15 A trader who fixes her prices by adding 50% to cost actually achieved a mark-up of 45%.Which of the following factors could account for the shortfall?1 Sales were lower than expected.2 The opening inventories had been overstated.3 The closing inventori
题目
15 A trader who fixes her prices by adding 50% to cost actually achieved a mark-up of 45%.
Which of the following factors could account for the shortfall?
1 Sales were lower than expected.
2 The opening inventories had been overstated.
3 The closing inventories of the business were higher than the opening inventories.
4 Goods taken from inventories by the proprietor were recorded by debiting drawings and crediting purchases with
the cost of the goods.
A All four factors
B 1, 2 and 4 only
C 2 only
D 3 and 4 only
相似考题
更多“15 A trader who fixes her prices by adding 50% to cost actually achieved a mark-up of 45%.Which of the following factors could account for the shortfall?1 Sales were lower than expected.2 The opening inventories had been overstated.3 The closing inventori”相关问题
-
第1题:
20 IAS 2 Inventories defines the extent to which overheads are included in the cost of inventories of finished goods.
Which of the following statements about the IAS 2 requirements in this area are correct?
1 Finished goods inventories may be valued on the basis of labour and materials cost only, without including overheads.
2 Carriage inwards, but not carriage outwards, should be included in overheads when valuing inventories of finished goods.
3 Factory management costs should be included in fixed overheads allocated to inventories of finished goods.
A All three statements are correct
B 1 and 2 only
C 1 and 3 only
D 2 and 3 only
正确答案:D
-
第2题:
The following information is relevant for questions 9 and 10
A company’s draft financial statements for 2005 showed a profit of $630,000. However, the trial balance did not agree,
and a suspense account appeared in the company’s draft balance sheet.
Subsequent checking revealed the following errors:
(1) The cost of an item of plant $48,000 had been entered in the cash book and in the plant account as $4,800.
Depreciation at the rate of 10% per year ($480) had been charged.
(2) Bank charges of $440 appeared in the bank statement in December 2005 but had not been entered in the
company’s records.
(3) One of the directors of the company paid $800 due to a supplier in the company’s payables ledger by a personal
cheque. The bookkeeper recorded a debit in the supplier’s ledger account but did not complete the double entry
for the transaction. (The company does not maintain a payables ledger control account).
(4) The payments side of the cash book had been understated by $10,000.
9 Which of the above items would require an entry to the suspense account in correcting them?
A All four items
B 3 and 4 only
C 2 and 3 only
D 1, 2 and 4 only
正确答案:B
-
第3题:
(50)These processes of particle creation and destruction had been predicted from Dirac’s theory before they were actually discovered in nature, and since then they have been observed millions of times.
正确答案:译文:粒子生成和毁灭的过程在真正被发现之前,迪拉克的理论已经对它们作出了预测,从那时起人们对此做过数百万次的观测。本体考核知识点:状语从句、被动语态的译法。
该句由两个并列的分句构成:These processes had been predicted和since then they have been observed。前一分句中of particle creation and destruction部分是介词短语作定语,修饰主语processes,应译为“粒子生成和毁灭的过程”。Before...in nature部分为时间状语,翻译时,可按照汉语习惯前置,译成“在...之前”。后一分句中的时间状语since then可译成“在..之后”或“从那时”。此外翻译被动语态结构had been predicted from Dirac’s theory时,为了突出施动者,可以按照汉语习惯,译为主动结构。
词汇:creation and destruction“生成和毁灭”。predict“预测,预言”,文中谈论的是科学现象,应该译为“预测”。in nature“实际上”。
-
第4题:
Mrs. Robson had lived in the house ______.
A. since she had sold her flat
B. for less than a decade
C . since she had been born
D. for more than ten years
正确答案:D42.答案为D 此考题为细节题。文章的第1段最后两句告诉我们:Since her husband had died ten years before...She had continued to live in their little house,alone,由于她丈夫在10年前去世,我们可以断定老妇人在此居住已10年有余,故选D。
-
第5题:
There are many sales this season,during which stores will lower their______prices.
A.normal
B.general
C.ordinary
D.usual
正确答案:A
解析:句意:这个季节有很多大减价活动,期间,商家会降低商品的正常价格。本题考查固定搭配。normal price表示“正常价格”。 -
第6题:
A new scheme for getting children to and from school is being started by the education authorities in part of Eastern England. This could end the worries of many parents fearful for their children's safety on the roads.
Until now the Country Council has only been prepared to provide bus services for children living more than three miles from their school, or sometimes less if special reasons existed. Now it has been decided that if a group of parents ask for help in organizing transport they will be prepared to go ahead, provided the arrangement will not lose money and that children taking part will be attending their nearest school.
