(b) Using the information provided, state the financial statement risks arising and justify an appropriate auditapproach for Indigo Co for the year ending 31 December 2005. (14 marks)
题目
(b) Using the information provided, state the financial statement risks arising and justify an appropriate audit
approach for Indigo Co for the year ending 31 December 2005. (14 marks)
相似考题
更多“(b) Using the information provided, state the financial statement risks arising and justify an appropriate auditapproach for Indigo Co for the year ending 31 December 2005. (14 marks)”相关问题
-
第1题:
(b) Describe with suitable calculations how the goodwill arising on the acquisition of Briars will be dealt with in
the group financial statements and how the loan to Briars should be treated in the financial statements of
Briars for the year ended 31 May 2006. (9 marks)
正确答案:(b) IAS21 ‘The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates’ requires goodwill arising on the acquisition of a foreign operation
and fair value adjustments to acquired assets and liabilities to be treated as belonging to the foreign operation. They should
be expressed in the functional currency of the foreign operation and translated at the closing rate at each balance sheet date.
Effectively goodwill is treated as a foreign currency asset which is retranslated at the closing rate. In this case the goodwillarising on the acquisition of Briars would be treated as follows:
At 31 May 2006, the goodwill will be retranslated at 2·5 euros to the dollar to give a figure of $4·4 million. Therefore this
will be the figure for goodwill in the balance sheet and an exchange loss of $1·4 million recorded in equity (translation
reserve). The impairment of goodwill will be expensed in profit or loss to the value of $1·2 million. (The closing rate has been
used to translate the impairment; however, there may be an argument for using the average rate.)
The loan to Briars will effectively be classed as a financial liability measured at amortised cost. It is the default category for
financial liabilities that do not meet the definition of financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss. For most entities,
most financial liabilities will fall into this category. When a financial liability is recognised initially in the balance sheet, the
liability is measured at fair value. Fair value is the amount for which a liability can be settled, between knowledgeable, willing
parties in an arm’s length transaction. In other words, fair value is an actual or estimated transaction price on the reporting
date for a transaction taking place between unrelated parties that have adequate information about the asset or liability being
measured.
Since fair value is a market transaction price, on initial recognition fair value generally is assumed to equal the amount of
consideration paid or received for the financial asset or financial liability. Accordingly, IAS39 specifies that the best evidence
of the fair value of a financial instrument at initial recognition generally is the transaction price. However for longer-term
receivables or payables that do not pay interest or pay a below-market interest, IAS39 does require measurement initially at
the present value of the cash flows to be received or paid.
Thus in Briars financial statements the following entries will be made: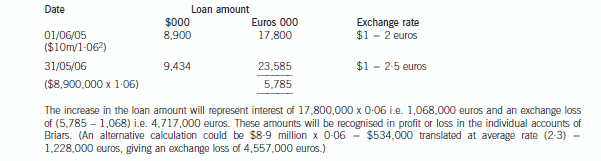
-
第2题:
(b) Discuss the relative costs to the preparer and benefits to the users of financial statements of increased
disclosure of information in financial statements. (14 marks)
Quality of discussion and reasoning. (2 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Increased information disclosure benefits users by reducing the likelihood that they will misallocate their capital. This is
obviously a direct benefit to individual users of corporate reports. The disclosure reduces the risk of misallocation of capital
by enabling users to improve their assessments of a company’s prospects. This creates three important results.
(i) Users use information disclosed to increase their investment returns and by definition support the most profitable
companies which are likely to be those that contribute most to economic growth. Thus, an important benefit of
information disclosure is that it improves the effectiveness of the investment process.
(ii) The second result lies in the effect on the liquidity of the capital markets. A more liquid market assists the effective
allocation of capital by allowing users to reallocate their capital quickly. The degree of information asymmetry between
the buyer and seller and the degree of uncertainty of the buyer and the seller will affect the liquidity of the market as
lower asymmetry and less uncertainty will increase the number of transactions and make the market more liquid.
Disclosure will affect uncertainty and information asymmetry.
(iii) Information disclosure helps users understand the risk of a prospective investment. Without any information, the user
has no way of assessing a company’s prospects. Information disclosure helps investors predict a company’s prospects.
Getting a better understanding of the true risk could lower the price of capital for the company. It is difficult to prove
however that the average cost of capital is lowered by information disclosure, even though it is logically and practically
impossible to assess a company’s risk without relevant information. Lower capital costs promote investment, which can
stimulate productivity and economic growth.
However although increased information can benefit users, there are problems of understandability and information overload.
Information disclosure provides a degree of protection to users. The benefit is fairness to users and is part of corporate
accountability to society as a whole.
The main costs to the preparer of financial statements are as follows:
(i) the cost of developing and disseminating information,
(ii) the cost of possible litigation attributable to information disclosure,
(iii) the cost of competitive disadvantage attributable to disclosure.
The costs of developing and disseminating the information include those of gathering, creating and auditing the information.
Additional costs to the preparers include training costs, changes to systems (for example on moving to IFRS), and the more
complex and the greater the information provided, the more it will cost the company.
Although litigation costs are known to arise from information disclosure, it does not follow that all information disclosure leads
to litigation costs. Cases can arise from insufficient disclosure and misleading disclosure. Only the latter is normally prompted
by the presentation of information disclosure. Fuller disclosure could lead to lower costs of litigation as the stock market would
have more realistic expectations of the company’s prospects and the discrepancy between the valuation implicit in the market
price and the valuation based on a company’s financial statements would be lower. However, litigation costs do not
necessarily increase with the extent of the disclosure. Increased disclosure could reduce litigation costs.
Disclosure could weaken a company’s ability to generate future cash flows by aiding its competitors. The effect of disclosure
on competitiveness involves benefits as well as costs. Competitive disadvantage could be created if disclosure is made relating
to strategies, plans, (for example, planned product development, new market targeting) or information about operations (for
example, production-cost figures). There is a significant difference between the purpose of disclosure to users and
competitors. The purpose of disclosure to users is to help them to estimate the amount, timing, and certainty of future cash
flows. Competitors are not trying to predict a company’s future cash flows, and information of use in that context is not
necessarily of use in obtaining competitive advantage. Overlap between information designed to meet users’ needs and
information designed to further the purposes of a competitor is often coincidental. Every company that could suffer competitive
disadvantage from disclosure could gain competitive advantage from comparable disclosure by competitors. Published figures
are often aggregated with little use to competitors.
Companies bargain with suppliers and with customers, and information disclosure could give those parties an advantage in
negotiations. In such cases, the advantage would be a cost for the disclosing entity. However, the cost would be offset
whenever information disclosure was presented by both parties, each would receive an advantage and a disadvantage.
There are other criteria to consider such as whether the information to be disclosed is about the company. This is both a
benefit and a cost criterion. Users of corporate reports need company-specific data, and it is typically more costly to obtain
and present information about matters external to the company. Additionally, consideration must be given as to whether the
company is the best source for the information. It could be inefficient for a company to obtain or develop data that other, more
expert parties could develop and present or do develop at present.
There are many benefits to information disclosure and users have unmet information needs. It cannot be known with any
certainty what the optimal disclosure level is for companies. Some companies through voluntary disclosure may have
achieved their optimal level. There are no quantitative measures of how levels of disclosure stand with respect to optimal
levels. Standard setters have to make such estimates as best they can, guided by prudence, and by what evidence of benefits
and costs they can obtain. -
第3题:
(ii) Using the previous overhead allocation basis (as per note 4), calculate the budgeted profit/(loss)
attributable to each type of service for the year ending 31 December 2006 and comment on the results
obtained using the previous and revised methods of overhead allocation. (5 marks)
正确答案: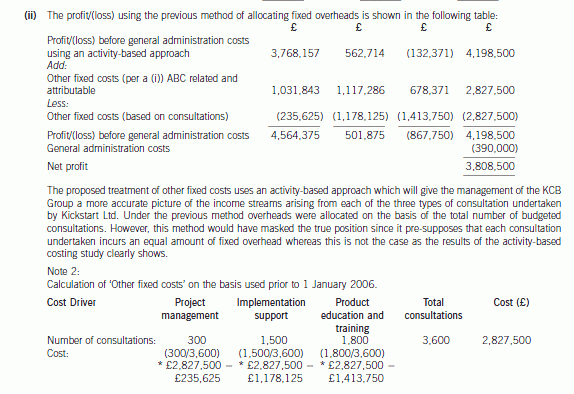
-
第4题:
(b) Calculate the corporation tax (CT) liabilities for Alantech Ltd, Boron Ltd and Bubble Ltd for the year ending
31 December 2004 on the assumption that loss reliefs are taken as early as possible. (9 marks)
正确答案:(b) Schedule D Case I calculation
The three companies form. a group for both group relief and capital gains purposes as all shareholdings pass the 75%
ownership test. The calculation of the corporation tax liabilities is as follows:
-
第5题:
(iii) State the value added tax (VAT) and stamp duty (SD) issues arising as a result of inserting Bold plc as
a holding company and identify any planning actions that can be taken to defer or minimise these tax
costs. (4 marks)
You should assume that the corporation tax rates for the financial year 2005 and the income tax rates
and allowances for the tax year 2005/06 apply throughout this question.
