst it is making losses. You should calculate the tax adjusted trading loss for the year
ending 31 March 2008 for both situations and indicate the years in which the loss relief will be obtained.
You are not required to prepare any other supporting calculations. (10 marks)
正确答案:(b) The new business
There are two tax advantages to operating the business as a partnership.
(i) Reduction in taxable income
If the new business is operated as a company, Cindy and Arthur would both be taxed at 40% on their salaries. In
addition, employer and employee national insurance contributions would be due on £105 (£5,000 – £4,895) in respect
of each of them.
If the new business is operated as a partnership, the partners would have no taxable trading income because the
partnership has made a loss; any salaries paid to the partners would be appropriations of the profit or loss of the
business and not employment income. They would, however, each have to pay Class 2 national insurance contributions
of £2·10 each per week.
(ii) Earlier relief for trading losses
If the new business is operated as a company, its tax adjusted trading loss in the year ending 31 March 2008 would
be as follows:
-
第5题:
(iii) State how your answer in (ii) would differ if the sale were to be delayed until August 2006. (3 marks)
正确答案:
-
第6题:
(ii) Advise Clifford of the capital gains tax implications of the alternative of selling the Oxford house and
garden by means of two separate disposals as proposed. Calculations are not required for this part of
the question. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) The implications of selling the Oxford house and garden in two separate disposals
The additional sales proceeds would result in an increase in Clifford’s capital gains and consequently his tax liability.
When computing the gain on the sale of the house together with a small part of the garden, the allowable cost would
be a proportion of the original cost. That proportion would be A/A + B where A is the value of the house and garden
that has been sold and B is the value of the part of the garden that has been retained. Principal private residence relief
and taper relief would be available in the same way as that set out in (i) above.
When computing the gain on the sale of the remainder of the garden, the cost would be the original cost of the property
less the amount used in computing the gain on the earlier disposal. Principal private residence relief would not be
available as the land sold is not a dwelling house or part of one. -
第7题:
(ii) Advise Mr Fencer of the income tax implications of the proposed financing arrangements. (2 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) The income tax implications of the proposed financing arrangements
Mr Fencer has borrowed money from a UK bank in order to make a loan to Rapier Ltd, a close company. The interest
paid by Mr Fencer to the bank will be an allowable charge on income as long as he continues to hold more than 5% of
Rapier Ltd. Charges on income are deductible in arriving at an individual’s statutory total income.
Mr Fencer will receive interest from Rapier Ltd net of 20% income tax. The gross amount of interest will be subject to
income tax at either 10%, 20% or 40% depending on whether the income falls into Mr Fencer’s starting rate, basic rate
or higher rate tax band. Mr Fencer will obtain a tax credit for the 20% income tax suffered at source. -
第8题:
(ii) The shares held in Date Inc and the dividend income received from that company. (7 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Shares held in Date Inc and the related dividend income
Degrouping charge
There will be a degrouping charge in Nikau Ltd in the year ending 31 March 2008 in respect of the shares in Date Inc.
This is because Nikau Ltd has left the Facet Group within six years of the no gain, no loss transfer of the shares whilst
still owning them.
Nikau Ltd is treated as if it has sold the shares in Date Inc for their market value as at the time of the no gain, no loss
transfer. This will give rise to a gain, ignoring indexation allowance, of £201,000 (£338,000 – £137,000).
This gain will give rise to additional corporation tax of £60,300 (£201,000 x 30%).
Controlled foreign company
Date Inc is a controlled foreign company. The profits of such a company are normally attributed to its UK resident
shareholders such that they are subject to UK corporation tax.
However, none of the profits of Date Inc will be attributed to Nikau Ltd because Date Inc distributes more than 90%
(£115,000/£120,000 = 95·8%) of its chargeable profits to its shareholders.
Dividend income
Nikau Ltd is a UK resident company and is therefore subject to corporation tax on its worldwide income.
The dividend income will be grossed up in respect of the withholding tax giving rise to taxable income of £39,792
(£38,200 x 100/96). There is no underlying tax as there are no taxes on income or capital profits in Palladia.
The corporation tax of £11,938 (£39,792 x 30%) will be reduced by unilateral double tax relief equal to the withholding
tax suffered of £1,592 (£39,792 x 4%) resulting in corporation tax due of £10,346 (£11,938 – £1,592). -
第9题:
(ii) The answers to any questions that the potential investors may raise in connection with the maximum
possible investment, borrowing to finance the subscription and the implications of selling the shares.
(7 marks)
Note: you should assume that Vostok Ltd and its trade qualify for the purposes of the enterprise investment
scheme and you are not required to list the conditions that need to be satisfied by the company, its
shares or its business activities.
正确答案:
(ii) Answers to questions from potential investors
Maximum investment
– For the relief to be available, a shareholder (together with spouse and children) cannot own more than 30% of the
company. Accordingly, the maximum investment by a single subscriber will be £315,000 (15,000 x £21).
Borrowing to finance the purchase
– There would normally be tax relief for the interest paid on a loan taken out to acquire shares in a close company
such as Vostok Ltd. However, this relief is not available when the shares qualify for relief under the enterprise
investment scheme.
Implications of a subscriber selling the shares in Vostok Ltd
– The income tax relief will be withdrawn if the shares in Vostok Ltd are sold within three years of subscription.
– Any profit arising on the sale of the shares in Vostok Ltd on which income tax relief has been given will be exempt
from capital gains tax provided the shares have been held for three years.