The new scheme is to be tried out this term for children living at Milton who attend Impington school. The children live just within the three-mile limit and the Council has said in the past it will not undertake to provide free transport to the school. But now they have agreed to organize a bus service from Milton to Impington and back, a plan which has the support of the school's headmaster.
Between 50 and 60 parents have said they would like their children to take part in. Final calculations have still to be carried out, but a council official has said the cost of parents should be less than $6.50 a tenn.
They have been able to arrange the service at a low cost because there is already an agreement with the bus company for a bus to take children who live further away to Impington. The same bus would now just make an extra journey to pick up the Milton children. The official said they would get in touch with other groups of parents who in the past had asked if transport could be provided for their children, to see if they would like to take part in the new scheme.
The children the Council ran buses for in the past were those__________.A.whose parents were worried about them
B.who would have had to walk otherwise
C.who could not walk
D.who had to travel a long way答案:D解析:根据第二段第一句可知,到现在为止,乡村政务会只给住在3英里以外的学生提供巴士服务,这表示这些学生离家很远,因此答案选D。 -
第7题:
On an annual ( ), house prices in Scotland are now only 1% lower than they were a year ago, but they are 8% down in Northern Ireland.A.plan
B.object
C.found
D.basis答案:D解析:本题考查近义词辨析。题目意为“在一个年度的_____上,苏格兰的房价现在仅比一年前低1%,但在北爱尔兰下降了8%。”A选项意为“计划、打算”。B项意为“物体、目标、对象”。C项意为“创办、成立”。D项意为“基础、基本原则”。 因此选D,在年度的基础上。
-
第8题:
This year's sales in many companies were lower than ().
- A、lat year's
- B、which of last year's
- C、last year
- D、in last year
正确答案:A -
第9题:
问答题The cost of hiring a private rail carriage is shared equally by all the passengers who paid an exact number of pounds which was less than £100 each. The carriage has seats for 50 passengers and the total bill amounts to £1887. How many seats were not occupied?正确答案: 13seats (37 people each paid £51.)解析:
(根据题目要求可知,1887英镑被一些人平分,人数少于50,每人所付钱数少于100英镑,可知如果分解1887的话,符合条件的两个因子应一个小于50,一个小于100。因为1887=3×17×37,即1887=3×629,或者1887=37×51,可知是37位乘客,每位乘客交了51英镑,则空座为13个。) -
第10题:
问答题Free trade is an economic policy under which the government does not interfere with trade. No tariffs are applied to imports or exports, and people are allowed to trade goods and services as they please. Supply and demand dictates the prices for which goods and services sell and are the only factors that determine how resources are allocated in society. Under a free trade system, there are no trade barriers. There is free access to markets and market information, and there are no government-imposed monopolies. The following are opinions from both sides. Read the excerpt carefully and write your response in about 300 words, in which you should: 1. summarize briefly the opinions from both sides, and then 2. give your comment. Marks will be awarded for content relevance, content sufficiency, organization and language quality. Failure to follow the above instructions may result in a loss of marks. Those who support free trade believe that it allows companies to come by raw materials and lower prices, which, in turn, results in lower prices on the open market. Supporters also believe that the levels of employment in a nation are determined by the monetary policy of that nation and not the trade policy. Additionally, when people must compete for a profit, they produce better products and are more motivated to increase their education and knowledge because these increases come with personal benefits. On the contrary, many believe that the government should dictate prices and impose more taxes on imports and exports. Critics often believe that many outsourced jobs are a result of free trade practices; and regulating trade could keep companies from finding cheaper labor and lower cost overseas. There are also concerns with the social burden of limited job security if companies put too much effort into looking for cheaper labor and lower cost. Critics feel that this results in a more worried, cautious public that is less likely to spend and invest in the economy. This is certainly not an advantage when the world economy is already in recession.正确答案:
【参考范文】
My View on Free Trade Free trade is a system in which goods, capital, and labor flow freely between nations, without barriers which could hinder the trade process. There are a number of arguments both for and against this practice. People for it believe that free trade can decrease the cost, then lower prices for goods and it can also prompt producers to improve the quality of products and motivate people to increase their education and knowledge. However, people against it think that it would bring many outsourced jobs, increase the social burden of limited job security and make people more worried and less likely to spend and invest. As far as I am concerned, every coin has two sides. Free trade is no exception.
On the one hand, it is helpful to improve profitability, promote the capital accumulation and make the economy continuous to develop. It is also supposed to encourage innovation, since competition between companies sparks a need to come up with innovative products and solutions to capture market share. In addition, free trade can also foster international cooperation, by encouraging nations to freely exchange goods and citizens. Agreements between trading partners can also promote educational advantages, such as sending engineers to train with people in the top of the engineering field in one nation, or sending agriculture experts to rural areas to teach people about new farming techniques and food safety practices.