正确答案:
(iii) Bold plc will be making a taxable supply of services, likely to exceed the VAT threshold. It should therefore consider
registering for VAT – either immediately on a voluntary basis, or when its cumulative taxable supplies in the previous
twelve months exceed £60,000.
As an alternative, the new group can apply for a group VAT registration. This will simplify its VAT administration as intragroup
transactions are broadly disregarded for VAT purposes, and only one VAT return is required for the group as a
whole.
Stamp duty normally applies at 0·5% on the consideration payable in respect of transactions in shares. However, an
exemption is available in the case of a takeover, reconstruction or amalgamation where there is no real change in
ownership, i.e. the new shareholdings mirror the old shareholdings, and the transaction is for commercial purposes. The
insertion of a new holding company over an existing company, as proposed here, would qualify for this exemption.
There is no VAT on transactions in shares. -
第6题:
(c) You have just been advised of management’s intention to publish its yearly marketing report in the annual report
that will contain the financial statements for the year ending 31 December 2005. Extracts from the marketing
report include the following:
‘Shire Oil Co sponsors national school sports championships and the ‘Shire Ward’ at the national teaching
hospital. The company’s vision is to continue its investment in health and safety and the environment.
‘Our health and safety, security and environmental policies are of the highest standard in the energy sector. We
aim to operate under principles of no-harm to people and the environment.
‘Shire Oil Co’s main contribution to sustainable development comes from providing extra energy in a cleaner and
more socially responsible way. This means improving the environmental and social performance of our
operations. Regrettably, five employees lost their lives at work during the year.’
Required:
Suggest performance indicators that could reflect the extent to which Shire Oil Co’s social and environmental
responsibilities are being met, and the evidence that should be available to provide assurance on their
accuracy. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(c) Social and environmental responsibilities
Performance indicators
■ Absolute ($) and relative (%) level of investment in sports sponsorship, and funding to the Shire Ward.
■ Increasing number of championship events and participating schools/students as compared with prior year.
■ Number of medals/trophies sponsored at events and/or number awarded to Shire sponsored schools/students.
■ Number of patients treated (successfully) a week/month. Average bed occupancy (daily/weekly/monthly and cumulative
to date).
■ Staffing levels (e.g. of volunteers for sports events, Shire Ward staff and the company):
? ratio of starters to leavers/staff turnover;
? absenteeism (average number of days per person per annum).
1 Withdrawal of the new licence would not create a going concern issue.
2 May also be described as ‘exploration and evaluation’ costs or ‘discovery and assessment’.
■ Number of:
– breaches of health and safety regulations and environmental regulations;
– oil spills;
– accidents and employee fatalities;
– insurance claims.
Evidence
Tutorial note: As there is a wide range of performance indicators that candidates could suggest, there is always a wide range
of possible sources of audit evidence. As the same evidence may contribute to providing assurance on more than one
measure they are not tabulated here, to avoid duplication. However, candidates may justifiably adopt a tabular layout. Also
note, that where measures may be expressed as evidence (e.g. trophies awarded) marks should be awarded only once.
■ Actual level of investment ($) compared with budget and budget compared with prior period.
Tutorial note: Would expect actual to be at least greater than prior year if performance in these areas (health and
safety) has improved.
■ Physical evidence of favourable increases on prior year, for example:
? medals/cups sponsored;
? number of beds available.
■ Increase in favourable press coverage/reports of sponsored events. (Decrease in adverse press about
accidents/fatalities.)
■ Independent surveys (e.g. by marine conservation organisations, welfare groups, etc) comparing Shire favourably with
other oil producers.
■ A reduction in fines paid compared with budget (and prior year).
■ Reduction in legal fees and claims being settled as evidenced by fee notes and correspondence files.
■ Amounts settled on insurance claims and level of insurance cover as compared with prior period. -
第7题:
(c) Comment on the matters to be considered in seeking to determine the extent of Indigo Co’s financial loss
resulting from the alleged fraud. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(c) Extent of alleged fraud – Matters to be considered
■ Details reported to police: The managing director may have made some estimate of the possible extent of the fraud in
reporting the chief accountant’s disappearance to the police.
■ The minimum loss (assuming no insurance) would be sales for the three days before he left. If not known (e.g. because
the only record of them was in the cash book) a simple estimate might be 3/20 × total recorded revenue for a typical
month.
■ The pattern of cash bankings extracted from bank statements: A falling trend starting during the year might mark the
time from which the chief accountant began to misappropriate cash.
■ Whether other managers have voiced their suspicions, if any, on the chief accountant’s behaviour. For example, if there
was any marked change in his lifestyle. (what he appeared to spend his money on, the hours he worked, etc).
■ The prior year auditor’s report was unmodified. If this was appropriate the chief accountant’s alleged fraudulent activities
may have only started in the current year.
■ The amount of fidelity insurance cover (i.e. against employees handling cash) that Indigo has taken out to meet any
claim for fraud.
■ The likelihood, if any, of recovering misappropriated amounts. For example, if the chief accountant has assets (e.g. a
house) that can be used to settle Indigo’s claims against him in the event that he is caught/successfully prosecuted. -
第8题:
(b) You are an audit manager with specific responsibility for reviewing other information in documents containing
audited financial statements before your firm’s auditor’s report is signed. The financial statements of Hegas, a
privately-owned civil engineering company, show total assets of $120 million, revenue of $261 million, and profit
before tax of $9·2 million for the year ended 31 March 2005. Your review of the Annual Report has revealed
the following:
(i) The statement of changes in equity includes $4·5 million under a separate heading of ‘miscellaneous item’
which is described as ‘other difference not recognized in income’. There is no further reference to this
amount or ‘other difference’ elsewhere in the financial statements. However, the Management Report, which
is required by statute, is not audited. It discloses that ‘changes in shareholders’ equity not recognized in
income includes $4·5 million arising on the revaluation of investment properties’.
The notes to the financial statements state that the company has implemented IAS 40 ‘Investment Property’
for the first time in the year to 31 March 2005 and also that ‘the adoption of this standard did not have a
significant impact on Hegas’s financial position or its results of operations during 2005’.
(ii) The chairman’s statement asserts ‘Hegas has now achieved a position as one of the world’s largest
generators of hydro-electricity, with a dedicated commitment to accountable ethical professionalism’. Audit
working papers show that 14% of revenue was derived from hydro-electricity (2004: 12%). Publicly
available information shows that there are seven international suppliers of hydro-electricity in Africa alone,
which are all at least three times the size of Hegas in terms of both annual turnover and population supplied.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of the above matters for the auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Hegas for the year ended 31 March 2005. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Implications for the auditor’s report
(i) Management Report
■ $4·5 million represents 3·75% of total assets, 1·7% of revenue and 48·9% profit before tax. As this is material
by any criteria (exceeding all of 2% of total assets, 1/2% revenue and 5% PBT), the specific disclosure requirements
of IASs need to be met (IAS 1 ‘Presentation of Financial Statements’).
■ The Management Report discloses the amount and the reason for a material change in equity whereas the financial
statements do not show the reason for the change and suggest that it is immaterial. As the increase in equity
attributable to this adjustment is nearly half as much as that attributable to PBT there is a material inconsistency
between the Management Report and the audited financial statements.
■ Amendment to the Management Report is not required.
Tutorial note: Marks will be awarded for arguing, alternatively, that the Management Report disclosure needs to
be amended to clarify that the revaluation arises from the first time implementation.
■ Amendment to the financial statements is required because the disclosure is:
– incorrect – as, on first adoption of IAS 40, the fair value adjustment should be against the opening balance
of retained earnings; and
– inadequate – because it is being ‘supplemented’ by additional disclosure in a document which is not within
the scope of the audit of financial statements.