– Any capital loss arising on the sale of the shares will be allowable regardless of how long the shares have been
held. However, the loss will be reduced by the amount of income tax relief obtained in respect of the investment.
The loss may be used to reduce the investor’s taxable income, and hence his income tax liability, for the tax year
of loss and/or the preceding tax year.
– Any gain deferred at the time of subscription will become chargeable in the year in which the shares in Vostok Ltd
are sold. -
第10题:
(b) State the enquiries you would make of the directors of Mulligan Co to ascertain the adequacy of the
$3 million finance requested for the new production facility. (7 marks)
正确答案:
(b) It is important to appreciate that the finance request should cover not only the cost of the construction of the new facility, but
also costs in order to get the business unit up and running, and enough cash to meet initial working capital requirements.
Mulligan Co may have sufficient cash to cover such additional expenses, but the bank will want comfort that this is the case.
Enquiries would include the following:
Who has prepared the forecast? It is important to evaluate the experience and competence of the preparer. If management
has previously prepared forecasts and capital expenditure budgets that were reliable and accurate, this adds a measure of
confidence in the preparation of the new forecast and the underlying assumptions used.
To what extent is internal finance available to cover any shortfall in the finance requirement? If there is surplus cash within
the organisation then the bank need not provide the full amount of finance necessary to start up the new business operation.
Has the cost of finance been included in the forecast? It appears that this cost is missing. Finance costs should be calculated
based on the anticipated interest rate to be applied to the loan advanced, and included in the total finance requirement.
What is the forecast operating cycle of the new business unit? In particular how long is the work in progress period, and how
much credit will be extended to customers? i.e. when will cash inflows specific to the new business unit be received? More
finance might be required to fund initial working capital shortfalls during the period when work in progress is occurring, and
before cash receipts from customers are received.
Will further raw materials be required? A request has been made for $250,000 for raw materials of timber. Other materials
may need to be purchased, for example, non-timber raw materials, and inventory of other consumables such as nuts and
bolts.
How long will the ‘initial’ inventory of raw material last? What is the planned work in progress time for the new product? More
finance may be needed to avoid a stock out of raw materials.
Construction of the new factory – is there any documentation to support the capital expenditure? For example, architect’s
plans, surveyor’s reports. This will support the accuracy of the finance requested and is an important source of evidence given
the materiality of the premises to the total amount of finance requested.
How likely is it that costs may be subject to inflation before actually being incurred? This could increase the amount of finance
required by several percentage points.
Have quotes been obtained for the new machinery to be purchased?
Purchase of new machinery – will any specific installation costs be incurred? These costs can be significant for large pieces
of capital equipment. Also, enquiries should be made regarding any delivery costs.
The budget does not appear to contain any finance request for overheads such as use of electricity during the construction
period, and hire of installation equipment. Have these overheads been included in the construction cost estimate?
Will staff need to be trained in using the new machinery? If so, any incremental costs should be included in the finance
request.
Advertising and marketing of new product – enquire of Patrick Tiler the methods that will be used to market the new product.
Some types of advertising are more of a cash drain due to their high expense e.g. television advertising is expensive and ‘up
front’ compared to magazine advertising, which is cheap and spread out. As Patrick Tiler is new to Mulligan Co, his forecast
is not based on past experience of this particular business.
LCT Bank will also consider the recoverability of the amount advanced by looking at the cash generating potential of the new
business unit. Enquiries should therefore be made regarding the likely success of the new products, for example:
– Has any market research been carried out to support the commercial viability of the new products?
– Have any contracts with retailers to carry the new products been negotiated?
– How quickly have past products generated a cash inflow?
– Is there a contingency plan in place in case the new products fail to be successful? -
第11题:
(a) The following information relates to Crosswire a publicly listed company.
Summarised statements of financial position as at:
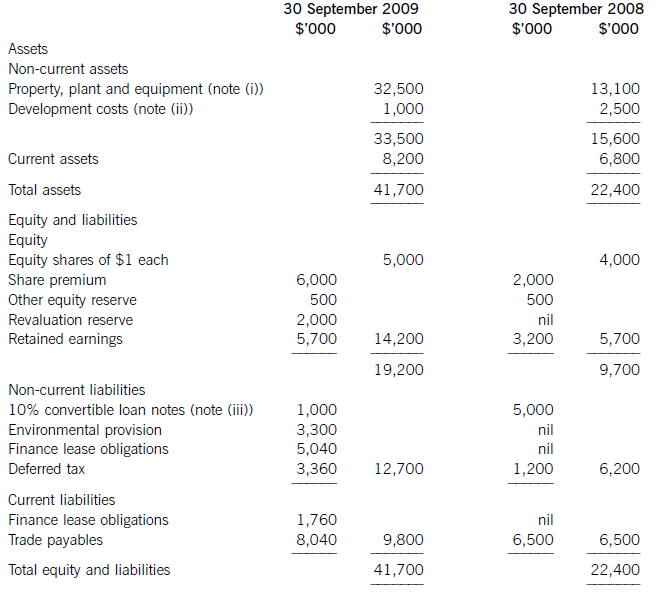
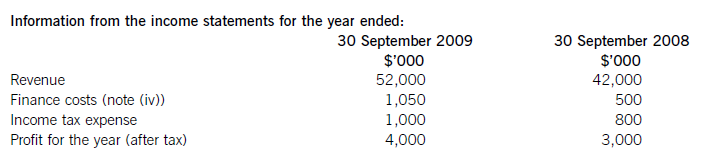
The following information is available:
(i) During the year to 30 September 2009, Crosswire embarked on a replacement and expansion programme for its non-current assets. The details of this programme are:
On 1 October 2008 Crosswire acquired a platinum mine at a cost of $5 million. A condition of mining the
platinum is a requirement to landscape the mining site at the end of its estimated life of ten years. The
present value of this cost at the date of the purchase was calculated at $3 million (in addition to the
purchase price of the mine of $5 million).