On the other hand, when trade introduces strong competitors, it may put domestic producers out of business. If developing countries have industries that are relatively new, then at the moment these industries would struggle against international competition. Some industries may appear “Matthew effect”, which is not conducive to harmonious and healthy development of industry.
In conclusion, there are pros and cons to free trade. We should take full advantage of it and avoid its disadvantages to serve our country’s own economy development. Thus it may bring significant benefits for us.解析:
【审题构思】
本题的写作主题是自由贸易。对此可以表示支持或反对,也可以保持中立。首先应该开门见山,引入话题,简要总结材料中正反方的观点,之后明确陈述自己对于这一话题的看法。然后提供一个或者两个理由支持自己的观点。最后得出结论,总结全文。 -
第11题:
单选题This year's sales in many companies were lower than ().Alat year's
Bwhich of last year's
Clast year
Din last year
正确答案: C解析: 暂无解析 -
第12题:
单选题The vehicle sales were greatly cut down becauseAthe car manufacturers were concerned about the American economy.
Bthe market’s performance was found to be the worst in 50 years.
Cthe prices of fuel rose to a level which was last seen in the 1950s.
Dthe fuel prices were so high and the economy was facing a depression.
正确答案: A解析:
事实细节题。新闻中提到,创纪录的燃油价格和经济衰退导致了销售额暴跌。D项中的depression是原文中recession的同义替换。因此,D项正确。
【听力原文】
A slump in vehicle sales by the three big US car manufacturers has renewed worries about the American economy. General Motors posted an 18% drop in sales in June, Ford unveiled a 29%slump, Chrysler’s sales were down by 36%. Mark Gregory reports.
The combination of record fuel prices and an economy close to recession has led to a slump in sales. On current trends, fewer than 14 million cars and light trucks will be sold in the US this year, the market’s worst performance in 15 years. Shares in General Motors, America’s biggest car maker, have fallen to a level last seen in the 1950s. -
第13题:
2 The draft financial statements of Choctaw, a limited liability company, for the year ended 31 December 2004 showed
a profit of $86,400. The trial balance did not balance, and a suspense account with a credit balance of $3,310 was
included in the balance sheet.
In subsequent checking the following errors were found:
(a) Depreciation of motor vehicles at 25 per cent was calculated for the year ended 31 December 2004 on the
reducing balance basis, and should have been calculated on the straight-line basis at 25 per cent.
Relevant figures:
Cost of motor vehicles $120,000, net book value at 1 January 2004, $88,000
(b) Rent received from subletting part of the office accommodation $1,200 had been put into the petty cash box.
No receivable balance had been recognised when the rent fell due and no entries had been made in the petty
cash book or elsewhere for it. The petty cash float in the trial balance is the amount according to the records,
which is $1,200 less than the actual balance in the box.
(c) Bad debts totalling $8,400 are to be written off.
(d) The opening accrual on the motor repairs account of $3,400, representing repair bills due but not paid at
31 December 2003, had not been brought down at 1 January 2004.
(e) The cash discount totals for December 2004 had not been posted to the discount accounts in the nominal ledger.
The figures were:
$
Discount allowed 380
Discount received 290
After the necessary entries, the suspense account balanced.
Required:
Prepare journal entries, with narratives, to correct the errors found, and prepare a statement showing the
necessary adjustments to the profit.
(10 marks)
正确答案:
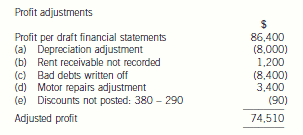
-
第14题:
2 The draft financial statements of Rampion, a limited liability company, for the year ended 31 December 2005
included the following figures:
$
Profit 684,000
Closing inventory 116,800
Trade receivables 248,000
Allowance for receivables 10,000
No adjustments have yet been made for the following matters:
(1) The company’s inventory count was carried out on 3 January 2006 leading to the figure shown above. Sales
between the close of business on 31 December 2005 and the inventory count totalled $36,000. There were no
deliveries from suppliers in that period. The company fixes selling prices to produce a 40% gross profit on sales.
The $36,000 sales were included in the sales records in January 2006.
(2) $10,000 of goods supplied on sale or return terms in December 2005 have been included as sales and
receivables. They had cost $6,000. On 10 January 2006 the customer returned the goods in good condition.
(3) Goods included in inventory at cost $18,000 were sold in January 2006 for $13,500. Selling expenses were
$500.
(4) $8,000 of trade receivables are to be written off.