■ Whilst it is true that the adoption of IAS 40 did not have a significant impact on results of operations, Hegas’s
financial position has increased by nearly 4% in respect of the revaluation (to fair value) of just one asset category
(investment properties). As this is significant, the statement in the notes should be redrafted.
■ If the financial statements are not amended, the auditor’s report should be qualified ‘except for’ on grounds of
disagreement (non-compliance with IAS 40) as the matter is material but not pervasive. Additional disclosure
should also be given (e.g. that the ‘other difference’ is a fair value adjustment).
■ However, it is likely that when faced with the prospect of a qualified auditor’s report Hegas’s management will
rectify the financial statements so that an unmodified auditor’s report can be issued.
Tutorial note: Marks will be awarded for other relevant points e.g. citing IAS 8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in
Accounting Estimates and Errors’.
(ii) Chairman’s statement
Tutorial note: Hegas is privately-owned therefore IAS 14 ‘Segment Reporting’ does not apply and the proportion of
revenue attributable to hydro-electricity will not be required to be disclosed in the financial statements. However, credit
will be awarded for discussing the implications for the auditor’s report if it is regarded as a material inconsistency on
the assumption that segment revenue (or similar) is reported in the financial statements.
■ The assertion in the chairman’s statement, which does not fall within the scope of the audit of the financial
statements, claims two things, namely that the company:
(1) is ‘one of the world’s largest generators of hydro-electricity’; and
(2) has ‘a dedicated commitment to accountable ethical professionalism’.
■ To the extent that this information does not relate to matters disclosed in the financial statements it may give rise
to a material misstatement of fact. In particular, the first statement presents a misleading impression of the
company’s size. In misleading a user of the financial statements with this statement, the second statement is not
true (as it is not ethical or professional to mislead the reader and potentially undermine the credibility of the
financial statements).
■ The first statement is a material misstatement of fact because, for example:
– the company is privately-owned, and publicly-owned international/multi-nationals are larger;
– the company’s main activity is civil engineering not electricity generation (only 14% of revenue is derived from
HEP);
– as the company ranks at best eighth against African companies alone it ranks much lower globally.
■ Hegas should be asked to reconsider the wording of the chairman’s statement (i.e. removing these assertions) and
consult, as necessary, the company’s legal advisor.
■ If the statement is not changed there will be no grounds for qualification of the opinion on the audited financial
statements. The audit firm should therefore take legal advice on how the matter should be reported.
■ However, an emphasis of matter paragraph may be used to report on matters other than those affecting the audited
financial statements. For example, to explain the misstatement of fact if management refuses to make the
amendment.
Tutorial note: Marks will also be awarded for relevant comments about the chairman’s statement being perceived by
many readers to be subject to audit and therefore that the unfounded statement might undermine the credibility of the
financial statements. Shareholders tend to rely on the chairman’s statement, even though it is not regulated or audited,
because modern financial statements are so complex. -
第9题:
5 You are an audit manager in Fox & Steeple, a firm of Chartered Certified Accountants, responsible for allocating staff
to the following three audits of financial statements for the year ending 31 December 2006:
(a) Blythe Co is a new audit client. This private company is a local manufacturer and distributor of sportswear. The
company’s finance director, Peter, sees little value in the audit and put it out to tender last year as a cost-cutting
exercise. In accordance with the requirements of the invitation to tender your firm indicated that there would not
be an interim audit.
(b) Huggins Co, a long-standing client, operates a national supermarket chain. Your firm provided Huggins Co with
corporate financial advice on obtaining a listing on a recognised stock exchange in 2005. Senior management
expects a thorough examination of the company’s computerised systems, and are also seeking assurance that
the annual report will not attract adverse criticism.
(c) Gray Co has been an audit client since 1999 after your firm advised management on a successful buyout. Gray
provides communication services and software solutions. Your firm provides Gray with technical advice on
financial reporting and tax services. Most recently you have been asked to conduct due diligence reviews on
potential acquisitions.
Required:
For these assignments, compare and contrast:
(i) the threats to independence;
(ii) the other professional and practical matters that arise; and
(iii) the implications for allocating staff.
(15 marks)
正确答案:
5 FOX & STEEPLE – THREE AUDIT ASSIGNMENTS
(i) Threats to independence
Self-interest
Tutorial note: This threat arises when a firm or a member of the audit team could benefit from a financial interest in, or
other self-interest conflict with, an assurance client.
■ A self-interest threat could potentially arise in respect of any (or all) of these assignments as, regardless of any fee
restrictions (e.g. per IFAC’s ‘Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants’), the auditor is remunerated by clients for
services provided.
■ This threat is likely to be greater for Huggins Co (larger/listed) and Gray Co (requires other services) than for Blythe Co
(audit a statutory necessity).
■ The self-interest threat may be greatest for Huggins Co. As a company listed on a recognised stock exchange it may
give prestige and credibility to Fox & Steeple (though this may be reciprocated). Fox & Steeple could be pressurised into
taking evasive action to avoid the loss of a listed client (e.g. concurring with an inappropriate accounting treatment).
Self-review
Tutorial note: This arises when, for example, any product or judgment of a previous engagement needs to be re-evaluated
in reaching conclusions on the audit engagement.
■ This threat is also likely to be greater for Huggins and Gray where Fox & Steeple is providing other (non-audit) services.
■ A self-review threat may be created by Fox & Steeple providing Huggins with a ‘thorough examination’ of its computerised
systems if it involves an extension of the procedures required to conduct an audit in accordance with International
Standards on Auditing (ISAs).
■ Appropriate safeguards must be put in place if Fox & Steeple assists Huggins in the performance of internal audit
activities. In particular, Fox & Steeple’s personnel must not act (or appear to act) in a capacity equivalent to a member
of Huggins’ management (e.g. reporting, in a management role, to those charged with governance).
■ Fox & Steeple may provide Gray with accounting and bookkeeping services, as Gray is not a listed entity, provided that
any self-review threat created is reduced to an acceptable level. In particular, in giving technical advice on financial
reporting, Fox & Steeple must take care not to make managerial decisions such as determining or changing journal
entries without obtaining Gray’s approval.
■ Taxation services comprise a broad range of services, including compliance, planning, provision of formal taxation
opinions and assistance in the resolution of tax disputes. Such assignments are generally not seen to create threats to
independence.
Tutorial note: It is assumed that the provision of tax services is permitted in the jurisdiction (i.e. that Fox and Steeple
are not providing such services if prohibited).
■ The due diligence reviews for Gray may create a self-review threat (e.g. on the fair valuation of net assets acquired).
However, safeguards may be available to reduce these threats to an acceptable level.
■ If staff involved in providing other services are also assigned to the audit, their work should be reviewed by more senior
staff not involved in the provision of the other services (to the extent that the other service is relevant to the audit).
■ The reporting lines of any staff involved in the audit of Huggins and the provision of other services for Huggins should
be different. (Similarly for Gray.)
Familiarity
Tutorial note: This arises when, by virtue of a close relationship with an audit client (or its management or employees) an
audit firm (or a member of the audit team) becomes too sympathetic to the client’s interests.
■ Long association of a senior member of an audit team with an audit client may create a familiarity threat. This threat
is likely to be greatest for Huggins, a long-standing client. It may also be significant for Gray as Fox & Steeple have had
dealings with this client for seven years now.
■ As Blythe is a new audit client this particular threat does not appear to be relevant.
■ Senior personnel should be rotated off the Huggins and Gray audit teams. If this is not possible (for either client), an
additional professional accountant who was not a member of the audit team should be required to independently review
the work done by the senior personnel.
■ The familiarity threat of using the same lead engagement partner on an audit over a prolonged period is particularly
relevant to Huggins, which is now a listed entity. IFAC’s ‘Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants’ requires that the
lead engagement partner should be rotated after a pre-defined period, normally no more than seven years. Although it
might be time for the lead engagement partner of Huggins to be changed, the current lead engagement partner may
continue to serve for the 2006 audit.
Tutorial note: Two additional years are permitted when an existing client becomes listed, since it may not be in the
client’s best interests to have an immediate rotation of engagement partner.
Intimidation
Tutorial note: This arises when a member of the audit team may be deterred from acting objectively and exercising
professional skepticism by threat (actual or perceived), from the audit client.
■ This threat is most likely to come from Blythe as auditors are threatened with a tendering process to keep fees down.
■ Peter may have already applied pressure to reduce inappropriately the extent of audit work performed in order to reduce
fees, by stipulating that there should not be an interim audit.