Also on 1 October 2008 Crosswire revalued its freehold land for the first time. The credit in the revaluation
reserve is the net amount of the revaluation after a transfer to deferred tax on the gain. The tax rate applicable to Crosswire for deferred tax is 20% per annum.
On 1 April 2009 Crosswire took out a finance lease for some new plant. The fair value of the plant was
$10 million. The lease agreement provided for an initial payment on 1 April 2009 of $2·4 million followed
by eight six-monthly payments of $1·2 million commencing 30 September 2009.
Plant disposed of during the year had a carrying amount of $500,000 and was sold for $1·2 million. The
remaining movement on the property, plant and equipment, after charging depreciation of $3 million, was
the cost of replacing plant.
(ii) From 1 October 2008 to 31 March 2009 a further $500,000 was spent completing the development
project at which date marketing and production started. The sales of the new product proved disappointing
and on 30 September 2009 the development costs were written down to $1 million via an impairment
charge.
(iii) During the year ended 30 September 2009, $4 million of the 10% convertible loan notes matured. The
loan note holders had the option of redemption at par in cash or to exchange them for equity shares on the
basis of 20 new shares for each $100 of loan notes. 75% of the loan-note holders chose the equity option.
Ignore any effect of this on the other equity reserve.
All the above items have been treated correctly according to International Financial Reporting Standards.
(iv) The finance costs are made up of:
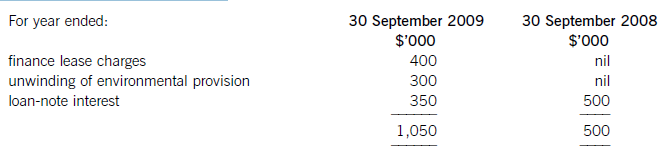
Required:
(i) Prepare a statement of the movements in the carrying amount of Crosswire’s non-current assets for the
year ended 30 September 2009; (9 marks)
(ii) Calculate the amounts that would appear under the headings of ‘cash flows from investing activities’
and ‘cash flows from financing activities’ in the statement of cash flows for Crosswire for the year ended
30 September 2009.
Note: Crosswire includes finance costs paid as a financing activity. (8 marks)
(b) A substantial shareholder has written to the directors of Crosswire expressing particular concern over the
deterioration of the company’s return on capital employed (ROCE)
Required:
Calculate Crosswire’s ROCE for the two years ended 30 September 2008 and 2009 and comment on the
apparent cause of its deterioration.
Note: ROCE should be taken as profit before interest on long-term borrowings and tax as a percentage of equity plus loan notes and finance lease obligations (at the year end). (8 marks)
正确答案:
(i)Thecashelementsoftheincreaseinproperty,plantandequipmentare$5millionforthemine(thecapitalisedenvironmentalprovisionisnotacashflow)and$2·4millionforthereplacementplantmakingatotalof$7·4million.(ii)Ofthe$4millionconvertibleloannotes(5,000–1,000)thatwereredeemedduringtheyear,75%($3million)ofthesewereexchangedforequitysharesonthebasisof20newsharesforeach$100inloannotes.Thiswouldcreate600,000(3,000/100x20)newsharesof$1eachandsharepremiumof$2·4million(3,000–600).As1million(5,000–4,000)newshareswereissuedintotal,400,000musthavebeenforcash.Theremainingincrease(aftertheeffectoftheconversion)inthesharepremiumof$1·6million(6,000–2,000b/f–2,400conversion)mustrelatetothecashissueofshares,thuscashproceedsfromtheissueofsharesis$2million(400nominalvalue+1,600premium).(iii)Theinitialleaseobligationis$10million(thefairvalueoftheplant).At30September2009totalleaseobligationsare$6·8million(5,040+1,760),thusrepaymentsintheyearwere$3·2million(10,000–6,800).(b)TakingthedefinitionofROCEfromthequestion:Fromtheaboveitcanbeclearlyseenthatthe2009operatingmarginhasimprovedbynearly1%point,despitethe$2millionimpairmentchargeonthewritedownofthedevelopmentproject.ThismeansthedeteriorationintheROCEisduetopoorerassetturnover.Thisimpliestherehasbeenadecreaseintheefficiencyintheuseofthecompany’sassetsthisyearcomparedtolastyear.Lookingatthemovementinthenon-currentassetsduringtheyearrevealssomemitigatingpoints:Thelandrevaluationhasincreasedthecarryingamountofproperty,plantandequipmentwithoutanyphysicalincreaseincapacity.Thisunfavourablydistortsthecurrentyear’sassetturnoverandROCEfigures.TheacquisitionoftheplatinummineappearstobeanewareaofoperationforCrosswirewhichmayhaveadifferent(perhapslower)ROCEtootherpreviousactivitiesoritmaybethatitwilltakesometimefortheminetocometofullproductioncapacity.Thesubstantialacquisitionoftheleasedplantwashalf-waythroughtheyearandcanonlyhavecontributedtotheyear’sresultsforsixmonthsatbest.Infutureperiodsafullyear’scontributioncanbeexpectedfromthisnewinvestmentinplantandthisshouldimprovebothassetturnoverandROCE.Insummary,thefallintheROCEmaybeduelargelytotheabovefactors(effectivelythereplacementandexpansionprogramme),ratherthantopooroperatingperformance,andinfutureperiodsthismaybereversed.ItshouldalsobenotedthathadtheROCEbeencalculatedontheaveragecapitalemployedduringtheyear(ratherthantheyearendcapitalemployed),whichisarguablymorecorrect,thenthedeteriorationintheROCEwouldnothavebeenaspronounced. -
第12题:
Moonstar Co is a property development company which is planning to undertake a $200 million commercial property development. Moonstar Co has had some difficulties over the last few years, with some developments not generating the expected returns and the company has at times struggled to pay its finance costs. As a result Moonstar Co’s credit rating has been lowered, affecting the terms it can obtain for bank finance. Although Moonstar Co is listed on its local stock exchange, 75% of the share capital is held by members of the family who founded the company. The family members who are shareholders do not wish to subscribe for a rights issue and are unwilling to dilute their control over the company by authorising a new issue of equity shares. Moonstar Co’s board is therefore considering other methods of financing the development, which the directors believe will generate higher returns than other recent investments, as the country where Moonstar Co is based appears to be emerging from recession.