(5) The allowance for receivables is to be adjusted to the equivalent of 5% of the trade receivables after allowing for
the above matters, based on past experience.
Required:
(a) Prepare a statement showing the effect of the adjustments on the company’s net profit for the year ended
31 December 2005. (5 marks)
正确答案:
-
第15题:
Before relativistic particle physics, the constituents of matter had always been considered as being either elementary units which were indestructible and unchangeable, or as composite objects which could be broken up into their constituent parts;
正确答案:译文:在相对论粒子物理学诞生之前,人们一直以为物质的构成成分要么是不可毁灭和不可改变的基本单位,要么是可以分解为其构成部分的合成物。
本题考核知识点:完成时的被动语态、状语从句、定语从句、either...or结构的译法。
该句的句子主干是:the constituents of matter had always been considered as either...or....。完成时的被动语态had always been considered,可按照汉语习惯译成主动语态,即“人们一直以为”。状语before...可直接翻译,在句中位置不变。Either...or...句型应该译成“或者...或者...”,也可以译成“要么...要么...”。本句中两个as...部分均为宾语补足语,与consider一起译成“看成是...”。两个which引导定语从句,修饰两个宾语补足语,翻译时采用前置法将定语提前。
词汇:relativistic particle physics“相对粒子物理学”,constituents of matter“物质构成成分”, composite objects“合成物”。
-
第16题:
Before deciding which form. of transport to use, a()will take into account the factors of cost, speed and safety.A、consignor
B、consignee
C、shipper
D、shipowner
参考答案:B
-
第17题:
Section B – TWO questions ONLY to be attempted
Perkin manufactures electronic components for export worldwide, from factories in Ceeland, for use in smartphones and hand held gaming devices. These two markets are supplied with similar components by two divisions, Phones Division (P) and Gaming Division (G). Each division has its own selling, purchasing, IT and research and development functions, but separate IT systems. Some manufacturing facilities, however, are shared between the two divisions.
Perkin’s corporate objective is to maximise shareholder wealth through innovation and continuous technological improvement in its products. The manufacturers of smartphones and gaming devices, who use Perkin’s components, update their products frequently and constantly compete with each other to launch models which are technically superior.
Perkin has a well-established incremental budgeting process. Divisional managers forecast sales volumes and costs months in advance of the budget year. These divisional budgets are then scrutinised by the main board, and revised significantly by them in line with targets they have set for the business. The finalised budgets are often approved after the start of the accounting year. Under pressure to deliver consistent returns to institutional shareholders, the board does not tolerate failure by either division to achieve the planned net profit for the year once the budget is approved. Last year’s results were poor compared to the annual budget. Divisional managers, who are appraised on the financial performance of their own division, have complained about the length of time that the budgeting process takes and that the performance of their divisions could have been better but was constrained by the budgets which were set for them.
In P Division, managers had failed to anticipate the high popularity of a new smartphone model incorporating a large screen designed for playing games, and had not made the necessary technical modifications to the division’s own components. This was due to the high costs of doing so, which had not been budgeted for. Based on the original sales forecast, P Division had already committed to manufacturing large quantities of the existing version of the component and so had to heavily discount these in order to achieve the planned sales volumes.
A critical material in the manufacture of Perkin’s products is silver, which is a commodity which changes materially in price according to worldwide supply and demand. During the year supplies of silver were reduced significantly for a short period of time and G Division paid high prices to ensure continued supply. Managers of G Division were unaware that P Division held large inventories of silver which they had purchased when the price was much lower.
Initially, G Division accurately forecasted demand for its components based on the previous years’ sales volumes plus the historic annual growth rate of 5%. However, overall sales volumes were much lower than budgeted. This was due to a fire at the factory of their main customer, which was then closed for part of the year. Reacting to this news, managers at G Division took action to reduce costs, including closing one of the three R&D facilities in the division.
However, when the customer’s factory reopened, G Division was unwilling to recruit extra staff to cope with increased demand; nor would P Division re-allocate shared manufacturing facilities to them, in case demand increased for its own products later in the year. As a result, Perkin lost the prestigious preferred supplier status from their main customer who was unhappy with G Division’s failure to effectively respond to the additional demand. The customer had been forced to purchase a more expensive, though technically superior, component from an alternative manufacturer.
The institutional shareholders’ representative, recently appointed to the board, has asked you as a performance management expert for your advice. ‘We need to know whether Perkin’s budgeting process is appropriate for the business, and how this contributed to last year’s poor performance’, she said, ‘and more importantly, how do we need to change the process to prevent this happening in the future, such as a move to beyond budgeting.’