■ The audit senior allocated to Blythe will need to be experienced in standing up to client management personnel such as
Peter.
Tutorial note: ‘Correct’ classification under ‘ethical’, ‘other professional’, ‘practical’ or ‘staff implications’ is not as important
as identifying the matters.
(ii) Other professional and practical matters
Tutorial note: ‘Other professional’ includes quality control.
■ The experience of staff allocated to each assignment should be commensurate with the assessment of associated risk.
For example, there may be a risk that insufficient audit evidence is obtained within the budget for the audit of Blythe.
Huggins, as a listed client, carries a high reputational risk.
■ Sufficient appropriate staff should be allocated to each audit to ensure adequate quality control (in particular in the
direction, supervision, review of each assignment). It may be appropriate for a second partner to be assigned to carry
out a ‘hot review’ (before the auditor’s report is signed) of:
– Blythe, because it is the first audit of a new client; and
– Huggins, as it is listed.
■ Existing clients (Huggins and Gray) may already have some expectation regarding who should be assigned to their
audits. There is no reason why there should not be some continuity of staff providing appropriate safeguards are put in
place (e.g. to overcome any familiarity threat).
■ Senior staff assigned to Blythe should be alerted to the need to exercise a high degree of professional skepticism (in the
light of Peter’s attitude towards the audit).
■ New staff assigned to Huggins and Gray would perhaps be less likely to assume unquestioned honesty than staff
previously involved with these audits.
Logistics (practical)
■ All three assignments have the same financial year end, therefore there will be an element of ‘competition’ for the staff
to be assigned to the year-end visits and final audit assignments. As a listed company, Huggins is likely to have the
tightest reporting deadline and so have a ‘priority’ for staff.
■ Blythe is a local and private company. Staff involved in the year-end visit (e.g. to attend the physical inventory count)
should also be involved in the final audit. As this is a new client, staff assigned to this audit should get involved at every
stage to increase their knowledge and understanding of the business.
■ Huggins is a national operation and may require numerous staff to attend year-end procedures. It would not be expected
that all staff assigned to year-end visits should all be involved in the final audit.
Time/fee/staff budgets
■ Time budgets will need to be prepared for each assignment to determine manpower requirements (and to schedule audit
work).
(iii) Implications for allocating staff
■ Fox & Steeple should allocate staff so that those providing other services to Huggins and Gray (that may create a selfreview
threat) do not participate in the audit engagement.
Competence and due care (Qualifications/Specialisation)
■ All audit assignments will require competent staff.
■ Huggins will require staff with an in-depth knowledge of their computerised system.
■ Gray will require senior audit staff to be experienced in financial reporting matters specific to communications and
software solutions (e.g. in revenue recognition issues and accounting for internally-generated intangible assets).
■ Specialists providing tax services and undertaking the due diligence reviews for Gray may not be required to have any
involvement in the audit assignment. -
第10题:
(c) Lamont owns a residential apartment above its head office. Until 31 December 2006 it was let for $3,000 a
month. Since 1 January 2007 it has been occupied rent-free by the senior sales executive. (6 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Lamont Co for the year ended
31 March 2007.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
正确答案:
(c) Rent-free accommodation
(i) Matters
■ The senior sales executive is a member of Lamont’s key management personnel and is therefore a related party.
■ The occupation of Lamont’s residential apartment by the senior sales executive is therefore a related party
transaction, even though no price is charged (IAS 24 Related Party Disclosures).
■ Related party transactions are material by nature and information about them should be disclosed so that users of
financial statements understand the potential effect of related party relationships on the financial statements.
■ The provision of ‘housing’ is a non-monetary benefit that should be included in the disclosure of key management
personnel compensation (within the category of short-term employee benefits).
■ The financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2007 should disclose the arrangement for providing the
senior sales executive with rent-free accommodation and its fair value (i.e. $3,000 per month).
Tutorial note: Since no price is charged for the transaction, rote-learned disclosures such as ‘the amount of outstanding
balances’ and ‘expense recognised in respect of bad debts’ are irrelevant.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Physical inspection of the apartment to confirm that it is occupied.
■ Written representation from the senior sales executive that he is occupying the apartment free of charge.
■ Written representation from the management board confirming that there are no related party transactions requiring
disclosure other than those that have been disclosed.
■ Inspection of the lease agreement with (or payments received from) the previous tenant to confirm the $3,000
monthly rental value. -
第11题:
(c) With specific reference to Hugh Co, discuss the objective of a review engagement and contrast the level of
assurance provided with that provided in an audit of financial statements. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(c) The objective of a review engagement is to enable the auditor to obtain moderate assurance as to whether the financial
statements have been prepared in accordance with an identified financial reporting framework. This is defined in ISRE 2400
Engagements to Review Financial Statements.
In order to obtain this assurance, it is necessary to gather evidence using analytical procedures and enquiries with
management. Detailed substantive procedures will not be performed unless the auditor has reason to believe that the
information may be materially misstated.
The auditor should approach the engagement with a high degree of professional scepticism, looking for circumstances that
may cause the financial statements to be misstated. For example, in Hugh Co, the fact that the preparer of the financial
statements is part-qualified may lead the auditor to believe that there is a high inherent risk that the figures are misstated.
As a result of procedures performed, the auditor’s objective is to provide a clear written expression of negative assurance on
the financial statements. In a review engagement the auditor would state that ‘we are not aware of any material modifications
that should be made to the financial statements….’
This is normally referred to as an opinion of ‘negative assurance’.
Negative assurance means that the auditor has performed limited procedures and has concluded that the financial statements
appear reasonable. The user of the financial statements gains some comfort that the figures have been subject to review, but
only a moderate level of assurance is provided. The user may need to carry out additional procedures of their own if they
want to rely on the financial statements. For example, if Hugh Co were to use the financial statements as a means to raise
further bank finance, the bank would presumably perform, or require Hugh Co to perform, additional procedures to provide
a higher level of assurance as to the validity of the figures contained in the financial statements.
In comparison, in an audit, a high level of assurance is provided. The auditors provide an opinion of positive, but not absolute
assurance. The user is assured that the figures are free from material misstatement and that the auditor has based the opinion
on detailed procedures. -
第12题:
You are an audit manager responsible for providing hot reviews on selected audit clients within your firm of Chartered
Certified Accountants. You are currently reviewing the audit working papers for Pulp Co, a long standing audit client,
for the year ended 31 January 2008. The draft statement of financial position (balance sheet) of Pulp Co shows total
assets of $12 million (2007 – $11·5 million).The audit senior has made the following comment in a summary of
issues for your review:
‘Pulp Co’s statement of financial position (balance sheet) shows a receivable classified as a current asset with a value
of $25,000. The only audit evidence we have requested and obtained is a management representation stating the
following:
(1) that the amount is owed to Pulp Co from Jarvis Co,
(2) that Jarvis Co is controlled by Pulp Co’s chairman, Peter Sheffield, and
(3) that the balance is likely to be received six months after Pulp Co’s year end.
The receivable was also outstanding at the last year end when an identical management representation was provided,
and our working papers noted that because the balance was immaterial no further work was considered necessary.
No disclosure has been made in the financial statements regarding the balance. Jarvis Co is not audited by our firm
and we have verified that Pulp Co does not own any shares in Jarvis Co.’
Required:
(b) In relation to the receivable recognised on the statement of financial position (balance sheet) of Pulp Co as
at 31 January 2008:
(i) Comment on the matters you should consider. (5 marks)
正确答案:
(b) (i) Matters to consider
Materiality
The receivable represents only 0·2% (25,000/12 million x 100) of total assets so is immaterial in monetary terms.
However, the details of the transaction could make it material by nature.
The amount is outstanding from a company under the control of Pulp Co’s chairman. Readers of the financial statements
would be interested to know the details of this transaction, which currently is not disclosed. Elements of the transaction
could be subject to bias, specifically the repayment terms, which appear to be beyond normal commercial credit terms.
Paul Sheffield may have used his influence over the two companies to ‘engineer’ the transaction. Disclosure is necessary
due to the nature of the transaction, the monetary value is irrelevant.
A further matter to consider is whether this is a one-off transaction, or indicative of further transactions between the two
companies.