Securitisation proposals
One of the non-executive directors of Moonstar Co has proposed that it should raise funds by means of a securitisation process, transferring the rights to the rental income from the commercial property development to a special purpose vehicle. Her proposals assume that the leases will generate an income of 11% per annum to Moonstar Co over a ten-year period. She proposes that Moonstar Co should use 90% of the value of the investment for a collateralised loan obligation which should be structured as follows:
– 60% of the collateral value to support a tranche of A-rated floating rate loan notes offering investors LIBOR plus 150 basis points
– 15% of the collateral value to support a tranche of B-rated fixed rate loan notes offering investors 12%
– 15% of the collateral value to support a tranche of C-rated fixed rate loan notes offering investors 13%
– 10% of the collateral value to support a tranche as subordinated certificates, with the return being the excess of receipts over payments from the securitisation process
The non-executive director believes that there will be sufficient demand for all tranches of the loan notes from investors. Investors will expect that the income stream from the development to be low risk, as they will expect the property market to improve with the recession coming to an end and enough potential lessees to be attracted by the new development.
The non-executive director predicts that there would be annual costs of $200,000 in administering the loan. She acknowledges that there would be interest rate risks associated with the proposal, and proposes a fixed for variable interest rate swap on the A-rated floating rate notes, exchanging LIBOR for 9·5%.
However the finance director believes that the prediction of the income from the development that the non-executive director has made is over-optimistic. He believes that it is most likely that the total value of the rental income will be 5% lower than the non-executive director has forecast. He believes that there is some risk that the returns could be so low as to jeopardise the income for the C-rated fixed rate loan note holders.
Islamic finance
Moonstar Co’s chief executive has wondered whether Sukuk finance would be a better way of funding the development than the securitisation.
Moonstar Co’s chairman has pointed out that a major bank in the country where Moonstar Co is located has begun to offer a range of Islamic financial products. The chairman has suggested that a Mudaraba contract would be the most appropriate method of providing the funds required for the investment.
Required:
(a) Calculate the amounts in $ which each of the tranches can expect to receive from the securitisation arrangement proposed by the non-executive director and discuss how the variability in rental income affects the returns from the securitisation. (11 marks)
(b) Discuss the benefits and risks for Moonstar Co associated with the securitisation arrangement that the non-executive director has proposed. (6 marks)
(c) (i) Discuss the suitability of Sukuk finance to fund the investment, including an assessment of its appeal to potential investors. (4 marks)
(ii) Discuss whether a Mudaraba contract would be an appropriate method of financing the investment and discuss why the bank may have concerns about providing finance by this method. (4 marks)
正确答案:(a) An annual cash flow account compares the estimated cash flows receivable from the property against the liabilities within the securitisation process. The swap introduces leverage into the arrangement.
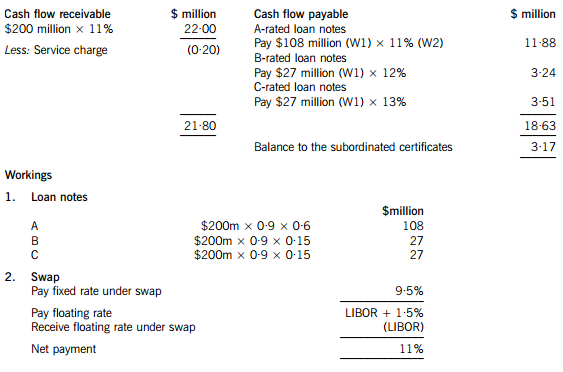
The holders of the certificates are expected to receive $3·17million on $18 million, giving them a return of 17·6%. If the cash flows are 5% lower than the non-executive director has predicted, annual revenue received will fall to $20·90 million, reducing the balance available for the subordinated certificates to $2·07 million, giving a return of 11·5% on the subordinated certificates, which is below the returns offered on the B and C-rated loan notes. The point at which the holders of the certificates will receive nothing and below which the holders of the C-rated loan notes will not receive their full income will be an annual income of $18·83 million (a return of 9·4%), which is 14·4% less than the income that the non-executive director has forecast.
(b) Benefits
The finance costs of the securitisation may be lower than the finance costs of ordinary loan capital. The cash flows from the commercial property development may be regarded as lower risk than Moonstar Co’s other revenue streams. This will impact upon the rates that Moonstar Co is able to offer borrowers.