Required:
(a) Evaluate the weaknesses in Perkin’s current budgeting system and whether it is suitable for the environment in which Perkin operates. (13 marks)
(b) Evaluate the impact on Perkin of moving to beyond budgeting. (12 marks)
正确答案:Tutor note: This is a detailed solution and candidates would not be expected to produce an answer of this length.
(a) Weaknesses in the current budget process at Perkin
Perkin uses a traditional approach to budgeting, which has a number of weaknesses.
First of all the budgeting system does not seem aligned with Perkin’s corporate objective which focuses on innovation and continuous product improvement. Innovation is a key competitive advantage to both component and device manufacturers in this industry and the products which incorporate Perkin’s components are subject to rapid technological change as well as changes in consumer trends. The markets in which the two divisions operate appear to be evolving, as seen by the high popularity of the smartphone model which was designed for playing games. This may mean the distinction between smartphone and gaming devices could be becoming less clear cut. Management time would probably be better spent considering these rapid changes and currently the budgeting process does not facilitate that.
In reality, the budget process at Perkin is time consuming and probably therefore a costly exercise. Divisional budgets go through a lengthy process of drafting and then revision by the main board before they are approved. The approval often happens after the start of the period to which they relate, at which point the budgets are already out of date. This also means divisional managers are trying to plan activities for the next financial year without a set of finalised targets agreed, which could impact the effectiveness of decisions made.
Another weakness is that the budgets are only prepared annually, which is clearly too infrequent for a business such as Perkin. The process is also rigid and inflexible as deviations from the planned targets are not tolerated. Sticking to rigid, annual budgets can lead to problems such as P Division not being able to cope with increasing popularity of a particular product and even other short-term changes in demand like those driven by seasonal factors, or one-off events such as the factory fire. Linked to this problem of budgetary constraints is that to cut costs to achieve the budgeted net profit, managers closed one of the three research and development facilities in G Division. As identified at the outset, a successful research and development function is a key source of long-term competitive advantage to Perkin.
It also appears that Perkin fails to flex the budgets and consequently the fixed budgets had discouraged divisional managers from deviating from the original plan. P Division did not make technical modifications to its components due to the cost of doing so, which meant they were unable to supply components for use in the new model of smartphone and had to discount the inventories of the old version. It is unclear why G Division did not take on additional staff to cope with increased demand following reopening of their customer’s factory, but it may be because managers felt constrained by the budget. This then caused long-term detriment to Perkin as they lost the preferred supplier status with their main customer.
Another problem created by annual budgeting is the management of short-term changes in costs and prices. A key component of Perkin’s products is silver, which fluctuates in price, and though it is not clear how much effect this has on Perkin’s costs, any problems in supply could disrupt production even if only a small amount of silver were required. Also Perkin exports goods worldwide and probably also purchases materials, including silver, from overseas. The business is therefore exposed to short-term movements in foreign currency exchange rates which may affect costs and selling prices.
Similarly, there also seems to be considerable uncertainty in sales volumes and prices which creates problems in the forecasting process for the two divisions. P Division did not anticipate the high demand for the new component which meant P Division had to discount products it had already manufactured in order to achieve its forecast sales volumes. G Division did correctly forecast the demand, but based on past growth in the market which may be too simplistic in a rapidly changing industry. Lack of up-to-date information will hinder decision-making and overall performance at Perkin. Perkin would perhaps be better adopting a rolling basis for forecasting.
The two divisions share manufacturing facilities and are likely to compete for other resources during the budgeting process. The current budgeting system does not encourage resource, information or knowledge sharing, for example, expertise in forecasting silver requirements. Divisional managers are appraised on the financial performance of their own division and hence are likely to prioritise the interests of their own division above those of Perkin as a whole. P Division would not re-allocate its manufacturing facilities to G Division, even though G Division needed this to cope with extra demand following reopening of the customer’s factory. The current system is therefore not encouraging goal congruence between the divisions and Perkin as a whole and a budgeting system, if done effectively, should encourage co-ordination and co-operation.
Managers may find the budgeting process demotivating because it is time-consuming for them and then the directors override the forecast which they had made. It is also unfair and demotivating to staff to appraise them on factors which are outside their control. This also identifies another weakness in Perkin’s budgeting system related to control as there does not seem to be any planning and operating variance analysis performed to assess exactly where performance is lacking and so no appropriate management information is provided. In fact it is not even clear just how often divisional managers receive reports on performance throughout the year. Any budgeting system without regular feedback would be ineffective. It should even be noted that for the industry in which Perkin operates the use of only budgetary targets as a measure of performance is narrow and internal. It should be utilising information from external sources as well to assess performance in a more relevant and contextual way.