Relevant accounting standard
The definitions in IAS 24 must be carefully considered to establish whether this actually constitutes a related party
transaction. The standard specifically states that two entities are not necessarily related parties just because they have
a director or other member of key management in common. The audit senior states that Jarvis Co is controlled by Peter
Sheffield, who is also the chairman of Pulp Co. It seems that Peter Sheffield is in a position of control/significant influence
over the two companies (though this would have to be clarified through further audit procedures), and thus the two
companies are likely to be perceived as related.
IAS 24 requires full disclosure of the following in respect of related party transactions:
– the nature of the related party relationship,
– the amount of the transaction,
– the amount of any balances outstanding including terms and conditions, details of security offered, and the nature
of consideration to be provided in settlement,
– any allowances for receivables and associated expense.
There is currently a breach of IAS 24 as no disclosure has been made in the notes to the financial statements. If not
amended, the audit opinion on the financial statements should be qualified with an ‘except for’ disagreement. In
addition, if practicable, the auditor’s report should include the information that would have been included in the financial
statements had the requirements of IAS 24 been adhered to.
Valuation and classification of the receivable
A receivable should only be recognised if it will give rise to future economic benefit, i.e. a future cash inflow. It appears
that the receivable is long outstanding – if the amount is unlikely to be recovered then it should be written off as a bad
debt and the associated expense recognised. It is possible that assets and profits are overstated.
Although a representation has been received indicating that the amount will be paid to Pulp Co, the auditor should be
sceptical of this claim given that the same representation was given last year, and the amount was not subsequently
recovered. The $25,000 could be recoverable in the long term, in which case the receivable should be reclassified as
a non-current asset. The amount advanced to Jarvis Co could effectively be an investment rather than a short term
receivable. Correct classification on the statement of financial position (balance sheet) is crucial for the financial
statements to properly show the liquidity position of the company at the year end.
Tutorial note: Digressions into management imposing a limitation in scope by withholding evidence are irrelevant in this
case, as the scenario states that the only evidence that the auditors have asked for is a management representation.
There is no indication in the scenario that the auditors have asked for, and been refused any evidence. -
第13题:
(b) Prepare a consolidated statement of financial position of the Ribby Group at 31 May 2008 in accordance
with International Financial Reporting Standards. (35 marks)
正确答案:

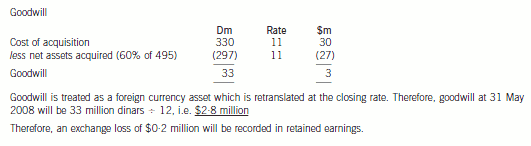
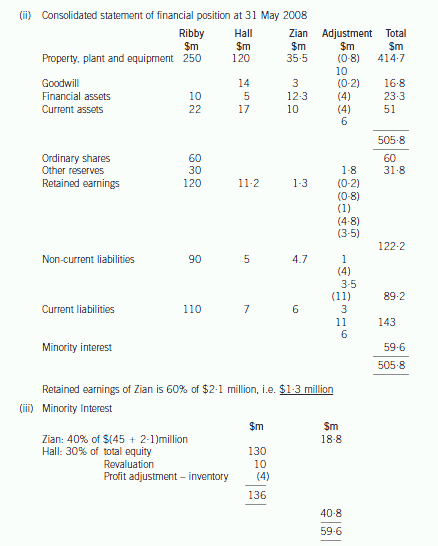

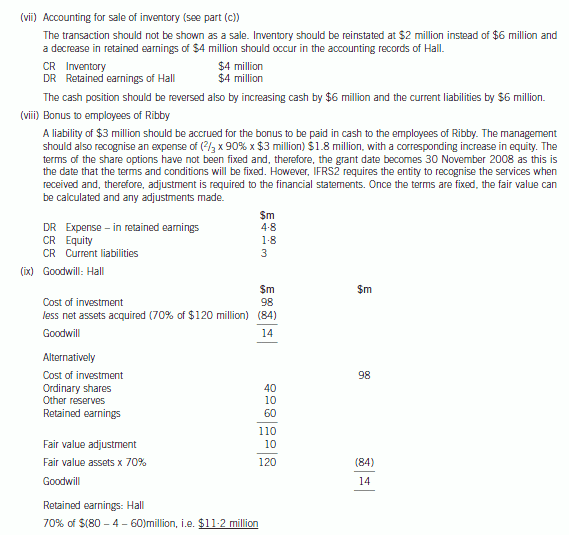


-
第14题:
(c) Using information from the case, assess THREE risks to the Giant Dam Project. (9 marks)
正确答案:
(c) Assessment of three risks
Disruption and resistance by Stop-the-dam. Stop-the-dam seems very determined to delay and disrupt progress as much as
possible. The impact of its activity can be seen on two levels. It is likely that the tunnelling and other ‘human’ disruption will
cause a short-term delay but the more significant impact is that of exposing the lenders. In terms of probability, the case says
that it ‘would definitely be attempting to resist the Giant Dam Project when it started’ but the probability of exposing the
lenders is a much lower probability event if the syndicate membership is not disclosed.
Impact/hazard: low
Probability/likelihood: high
The risk to progress offered by First Nation can probably be considered to be low impact/hazard but high probability. The case
says that it ‘would be unlikely to disrupt the building of the dam’, meaning low impact/hazard, but that ‘it was highly likely
that they would protest’, meaning a high level of probability that the risk event would occur.
Impact: low
Probability: high
There are financing risks as banks seems to be hesitant when it comes to lending to R&M for the project. Such a risk event,
if realised, would have a high potential for disruption to progress as it may leave R&M with working capital financing
difficulties. The impact would be high because the bank may refuse to grant or extend loans if exposed (subject to existing
contractual terms). It is difficult to estimate the probability. Perhaps there will be a range of attitudes by the lending banks
with some more reticent than others (perhaps making it a ‘medium’ probability event).
Impact: medium to high (depending on the reaction of the bank)
Probability: low to medium (depending on how easy it would be to discover the lender) -
第15题:
(b) Comment (with relevant calculations) on the performance of the business of Quicklink Ltd and Celer
Transport during the year ended 31 May 2005 and, insofar as the information permits, its projected
performance for the year ending 31 May 2006. Your answer should specifically consider:
(i) Revenue generation per vehicle
(ii) Vehicle utilisation and delivery mix
(iii) Service quality. (14 marks)
正确答案: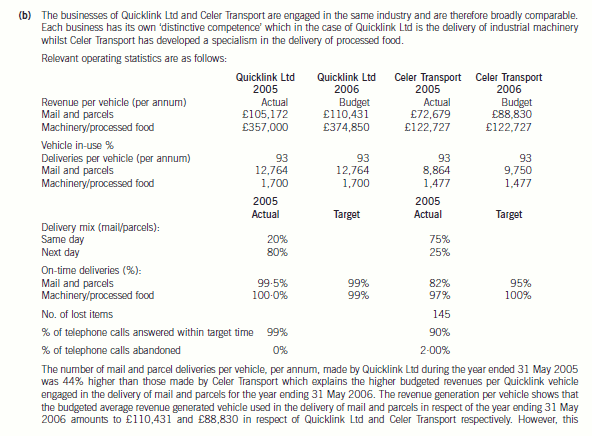
difference will reduce in the year ending 31 May 2006 due to the projected growth in sales volumes of the Celer Transport
business. The average mail/parcels delivery of mail/parcels per vehicle of the Quicklink Ltd part of the business is budgeted
at 12,764 which is still 30·91% higher than that of the Celer Transport business.
As far as specialist activities are concerned, Quicklink Ltd is budgeted to generate average revenues per vehicle amounting to
£374,850 whilst Celer Transport is budgeted to earn an average of £122,727 from each of the vehicles engaged in delivery
of processed food. It is noticeable that all contracts with major food producers were renewed on 1 June 2005 and it would
appear that there were no increases in the annual value of the contracts with major food producers. This might have been
the result of a strategic decision by the management of the combined entity in order to secure the future of this part of the
business which had been built up previously by the management of Celer Transport.
Each vehicle owned by Quicklink Ltd and Celer Transport is in use for 340 days during each year, which based on a
365 day year would give an in use % of 93%. This appears acceptable given the need for routine maintenance and repairs
due to wear and tear.
During the year ended 31 May 2005 the number of on-time deliveries of mail and parcel and industrial machinery deliveries
were 99·5% and 100% respectively. This compares with ratios of 82% and 97% in respect of mail and parcel and processed
food deliveries made by Celer Transport. In this critical area it is worth noting that Quicklink Ltd achieved their higher on-time
delivery target of 99% in respect of each activity whereas Celer Transport were unable to do so. Moreover, it is worth noting
that Celer Transport missed their target time for delivery of food products on 975 occasions throughout the year 31 May 2005
and this might well cause a high level of customer dissatisfaction and even result in lost business.