The securitisation matches the assets of the future cash flows to the liabilities to loan note holders. The non-executive director is assuming a steady stream of lease income over the next 10 years, with the development probably being close to being fully occupied over that period.
The securitisation means that Moonstar Co is no longer concerned with the risk that the level of earnings from the properties will be insufficient to pay the finance costs. Risks have effectively been transferred to the loan note holders.
Risks
Not all of the tranches may appeal to investors. The risk-return relationship on the subordinated certificates does not look very appealing, with the return quite likely to be below what is received on the C-rated loan notes. Even the C-rated loan note holders may question the relationship between the risk and return if there is continued uncertainty in the property sector.
If Moonstar Co seeks funding from other sources for other developments, transferring out a lower risk income stream means that the residual risks associated with the rest of Moonstar Co’s portfolio will be higher. This may affect the availability and terms of other borrowing.
It appears that the size of the securitisation should be large enough for the costs to be bearable. However Moonstar Co may face unforeseen costs, possibly unexpected management or legal expenses.
(c) (i) Sukuk finance could be appropriate for the securitisation of the leasing portfolio. An asset-backed Sukuk would be the same kind of arrangement as the securitisation, where assets are transferred to a special purpose vehicle and the returns and repayments are directly financed by the income from the assets. The Sukuk holders would bear the risks and returns of the relationship.
The other type of Sukuk would be more like a sale and leaseback of the development. Here the Sukuk holders would be guaranteed a rental, so it would seem less appropriate for Moonstar Co if there is significant uncertainty about the returns from the development.
The main issue with the asset-backed Sukuk finance is whether it would be as appealing as certainly the A-tranche of the securitisation arrangement which the non-executive director has proposed. The safer income that the securitisation offers A-tranche investors may be more appealing to investors than a marginally better return from the Sukuk. There will also be costs involved in establishing and gaining approval for the Sukuk, although these costs may be less than for the securitisation arrangement described above.
(ii) A Mudaraba contract would involve the bank providing capital for Moonstar Co to invest in the development. Moonstar Co would manage the investment which the capital funded. Profits from the investment would be shared with the bank, but losses would be solely borne by the bank. A Mudaraba contract is essentially an equity partnership, so Moonstar Co might not face the threat to its credit rating which it would if it obtained ordinary loan finance for the development. A Mudaraba contract would also represent a diversification of sources of finance. It would not require the commitment to pay interest that loan finance would involve.
Moonstar Co would maintain control over the running of the project. A Mudaraba contract would offer a method of obtaining equity funding without the dilution of control which an issue of shares to external shareholders would bring. This is likely to make it appealing to Moonstar Co’s directors, given their desire to maintain a dominant influence over the business.
The bank would be concerned about the uncertainties regarding the rental income from the development. Although the lack of involvement by the bank might appeal to Moonstar Co's directors, the bank might not find it so attractive. The bank might be concerned about information asymmetry – that Moonstar Co’s management might be reluctant to supply the bank with the information it needs to judge how well its investment is performing.
-
第13题:
(ii) Recommend which of the refrigeration systems should be purchased. You should state your reasons
which must be supported by relevant calculations. (3 marks)
正确答案:
-
第14题:
(ii) Explain the income tax (IT), national insurance (NIC) and capital gains tax (CGT) implications arising on
the grant to and exercise by an employee of an option to buy shares in an unapproved share option
scheme and on the subsequent sale of these shares. State clearly how these would apply in Henry’s
case. (8 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Exercising of share options
The share option is not part of an approved scheme, and will not therefore enjoy the benefits of such a scheme. There
are three events with tax consequences – grant, exercise and sale.
Grant. If shares or options over shares are sold or granted at less than market value, an income tax charge can arise on
the difference between the price paid and the market value. [Weight v Salmon]. In addition, if options can be exercised
more than 10 years after the date of the grant, an employment income charge can arise. This is based on the market
value at the date of grant less the grant and exercise priced.
In Henry’s case, the options were issued with an exercise price equal to the then market value, and cannot be exercised
more than 10 years from the grant. No income tax charge therefore arises on grant.
Exercise. On exercise, the individual pays the agreed amount in return for a number of shares in the company. The price
paid is compared with the open market value at that time, and if less, the difference is charged to income tax. National
insurance also applies, and the company has to pay Class 1 NIC. If the company and shareholder agree, the national
insurance can be passed onto the individual, and the liability becomes a deductible expense in calculating the income
tax charge.
In Henry’s case on exercise, the difference between market value (£14) and the price paid (£1) per share will be taxed
as income. Therefore, £130,000 (10,000 x (£14 – £1)) will be taxed as income. In addition, national insurance will
be chargeable on the company at 12·8% (£16,640) and on Henry at the rate of 1% (£1,300).
Sale. The base cost of the shares is taken to be the market value at the time of exercise. On the sale of the shares, any
gain or loss arising falls under the capital gains tax rules, and CGT will be payable on any gain. Business asset taper
relief will be available as the company is an unquoted trading company, but the relief will only run from the time that
the share options are exercised – i.e. from the time when the shares were acquired.
In Henry’s case, the sale of the shares will immediately follow the exercise of the option (6 days later). The sale proceeds
and the market value at the time of exercise are likely to be similar; thus little to no gain is likely to arise. -
第15题:
(ii) Compute the annual income tax saving from your recommendation in (i) above as compared with the
situation where Cindy retains both the property and the shares. Identify any other tax implications
arising from your recommendation. Your answer should consider all relevant taxes. (3 marks)
正确答案:
-
第16题:
(b) (i) State the condition that would need to be satisfied for the exercise of Paul’s share options in Memphis
plc to be exempt from income tax and the tax implications if this condition is not satisfied.