Given the rapidly changing external environment and the emphasis on innovation and continuous product development, the current traditional budgeting method does not seem appropriate for Perkin.
(b) Beyond budgeting moves away from traditional budgeting processes and is suitable for businesses operating in a rapidly changing external environment and has the following features:
1. Encourages management to focus on the present and the future. Performance is assessed by reference to external benchmarks, utilising rolling forecasts and more non-financial information. This encourages a longer term view.
2. More freedom is given to managers to make decisions, which are consistent with the organisation’s goals and achieving competitive success.
3. Resources are made available on demand, for example, to enable a division to take advantage of an opportunity in the market, rather than being constrained by budgets.
4. Management focus is switched to the customer and managers are motivated towards actions which benefit the whole organisation, not just their own divisions.
5. Effective information systems are required to provide fast and easily accessible information across the whole organisation to allow for robust planning and control at all levels.
Taking each of the elements of beyond budgeting in turn, the impact of introducing this technique into Perkin can be assessed.
At Perkin, there are rapid technological changes in the products being produced by customers and competitors as a result of changes demanded by the market, which mean that Perkin must respond and continuously innovate and develop its products. This will support Perkin’s corporate objective. Consequently, this means that Perkin must change its plans frequently to be able to compete effectively with other component manufacturers and therefore will need to move away from annual incremental budgeting to introducing regular rolling forecasts. This process will need supporting by KPIs which will have a longer term focus. The impact of this will be that Perkin will need to develop a coherent set of strategies which supports its corporate objective, which will then need to be translated into targets and appropriate KPIs selected and developed. It will also mean that performance measures at the operational level will need to be revised from annual budgetary targets to these longer term objectives. Management at all levels will require training on the production of rolling forecasts and Perkin will need to assess if additional resources will also be required to run this new system.
Beyond budgeting focuses on the long-term success of the business by division managers working towards targets which may be non-financial. The use of external benchmarks and non-financial information will mean Perkin will need to put processes in place to collect this information and analyse it to assess performance. This will be a learning process as Perkin does not currently do this. The status of preferred supplier with key customers, for example, would be important to the long-term success of the business and this could be an objective which Perkin sets for its divisional managers.
Beyond budgeting allows authority to be delegated to suitably trained and supported managers to take decisions in the long-term interests of the business. It allows managers to respond quickly and effectively to changes in the external environment, and encourages them to develop innovative solutions to external change. In Perkin, budgets proposed by divisional managers are changed by the board to reflect its overall plans for the business. This means that a change in the approach to communication between the board and the divisions will be necessary as Perkin would need to switch from the top down process currently adopted to a more devolved decision-making structure. This will again require training for management to enable them to be ready to deal with this delegated authority as it will be very different from their existing approach.
Traditional budgeting may constrain managers who are not allowed to fail to meet the approved budget. This can be seen when P Division did not adapt its components because it did not want to incur the costs of doing so, which had not been budgeted for. Similarly, prices of raw materials are known to be volatile. Beyond budgeting makes resources available for managers to take advantage of opportunities in the market, such as the smartphone designed for playing games. Managers would also be able to react to changes in the price of materials or changes in foreign currency exchange rates, for example, by having the authority to purchase silver for inventory at times when the price of silver is low. This will mean that as a result there will be fewer budgetary constraints; however, these resources and targets will still need to be effectively managed. This management will mean that strategic initiatives invested in will need monitoring rather than closely scrutinising departmental budgets, which will be a significant change in Perkin.
In Perkin, the two divisions share some manufacturing facilities and are likely to compete for other resources, for example, when setting budgets. When manufacturing facilities are in short supply, each division will prioritise its own requirements rather than those of the business as a whole. Beyond budgeting encourages managers to work together for the good of the business and to share knowledge and resources. This is important in a business such as Perkin where product innovation is key and where the activities and products of the two divisions are similar. This coordinated approach will be new to Perkin so there will be a culture change. Also, the customer-oriented element of beyond budgeting is key here and will require the setup of customer focused teams which will require more harmonised actions in the divisions.
Each division currently has its own IT systems. In order to effectively share knowledge and to be able to respond to the external environment, which are key elements of beyond budgeting, it would be preferable for them to have shared IT facilities. This will mean that Perkin may have to invest in new technology capable of sharing information across the organisation in a rapid and open fashion but also be able to collect all relevant comparative data to allow for continuous monitoring of performance. This will facilitate better planning and control across all levels of Perkin.
With appropriate training of managers and investment in information systems, it would be relevant for Perkin to adopt beyond budgeting because of the rapid changes in the external environment in which it operates.
-
第18题:
Questions 95-98 refer to the following advertisement.