It is interesting to note that whilst the businesses operate in the same industry they have a rather different delivery mix in
terms of same day/next day demands by clients. Same day deliveries only comprise 20% of the business of Quicklink Ltd
whereas they comprise 75% of the business of Celer Transport. This may explain why the delivery performance of Celer
Transport with regard to mail and parcel deliveries was not as good as that of Quicklink Ltd.
The fact that 120 items of mail and 25 parcels were lost by the Celer Transport business is most disturbing and could prove
damaging as the safe delivery of such items is the very substance of the business and would almost certainly have resulted
in a loss of customer goodwill. This is an issue which must be addressed as a matter of urgency.
The introduction of the call management system by Quicklink Ltd on 1 June 2004 is now proving its worth with 99% of calls
answered within the target time of 20 seconds. This compares favourably with the Celer Transport business in which only
90% of a much smaller volume of calls were answered within a longer target time of 30 seconds. Future performance in this
area will improve if the call management system is applied to the Celer Transport business. In particular, it is likely that the
number of abandoned calls will be reduced and enhance the ‘image’ of the Celer Transport business.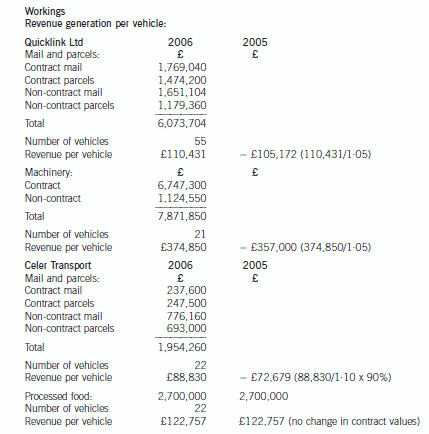

-
第16题:
(c) (i) Provide three examples of personal financial planning protection products that would be of use in
Henry’s situation. Justify your selections by reference to the type of protection provided. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(c) (i) Protection products
Henry is still working and has a mortgage to support. He therefore needs to protect not only his assets but also cover
any debt, or the ability to repay. The following protection policies are relevant to Henry’s situation.
Life assurance
This is a form. of insurance that pays out on a chargeable event, usually death. The main types are:
– Term Assurance which provides cover for a fixed term with the sum assured payable only on death. No investment
benefits or payments arise on survival.
– Whole of Life Assurance where the policy provides life protection. The sum assured is payable on death at any time
and usually some form. of investment benefit will accrue in the form. of a surrender value.
A qualifying policy will give a tax-free lump sum that could, for example, be used to repay the mortgage.
Permanent health insurance
Permanent health insurance policies are designed to provide the policyholder with a benefit if s/he is unable to work
through sickness or if s/he needs medical expenses or long-term care.
This would provide Henry with an income in the event of illness – again useful given his mortgage, and would avoid
the need to liquidate other assets to pay the mortgage or ongoing costs.
Critical illness insurance
These policies provide a capital sum where a critical illness (from a large range listed in the policy) is diagnosed.
For the same reasons above, Henry should consider this in conjunction with permanent health insurance.
Note: Marks will also be given for other relevant protection products, e.g. specific mortgage protection insurance linked
to an event other than death. -
第17题:
(ii) The use of the trading loss of Tethys Ltd for the year ending 31 December 2008; (6 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Tethys Ltd – Use of trading loss
– The two companies will not be in a group relief group as Saturn Ltd will not own 75% of Tethys Ltd.
– For a consortium to exist, 75% of the ordinary share capital of Tethys Ltd must be held by companies which each
hold at least 5%. Accordingly, Tethys Ltd will be a consortium company if the balance of its share capital is owned
by Clangers Ltd but not if it is owned by Edith Clanger.
– If Tethys Ltd qualifies as a consortium company: 65% of its trading losses in the period from 1 August 2008 to
31 December 2008 can be surrendered to Saturn Ltd, i.e. £21,667 (£80,000 x 5/12 x 65%).
– If Tethys Ltd does not qualify as a consortium company: none of its loss can be surrendered to Saturn Ltd.
– The acquisition of 65% of Tethys Ltd is a change in ownership of the company. If there is a major change in the
nature or conduct of the trade of Tethys Ltd within three years of 1 August 2008, the loss arising prior to that date
cannot be carried forward for relief in the future.
Further information required:
– Ownership of the balance of the share capital of Tethys Ltd. -
第18题:
2 Your firm was appointed as auditor to Indigo Co, an iron and steel corporation, in September 2005. You are the
manager in charge of the audit of the financial statements of Indigo, for the year ending 31 December 2005.
Indigo owns office buildings, a workshop and a substantial stockyard on land that was leased in 1995 for 25 years.
Day-to-day operations are managed by the chief accountant, purchasing manager and workshop supervisor who
report to the managing director.
All iron, steel and other metals are purchased for cash at ‘scrap’ prices determined by the purchasing manager. Scrap
metal is mostly high volume. A weighbridge at the entrance to the stockyard weighs trucks and vans before and after
the scrap metals that they carry are unloaded into the stockyard.
Two furnaces in the workshop melt down the salvageable scrap metal into blocks the size of small bricks that are then
stored in the workshop. These are sold on both credit and cash terms. The furnaces are now 10 years old and have
an estimated useful life of a further 15 years. However, the furnace linings are replaced every four years. An annual
provision is made for 25% of the estimated cost of the next relining. A by-product of the operation of the furnaces is
the production of ‘clinker’. Most of this is sold, for cash, for road surfacing but some is illegally dumped.
Indigo’s operations are subsidised by the local authority as their existence encourages recycling and means that there
is less dumping of metal items. Indigo receives a subsidy calculated at 15% of the market value of metals purchased,
as declared in a quarterly return. The return for the quarter to 31 December 2005 is due to be submitted on
21 January 2006.
Indigo maintains manual inventory records by metal and estimated quality. Indigo counted inventory at 30 November
2005 with the intention of ‘rolling-forward’ the purchasing manager’s valuation as at that date to the year-end
quantities per the manual records. However, you were not aware of this until you visited Indigo yesterday to plan
your year-end procedures.
During yesterday’s tour of Indigo’s premises you saw that:
(i) sheets of aluminium were strewn across fields adjacent to the stockyard after a storm blew them away;
(ii) much of the vast quantity of iron piled up in the stockyard is rusty;
(iii) piles of copper and brass, that can be distinguished with a simple acid test, have been mixed up.
The count sheets show that metal quantities have increased, on average, by a third since last year; the quantity of
aluminium, however, is shown to be three times more. There is no suitably qualified metallurgical expert to value
inventory in the region in which Indigo operates.
The chief accountant disappeared on 1 December, taking the cash book and cash from three days’ sales with him.
The cash book was last posted to the general ledger as at 31 October 2005. The managing director has made an
allegation of fraud against the chief accountant to the police.
The auditor’s report on the financial statements for the year ended 31 December 2004 was unmodified.
Required:
(a) Describe the principal audit procedures to be carried out on the opening balances of the financial statements
of Indigo Co for the year ending 31 December 2005. (6 marks)
正确答案:
2 INDIGO CO
(a) Opening balances – principal audit procedures
Tutorial note: ‘Opening balances’ means those account balances which exist at the beginning of the period. The question
clearly states that the prior year auditor’s report was unmodified therefore any digression into the prior period opinion being
other than unmodified or the prior period not having been audited will not earn marks.
■ Review of the application of appropriate accounting policies in the financial statements for the year ended 31 December
2004 to ensure consistent with those applied in 2005.
■ Where permitted (e.g. if there is a reciprocal arrangement with the predecessor auditor to share audit working papers
on a change of appointment), a review of the prior period audit working papers.
Tutorial note: There is no legal, ethical or other professional duty that requires a predecessor auditor to make available
its working papers.
■ Current period audit procedures that provide evidence concerning the existence, measurement and completeness of
rights and obligations. For example:
? after-date receipts (in January 2005 and later) confirming the recoverable amount of trade receivables at
31 December 2004;
? similarly, after-date payments confirming the completeness of trade and other payables (for services);
? after-date sales of inventory held at 31 December 2004;
? review of January 2005 bank reconciliation (confirming clearance of reconciling items at 31 December 2004).