(2 marks)
正确答案:
(b) (i) Paul has options in an HMRC approved share scheme. Under such schemes, no tax liabilities arise either on the grant
or exercise of the option. The excess of the proceeds over the price paid for the shares (the exercise price) is charged to
capital gains tax on their disposal.
However, in order to secure this treatment, one of the conditions to be satisfied is that the options cannot be exercised
within three years of the date of grant. If Paul were to exercise his options now (i.e. before the third anniversary of the
grant), the exercise would instead be treated as an unapproved exercise. At that date, income tax would be charged on
the difference between the market value of the shares on exercise and the price paid to exercise the option. -
第17题:
(ii) Advise Andrew of the tax implications arising from the disposal of the 7% Government Stock, clearly
identifying the tax year in which any liability will arise and how it will be paid. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Government stock is an exempt asset for the purposes of capital gains tax, however, as Andrew’s holding has a nominal
value in excess of £5,000, a charge to income tax will arise under the accrued income scheme. This charge to income
tax will arise in 2005/06, being the tax year in which the next interest payment following disposal falls due (20 April
2005) and it will relate to the income accrued for the period 21 October 2004 to 14 March 2005 of £279 (145/182
x £350). As interest on Government Stock is paid gross (unless the holder applies to receive it net), the tax due of £112
(£279 x 40%) will be collected via the self-assessment system and as the interest was an ongoing source of income
will be included within Andrew’s half yearly payments on account payable on 31 January and 31 July 2006. -
第18题:
(ii) The UK value added tax (VAT) implications for Razor Ltd of selling tools to and purchasing tools from
Cutlass Inc; (2 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Value added tax (VAT)
Goods exported are zero-rated. Razor Ltd must retain appropriate documentary evidence that the export has taken place.
Razor Ltd must account for VAT on the value of the goods purchased from Cutlass Inc at the time the goods are brought
into the UK. The VAT payable should be included as deductible input tax on the company’s VAT return. -
第19题:
(ii) A proposal which will increase the after tax proceeds from the sale of the Snapper plc loan stock and a
reasoned recommendation of a more appropriate form. of external finance. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Proposal to increase the after tax proceeds from the sale of the loan stock
AS should delay the sale of the loan stock until after 5 April 2008. The gain made at the time of the takeover would
then crystallise in 2008/09 and would be covered by the annual exemption for that year. The net proceeds would be
increased by the capital gains tax saved of £3,446 (£8,616 x 40%).
More appropriate forms of external finance
A bank overdraft is not the most appropriate form. of long term business finance. This is because the bank can demand
repayment of the overdraft at any time and the rates of interest charged are fairly high.
AS should seek long term finance for his long term business needs, for example a bank loan secured on the theatre, and
use the bank overdraft to finance the working capital required on a day-to-day basis. -
第20题:
(c) (i) Explain how Messier Ltd can assist Galileo with the cost of relocating to the UK and/or provide him with
interest-free loan finance for this purpose without increasing his UK income tax liability; (3 marks)
正确答案:
(c) (i) Relocation costs
Direct assistance
Messier Ltd can bear the cost of certain qualifying relocation costs of Galileo up to a maximum of £8,000 without
increasing his UK income tax liability. Qualifying costs include the legal, professional and other fees in relation to the
purchase of a house, the costs of travelling to the UK and the cost of transporting his belongings. The costs must be
incurred before the end of the tax year following the year of the relocation, i.e. by 5 April 2010.
Assistance in the form. of a loan
Messier Ltd can provide Galileo with an interest-free loan of up to £5,000 without giving rise to any UK income tax. -
第21题:
(ii) Briefly explain the implications of Parr & Co’s audit opinion for your audit opinion on the consolidated
financial statements of Cleeves Co for the year ended 30 September 2006. (3 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Implications for audit opinion on consolidated financial statements of Cleeves
■ If the potential adjustments to non-current asset carrying amounts and loss are not material to the consolidated
financial statements there will be no implication. However, as Howard is material to Cleeves and the modification
appears to be ‘so material’ (giving rise to adverse opinion) this seems unlikely.
Tutorial note: The question clearly states that Howard is material to Cleeves, thus there is no call for speculation
on this.
■ As Howard is wholly-owned the management of Cleeves must be able to request that Howard’s financial statements
are adjusted to reflect the impairment of the assets. The auditor’s report on Cleeves will then be unmodified
(assuming that any impairment of the investment in Howard is properly accounted for in the separate financial
statements of Cleeves).
■ If the impairment losses are not recognised in Howard’s financial statements they can nevertheless be adjusted on
consolidation of Cleeves and its subsidiaries (by writing down assets to recoverable amounts). The audit opinion
on Cleeves should then be unmodified in this respect.
■ If there is no adjustment of Howard’s asset values (either in Howard’s financial statements or on consolidation) it
is most likely that the audit opinion on Cleeves’s consolidated financial statements would be ‘except for’. (It should
not be adverse as it is doubtful whether even the opinion on Howard’s financial statements should be adverse.)