As the number of new infections and deaths rise in the Ebola outbreak, fear and suspicion in rising, too, making a more difficult for health care workers to get the sick into hospitals, even as increasingly angry crowds are calling for more government action.
The growing chaos caused by this current Ebola outbreak, which is already the worst on record with more than 1,300 infected and 700 dead in three countries in West Africa, was witnessed in a low income community in the Bushrod Island area of Monrovia.
The community members had called the Health
Ministry to come pick up the body of a man who had been dead in his home since Thursday. Late Friday or early Saturday, a woman had died in the same neighborhood, and she was also still in her home. Both were suspected Ebola deaths, and the protesters were saying that the government should remove them.
A man in the crowd said that since they called the government on Thursday, workers had come to examine the scene, but they had not returned. He said that if the government did not respond to the request of community members to remove the bodies, there would be serious consequences.
Which of the following is true about the current Ebola outbreak?A. More than 700 people were infected in this outbreak.
B. Ebola proved to be the worst infectious disease in history.
C. More than 700 people died in this outbreak.
D. It was limited to the Bushrod Island area of Monrovia.答案:B解析:细节题。文章第二段第一句通过which 引导的定语从句说明埃博拉病毒的爆发已经在西非三个国家中造成超过1300 例感染和700 例死亡,这已经是历史记录中最糟糕的状况。B 项中的in history 照应原文中的on record,故选B。 -
第19题:
共用题干
Helen and Martin
With a thoughtful sigh,Helen turned away from the window and walked back to her favourite armchair.______(1) her brother never arrive?For a brief moment,she wondered if she really cared that much.
Over the years Helen had given______(2) waiting for Martin to take an interest in her.Her feelings for him had gradually______(3) until now,as she sat waiting for him,she experienced no more than a sister's ______(4) to see what had ______(5) of her brother.
Almost without______(6) ,Martin had lost his job with a busy publishing company after spending the last eight years in New York as a key figure in the US office.Somehow the two of them hadn't______(7) to keep in touch and,left alone,Helen had slowly found her______(8) in her own judgment growing.______(9) the wishes of her parents,she had left university halfway______(10) her course and now,to the astonishment of the whole family,she was______(11) a fast-growing reputation in the pages of respected art magazines and was actually earning enough to live______(12) from her paintings.
Of course,she______(13) no pleasure in Martin's sudden misfortune,but she couldn't______(14) looking forward to her brother's arrival with______(15) satisfaction at what she had achieved.11._________
A:gaining
B:reaching
C:starting
D:opening答案:A解析:考查情态动词。根据句意“哥哥将永远不再回来了吗?”有“应该”“应”意思的B,D选项被排除。只有would有将要的意思,符合句意。故选C。
考查介词搭配。此句意为“这些年来,海伦已经放弃了等待马丁对她产生兴趣。”give in意为“屈服,让步”,give up意为“放弃”,符合句意;give out意为“分发,公布”, give away意为“泄露,出卖”。故选B。
A项depress偏重表达“数量的减少或价值的降低”;B项weaken一般来说偏重“情感”方面的减弱、变淡;C项lower偏重在“数量或质量”上的减少或降低;D项faint偏重于“视觉”的变淡、模糊。此句表达的是Helen对他的感情慢慢变淡,故选B。
此句表达的是Helen非常急切地想知道她的哥哥到底发生了什么事的一种 “急切的好奇的”感觉,故四个选项中只有curiosity最贴切,故选C。
become of sb./sth.…是短语,意为“发生某种情况;遭遇……”。故选A。
根据上下文可知,Martin在没有任何征兆的情况下就失去了工作。A项 caution指“警察的口头警告”,C项advice意为“劝告,忠告”,D项signal意为“信号,暗号”,只有B项warning有“征兆,前兆”之意。故选B。
此句意为“在某种程度上他俩不会因为彼此联系或不联系而烦扰”,其中A 项mind意为“介意”,B项concern意为“担心,担忧”;C项worry意为“使担心,使焦虑”,只有 D项bother有“烦扰”之意。故选D。
此句表达的是Helen对自己的判断的“信心”渐渐增加。A项dependence 意为“依靠、依赖”;C项certainty意为“确定性,无疑”;D项courage意为“勇气,胆量”;B项 confidence可与介词in搭配,意为“对……有信心”。故选B。
ignore“不顾,不理,忽视”,omit“省略,疏,” ,avoid“回避,避免”,prevent“防止,预防”。此句表达的是“Hele不顾及父母的意愿”。故选A。
此句强调的是在学业过程中,故应用through一词;across强调“横穿”,故选C。
gain意再些获得,博得”,reach意为“达到”,start意为“开始”,open意为“打开”,此句表达Helen很快声名鹊起。故选A。
考查介词搭配。此处意为“……而且她的画作足以维持生活”。live for意为“盼望,为……而生活”;live by意为“以……为生”;live with意为“忍受,承认”;而live on意为“靠……生活”,与句意相符。故选D。
短语take no pleasure in…“不以……为乐/感到高兴”。故选B。
短语couldn't help doing sth.“情不自禁做某事”。故选A。
soft意为“柔软的”,fine意为“好的”,quiet意为“暗中的,未表露的”,still 意为“静止的,不动的”。此句表达Helen的那种未言语的欣慰之情,故选C。 -
第20题:
The economy of the United states after 1952 was the econnomy of a well-fed,almost fully employed people. Despit occasional alarms, the country escaped any postwar depression and lived in a state of boom. A n economic survey of the year 1955, a typical year of the 1950’s, may be typical as illustrating the rapid economic growth of the decade. The national output was value at 10 percent above that of 1954 (1955 output was estimated at 392 billion dollars). The production of manufacturers was about 40 percent more than it had averaged in the years immediately following World War 2. The country’s business spent about 30billion dollars for new factories and machinery. National income available for spending was almost a third greater than it had been it had been in 1950. Consumers spent about 256 billion dollars; that is about 700 million dollars a day ,or about twenty-five million dollars every hour , all round the clock. Sixty-five million people held jobs and only a little more than two million wanted jobs but could not find them . Only agriculture complained that it was not sharing in the room. To some observers this was an ominous echo of the mid-1920’s . As farmer’s shre of their products declined , marketing costs rose. But there were , among the observers of the national economy, a few who were not as confident as the majority . Those few seemed to fear that the boom could not last and would eventually lead to the oppsite-depression. Which of the following were LEAST satisfied with the national economy in the 1950’s?()
- A、Economists
- B、Frmaers
- C、Politicians
- D、Steelworkers
正确答案:B -
第21题:
单选题They achieved more than they had ever dreamed, lending a magic to their family story that no tale or ordinary life could possibly rival.Aconfirm
Bachieve
Cmatch
Dexaggerate
正确答案: D解析:
句意:他们取得了比预想大得多的成就,使他们的家族故事充满魔力,以至于没有任何神话故事和普通生活可以与之相提并论。rival相匹敌。match“相配,相比”与之相符。confirm确定。achieve达到,完成。exaggerate夸大,夸张。 -
第22题:
问答题Practice 6 With a high degree of specialization, the frontiers of knowledge are steadily being pushed back more rapidly than ever before. But this has not been achieved without considerable cost. The scientist, who outside his own particular subject is little more than an idiot, is a modern phenomenon; as is the man of letters who is barely aware of the tremendous strides that have been made in technology. Similarly, specialization has indirectly affected quite ordinary people in every walk of life. Many activities which were once pursued for their own sakes are often given up in despair: they require techniques, the experts tell us, which take a life-time to master. Why learn to play the piano, when you can listen to the world’s greatest pianists in your own drawing-room?正确答案: 【参考译文】
随着知识的高度专业化,各学科正以前所未有的速度不断发展,但为此也付出了高昂的代价。一个科学家一旦脱离了其自身研究领域,即与白痴无异,这不能不说是现代社会的咄咄怪事。而对于科技方面的重大进展,文人也同样几乎一无所知。同样,专业化也使各行各业的普通人受到间接的影响。人们以往的那些兴趣爱好,现在却不得不绝望地放弃,因为专家告诉我们,兴趣需要技术,且穷尽一生才能掌握。当你能在自己的客厅欣赏到世界上最伟大的钢琴家演奏时,你还学习钢琴干什么呢? 解析: 暂无解析 -
第23题:
单选题When Brad offered his old wooden desk at a garage sale, no one bought it, even though he offered it for only $10. When he offered it at the local auction house, however, someone bought it for $850. Which of the following, if true, best explains why Brad was able to sell the desk for a high price at the auction while he could not sell it for a much lower price at the garage sale?ABrad advertised that the proceeds of the garage sale would benefit a local charity, while he made no such claims for the proceeds from the auction.
BOne of the legs of the desk was shorter than the other three, producing an unbalanced writing surface.
CThe auction house specializes in selling antique furniture, which is generally valued more highly than the discarded furniture sold at garage sales.
DBrad insisted that anyone who bought the desk had to use it as an actual workspace.
EProspective buyers at auctions are often more interested in the auction process than in the items up for bid.
正确答案: D解析:
C项暗示Brad的桌子在典当行销售的时候被鉴定成为一件文物,而不是一件不用的旧家具,这样Brad卖出的价钱就增多了,故本题选C项。