■ Analytical procedures on ratios calculated month-on-month from 31 December 2004 to date and further investigation
of any distortions identified at the beginning of the current reporting period. For example:
? inventory turnover (by category of metal);
? average collection payment;
? average payment period;
? gross profit percentage (by metal).
■ Examination of historic accounting records for non-current assets and liabilities (if necessary). For example:
? agreeing balances on asset registers to the client’s trial balance as at 31 December 2004;
? agreeing statements of balances on loan accounts to the financial statements as at 31 December 2004.
■ If the above procedures do not provide sufficient evidence, additional substantive procedures should be performed. For
example, if additional evidence is required concerning inventory at 31 December 2004, cut-off tests may be
reperformed. -
第19题:
4 (a) Explain the auditor’s responsibilities in respect of subsequent events. (5 marks)
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of the above matters for the auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Jinack Co for the year ended 30 September 2005 and, where appropriate, the year ending
30 September 2006.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the matters.
正确答案:
4 JINACK CO
(a) Auditor’s responsibilities for subsequent events
■ Auditors must consider the effect of subsequent events on:
– the financial statements;
– the auditor’s report.
■ Subsequent events are all events occurring after a period end (i.e. reporting date) i.e.:
– events after the balance sheet date (as defined in IAS 10); and
– events after the financial statements have been authorised for issue.
Events occurring up to date of auditor’s report
■ The auditor is responsible for carrying out procedures designed to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence that all
events up to the date of the auditor’s report that may require adjustment of, or disclosure in, the financial statements
have been identified.
■ These procedures are in addition to those applied to specific transactions occurring after the period end that provide
audit evidence of period-end account balances (e.g. inventory cut-off and receipts from trade receivables). Such
procedures should ordinarily include:
– reviewing minutes of board/audit committee meetings;
– scrutinising latest interim financial statements/budgets/cash flows, etc;
– making/extending inquiries to legal advisors on litigation matters;
– inquiring of management whether any subsequent events have occurred that might affect the financial statements
(e.g. commitments entered into).
■ When the auditor becomes aware of events that materially affect the financial statements, the auditor must consider
whether they have been properly accounted for and adequately disclosed in the financial statements.
Facts discovered after the date of the auditor’s report but before financial statements are issued
Tutorial note: After the date of the auditor’s report it is management’s responsibility to inform. the auditor of facts which
may affect the financial statements.
■ If the auditor becomes aware of such facts which may materially affect the financial statements, the auditor:
– considers whether the financial statements need amendment;
– discusses the matter with management; and
– takes appropriate action (e.g. audit any amendments to the financial statements and issue a new auditor’s report).
■ If management does not amend the financial statements (where the auditor believes they need to be amended) and the
auditor’s report has not been released to the entity, the auditor should express a qualified opinion or an adverse opinion
(as appropriate).
■ If the auditor’s report has been released to the entity, the auditor must notify those charged with governance not to issue
the financial statements (and the auditor’s report thereon) to third parties.
Tutorial note: The auditor would seek legal advice if the financial statements and auditor’s report were subsequently issued.
Facts discovered after the financial statements have been issued
■ The auditor has no obligation to make any inquiry regarding financial statements that have been issued.
■ However, if the auditor becomes aware of a fact which existed at the date of the auditor’s report and which, if known
at that date, may have caused the auditor’s report to be modified, the auditor should:
– consider whether the financial statements need revision;
– discuss the matter with management; and
– take appropriate action (e.g. issuing a new report on revised financial statements). -
第20题:
(b) Identify and explain the financial statement risks to be taken into account in planning the final audit.
(12 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Financial statement risks
Tutorial note: Note the timeframe. Financial statements for the year to 30 June 2006 are draft. Certain misstatements
may therefore exist due to year-end procedures not yet having taken place.
Revenue/(Receivables)
■ Revenue has increased by 11·8% ((161·5 – 144·4)/144·4 × 100). Overstatement could arise if rebates due to customers
have not yet been accounted for in full (as they are calculated in arrears). If rebates have still to be accounted for trade
receivables will be similarly overstated.
Materials expense
■ Materials expense has increased by 17·8% ((88.0 – 74·7)/74·7 × 100). This is more than the increase in revenue. This
could be legitimate (e.g. if fuel costs have increased significantly). However, the increase could indicate misclassification
of:
– revenue expenditure (see fall in other expenses below);
– capital expenditure (e.g. on overhauls or major refurbishment) as revenue;
– finance lease payments as operating lease.
Depreciation/amortisation
■ This has fallen by 10·5% ((8·5 – 9·5)/9·5 × 100). This could be valid (e.g. if Yates has significant assets already fully
depreciated or the asset base is lower since last year’s restructuring). However, there is a risk of understatement if, for
example:
– not all assets have been depreciated (or depreciated at the wrong rates, or only for 11 months of the year);
– cost of non-current assets is understated (e.g. due to failure to recognise capital expenditure)1;
– impairment losses have not been recognised (as compared with the prior year).
Tutorial note: Depreciation on vehicles and transport equipment represents only 7% of cost. If all items were being
depreciated on a straight-line basis over eight years this should be 12·5%. The depreciation on other equipment looks more
reasonable as it amounts to 14% which would be consistent with an average age of vehicles of seven years (i.e. in the middle
of the range 3 – 13 years).
Other expenses
■ These have fallen by 15·5% ((19·6 – 23·2)/23·2 × 100). They may have fallen (e.g. following the restructuring) or may be
understated due to:
– expenses being misclassified as materials expense;
– underestimation of accrued expenses (especially as the financial reporting period has not yet expired).
Intangibles
■ Intangible assets have increased by $1m (16% on the prior year). Although this may only just be material to the
financial statements as a whole (see (a)) this is the net movement, therefore additions could be material.
■ Internally-generated intangibles will be overstated if:
– any of the IAS 38 recognition criteria cannot be demonstrated;
– any impairment in the year has not yet been written off in accordance with IAS 36 ‘Impairment of Assets’.
Tangible assets
■ The net book value of property (at cost) has fallen by 5%, vehicles are virtually unchanged (increased by just 2·5%)
and other equipment (though the least material category) has fallen by 20·4%.
■ Vehicles and equipment may be overstated if:
– disposals have not been recorded;
– depreciation has been undercharged (e.g. not for a whole year);
– impairments have not yet been accounted for.
■ Understatement will arise if finance leases are treated as operating leases.
Receivables
■ Trade receivables have increased by just 2·2% (although sales increased by 11·8%) and may be understated due to a
cutoff error resulting in overstatement of cash receipts.
■ There is a risk of overstatement if sufficient allowances have not been made for the impairment of individually significant
balances and for the remainder assessed on a portfolio or group basis.
Restructuring provision
■ The restructuring provision that was made last year has fallen/been utilised by 10·2%. There is a risk of overstatement
if the provision is underutilised/not needed for the purpose for which it was established.
Finance lease liabilities
■ Although finance lease liabilities have increased (by $1m) there is a greater risk of understatement than overstatement
if leased assets are not recognised on the balance sheet (i.e. capitalised).
■ Disclosure risk arises if the requirements of IAS 17 ‘Leases’ (e.g. in respect of minimum lease payments) are not met.
Trade payables
■ These have increased by only 5·3% compared with the 17·8% increase in materials expense. There is a risk of
understatement as notifications (e.g. suppliers’ invoices) of liabilities outstanding at 30 June 2006 may have still to be
received (the month of June being an unexpired period).
Other (employee) liabilities
■ These may be understated as they have increased by only 7·5% although staff costs have increased by 14%. For
example, balances owing in respect of outstanding holiday entitlements at the year end may not yet be accurately
estimated.
Tutorial note: Credit will be given to other financial statements risks specific to the scenario. For example, ‘time-sensitive
delivery schedules’ might give rise to penalties or claims, that could result in understated provisions or undisclosed
contingent liabilities. Also, given that this is a new audit and the result has changed significantly (from loss to profit) might
suggest a risk of misstatement in the opening balances (and hence comparative information).
1 Tutorial note: This may be unlikely as other expenses have fallen also. -
第21题:
(b) Explain what effect the acquisition of Di Rollo Co will have on the planning of your audit of the consolidated
financial statements of Murray Co for the year ending 31 March 2008. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Effect of acquisition on planning the audit of Murray’s consolidated financial statements for the year ending 31 March
2008
Group structure
The new group structure must be ascertained to identify all entities that should be consolidated into the Murray group’s
financial statements for the year ending 31 March 2008.