Tutorial note: There is currently no requirement in ISA 600 to disclose that components have been audited by another
auditor unless the principal auditor is permitted to base their opinion solely upon the report of another auditor. -
第22题:
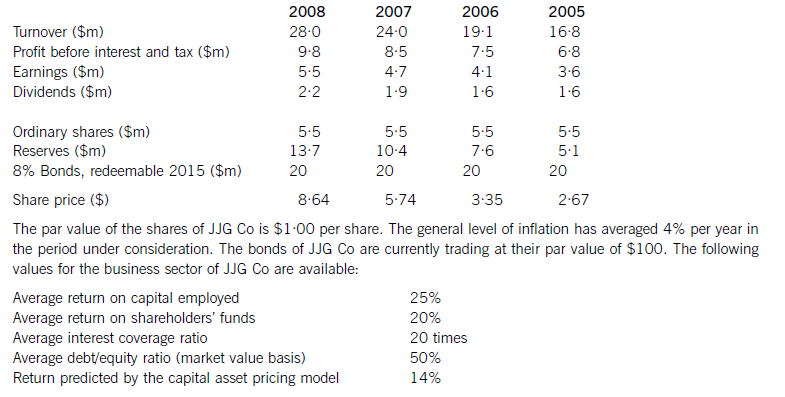
JJG Co is planning to raise $15 million of new finance for a major expansion of existing business and is considering a rights issue, a placing or an issue of bonds. The corporate objectives of JJG Co, as stated in its Annual Report, are to maximise the wealth of its shareholders and to achieve continuous growth in earnings per share. Recent financial information on JJG Co is as follows:
Required:
(a) Evaluate the financial performance of JJG Co, and analyse and discuss the extent to which the company has achieved its stated corporate objectives of:
(i) maximising the wealth of its shareholders;
(ii) achieving continuous growth in earnings per share.
Note: up to 7 marks are available for financial analysis.(12 marks)
(b) If the new finance is raised via a rights issue at $7·50 per share and the major expansion of business has
not yet begun, calculate and comment on the effect of the rights issue on:
(i) the share price of JJG Co;
(ii) the earnings per share of the company; and
(iii) the debt/equity ratio. (6 marks)
(c) Analyse and discuss the relative merits of a rights issue, a placing and an issue of bonds as ways of raising the finance for the expansion. (7 marks)
正确答案:
AchievementofcorporateobjectivesJJGCohasshareholderwealthmaximisationasanobjective.Thewealthofshareholdersisincreasedbydividendsreceivedandcapitalgainsonsharesowned.Totalshareholderreturncomparesthesumofthedividendreceivedandthecapitalgainwiththeopeningshareprice.TheshareholdersofJJGCohadareturnof58%in2008,comparedwithareturnpredictedbythecapitalassetpricingmodelof14%.Thelowestreturnshareholdershavereceivedwas21%andthehighestreturnwas82%.Onthisbasis,theshareholdersofthecompanyhaveexperiencedasignificantincreaseinwealth.Itisdebatablewhetherthishasbeenasaresultoftheactionsofthecompany,however.Sharepricesmayincreaseirrespectiveoftheactionsanddecisionsofmanagers,orevendespitethem.Infact,lookingatthedividendpersharehistoryofthecompany,therewasoneyear(2006)wheredividendswereconstant,eventhoughearningspershareincreased.Itisalsodifficulttoknowwhenwealthhasbeenmaximised.Anotherobjectiveofthecompanywastoachieveacontinuousincreaseinearningspershare.Analysisshowsthatearningspershareincreasedeveryyear,withanaverageincreaseof14·9%.Thisobjectiveappearstohavebeenachieved.CommentonfinancialperformanceReturnoncapitalemployed(ROCE)hasbeengrowingtowardsthesectoraverageof25%onayear-by-yearbasisfrom22%in2005.Thissteadygrowthintheprimaryaccountingratiocanbecontrastedwithirregulargrowthinturnover,thereasonsforwhichareunknown.Returnonshareholders’fundshasbeenconsistentlyhigherthantheaverageforthesector.ThismaybeduemoretothecapitalstructureofJJGCothantogoodperformancebythecompany,however,inthesensethatshareholders’fundsaresmalleronabookvaluebasisthanthelong-termdebtcapital.Ineverypreviousyearbut2008thegearingofthecompanywashigherthanthesectoraverage.(b)CalculationoftheoreticalexrightspershareCurrentshareprice=$8·64pershareCurrentnumberofshares=5·5millionsharesFinancetoberaised=$15mRightsissueprice=$7·50pershareNumberofsharesissued=15m/7·50=2millionsharesTheoreticalexrightspricepershare=((5·5mx8·64)+(2mx7·50))/7·5m=$8·34pershareThesharepricewouldfallfrom$8·64to$8·34pershareHowever,therewouldbenoeffectonshareholderwealthEffectofrightsissueonearningspershareCurrentEPS=100centspershareRevisedEPS=100x5·5m/7·5m=73centspershareTheEPSwouldfallfrom100centspershareto73centspershareHowever,asmentionedearlier,therewouldbenoeffectonshareholderwealthEffectofrightsissueonthedebt/equityratioCurrentdebt/equityratio=100x20/47·5=42%Revisedmarketvalueofequity=7·5mx8·34=$62·55millionReviseddebt/equityratio=100x20/62·55=32%Thedebt/equityratiowouldfallfrom42%to32%,whichiswellbelowthesectoraveragevalueandwouldsignalareductioninfinancialrisk(c)Thecurrentdebt/equityratioofJJGCois42%(20/47·5).Althoughthisislessthanthesectoraveragevalueof50%,itismoreusefulfromafinancialriskperspectivetolookattheextenttowhichinterestpaymentsarecoveredbyprofits.Theinterestonthebondissueis$1·6million(8%of$20m),givinganinterestcoverageratioof6·1times.IfJJGCohasoverdraftfinance,theinterestcoverageratiowillbelowerthanthis,butthereisinsufficientinformationtodetermineifanoverdraftexists.Theinterestcoverageratioisnotonlybelowthesectoraverage,itisalsolowenoughtobeacauseforconcern.Whiletheratioshowsanupwardtrendovertheperiodunderconsideration,itstillindicatesthatanissueoffurtherdebtwouldbeunwise.Aplacing,oranyissueofnewsharessuchasarightsissueorapublicoffer,woulddecreasegearing.Iftheexpansionofbusinessresultsinanincreaseinprofitbeforeinterestandtax,theinterestcoverageratiowillincreaseandfinancialriskwillfall.GiventhecurrentfinancialpositionofJJGCo,adecreaseinfinancialriskiscertainlypreferabletoanincrease.Aplacingwilldiluteownershipandcontrol,providingthenewequityissueistakenupbynewinstitutionalshareholders,whilearightsissuewillnotdiluteownershipandcontrol,providingexistingshareholderstakeuptheirrights.Abondissuedoesnothaveownershipandcontrolimplications,althoughrestrictiveornegativecovenantsinbondissuedocumentscanlimittheactionsofacompanyanditsmanagers.Allthreefinancingchoicesarelong-termsourcesoffinanceandsoareappropriateforalong-terminvestmentsuchastheproposedexpansionofexistingbusiness.Equityissuessuchasaplacingandarightsissuedonotrequiresecurity.Noinformationisprovidedonthenon-currentassetsofJJGCo,butitislikelythattheexistingbondissueissecured.Ifanewbondissuewasbeingconsidered,JJGCowouldneedtoconsiderwhetherithadsufficientnon-currentassetstoofferassecurity,althoughitislikelythatnewnon-currentassetswouldbeboughtaspartofthebusinessexpansion. -
第23题:
(a) The following figures have been calculated from the financial statements (including comparatives) of Barstead for
the year ended 30 September 2009:
increase in profit after taxation 80%
increase in (basic) earnings per share 5%
increase in diluted earnings per share 2%
Required:
Explain why the three measures of earnings (profit) growth for the same company over the same period can
give apparently differing impressions. (4 marks)
(b) The profit after tax for Barstead for the year ended 30 September 2009 was $15 million. At 1 October 2008 the company had in issue 36 million equity shares and a $10 million 8% convertible loan note. The loan note will mature in 2010 and will be redeemed at par or converted to equity shares on the basis of 25 shares for each $100 of loan note at the loan-note holders’ option. On 1 January 2009 Barstead made a fully subscribed rights issue of one new share for every four shares held at a price of $2·80 each. The market price of the equity shares of Barstead immediately before the issue was $3·80. The earnings per share (EPS) reported for the year ended 30 September 2008 was 35 cents.
Barstead’s income tax rate is 25%.
Required:
Calculate the (basic) EPS figure for Barstead (including comparatives) and the diluted EPS (comparatives not required) that would be disclosed for the year ended 30 September 2009. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(a)Whilstprofitaftertax(anditsgrowth)isausefulmeasure,itmaynotgiveafairrepresentationofthetrueunderlyingearningsperformance.Inthisexample,userscouldinterpretthelargeannualincreaseinprofitaftertaxof80%asbeingindicativeofanunderlyingimprovementinprofitability(ratherthanwhatitreallyis:anincreaseinabsoluteprofit).Itispossible,evenprobable,that(someof)theprofitgrowthhasbeenachievedthroughtheacquisitionofothercompanies(acquisitivegrowth).Wherecompaniesareacquiredfromtheproceedsofanewissueofshares,orwheretheyhavebeenacquiredthroughshareexchanges,thiswillresultinagreaternumberofequitysharesoftheacquiringcompanybeinginissue.ThisiswhatappearstohavehappenedinthecaseofBarsteadastheimprovementindicatedbyitsearningspershare(EPS)isonly5%perannum.ThisexplainswhytheEPS(andthetrendofEPS)isconsideredamorereliableindicatorofperformancebecausetheadditionalprofitswhichcouldbeexpectedfromthegreaterresources(proceedsfromthesharesissued)ismatchedwiththeincreaseinthenumberofshares.Simplylookingatthegrowthinacompany’sprofitaftertaxdoesnottakeintoaccountanyincreasesintheresourcesusedtoearnthem.Anyincreaseingrowthfinancedbyborrowings(debt)wouldnothavethesameimpactonprofit(asbeingfinancedbyequityshares)becausethefinancecostsofthedebtwouldacttoreduceprofit.ThecalculationofadilutedEPStakesintoaccountanypotentialequitysharesinissue.Potentialordinarysharesarisefromfinancialinstruments(e.g.convertibleloannotesandoptions)thatmayentitletheirholderstoequitysharesinthefuture.ThedilutedEPSisusefulasitalertsexistingshareholderstothefactthatfutureEPSmaybereducedasaresultofsharecapitalchanges;inasenseitisawarningsign.InthiscasethelowerincreaseinthedilutedEPSisevidencethatthe(higher)increaseinthebasicEPShas,inpart,beenachievedthroughtheincreaseduseofdilutingfinancialinstruments.Thefinancecostoftheseinstrumentsislessthantheearningstheirproceedshavegeneratedleadingtoanincreaseincurrentprofits(andbasicEPS);however,inthefuturetheywillcausemoresharestobeissued.ThiscausesadilutionwherethefinancecostperpotentialnewshareislessthanthebasicEPS.