Materiality assessment
Preliminary materiality for the group will be much higher, in monetary terms, than in the prior year. For example, if a % of
total assets is a determinant of the preliminary materiality, it may be increased by 10% (as the fair value of assets acquired,
including goodwill, is $2,373,000 compared with $21·5m in Murray’s consolidated financial statements for the year ended
31 March 2007).
The materiality of each subsidiary should be re-assessed, in terms of the enlarged group as at the planning stage. For
example, any subsidiary that was just material for the year ended 31 March 2007 may no longer be material to the group.
This assessment will identify, for example:
– those entities requiring an audit visit; and
– those entities for which substantive analytical procedures may suffice.
As Di Rollo’s assets are material to the group Ross should plan to inspect the South American operations. The visit may
include a meeting with Di Rollo’s previous auditors to discuss any problems that might affect the balances at acquisition and
a review of the prior year audit working papers, with their permission.
Di Rollo was acquired two months into the financial year therefore its post-acquisition results should be expected to be
material to the consolidated income statement.
Goodwill acquired
The assets and liabilities of Di Rollo at 31 March 2008 will be combined on a line-by-line basis into the consolidated financial
statements of Murray and goodwill arising on acquisition recognised.
Audit work on the fair value of the Di Rollo brand name at acquisition, $600,000, may include a review of a brand valuation
specialist’s working papers and an assessment of the reasonableness of assumptions made.
Significant items of plant are likely to have been independently valued prior to the acquisition. It may be appropriate to plan
to place reliance on the work of expert valuers. The fair value adjustment on plant and equipment is very high (441% of
carrying amount at the date of acquisition). This may suggest that Di Rollo’s depreciation policies are over-prudent (e.g. if
accelerated depreciation allowed for tax purposes is accounted for under local GAAP).
As the amount of goodwill is very material (approximately 50% of the cash consideration) it may be overstated if Murray has
failed to recognise any assets acquired in the purchase of Di Rollo in accordance with IFRS 3 Business Combinations. For
example, Murray may have acquired intangible assets such as customer lists or franchises that should be recognised
separately from goodwill and amortised (rather than tested for impairment).
Subsequent impairment
The audit plan should draw attention to the need to consider whether the Di Rollo brand name and goodwill arising have
suffered impairment as a result of the allegations against Di Rollo’s former chief executive.
Liabilities
Proceedings in the legal claim made by Di Rollo’s former chief executive will need to be reviewed. If the case is not resolved
at 31 March 2008, a contingent liability may require disclosure in the consolidated financial statements, depending on the
materiality of amounts involved. Legal opinion on the likelihood of Di Rollo successfully defending the claim may be sought.
Provision should be made for any actual liabilities, such as legal fees.
Group (related party) transactions and balances
A list of all the companies in the group (including any associates) should be included in group audit instructions to ensure
that intra-group transactions and balances (and any unrealised profits and losses on transactions with associates) are
identified for elimination on consolidation. Any transfer pricing policies (e.g. for clothes manufactured by Di Rollo for Murray
and sales of Di Rollo’s accessories to Murray’s retail stores) must be ascertained and any provisions for unrealised profit
eliminated on consolidation.
It should be confirmed at the planning stage that inter-company transactions are identified as such in the accounting systems
of all companies and that inter-company balances are regularly reconciled. (Problems are likely to arise if new inter-company
balances are not identified/reconciled. In particular, exchange differences are to be expected.)
Other auditors
If Ross plans to use the work of other auditors in South America (rather than send its own staff to undertake the audit of Di
Rollo), group instructions will need to be sent containing:
– proforma statements;
– a list of group and associated companies;
– a statement of group accounting policies (see below);
– the timetable for the preparation of the group accounts (see below);
– a request for copies of management letters;
– an audit work summary questionnaire or checklist;
– contact details (of senior members of Ross’s audit team).
Accounting policies
Di Rollo may have material accounting policies which do not comply with the rest of the Murray group. As auditor to Di Rollo,
Ross will be able to recalculate the effect of any non-compliance with a group accounting policy (that Murray’s management
would be adjusting on consolidation).
Timetable
The timetable for the preparation of Murray’s consolidated financial statements should be agreed with management as soon
as possible. Key dates should be planned for:
– agreement of inter-company balances and transactions;
– submission of proforma statements;
– completion of the consolidation package;
– tax review of group accounts;
– completion of audit fieldwork by other auditors;
– subsequent events review;
– final clearance on accounts of subsidiaries;
– Ross’s final clearance of consolidated financial statements.
Tutorial note: The order of dates is illustrative rather than prescriptive. -
第22题:
(b) Describe the potential benefits for Hugh Co in choosing to have a financial statement audit. (4 marks)
正确答案:
(b) There are several benefits for Hugh Co in choosing a voluntary financial statement audit.
An annual audit will ensure that any material mistakes made by the part-qualified accountant in preparing the year end
financial statements will be detected. This is important as the directors will be using the year end accounts to review their
progress in the first year of trading and will need reliable figures to assess performance. An audit will give the directors comfort
that the financial statements are a sound basis for making business decisions.
Accurate first year figures will also enable more effective budgeting and forecasting, which will be crucial if rapid growth is to
be achieved.
The auditors are likely to use the quarterly management accounts as part of normal audit procedures. The auditors will be
able to advise Monty Parkes of any improvements that could be made to the management accounts, for example, increased
level of detail, more frequent reporting. Better quality management accounts will help the day-to-day running of the business
and enable a speedier response to any problems arising during the year.
As a by-product of the audit, a management letter (report to those charged with governance) will be produced, identifying
weaknesses and making recommendations on areas such as systems and controls which will improve the smooth running of
the business.
It is likely that Hugh Co will require more bank funding in order to expand, and it is likely that the bank would like to see
audited figures for review, before deciding on further finance. It will be easier and potentially cheaper to raise finance from
other providers with an audited set of financial statements.
As the business deals in cash sales, and retails small, luxury items there is a high risk of theft of assets. The external audit
can act as both a deterrent and a detective control, thus reducing the risk of fraud and resultant detrimental impact on the
financial statements.
Accurate financial statements will be the best basis for tax assessment and tax planning. An audit opinion will enhance the
credibility of the figures.
If the business grows rapidly, then it is likely that at some point in the future, the audit exemption limit will be exceeded and
thus an audit will become mandatory.
Choosing to have an audit from the first year of incorporation will reduce potential errors carried down to subsequent periods
and thus avoid qualifications of opening balances. -
第23题:
(ii) Identify and explain the potential financial statement risks caused by the breach of planning regulations
discussed in the press cutting. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(ii) Several significant financial statement risks are indicated by the press cutting.
Overstatement of property, plant and equipment
Medix Co has constructed a research laboratory which is likely to be impaired at the year end. The local authority has
the power to shut down the facility, and it is clear from the press cutting that this is likely to happen before the year end.
Following IAS 36 Impairment of Assets, the premises should be written down to recoverable amount, and the
impairment loss recognised as an expense. The directors should carry out an impairment review before the year end. If
the premises cannot be used as intended then the recoverable amount (measured using the higher of value in use and
fair value less selling cost) is likely to be less than current carrying value. In this case, assuming the local authority is
successful in shutting down the research laboratory, the recoverable amount is likely to be nil, as the premises have no
value in use, as it will never be used commercially, and has no market value as it is likely to be demolished.
In addition, any tangible assets such as laboratory equipment located at the premises should be tested for impairment
as if the company cannot use the premises then the assets contained within it are likely to have a lower recoverable
amount than carrying value.
Contingency – fines or penalties imposed by local authority
The press cutting indicates that Medix Co has been sued before, and that the local authority may again take legal action
against the company. IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets states that a provision should be
recognised if the company has a probable obligation at the year end which can be measured reliably. If payment is
deemed only possible at the year end, then disclosure of the contingent liability should be made in a note to the financial
statements.
If the local authority commences legal proceedings against Medix Co before the year end of 30 June 2008, then
management should assess the probability of payment. The financial statement risk is not recognising a provision (and
associated expense within the income statement), or not disclosing a contingency.
Demolition costs
The local authority may require Medix Co to demolish the premises. If this demand is made before the year end, Medix
Co should recognise a provision for demolition costs as an unavoidable legal obligation would have been created. The
financial statement risk is that in this situation, Medix Co fails to recognise a provision and associated expense within
the income statement.
Going concern
The above issues could indicate that the company may not continue in operational existence. The potential lack of
disclosure of these issues represents a financial statement risk.
